Abstract
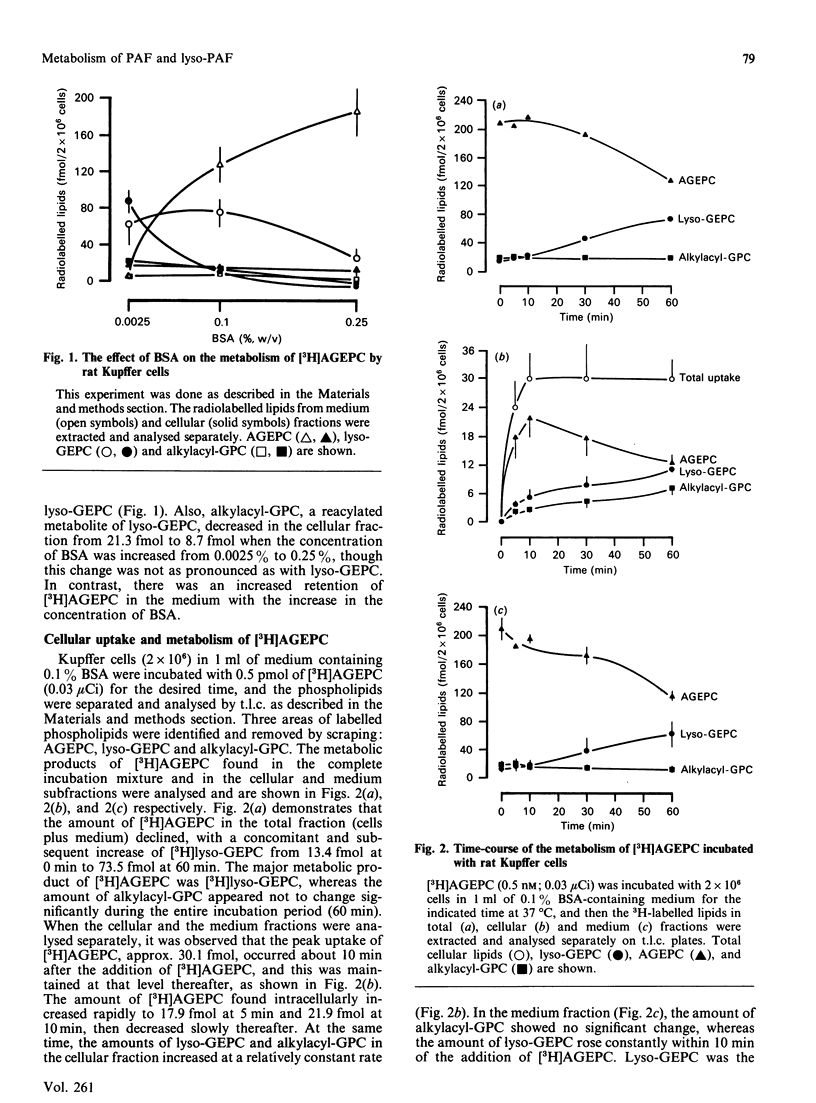
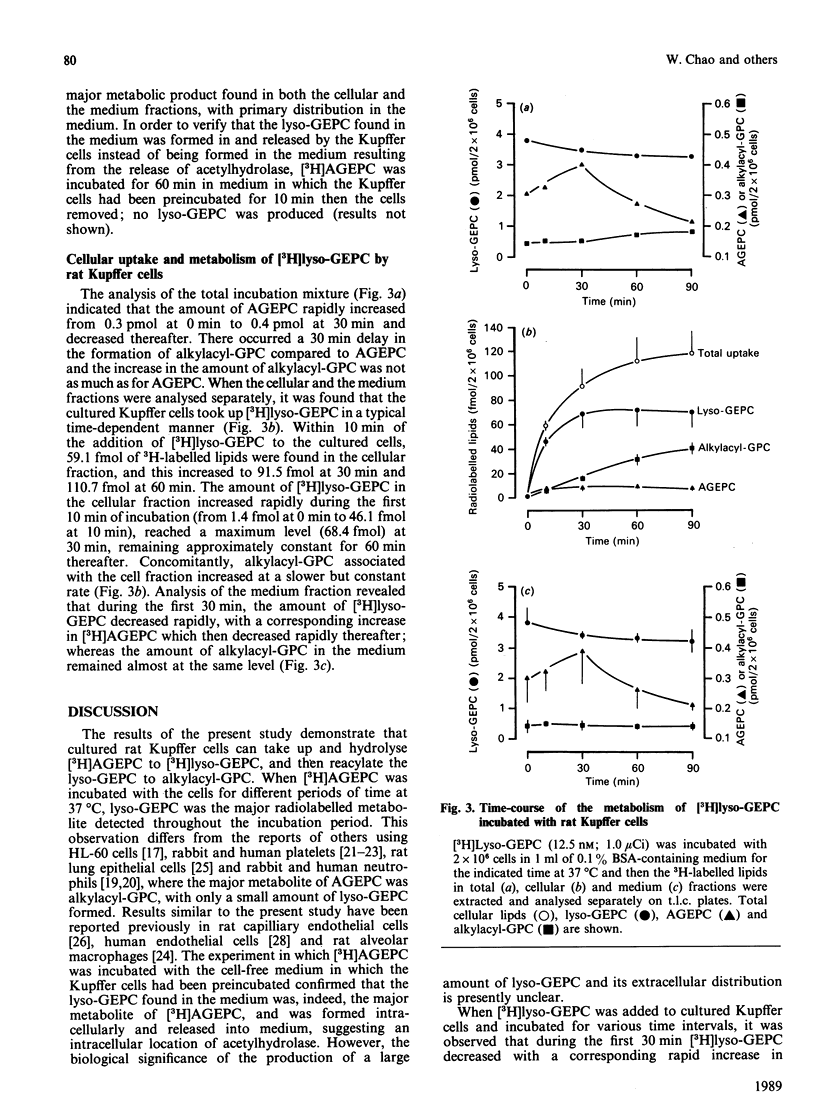
The metabolism of platelet-activating factor (PAF; identified as AGEPC: 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) and lyso-PAF (lyso-GEPC: 1-O-alkyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) was investigated in cultured rat Kupffer cells. The rat Kupffer cells accumulated [3H]AGEPC and deacetylated this compound to the corresponding [3H]lyso-GEPC, which was the major metabolic product of [3H]AGEPC. [3H]Lyso-GEPC was distributed primarily in the supernatant fraction of incubated cells throughout the experimental interval. Only a very small portion of the [3H]lyso-GEPC was further converted to 1-O-alkyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (alkylacyl-GPC), indicating that this acylation process was not particularly active in these cells. When [3H]lyso-GEPC was incubated with Kupffer cells, the conversion of lyso-GEPC to AGEPC via the acetyltransferase reaction increased up to 30 min and declined thereafter. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) had a substantial influence on both the cellular uptake and the metabolism of [3H]AGEPC. An increase in the BSA concentration in the incubation media reduced the cellular uptake of [3H]AGEPC and the subsequent formation of lyso-GEPC. The results of this study suggest that the hepatic Kupffer cells play an important role in the metabolism of PAF. Moreover, these results infer that the regulation of the PAF level in certain hepatic pathophysiological situations may be a consequence of the production and subsequent metabolism of this potent lipid autacoid in the Kupffer cells of the liver.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets. The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1356–1377. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J. Release of platelet-activating factor by peritoneal and alveolar macrophages. Monogr Allergy. 1979;14:138–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Cress E. A., Whittle T., Snyder F. In vivo metabolism of a new class of biologically active phospholipids: 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, a platelet activating-hypotensive phospholipid. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 24;29(8):769–775. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Snyder F., Byers L. W., Brooks B., Muirhead E. E. Antihypertensive activity of an alkyl ether analog of phosphatidylcholine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 29;90(4):1194–1200. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Spector A. A., Kaduce T. L., Lee T. C., Snyder F. Metabolism of platelet activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) and 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol by human endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 21;876(3):373–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Breviario F., Tetta C., Aglietta M., Mantovani A., Dejana E. Interleukin 1 stimulates platelet-activating factor production in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):2027–2033. doi: 10.1172/JCI112532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and platelet-activating factor production by heat-aggregated immunoglobulin G in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13758–13761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Shukla S. D., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Stimulation of hepatic glycogenolysis by acetylglyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1468–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Blank M. L., Welsh C. J., Horan M. J., Cress E. A., Snyder F. Metabolism of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine by cell cultures. Life Sci. 1982 Dec 20;31(25):2891–2898. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90680-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao W., Siafaka-Kapadai A., Olson M. S., Hanahan D. J. Biosynthesis of platelet-activating factor by cultured rat Kupffer cells stimulated with calcium ionophore A23187. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):823–829. doi: 10.1042/bj2570823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., O'Flaherty J. T., Ellis J. M., Swendsen C. L., Wykle R. L. Metabolic fate of platelet-activating factor in neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6357–6361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., O'Flaherty J. T., Ellis J. M., Swendsen C. L., Wykle R. L. Selective acylation of lyso platelet activating factor by arachidonate in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7268–7271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J., Demopoulos C. A., Liehr J., Pinckard R. N. Identification of platelet activating factor isolated from rabbit basophils as acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5514–5516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Patton G. M., Pritzker C. R., Deykin D. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor in human platelets. Transacylase-mediated synthesis of 1-O-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13316–13320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravis T. C., Henson P. M. IgE-induced release of a platelet-activating factor from rabbit lung. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1677–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., King R. J., Martin H. M., Hanahan D. J. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor (alkylacetylphosphocholine) by type-II epithelial cells and fibroblasts from rat lungs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 13;917(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe D. S., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Mobilization of hepatic calcium pools by platelet activating factor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1568–1574. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi R., Burke J. A., Guo Z. G., Hattori Y., Hoppens C. M., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (AGEPC). A putative mediator of cardiac anaphylaxis in the guinea pig. Circ Res. 1984 Feb;54(2):117–124. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone B., Lee T., Snyder F. Inactivation of platelet activating factor by rabbit platelets. Lyso-platelet activating factor as a key intermediate with phosphatidylcholine as the source of arachidonic acid in its conversion to a tetraenoic acylated product. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1531–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Human platelet stimulation by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):903–906. doi: 10.1172/JCI110108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L., Miller C. H., Lewis J. C., Waite M., Bass D. A., McCall C. E., DeChatelet L. R. 1-O-Alkyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholines: a novel class of neutrophil stimulants. Am J Pathol. 1981 Apr;103(1):70–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayasu T., Hoshii K., Seyama K., Ishibashi T., Imai Y. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor in primary cultured adult rat hepatocytes by a new pathway involving phospholipase C and alkyl monooxygenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 21;876(1):58–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni G., Hanahan D. J. Metabolic behavior of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine on interaction with rabbit platelets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 15;224(2):485–493. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Farr R. S., Hanahan D. J. Physicochemical and functional identity of rabbit platelet-activating factor (PAF) released in vivo during IgE anaphylaxis with PAF released in vitro from IgE sensitized basophils. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1847–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotzky E., Ninio E., Bidault J., Pfister A., Benveniste J. Biosynthesis of platelet-activating factor. VI. Precursor of platelet-activating factor and acetyltransferase activity in isolated rat kidney cells. Lab Invest. 1984 Nov;51(5):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Human endothelial cells in culture produce platelet-activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) when stimulated with thrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3534–3538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renooij W., Snyder F. Biosynthesis of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor and a hypotensive lipid) by cholinephosphotransferase in various rat tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 23;663(2):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Snyder F. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor by rat alveolar macrophages: lyso-PAF as an obligatory intermediate in the formation of alkylarachidonoyl glycerophosphocholine species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 23;837(1):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubin R., Dulioust A., Haye-Legrand I., Ninio E., Benveniste J. Biosynthesis of paf-acether: VIII: Impairment of paf-acether production in activated macrophages does not depend upon acetyltransferase activity. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D., Buxton D. B., Olson M. S., Hanahan D. J. Acetylglyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. A potent activator of hepatic phosphoinositide metabolism and glycogenolysis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10212–10214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P., Osler A. G. Destruction of rabbit platelets in the allergic response of sensitized leukocytes. I. Demonstration of a fluid phase intermediate. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1244–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. L., Snyder F. Metabolism of platelet activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) by capillary endothelial cells isolated from rat epididymal adipose tissue. Thromb Res. 1985 Jun 15;38(6):713–717. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touqui L., Hatmi M., Vargaftig B. B. Human platelets stimulated by thrombin produce platelet-activating factor (1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) when the degrading enzyme acetyl hydrolase is blocked. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 1;229(3):811–816. doi: 10.1042/bj2290811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita M., Homma H., Inoue K., Nojima S. The metabolism of platelet activating factor in platelets and plasma of various animals. J Toxicol Sci. 1983 Aug;8(3):177–188. doi: 10.2131/jts.8.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


