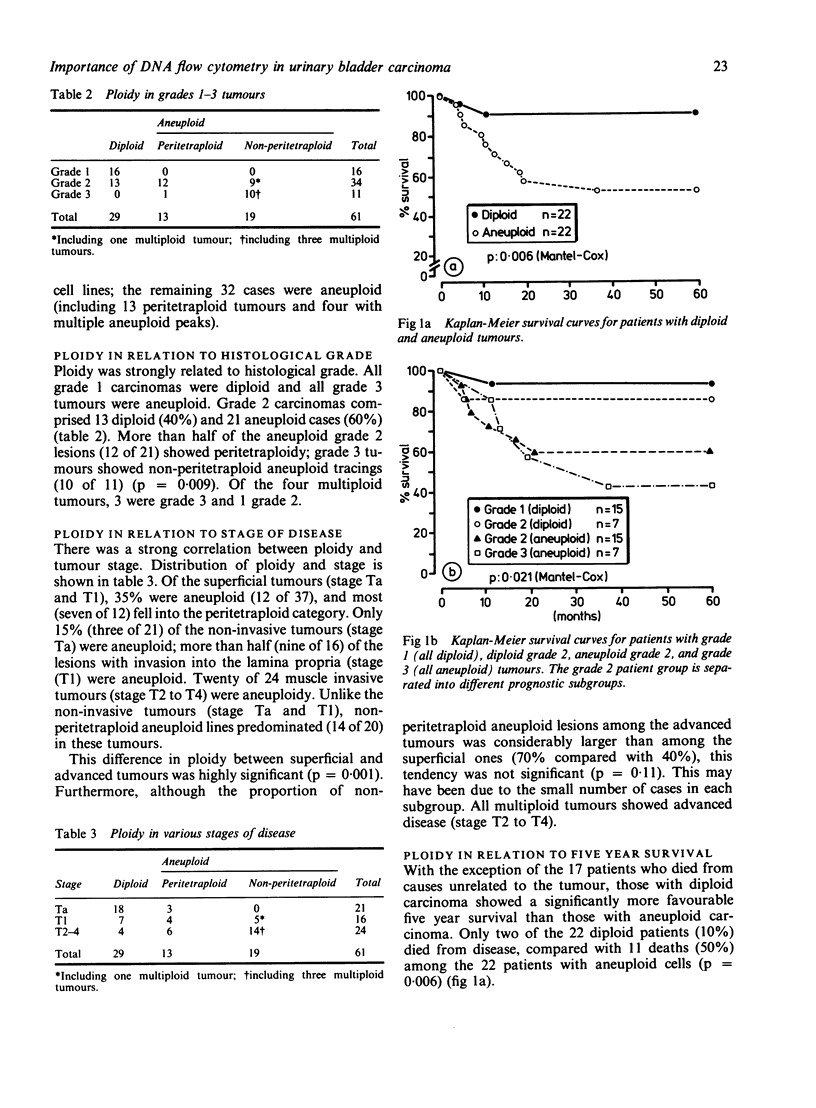
Abstract
Cellular DNA content was determined by flow cytometry on routinely processed paraffin sections of 61 primary and untreated transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder, and correlated with tumour grade and stage and clinical follow up. All 16 (25%) grade 1 carcinomas were diploid and all 11 (20%) grade 3 tumours were aneuploid. The 34 (55%) grade 2 carcinomas comprised 13 (40%) diploid and 21 (60%) aneuploid cases. Among the 37 superficial carcinomas (stage Ta and T1), 25 (65%) were diploid; 20 (85%) of the 24 advanced tumours (stage T2 to T4) had aneuploid tracings. Ploidy was a significant prognostic indicator (p: 0.006) of five year survival. The initial presence of aneuploidy in superficial bladder carcinoma (stage Ta and T1) is a strong argument for more aggressive treatment than is customary.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes R., Hadley H., Dick A., Johnston O., Dexter J. Changes in grade and stage of recurrent bladder tumors. J Urol. 1977 Jul;118(1 Pt 2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)57940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergkvist A., Ljungqvist A., Moberger G. Classification of bladder tumours based on the cellular pattern. Preliminary report of a clinical-pathological study of 300 cases with a minimum follow-up of eight years. Acta Chir Scand. 1965 Oct;130(4):371–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruthers J. M., Bonneville M. A. Luminal plasma membrane alterations in bladder cancer. Invest Urol. 1980 Mar;17(5):364–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. L., Huben R. P., Nava E., Rustum Y. M., Greco J. M., Pontes J. E., Frankfurt O. S. Flow cytometric analysis of DNA content in human bladder tumors and irrigation fluids. Cancer. 1985 Oct 1;56(7):1677–1681. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19851001)56:7<1677::aid-cncr2820560734>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collste L. G., Devonec M., Darzynkiewicz Z., Traganos F., Sharpless T. K., Whitmore W. F., Jr, Melamed M. R. Bladder cancer diagnosis by flow cytometry. Correlation between cell samples from biopsy and bladder irrigation fluid. Cancer. 1980 May 1;45(9):2389–2394. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800501)45:9<2389::aid-cncr2820450925>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon J. S., Weinstein R. S., Summers J. L. Blood group precursor T-antigen expression in human urinary bladder carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jun;77(6):692–699. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.6.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decenzo J. M., Howard P., Irish C. E. Antigenic deletion and prognosis of patients with stage A transitional cell bladder carcinoma. J Urol. 1975 Dec;114(6):874–878. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)67163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falor W. H. Chromosomes in noninvasive papillary carcinoma of the bladder. JAMA. 1971 May 3;216(5):791–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsund T., Hoestmark J. G., Laerum O. D. Relation between flow cytometric DNA distribution and pathology in human bladder cancer. A report on 69 cases. Cancer. 1984 Nov 1;54(9):1771–1777. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19841101)54:9<1771::aid-cncr2820540904>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson H., Tribukait B. Characterization of bladder carcinomas by flow DNA analysis. Eur Urol. 1985;11(6):410–417. doi: 10.1159/000472552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson H., Tribukait B., Esposti P. L. DNA profile and tumour progression in patients with superficial bladder tumours. Urol Res. 1982 Feb;10(1):13–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00256518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W., Rugg C. A., Musgrove E. A. Method for analysis of cellular DNA content of paraffin-embedded pathological material using flow cytometry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Nov;31(11):1333–1335. doi: 10.1177/31.11.6619538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins G. A., Jr, Amadeo J. H., McElhinney J., McCaughan J. J., Keehn R. J. Efficacy of prolonged intermittent therapy with combined 5-fluorouracil and methyl-CCNU following resection for carcinoma of the large bowel. A Veterans Administration Surgical Oncology Group report. Cancer. 1984 Jan 1;53(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840101)53:1<1::aid-cncr2820530102>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhl B. R., Hartzen S. H., Hainau B. A, B, H antigen expression in transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder. Cancer. 1986 May 1;57(9):1768–1775. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860501)57:9<1768::aid-cncr2820570910>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye K. W., Lange P. H. Mode of presentation of invasive bladder cancer: reassessment of the problem. J Urol. 1982 Jul;128(1):31–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)52738-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb D. Correlation of chromosome counts with histological appearances and prognosis in transitional-cell carcinoma of bladder. Br Med J. 1967 Feb 4;1(5535):273–277. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5535.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer B., Mikuz G., Gütter W., zur Needen G. Zytophotometrische Untersuchungen von Tumoren des Ubergangsepithels der Harnblase. Vergleich zytophotometrischer Untersuchungsergebnisse mit dem histologischen Grading. Beitr Pathol. 1972;147(4):379–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELICOW M. M. Tumors of the urinary bladder: a clinico-pathological analysis of over 2500 specimens and biopsies. J Urol. 1955 Oct;74(4):498–521. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)67309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooms E. C., Anderson W. A., Alons C. L., Boon M. E., Veldhuizen R. W. Analysis of the performance of pathologists in the grading of bladder tumors. Hum Pathol. 1983 Feb;14(2):140–143. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner M. E., Cooper E. H. Chromosome constitution of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Cancer. 1972 May;29(5):1401–1412. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197205)29:5<1401::aid-cncr2820290543>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas V., Kiruluta H. G. ABO(H) isoantigens in bladder tumors: a new technique of quantitative analysis. J Urol. 1984 Feb;131(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)50327-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sträuli P., Weiss L. Cell locomation and tumor penetration. Report on a workshop of the EORTC cell surface project group. Eur J Cancer. 1977 Jan;13(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(77)90222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribukait B., Gustafson H., Esposti P. L. The significance of ploidy and proliferation in the clinical and biological evaluation of bladder tumours: a study of 100 untreated cases. Br J Urol. 1982 Apr;54(2):130–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1982.tb13536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijkström H., Gustafson H., Tribukait B. Deoxyribonucleic acid analysis in the evaluation of transitional cell carcinoma before cystectomy. J Urol. 1984 Nov;132(5):894–898. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)49936-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley E. L., Mendelsohn G., Droller M. J., Eggleston J. C. Immunoperoxidase detection of carcinoembryonic antigen and blood group substances in papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol. 1982 Aug;128(2):276–280. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)52885-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


