Abstract
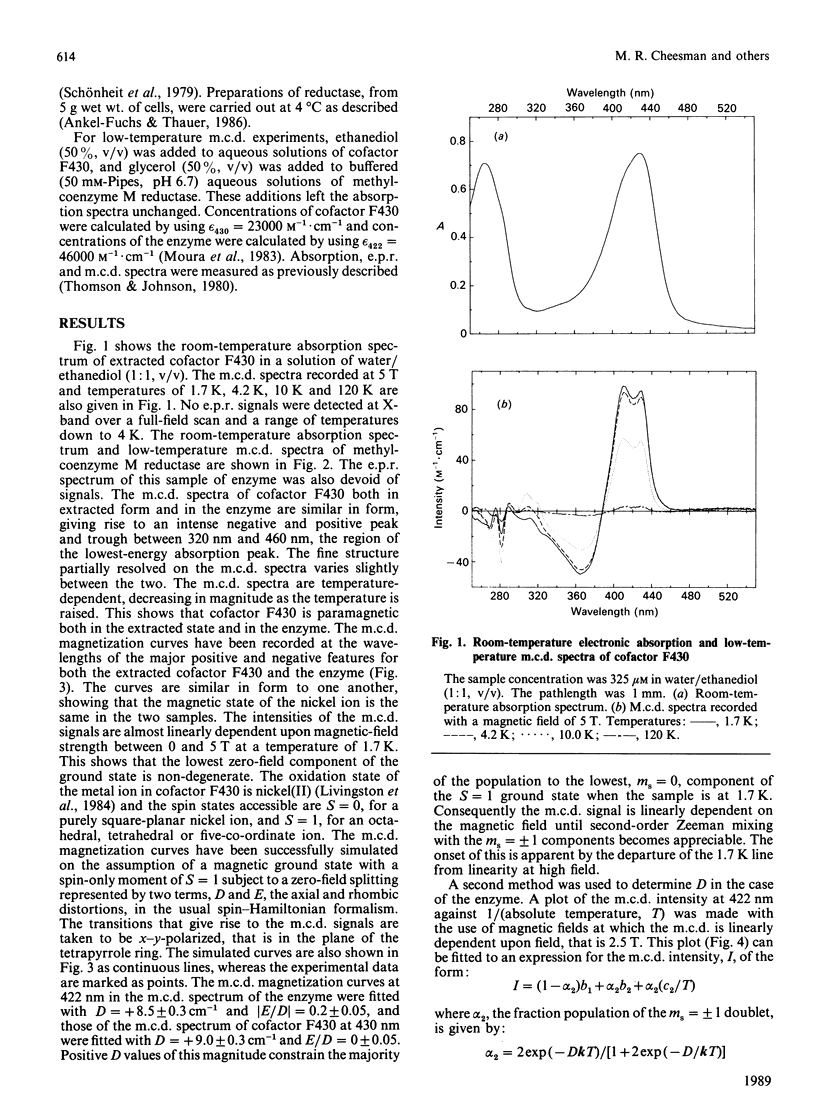
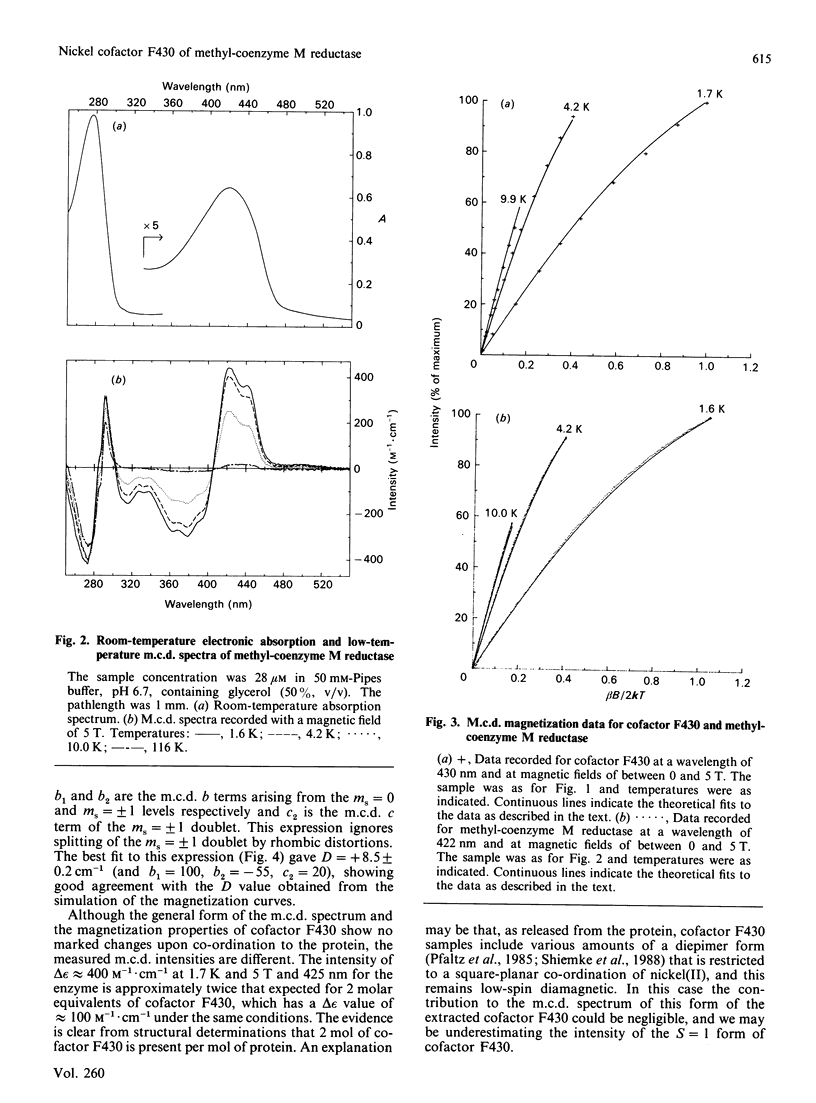
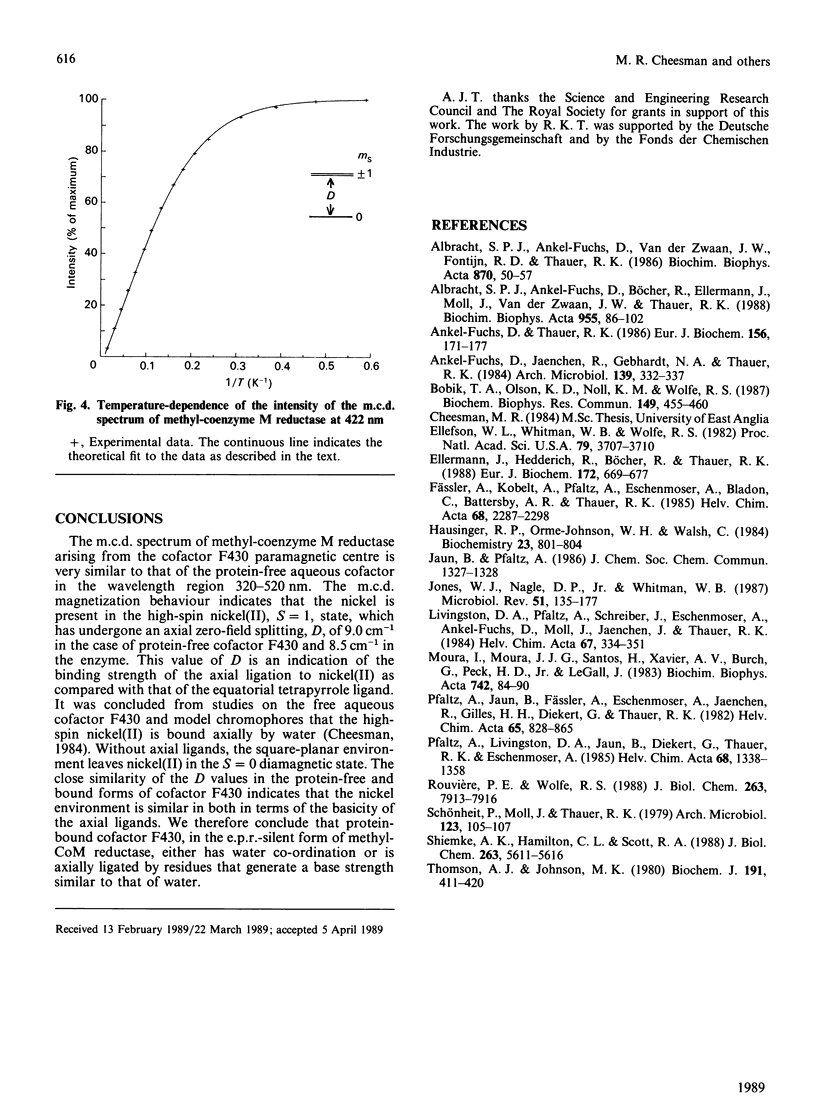
Cofactor 430 of methyl-coenzyme M reductase from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum was studied in both the extracted form in aqueous solution and protein-bound by using low-temperature magnetic-circular-dichroism spectroscopy. In both forms the nickel was present as high-spin paramagnetic nickel(II), spin S = 1, subject to almost equal zero-field splitting (cofactor F430, D = +9.0 cm-1, E/D = 0; methyl-coenzyme M reductase, D = +8.5 cm-1, [E/D[ = 0.2). This suggests identical axial co-ordination by oxygen ligand(s) both in aqueous cofactor F430 and in the investigated state of the protein.
Full text
PDF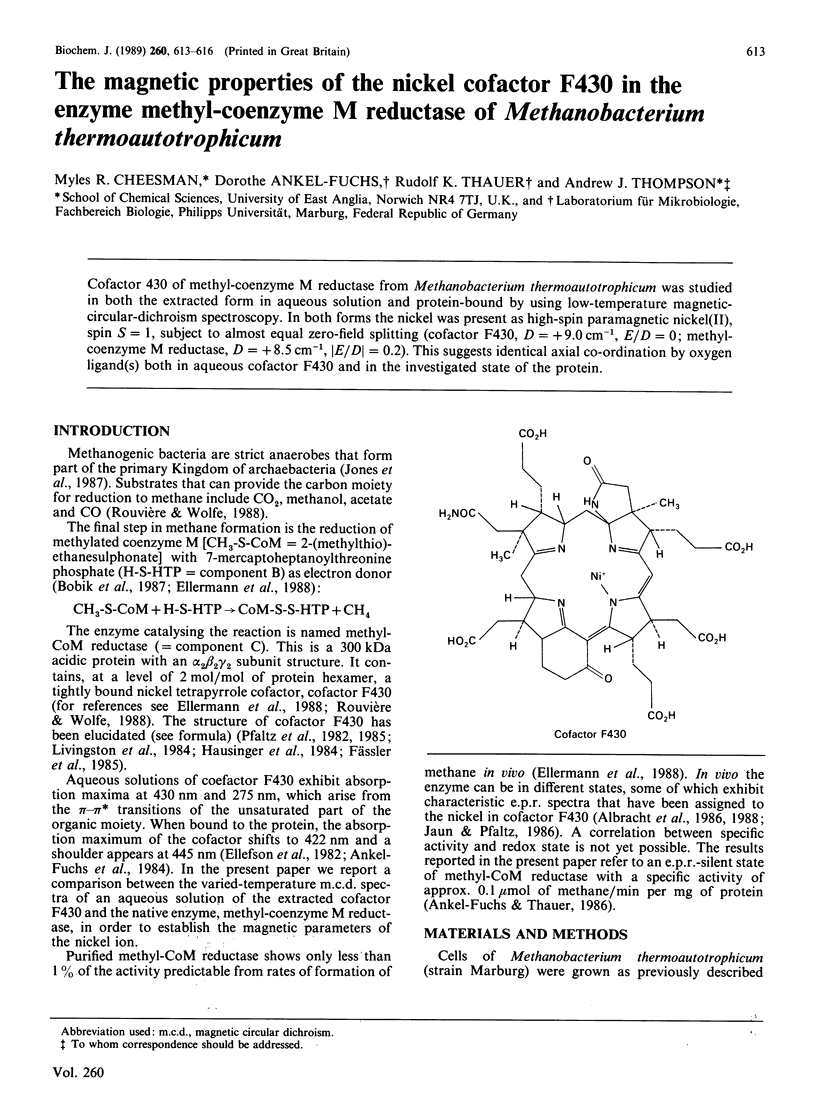
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankel-Fuchs D., Thauer R. K. Methane formation from methyl-coenzyme M in a system containing methyl-coenzyme M reductase, component B and reduced cobalamin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobik T. A., Olson K. D., Noll K. M., Wolfe R. S. Evidence that the heterodisulfide of coenzyme M and 7-mercaptoheptanoylthreonine phosphate is a product of the methylreductase reaction in Methanobacterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):455–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90389-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellefson W. L., Whitman W. B., Wolfe R. S. Nickel-containing factor F430: chromophore of the methylreductase of Methanobacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3707–3710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellermann J., Hedderich R., Böcher R., Thauer R. K. The final step in methane formation. Investigations with highly purified methyl-CoM reductase (component C) from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum (strain Marburg). Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):669–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. J., Nagle D. P., Jr, Whitman W. B. Methanogens and the diversity of archaebacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):135–177. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.135-177.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière P. E., Wolfe R. S. Novel biochemistry of methanogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7913–7916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönheit P., Moll J., Thauer R. K. Nickel, cobalt, and molybdenum requirement for growth of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Oct;123(1):105–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00403508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiemke A. K., Hamilton C. L., Scott R. A. Structural heterogeneity and purification of protein-free F430 from the cytoplasm of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5611–5616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. J., Johnson M. K. Magnetization curves of haemoproteins measured by low-temperature magnetic-circular-dichroism spectroscopy. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):411–420. doi: 10.1042/bj1910411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


