Abstract
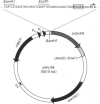
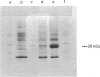
The cDNA coding for human dihydropteridine reductase [Dahl, Hutchinson, McAdam, Wake, Morgan & Cotton (1987) Nucleic Acids Res. 15, 1921-1936] was inserted downstream of tandem bacteriophage lambda PR and PL promoters in Escherichia coli vector pCE30. Since pCE30 also expresses the lambda c1857ts gene, transcription may be controlled by variation of temperature. The recombinant plasmid in an E. coli K12 strain grown at 30 degrees C, then at 45 degrees C, directed the synthesis of dihydropteridine reductase to very high levels. The protein was soluble, at least as active as the authentic human enzyme, and lacked the N-terminal amino acid protection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armarego W. L., Ohnishi A., Taguchi H. New pteridine substrates for dihydropteridine reductase and horseradish peroxidase. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):335–342. doi: 10.1042/bj2340335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armarego W. L., Randles D., Taguchi H. Peroxidase catalysed aerobic degradation of 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin at physiological pH. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):393–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armarego W. L., Randles D., Waring P. Dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR), its cofactors, and its mode of action. Med Res Rev. 1984 Jul-Sep;4(3):267–321. doi: 10.1002/med.2610040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Jennings I. G. Affinity chromatography of phenylalanine hydroxylase. The structure of a pteridine adsorbent. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):357–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl H. H., Hutchison W., McAdam W., Wake S., Morgan F. J., Cotton R. G. Human dihydropteridine reductase: characterisation of a cDNA clone and its use in analysis of patients with dihydropteridine reductase deficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):1921–1932. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks D. M., Bartholomé K., Clayton B. E., Curtius H., Gröbe H., Kaufman S., Leeming R., Pfleiderer W., Rembold H., Rey F. Malignant hyperphenylalaninaemia--current status (June 1977). J Inherit Metab Dis. 1978;1(2):49–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01801843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firgaira F. A., Cotton R. G., Danks D. M. Isolation and characterization of dihydropteridine reductase from human liver. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):31–43. doi: 10.1042/bj1970031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockyer J., Cook R. G., Milstien S., Kaufman S., Woo S. L., Ledley F. D. Structure and expression of human dihydropteridine reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3329–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rembold H., Buff K. Tetrahydrobiopterin, a cofactor in mitochondrial electron transfer. A soluble transfer system. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 4;28(4):586–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIETZ A., LINDBERG M., KENNEDY E. P. A NEW PTERIDINE-REQUIRING ENZYME SYSTEM FOR THE OXIDATION OF GLYCERYL ETHERS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4081–4090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan S. G., Shaw D. C., Armarego W. L. Dihydropteridine reductase from Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):581–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]