Abstract
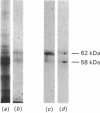
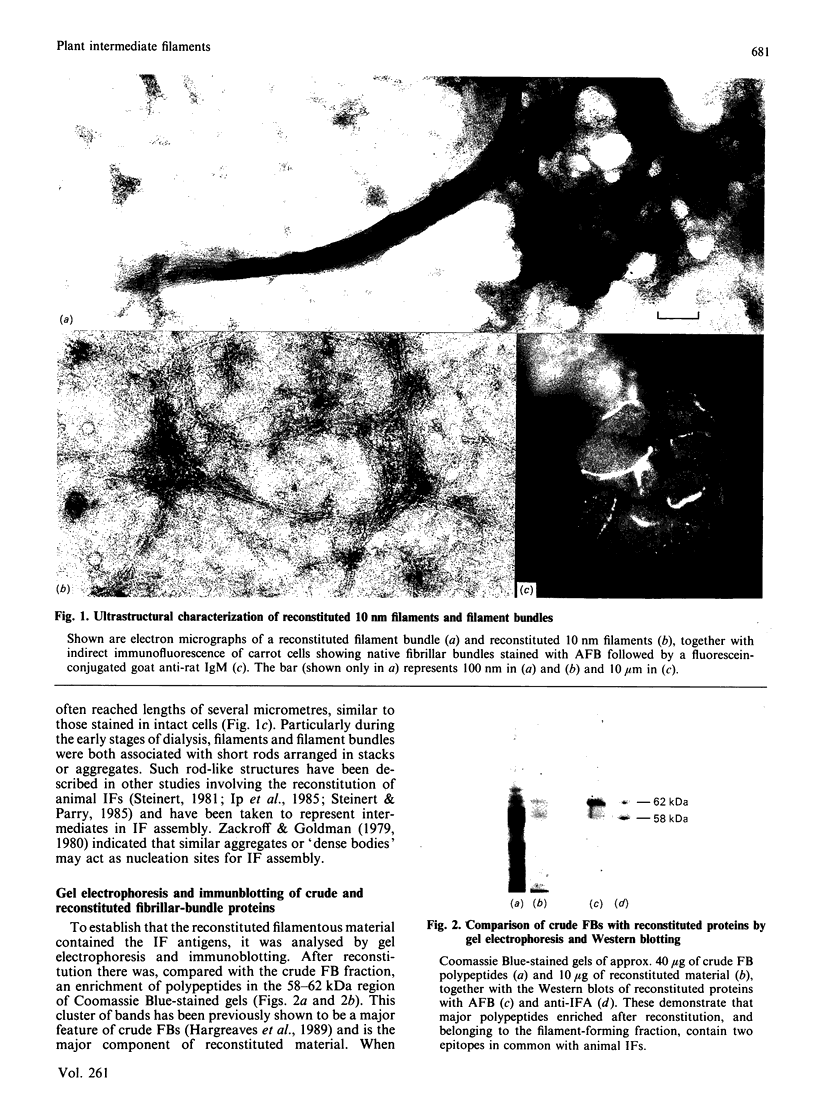
Immunological studies have shown that plants contain intermediate-filament antigens, but it is not known whether these proteins are capable in themselves of forming filaments. To address this problem, a detergent-resistant and high-salt-insoluble fraction from carrot (Daucus carota L.) suspension cells was solubilized with 9 M-urea and then subjected to a two-step dialysis procedure, devised for the reconstitution of animal intermediate filaments. This induced the self-assembly of 10 nm filaments and large bundles of filaments. The predominant components of reconstituted material were polypeptides with apparent molecular masses between 58 and 62 kDa. These polypeptides immunoblotted with two monoclonal antibodies known to show broad cross-reactivity with intermediate filaments across the phylogenetic spectrum. This establishes that the antigens are able to self-assemble into intermediate-sized filaments.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dawson P. J., Hulme J. S., Lloyd C. W. Monoclonal antibody to intermediate filament antigen cross-reacts with higher plant cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1793–1798. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Grund C., Geiger B. Intermediate filament proteins in nonfilamentous structures: transient disintegration and inclusion of subunit proteins in granular aggregates. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Winter S., Osborn M., Weber K. Widespread occurrence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):25–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Winter S., Grund C., Schmid E., Schiller D. L., Jarasch E. D. Isolation and characterization of desmosome-associated tonofilaments from rat intestinal brush border. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):116–127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Fischer S., Plessmann U., Weber K. Neurofilament architecture combines structural principles of intermediate filaments with carboxy-terminal extensions increasing in size between triplet proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1295–1302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Self-assembly in Vitro of the 68,000 molecular weight component of the mammalian neurofilament triplet proteins into intermediate-sized filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Pair formation and promiscuity of cytokeratins: formation in vitro of heterotypic complexes and intermediate-sized filaments by homologous and heterologous recombinations of purified polypeptides. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1826–1841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip W., Hartzer M. K., Pang Y. Y., Robson R. M. Assembly of vimentin in vitro and its implications concerning the structure of intermediate filaments. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann E., Weber K., Geisler N. Intermediate filament forming ability of desmin derivatives lacking either the amino-terminal 67 or the carboxy-terminal 27 residues. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 20;185(4):733–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke J. M., Miller C. C., Cowell I., Dodson A., Dowding A., Downes M., Duckett J. G., Anderton B. J. Monoclonal antibodies against plant proteins recognise animal intermediate filaments. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(4):312–323. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell A. J., Peace G. W., Slabas A. R., Lloyd C. W. The detergent-resistant cytoskeleton of higher plant protoplasts contains nucleus-associated fibrillar bundles in addition to microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1982 Aug;56:319–335. doi: 10.1242/jcs.56.1.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Mirsky R., Raff M. C., Thorpe R., Dowding A. J., Anderton B. H. All classes of intermediate filaments share a common antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Parry D. A. Intermediate filaments: conformity and diversity of expression and structure. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:41–65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. F., Biessmann H. A non-filamentous configuration of intermediate-sized filament proteins in Drosophila Kc tissue culture cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;23(6):453–458. doi: 10.1007/BF02623863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. F., Biessmann H. Intermediate-sized filaments in Drosophila tissue culture cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1468–1477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Goldman R. D. In vitro assembly of intermediate filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Goldman R. D. In vitro reassembly of squid brain intermediate filaments (neurofilaments): purification by assembly-disassembly. Science. 1980 Jun 6;208(4448):1152–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.7189605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]