Abstract
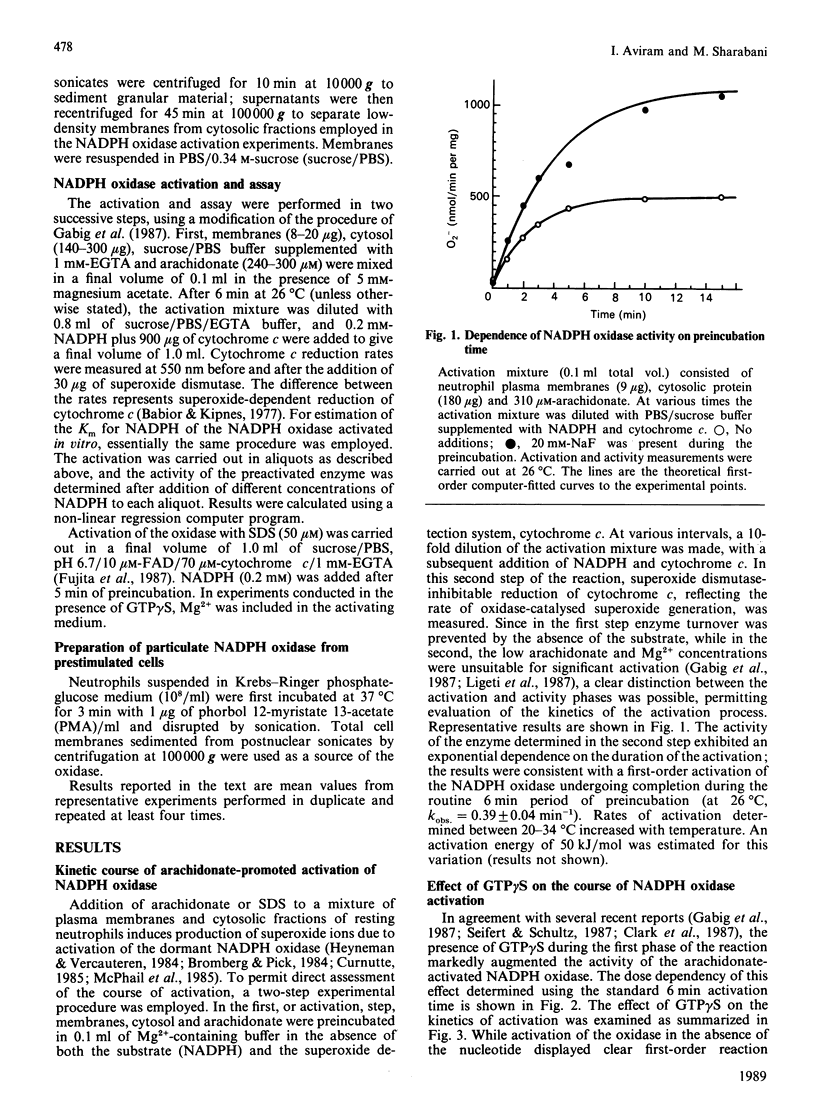
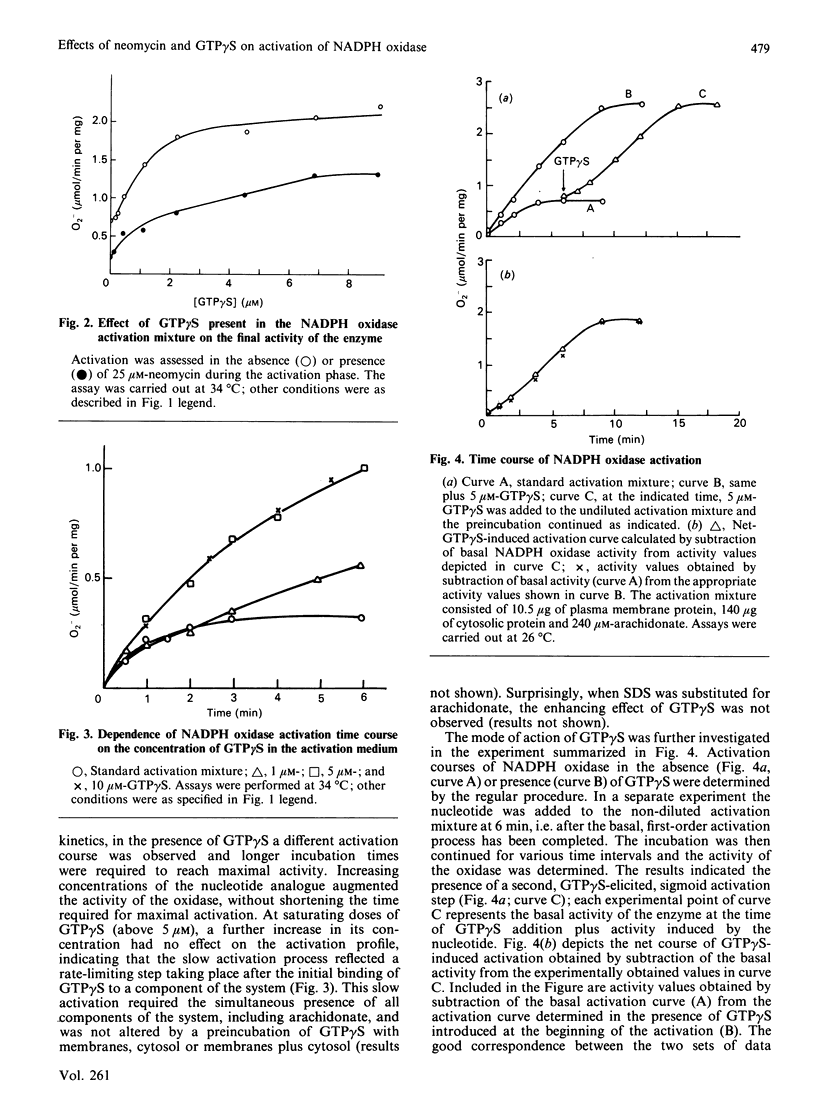
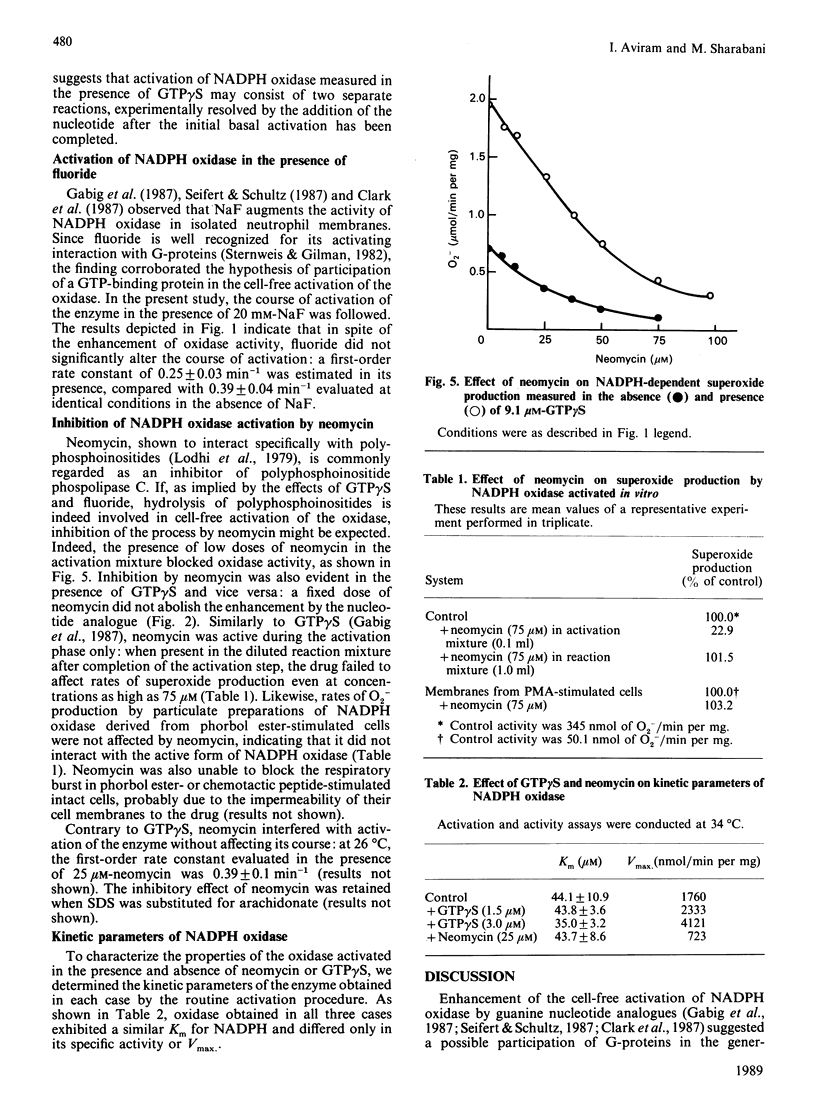
The effects of neomycin, fluoride and the non-hydrolysable guanine nucleotide analogue GTP gamma S on the kinetics of cell-free activation of NADPH oxidase in membranes of resting human neutrophils were investigated. Arachidonate-mediated activation of the oxidase followed a first-order reaction course (kobs. = 0.39 min-1 at 26 degrees C). In the presence of NaF during the activation process, activity was enhanced while the activation rate was slightly reduced (kobs. = 0.25 min-1 at 26 degrees C). Neomycin blocked activation (half-maximal effect at 25 microM) without affecting rates of superoxide release by preactivated enzyme in vitro or in vivo. In spite of reduced specific activity neither the first-order rate constant of the activation nor the Km of the oxidase were altered by neomycin. Oxidase activated in the presence of GTP gamma S exhibited increased specific activity and unchanged Km; the course of the reaction deviated from first-order kinetics. Kinetic evidence is presented for two separate activation reactions: a GTP gamma S-independent, basal, first-order process and a GTP gamma S-dependent sigmoid activation process. The results are compatible with the existence in neutrophil membranes of two separate pools of dormant oxidase. An alternative scheme of the formation of two active forms of NADPH oxidase is also presented.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S. Superoxide-forming enzyme from human neutrophils: evidence for a flavin requirement. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):517–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kuver R., Curnutte J. T. Kinetics of activation of the respiratory burst oxidase in a fully soluble system from human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1713–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badwey J. A., Curnutte J. T., Robinson J. M., Berde C. B., Karnovsky M. J., Karnovsky M. L. Effects of free fatty acids on release of superoxide and on change of shape by human neutrophils. Reversibility by albumin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7870–7877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg Y., Pick E. Activation of NADPH-dependent superoxide production in a cell-free system by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13539–13545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg Y., Pick E. Unsaturated fatty acids stimulate NADPH-dependent superoxide production by cell-free system derived from macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 1;88(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Luini A., Axelrod J. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C are activated by distinct GTP-binding proteins in response to alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation in FRTL5 thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7201–7205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Leidal K. G., Pearson D. W., Nauseef W. M. NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils. Subcellular localization and characterization of an arachidonate-activatable superoxide-generating system. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4065–4074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. A., Jeng A. Y., Blumberg P. M., Tauber A. I. Comparison of subcellular activation of the human neutrophil NADPH-oxidase by arachidonic acid, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and phorbol myristate acetate (PMA). J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1884–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. A., Jeng A. Y., Sharkey N. A., Blumberg P. M., Tauber A. I. Activation of the human neutrophil nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-oxidase by protein kinase C. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1932–1938. doi: 10.1172/JCI112190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Activation of human neutrophil nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced (triphosphopyridine nucleotide, reduced) oxidase by arachidonic acid in a cell-free system. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1740–1743. doi: 10.1172/JCI111885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doussiere J., Pilloud M. C., Vignais P. V. Activation of bovine neutrophil oxidase in a cell free system. GTP-dependent formation of a complex between a cytosolic factor and a membrane protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):993–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80382-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita I., Takeshige K., Minakami S. Characterization of the NADPH-dependent superoxide production activated by sodium dodecyl sulfate in a cell-free system of pig neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 22;931(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., English D., Akard L. P., Schell M. J. Regulation of neutrophil NADPH oxidase activation in a cell-free system by guanine nucleotides and fluoride. Evidence for participation of a pertussis and cholera toxin-insensitive G protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1685–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyneman R. A., Vercauteren R. E. Activation of a NADPH oxidase from horse polymorphonuclear leukocytes in a cell-free system. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Dec;36(6):751–759. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.6.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligeti E., Doussiere J., Vignais P. V. Activation of the O2(.-)-generating oxidase in plasma membrane from bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophils by arachidonic acid, a cytosolic factor of protein nature, and nonhydrolyzable analogues of GTP. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):193–200. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodhi S., Weiner N. D., Schacht J. Interactions of neomycin with monomolecular films of polyphosphoinositides and other lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Shirley P. S., Clayton C. C., Snyderman R. Activation of the respiratory burst enzyme from human neutrophils in a cell-free system. Evidence for a soluble cofactor. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1735–1739. doi: 10.1172/JCI111884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima S., Tohmatsu T., Shirato L., Takenaka A., Nozawa Y. Neomycin is a potent agent for arachidonic acid release in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):820–826. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90604-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polascik T., Godfrey P. P., Watson S. P. Neomycin cannot be used as a selective inhibitor of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in intact or semi-permeabilized human platelets. Aminoglycosides activate semi-permeabilized platelets. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):815–819. doi: 10.1042/bj2430815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F. The O2- -forming NADPH oxidase of the phagocytes: nature, mechanisms of activation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 4;853(1):65–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(86)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Jones O. T. Novel cytochrome b system in phagocytic vacuoles of human granulocytes. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):515–517. doi: 10.1038/276515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Schultz G. Fatty-acid-induced activation of NADPH oxidase in plasma membranes of human neutrophils depends on neutrophil cytosol and is potentiated by stable guanine nucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):563–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Shefcyk J., Huang C. K., Marsh M. L., Munoz J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits fMet-Leu-Phe- but not phorbol ester-stimulated changes in rabbit neutrophils: role of G proteins in excitation response coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


