Abstract
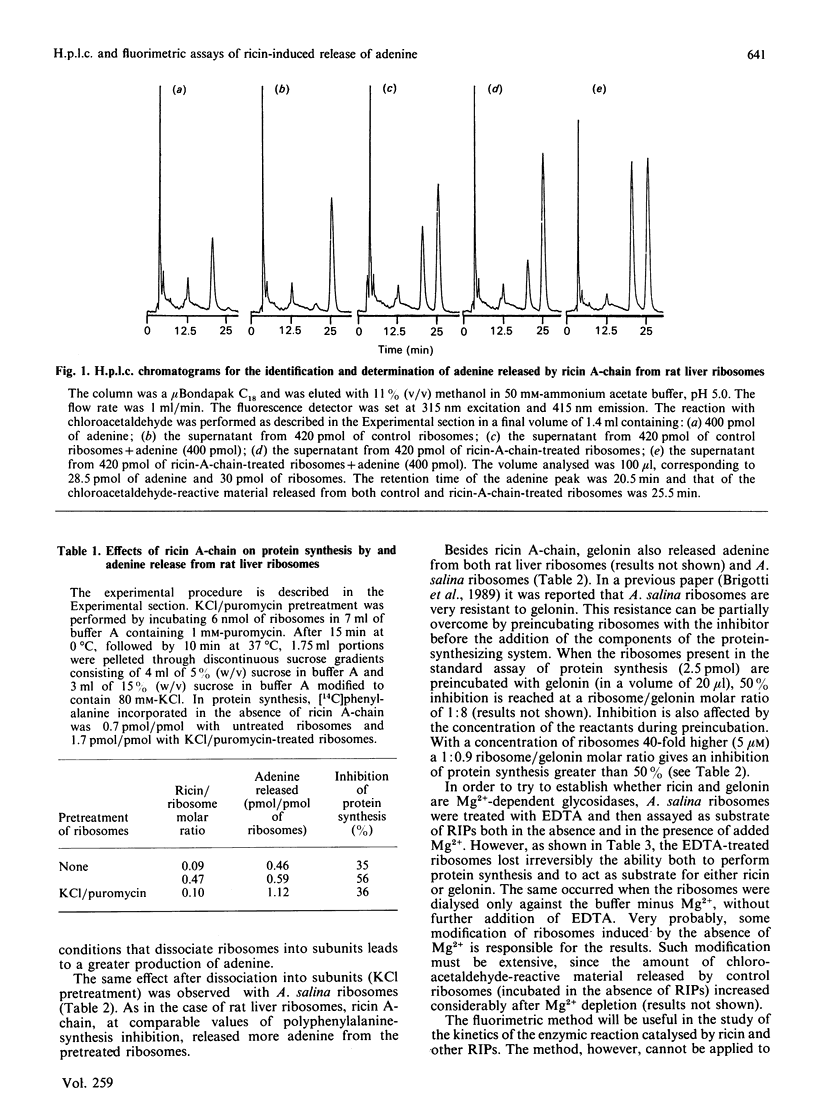
The high fluorescence of adenine-containing compounds after reaction with chloroacetaldehyde was used to measure the adenine released from rat liver and Artemia salina ribosomes by the action of ricin A chain and gelonin, two ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) that share the same mechanism of action, consisting in the hydrolysis of the N-glycosidic bond of A-4324 of 28 S rRNA. Two methods were employed: (i) h.p.l.c. of the chloroacetaldehyde-reactive material released by RIPs; h.p.l.c. associated with a fluorescence detector allows the identification of adenine and its dosage at quantities as low as 2 ng; (ii) the direct fluorimetric measurement of the material that had reacted with chloroacetaldehyde. The amount of adenine released increases when ribosomes are pretreated in conditions that lead to their dissociation into subunits. Adenine protects ribosomes from the inhibition by ricin A-chain. When ribosomes were incubated with ricin A-chain in the presence of [14C]adenine no incorporation of radioisotope in ribosomes was observed, indicating that neither exchange nor reversal reactions occurred. A binding of [14C]adenine to ricin A chain was not detected by equilibrium dialysis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. H., SCHWEET R. S. Synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system. I. Properties of the complete system. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrio J. R., Secrist J. A., 3rd, Leonard N. J. Fluorescent adenosine and cytidine derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):597–604. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Sabatini D. Dissociation of mammalian polyribosomes into subunits by puromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigotti M., Rambelli F., Zamboni M., Montanaro L., Sperti S. Effect of alpha-sarcin and ribosome-inactivating proteins on the interaction of elongation factors with ribosomes. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):723–727. doi: 10.1042/bj2570723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Franz H. The site of action of the A-chain of mistletoe lectin I on eukaryotic ribosomes. The RNA N-glycosidase activity of the protein. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):378–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80853-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Lambert J. M. The site of action of six different ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants on eukaryotic ribosomes: the RNA N-glycosidase activity of the proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90733-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPEL L. A., HILMOE R. J. [Phosphorolysis and hydrolysis of purine ribosides by enzymes from yeast]. J Biol Chem. 1952 Oct;198(2):683–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ J., HEPPEL L. A., HORECKER B. L. The enzymatic cleavage of adenylic acid to adenine and ribose 5-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):525–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin T., Náslund P. H. Stimulation of enzymatic phe-tRNA binding to mammalian ribosomes by thallium ions at concentrations blocking other ribosomal functions. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 17;88(1):143–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard N. J., Barrio J. R., Secrist J. A., 3rd A spray reagent for adenine-containing residues: detection by fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 29;269(3):531–532. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAZELIS M., CREVELING R. K. AN ADENOSINE HYDROLASE FROM BRUSSELS SPROUTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3358–3361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann W. P., Hall L. M., Siler W., Barton N., Whitley R. J. High-pressure liquid chromatographic methods for determining arabinosyladenine-5'-monophosphate, arabinosyladenine, and arabinosylhypoxanthine in plasma and urine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):265–273. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H., Rodnight R. Breakdown of cozymase by a system from nervous tissue. Biochem J. 1949;44(4):470–477. doi: 10.1042/bj0440470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S., Zamboni M., Denaro M., Testoni G., Gasperi-Campani A., Stirpe F. Effect of modeccin on the steps of peptide-chain elongation. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):371–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1760371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Moran T. P., Colinas R. J. Ribonuclease activity associated with the 60S ribosome-inactivating proteins ricin A, phytolaccin and Shiga toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90498-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secrist J. A., 3rd, Barrio J. R., Leonard N. J., Weber G. Fluorescent modification of adenosine-containing coenzymes. Biological activities and spectroscopic properties. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3499–3506. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra J. M., Meier D., Ochoa S. Effect of development on the translation of messenger RNA in Artemia salina embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2693–2697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L. Competitive binding of adenine and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide to diphtheria toxin. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):730–732. doi: 10.1042/bj1070730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A., Stirpe F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro: 60 S ribosomal subunit as the target of the toxin. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):813–815. doi: 10.1042/bj1360813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Rambelli F. Dye affinity chromatography of ricin subunits. Biosci Rep. 1986 Dec;6(12):1035–1040. doi: 10.1007/BF01141024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Bailey S., Miller S. P., Bodley J. W. Modification of ribosomal RNA by ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1349–1357. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAGI Y., HORECKER B. L. Purification and properties of a bacterial riboside hydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):77–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZATMAN L. J., KAPLAN N. O., COLOWICK S. P. Inhibition of spleen diphosphopyridine nucleotidase by nicotinamide, an exchange reaction. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):197–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. A supernatant factor involved in initiation complex formation with eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


