Abstract
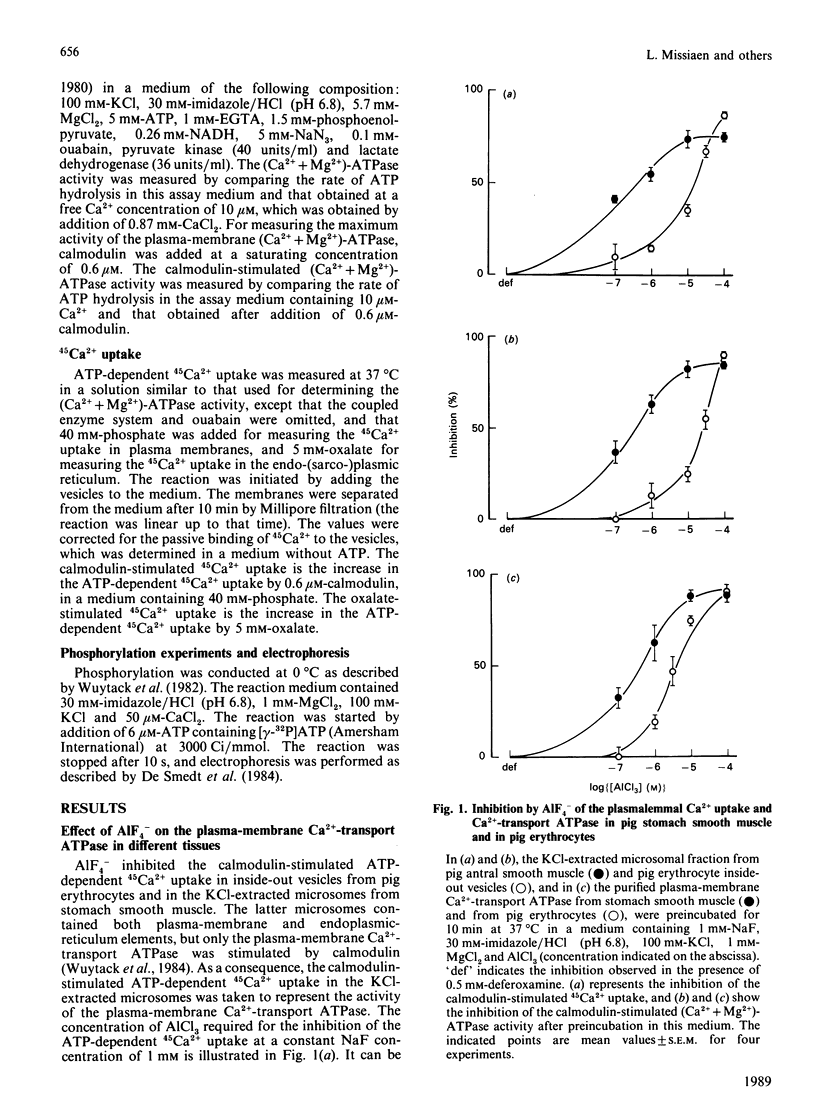
AIF4- inhibits the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase activity of the plasma-membrane and the sarcoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-transport ATPase [Missiaen, Wuytack, De Smedt, Vrolix & Casteels (1988) Biochem. J. 253, 827-833]. The aim of the present work was to investigate this inhibition further. We now report that AIF4- inhibits not only the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase activity, but also the ATP-dependent 45Ca2+ transport, and the formation of the phosphoprotein intermediate by these pumps. Mg2+ potentiated the effect of AIF4-, whereas K+ had no such effect. The plasma-membrane Ca2+-transport ATPase from erythrocytes was 20 times less sensitive to inhibition by AIF4- as compared with the Ca2+-transport ATPase from smooth muscle. The endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-transport ATPase from smooth muscle was inhibited to a greater extent than the sarcoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-transport ATPase of slow and fast skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF
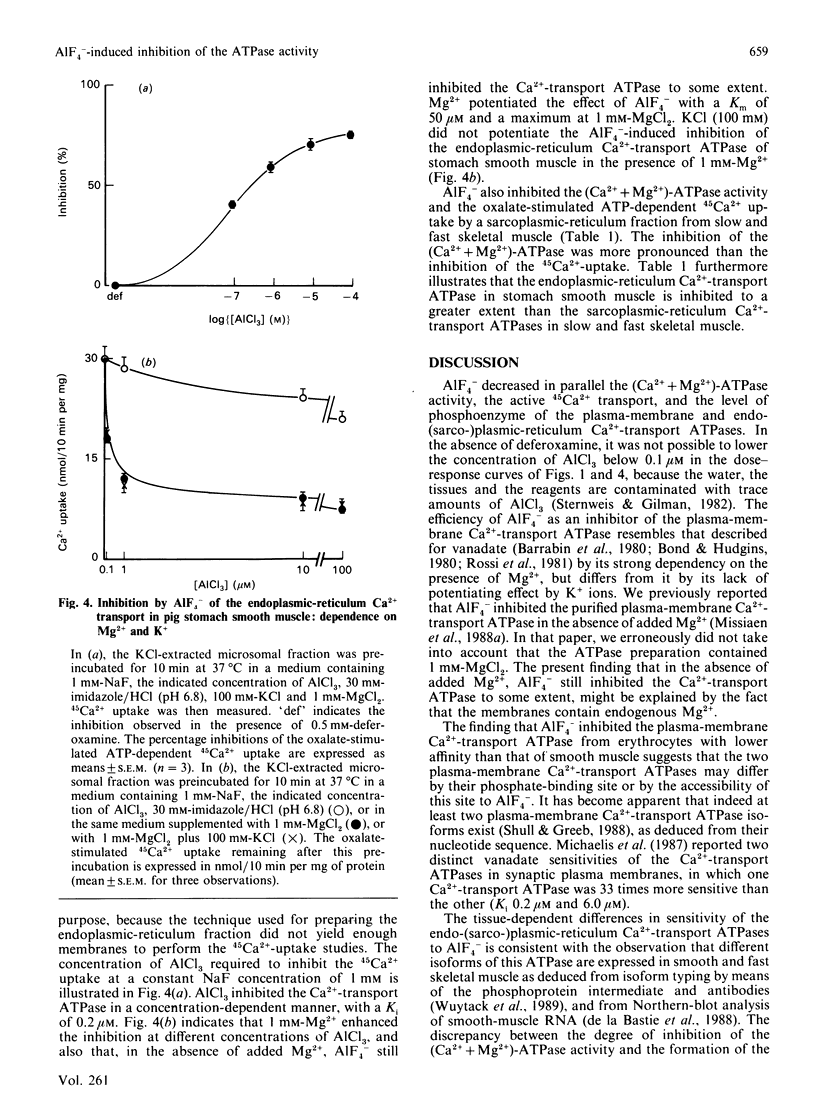

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrabin H., Garrahan P. J., Rega A. F. Vanadate inhibition of the Ca2+-ATPase from human red cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):796–804. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond G. H., Hudgins P. M. Inhibition of red cell Ca2+-ATPase by vanadate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):781–790. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Smedt H., Parys J. B., Wuytack F., Borghgraef R. Calcium-induced phosphorylations and [125I]calmodulin binding in renal membrane preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 19;776(1):122–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann C., Brdiczka D., Nickel E., Pette D. ATPase activities, Ca2+ transport and phosphoprotein formation in sarcoplasmic reticulum subfractions of fast and slow rabbit muscles. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec 1;81(2):211–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo T. H. Guanine nucleotide-, and inositol triphosphate-induced inhibition of the CA2+ pump in rat heart sarcolemmal vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis M. L., Kitos T. E., Nunley E. W., Lecluyse E., Michaelis E. K. Characteristics of Mg2+-dependent, ATP-activated Ca2+ transport in synaptic and microsomal membranes and in permeabilized synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4182–4189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., Kanmura Y., Wuytack F., Casteels R. Carbachol partially inhibits the plasma-membrane Ca2+-pump in microsomes from pig stomach smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):681–686. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90445-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., Wuytack F., De Smedt H., Vrolix M., Casteels R. AlF4- reversibly inhibits 'P'-type cation-transport ATPases, possibly by interacting with the phosphate-binding site of the ATPase. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):827–833. doi: 10.1042/bj2530827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. The interaction of vanadate ions with the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6111–6119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers L., Wuytack F., Casteels R. Subcellular fractionation of pig stomach smooth muscle. A study of the distribution of the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase activity in plasmalemma and endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):441–454. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. P., Garrahan P. J., Rega A. F. Vanadate inhibition of active Ca2+ transport across human red cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 6;648(2):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J. Molecular cloning of two isoforms of the plasma membrane Ca2+-transporting ATPase from rat brain. Structural and functional domains exhibit similarity to Na+,K+- and other cation transport ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8646–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
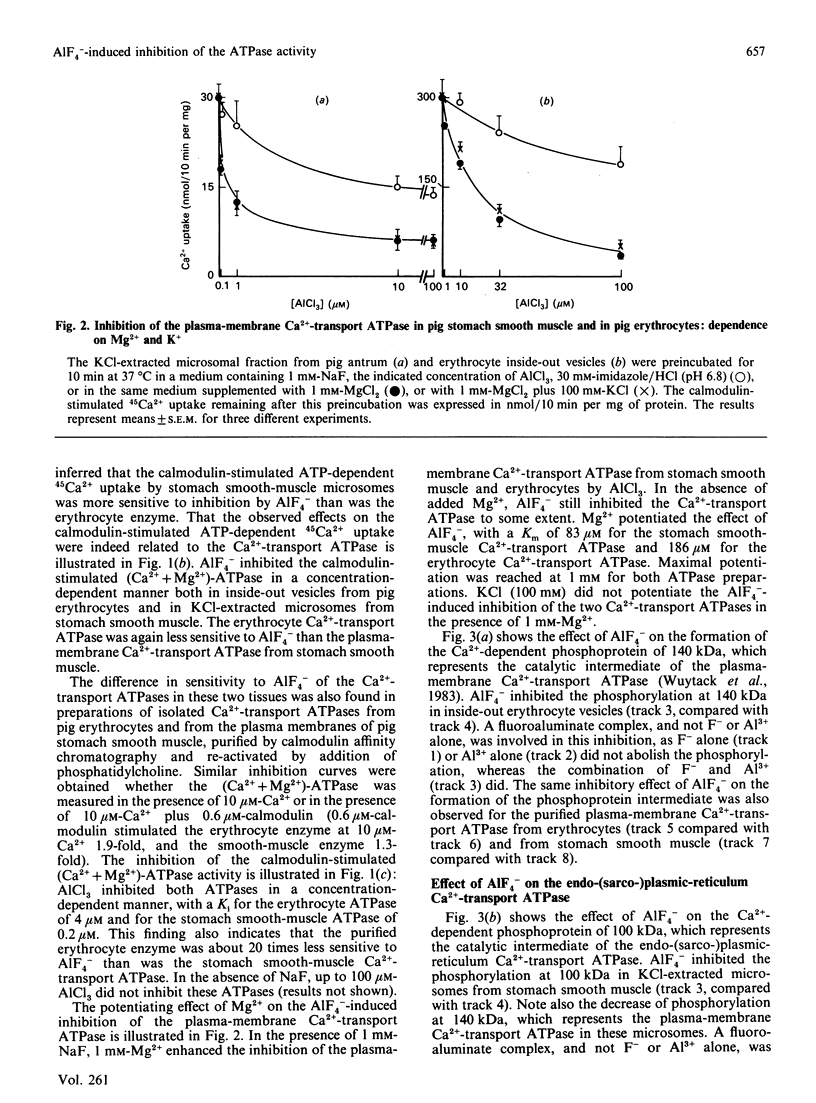
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrolix M., Raeymaekers L., Wuytack F., Hofmann F., Casteels R. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase stimulates the plasmalemmal Ca2+ pump of smooth muscle via phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):855–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2550855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Casteels R. Demonstration of a (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase activity probably related to Ca2+ transport in the microsomal fraction of porcine coronary artery smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., De Schutter G., Casteels R. Purification of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from smooth muscle by calmodulin affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 6;129(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., De Schutter G., Verbist J., Casteels R. Antibodies to the calmodulin-binding Ca2+-transport ATPase from smooth muscle. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 5;154(1):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80901-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Kanmura Y., Eggermont J. A., Raeymaekers L., Verbist J., Hartweg D., Gietzen K., Casteels R. Smooth muscle expresses a cardiac/slow muscle isoform of the Ca2+-transport ATPase in its endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 1;257(1):117–123. doi: 10.1042/bj2570117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Raeymaekers L., De Schutter G., Casteels R. Demonstration of the phosphorylated intermediates of the Ca2+-transport ATPase in a microsomal fraction and in a (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase purified from smooth muscle by means of calmodulin affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 8;693(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Raeymaekers L., Verbist J., De Smedt H., Casteels R. Evidence for the presence in smooth muscle of two types of Ca2+-transport ATPase. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):445–451. doi: 10.1042/bj2240445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
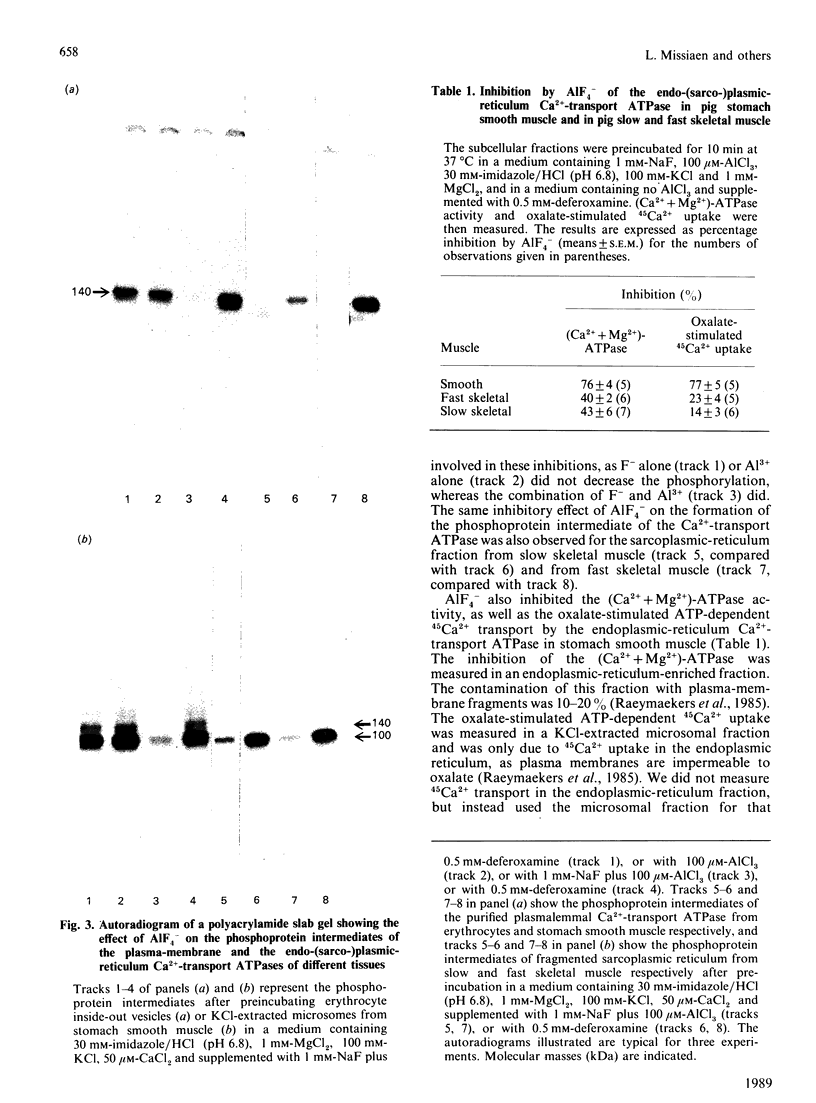
- de la Bastie D., Wisnewsky C., Schwartz K., Lompré A. M. (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-dependent ATPase mRNA from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum differs from that in cardiac and fast skeletal muscles. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]