Abstract
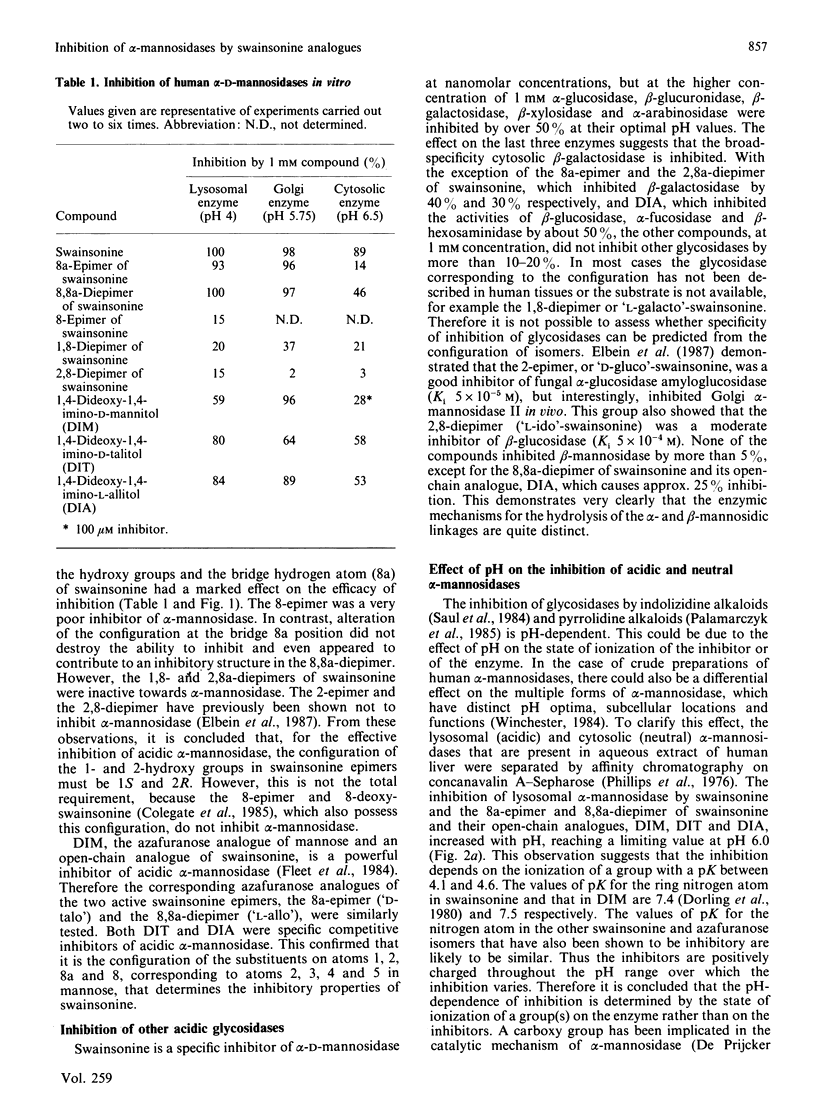
The inhibitory properties of a series of synthetic epimers and analogues of swainsonine towards the multiple forms of human alpha-mannosidases were studied in vitro and in cells in culture. Of the five epimers tested, only the 8a-epimer and 8,8a-diepimer of swainsonine were specific and competitive inhibitors (Ki values of 7.5 x 10(-5) and 2 x 10(-6) M respectively) of lysosomal alpha-mannosidases in vitro and induced storage of mannose-rich oligosaccharides in human fibroblasts in culture. The structures of these storage products indicated that processing alpha-mannosidases had also been inhibited. This was consistent with the observed inhibition in vitro of these enzymes by these compounds. In contrast, the 8-epimer, 1,8-diepimer and 2,8a-diepimer of swainsonine had no appreciable effect on any alpha-mannosidases. The corresponding open-chain analogues of swainsonine, namely 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-D-mannitol, of the 8a-epimer, namely 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-D-talitol, and of the 8,8a-diepimer, namely 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-L-allitol, were weaker competitive inhibitors of lysosomal alpha-mannosidase, with Ki values of 1.3 x 10(-5), 1.2 x 10(-4) and 1.2 x 10(-4) M respectively. These analogues also proved less effective at inducing oligosaccharide accumulation and in disturbing glycoprotein processing. These compounds offer the opportunity to determine which alterations in the chirality of the swainsonine molecule affect its inhibitory specificity. A comparison of their biological activities has identified reagents that will be useful for studying steps in the biosynthesis and catabolism of glycoproteins and that may be of potential value in chemotherapy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burditt L. J., Chotai K. A., Winchester B. G. Evidence that the mutant enzyme in fibroblasts of a patient with mannosidosis does not crossreact with antiserum raised against normal acidic alpha-D-mannosidase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 15;91(2):186–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burditt L., Chotai K., Halley D., Winchester B. Comparison of the residual acidic alpha-D-mannosidase in three cases of mannosidosis. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Jun 10;104(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenci di Bello I., Dorling P., Winchester B. The storage products in genetic and swainsonine-induced human mannosidosis. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):693–696. doi: 10.1042/bj2150693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chotai K., Jennings C., Winchester B., Dorling P. The uptake of swainsonine, a specific inhibitor of alpha-D-mannosidase, into normal human fibroblasts in culture. J Cell Biochem. 1983;21(2):107–117. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240210202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Prijcker J., Vervoort A., De Bruyne C. Purification and properties of alpha-D-mannosidase from Medicago sativa L. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):561–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis J. W. Effects of swainsonine and polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid on murine tumor cell growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):5131–5136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorling P. R., Huxtable C. R., Colegate S. M. Inhibition of lysosomal alpha-mannosidase by swainsonine, an indolizidine alkaloid isolated from Swainsona canescens. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):649–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1910649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharide chains. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:497–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Szumilo T., Sanford B. A., Sharpless K. B., Adams C. Effect of isomers of swainsonine on glycosidase activity and glycoprotein processing. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2502–2510. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann U., Bause E., Ploegh H. Inhibitors of oligosaccharide processing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 24;825(2):95–110. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruters R. A., Neefjes J. J., Tersmette M., de Goede R. E., Tulp A., Huisman H. G., Miedema F., Ploegh H. L. Interference with HIV-induced syncytium formation and viral infectivity by inhibitors of trimming glucosidase. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):74–77. doi: 10.1038/330074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirani S., Winchester B. The multiple forms of alpha-D-mannosidase in human plasma. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):583–592. doi: 10.1042/bj1790583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Matsumoto K., White S. L., Olden K. Inhibition of experimental metastasis by castanospermine in mice: blockage of two distinct stages of tumor colonization by oligosaccharide processing inhibitors. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):5215–5222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxtable C. R., Dorling P. R. Animal model of human disease. Mannosidosis. Swainsonine-induced mannosidosis. Am J Pathol. 1982 Apr;107(1):124–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G., Jülich E. Synthesis of 5-amino-5-deoxy-D-mannopyranose and 1,5-dideoxy-1,5-imino-D-mannitol, and inhibition of alpha- and beta-D-mannosidases. Carbohydr Res. 1984 May 15;128(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(84)85084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monis E., Bonay P., Hughes R. C. Characterization of a mannosidase acting on alpha 1----3- and alpha 1----6-linked mannose residues of oligomannosidic intermediates of glycoprotein processing. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):287–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palamarczyk G., Mitchell M., Smith P. W., Fleet G. W., Elbein A. D. 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-imino-D-mannitol inhibits glycoprotein processing and mannosidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 15;243(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90771-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips N. C., Robinson D., Winchester B. G. Characterization of human liver alpha-D-mannosidase purified by affinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):579–587. doi: 10.1042/bj1530579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul R., Ghidoni J. J., Molyneux R. J., Elbein A. D. Castanospermine inhibits alpha-glucosidase activities and alters glycogen distribution in animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):93–97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul R., Molyneux R. J., Elbein A. D. Studies on the mechanism of castanospermine inhibition of alpha- and beta-glucosidases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):668–675. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Harris T. M., Touster O. Swainsonine inhibits the biosynthesis of complex glycoproteins by inhibition of Golgi mannosidase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7936–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyms A. S., Berrie E. M., Ryder T. A., Nash R. J., Hegarty M. P., Taylor D. L., Mobberley M. A., Davis J. M., Bell E. A., Jeffries D. J. Castanospermine and other plant alkaloid inhibitors of glucosidase activity block the growth of HIV. Lancet. 1987 Oct 31;2(8566):1025–1026. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92588-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester B. Role of alpha-D-mannosidases in the biosynthesis and catabolism of glycoproteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Jun;12(3):522–524. doi: 10.1042/bst0120522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]