Abstract
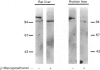
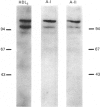
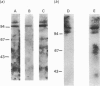
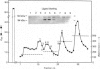
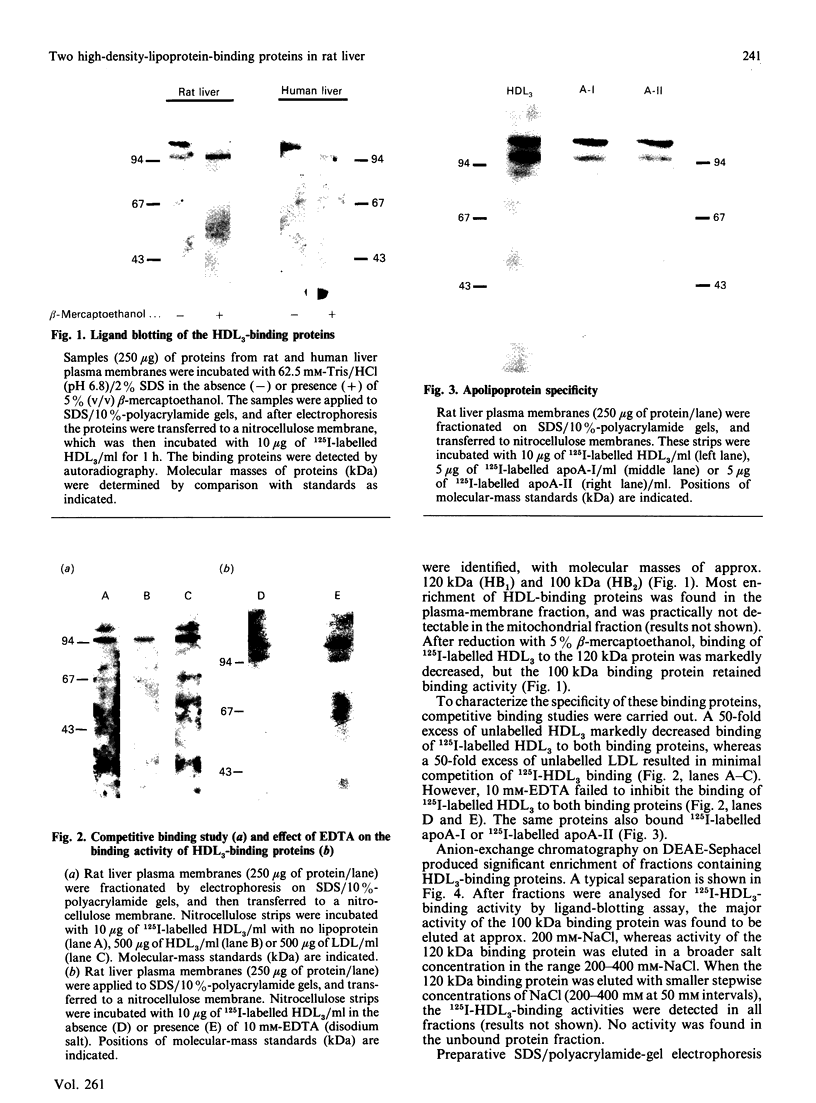
The liver plays a major role in the metabolism of plasma high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Several groups have postulated, but others refuted, the existence of a classical membrane receptor which recognizes HDL. In the present study, we identified and purified two liver HDL-binding proteins of 120 kDa (HB1) and 100 kDa (HB2), with apparent specificity for HDL3 devoid of E apolipoprotein. The plasma membrane was the richest source of the HDL-binding protein. Both proteins bound A-I and A-II apolipoproteins and retained HDL-binding activity after final purification. HB1 activity, but not that of HB2, was lost after treatment with beta-mercaptoethanol, but reduction did not change the apparent molecular mass of either protein. Antibodies against HB1 or HB2 did not cross-react, and preliminary structural investigations provide evidence to suggest that HB1 and HB2 are not structurally related. We thus provide evidence for at least two liver plasma-membrane proteins which bind HDL apolipoproteins, suggesting that protein-protein interaction participates to some degree in the mechanism of HDL recognition by cells.
Full text
PDF

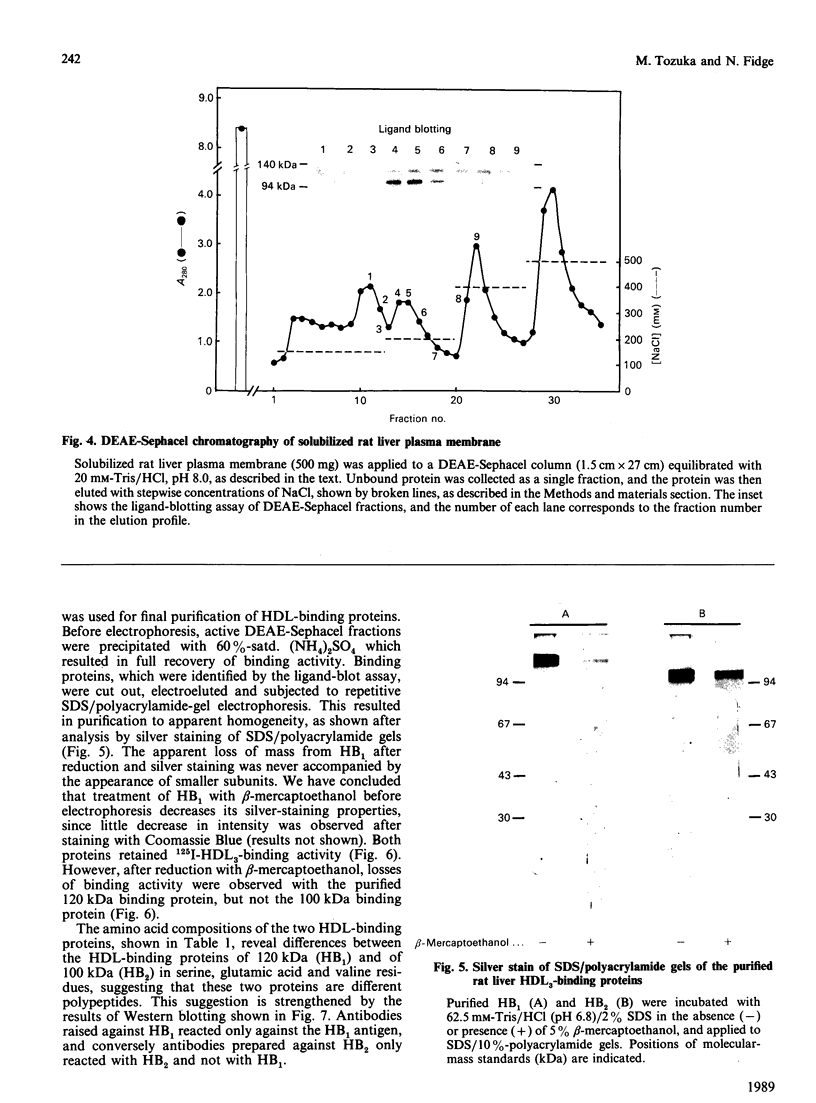
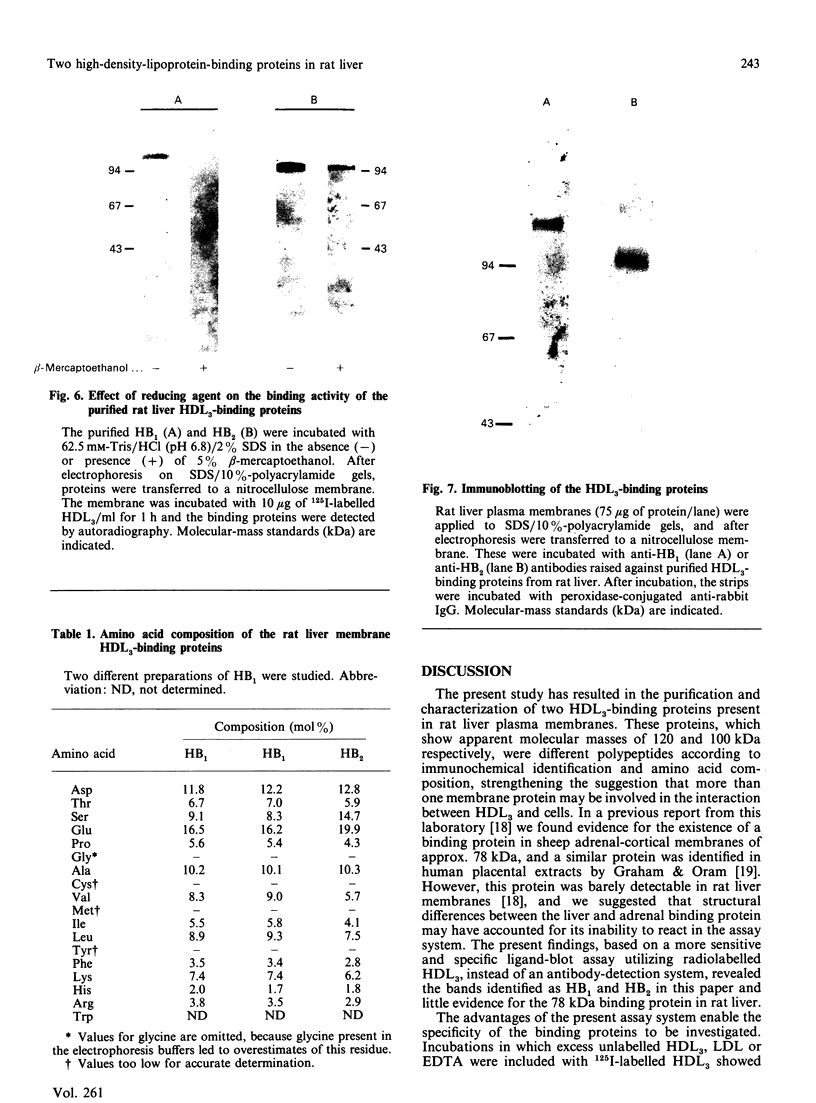

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbaras R., Grimaldi P., Negrel R., Ailhaud G. Characterization of high-density lipoprotein binding and cholesterol efflux in cultured mouse adipose cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 19;888(2):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaras R., Puchois P., Grimaldi P., Barkia A., Fruchart J. C., Ailhaud G. Relationship in adipose cells between the presence of receptor sites for high density lipoproteins and the promotion of reverse cholesterol transport. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesbroeck R., Oram J. F., Albers J. J., Bierman E. L. Specific high-affinity binding of high density lipoproteins to cultured human skin fibroblasts and arterial smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):525–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI110797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko G. K. Characterization of high-density lipoprotein binding sites in rat liver and testis membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 12;795(2):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. S., Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J. Initial plasma high-density lipoprotein distribution in the rat: effects of age, sex, and fasting. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):G369–G376. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.3.G369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J. Identification of apolipoproteins involved in the interaction of human high density lipoprotein3 with receptors on cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3570–3575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H. Partial purification of a high density lipoprotein-binding protein from rat liver and kidney membranes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 21;199(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Poulis P. Studies on the radioiodination of very low density lipoprotein obtained from different mammalian species. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Mar;52(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N., Leonard-Kanevsky M., Nestel P. The hormonal stimulation of high-density lipoprotein binding, internalization and degradation by cultured rat adrenal cortical cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 18;793(2):180–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90319-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Kervina M. Subcellular fractionation of rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:6–41. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong B. S., Rodrigues P. O., Salter A. M., Yip B. P., Despres J. P., Angel A., Gregg R. E. Characterization of high density lipoprotein binding to human adipocyte plasma membranes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1804–1812. doi: 10.1172/JCI111893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D. K., Menon K. M. Induction of high-density-lipoprotein receptors in rat corpus luteum by human choriogonadotropin. Evidence of protein synthesis de novo. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):471–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2440471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C., Pittman R. C., Civen M., Steinberg D. Uptake of high-density lipoprotein-associated apoprotein A-I and cholesterol esters by 16 tissues of the rat in vivo and by adrenal cells and hepatocytes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):744–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C., Pittman R. C., Weinstein D. B., Steinberg D. Dissociation of tissue uptake of cholesterol ester from that of apoprotein A-I of rat plasma high density lipoprotein: selective delivery of cholesterol ester to liver, adrenal, and gonad. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5435–5439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. L., Oram J. F. Identification and characterization of a high density lipoprotein-binding protein in cell membranes by ligand blotting. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne J. T., Hess B. Binding and degradation of human 125I-HDL by rat adrenocortical cells. Metabolism. 1978 Nov;27(11):1593–1600. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeg J. M., Demosky S. J., Jr, Edge S. B., Gregg R. E., Osborne J. C., Jr, Brewer H. B., Jr Characterization of a human hepatic receptor for high density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):228–237. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.3.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keso L., Lukka M., Ehnholm C., Baumann M., Vihko P., Olkinuora M. Apolipoprotein A-I-binding protein from human term placenta. Purification and partial characterization. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 4;215(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Sherrill B. C., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Correlation of low and high density lipoprotein binding in vivo with rates of lipoprotein degradation in the rat. A comparison of lipoproteins of rat and human origin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8061–8072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Schneider W. J., Hillman G. M., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Separate mechanisms for the uptake of high and low density lipoproteins by mouse adrenal gland in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5498–5505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel C. M., Kunitake S. T., Kane J. P., Kempner E. S. Radiation inactivation of binding sites for high density lipoproteins in human fibroblast membranes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1314–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Brinton E. A., Bierman E. L. Regulation of high density lipoprotein receptor activity in cultured human skin fibroblasts and human arterial smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1611–1621. doi: 10.1172/JCI111120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K. A modified method for the isolation of the plasma membrane from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearne P. A., van Driel I. R., Grego B., Simpson R. J., Goding J. W. The murine plasma cell antigen PC-1: purification and partial amino acid sequence. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Fidge N., Nestel P., Yin J. Interaction of serum lipoproteins with the intestine. Evidence for specific high density lipoprotein-binding sites on isolated rat intestinal mucosal cells. J Lipid Res. 1983 Mar;24(3):253–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sviridov D. D., Safonova I. G., Gusev V. A., Talalaev A. G., Tsibulsky V. P., Ivanov V. O., Preobrazensky S. N., Repin V. S., Smirnov V. N. Specific high affinity binding and degradation of high density lipoproteins by isolated epithelial cells of human small intestine. Metabolism. 1986 Jul;35(7):588–595. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabas I., Tall A. R. Mechanism of the association of HDL3 with endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and fibroblasts. Evidence against the role of specific ligand and receptor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13897–13905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]