Abstract
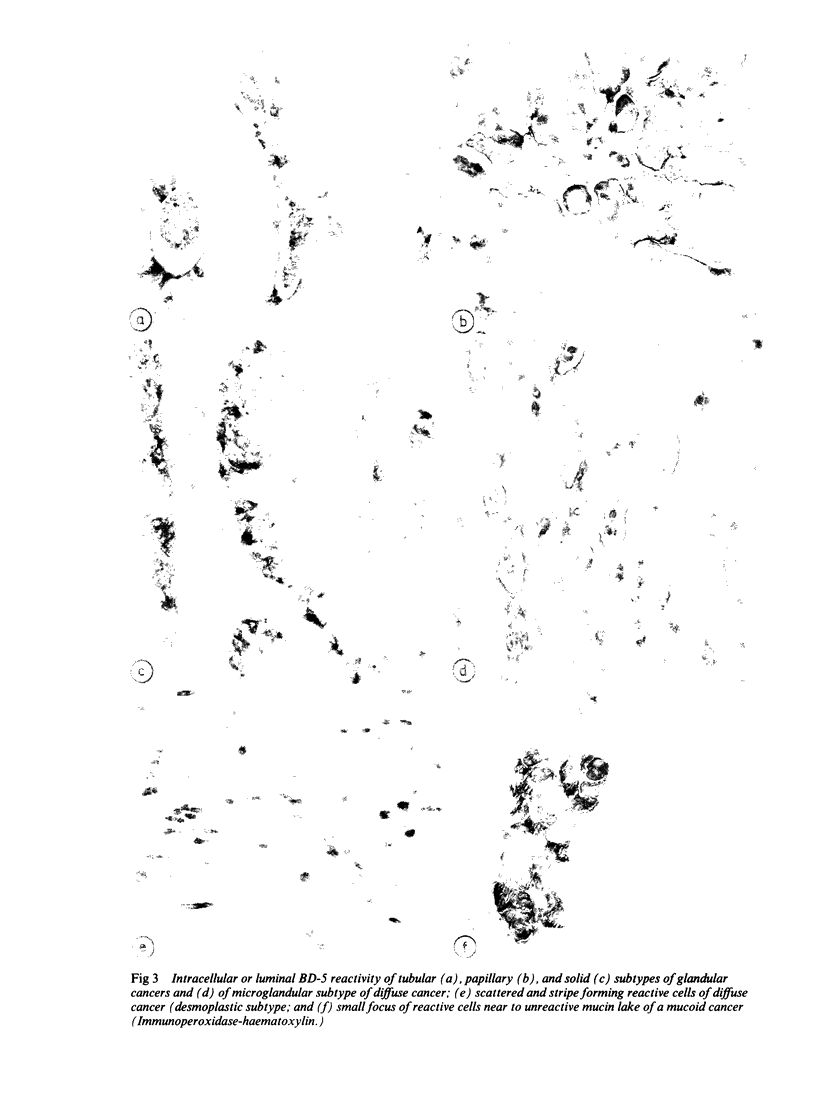
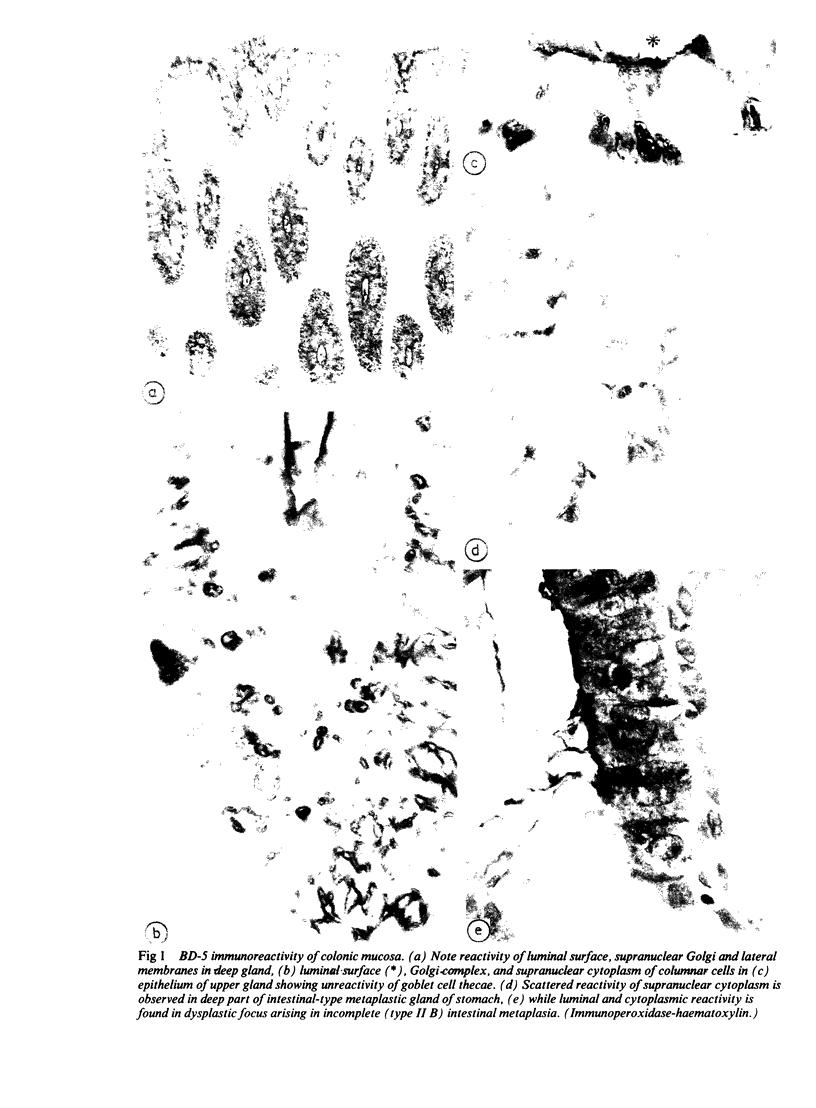
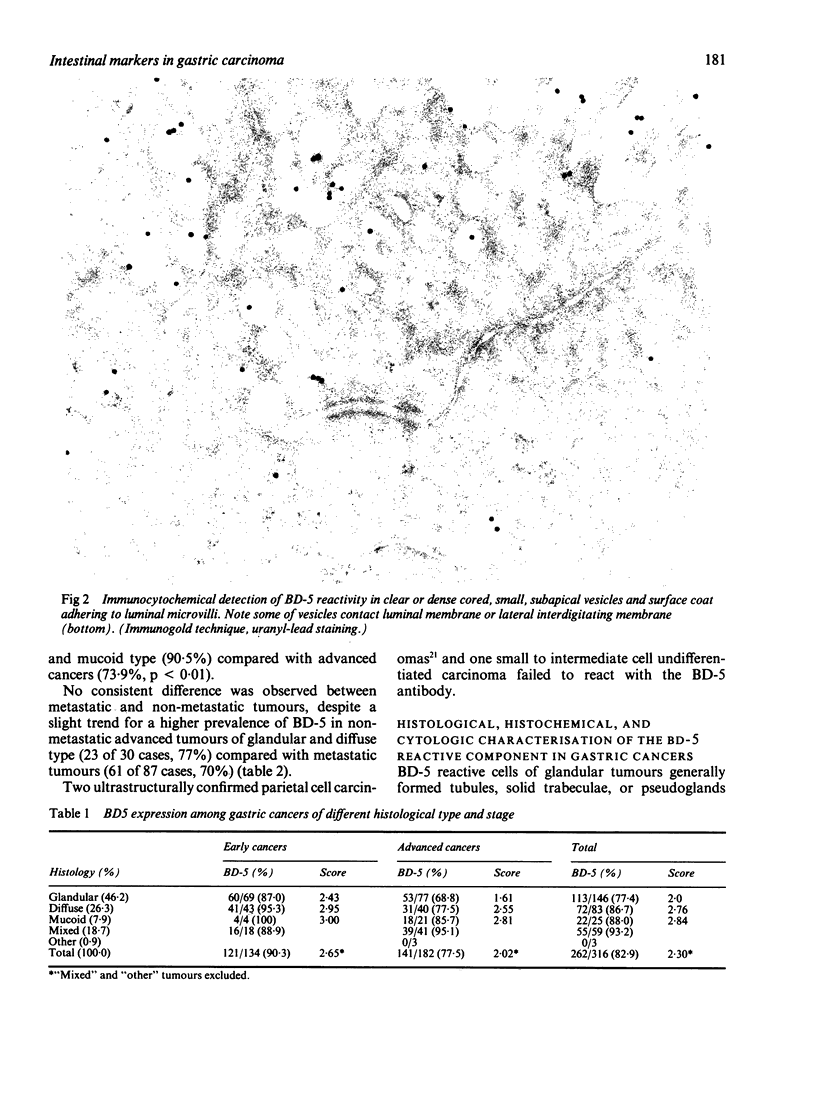
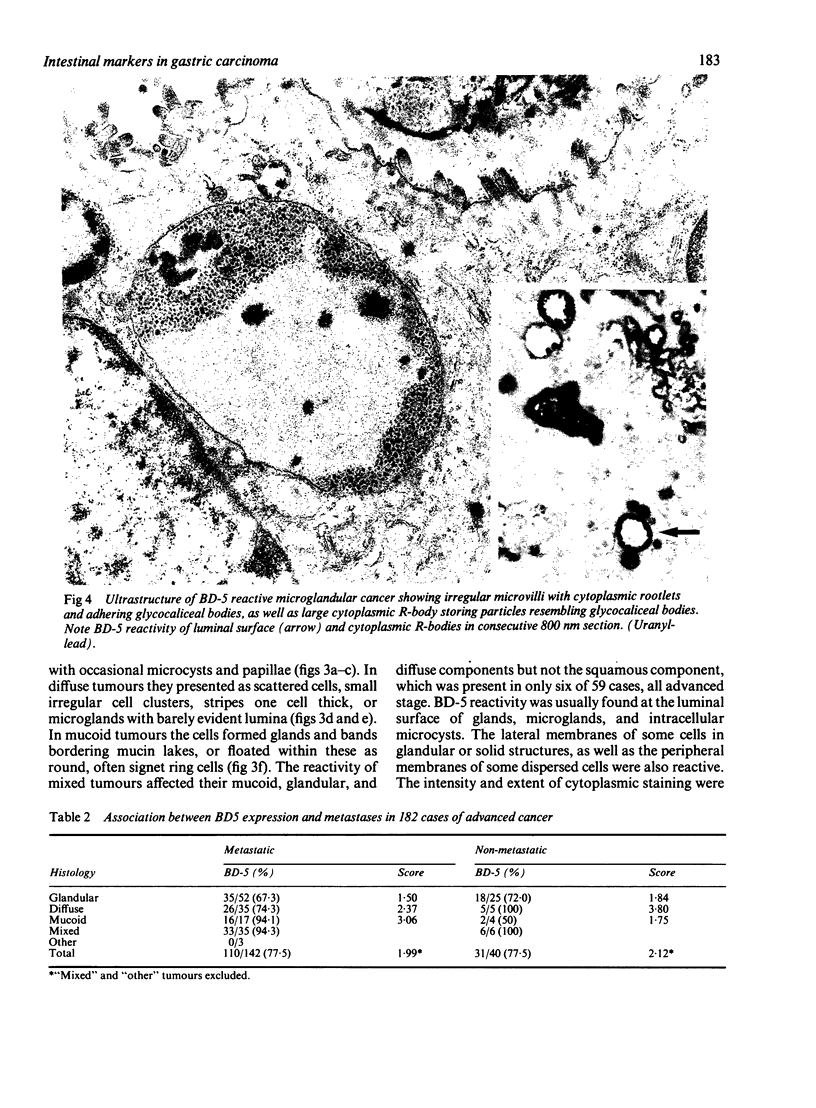
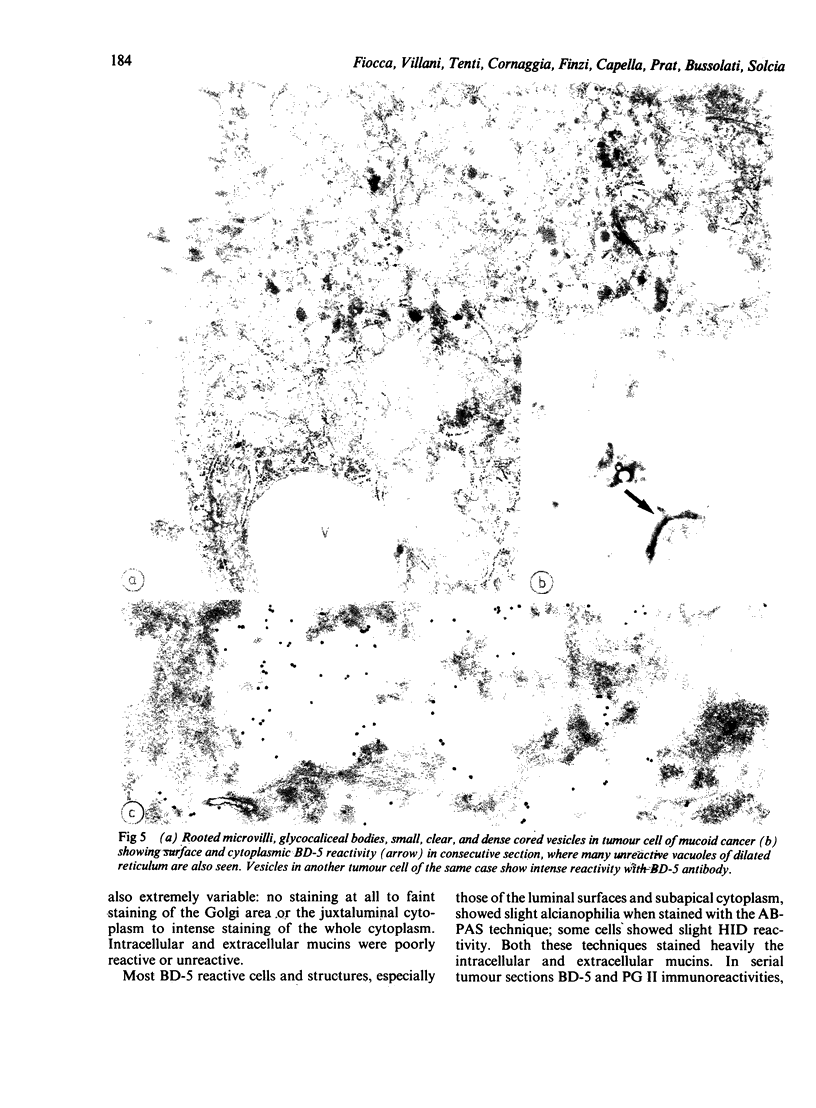
BD-5 monoclonal antibody reacted with tumour cells in 262 of 316 cases of gastric cancers, including 121 of 134 early, 141 of 182 advanced tumours (p less than 0.01), and 113 of 146 glandular, 72 of 83 diffuse, 22 of 25 mucoid, and 55 of 59 mixed tumours. No difference in reactivity was observed between metastatic and non-metastatic advanced tumours. Immunocytochemical techniques applied to light and electron microscopical specimens of colorectal mucosa and gastric cancer showed that BD-5 immunoreactive material occurred in the Golgi complex, in small clear, to dense cored, cytoplasmic vesicles, and in the glycocalix of the luminal and lateral membranes of normal and neoplastic cells in the glands, as well as in the peripheral membrane of dispersed neoplastic cells. Mucin granules stored in the cytoplasm of goblet cells were unreactive or poorly reactive. Ultrastructural features consistent with colorectal type differentiation were observed in many reactive tumours. Unreactive tumours showing ultrastructural patterns consistent with intestinal differentiation, especially of small bowel type, were also observed. Signs of intestinal differentiation, including BD-5 immunoreactivity, often occur in gastric cancer, irrespective of histological type and stage of disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bara J., Hamelin L., Martin E., Burtin P. Intestinal M3 antigen, a marker for the intestinal-type differentiation of gastric carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1981 Dec;28(6):711–719. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bara J., Loisillier F., Burtin P. Antigens of gastric and intestinal mucous cells in human colonic tumours. Br J Cancer. 1980 Feb;41(2):209–221. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biempica L., Sternlieb I., Sohn H. B., Ali M. R-bodies of human rectal epithelial cells. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Feb;100(2):78–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capella C., Frigerio B., Cornaggia M., Solcia E., Pinzon-Trujillo Y., Chejfec G. Gastric parietal cell carcinoma--a newly recognized entity: light microscopic and ultrastructural features. Histopathology. 1984 Sep;8(5):813–824. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1984.tb02397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornaggia M., Riva C., Capella C., Solcia E., Samloff I. M. Subcellular localization of pepsinogen II in stomach and duodenum by the immunogold technique. Gastroenterology. 1987 Mar;92(3):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiocca R., Sessa F., Tenti P., Usellini L., Capella C., O'Hare M. M., Solcia E. Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells in the PP-rich lobe of the human pancreas are identified ultrastructurally and immunocytochemically as F cells. Histochemistry. 1983;77(4):511–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00495805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiocca R., Villani L., Tenti P., Solcia E., Cornaggia M., Frigerio B., Capella C. Characterization of four main cell types in gastric cancer: foveolar, mucopeptic, intestinal columnar and goblet cells. An histopathologic, histochemical and ultrastructural study of "early" and "advanced" tumours. Pathol Res Pract. 1987 Jun;182(3):308–325. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(87)80066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furihata C., Tatematsu M., Miki K., Katsuyama T., Sudo K., Miyagi N., Kubota T., Jin S. S., Kodama K., Ito N. Gastric- and intestinal-type properties of human gastric cancers transplanted into nude mice. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):727–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman H., Ming S. C. Fine structure of intestinal metaplasia and adenocarcinoma of the human stomach. Lab Invest. 1968 Feb;18(2):203–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman H., Ming S. C. Mucins in normal and neoplastic gastrointestinal epithelium. Histochemical distribution. Arch Pathol. 1968 Jun;85(6):580–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey W. F., Seiler M. W. Ultrastructural markers of colonic adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 1981 Jan 1;47(1):140–145. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)47:1<140::aid-cncr2820470124>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häkkinen I., Järvi O., Grönroos J. Sulphoglycoprotein antigens in the human alimentary canal and gastric cancer. An immunohistological study. Int J Cancer. 1968 Sep 15;3(5):572–581. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Ikegami N., Hosoda Y., Koide O., Kaneko M. The biological behaviour of gastric cancer. J Pathol. 1981 Jun;134(2):97–115. doi: 10.1002/path.1711340202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jass J. R. Role of intestinal metaplasia in the histogenesis of gastric carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Sep;33(9):801–810. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.9.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T. Histologic appearance of gastric carcinoma in high and low mortality countries: comparison between Kyushu, Japan and Minnesota, USA. Cancer. 1971 Sep;28(3):726–734. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197109)28:3<726::aid-cncr2820280331>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSON B. C. Carcinoma arising from areas of intestinal metaplasia in the gastric mucosa. Br J Cancer. 1955 Sep;9(3):377–385. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1955.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., De Boer W. G., Nayman J. Intestinal mucinous substances in gastric intestinal metaplasia and carcinoma studied by immunofluorescence. Cancer. 1982 Apr 15;49(8):1664–1667. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820415)49:8<1664::aid-cncr2820490822>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. B., Martin J. H., Green R. H., Krouse M. A. Glycocalyceal bodies and microvillous core rootlets: their value in tumor typing. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1979 Feb;103(2):89–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mughal S., Filipe M. I., Jass J. R. A comparative ultrastructural study of hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps, incidental and in association with colorectal cancer. Cancer. 1981 Dec 15;48(12):2746–2755. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19811215)48:12<2746::aid-cncr2820481232>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGAYO T., KOMAGOE T. Histological studies of gastric mucosal cancer with special reference to relationship of histological pictures between the mucosal cancer and the cancer-bearing gastric mucosa. Gan. 1961 Jun;52:109–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Sugano H., Takagi K. Carcinoma of the stomach in incipient phase: its histogenesis and histological appearances. Gan. 1968 Jun;59(3):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Bara J., Rosa B., Burtin P. Intestinal metaplasia and carcinomas of the human stomach: an immunohistological study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Mar;31(3):366–375. doi: 10.1177/31.3.6338105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevalainen T. J., Järvi O. H. Ultrastructure of intestinal and diffuse type gastric carcinoma. J Pathol. 1977 Jul;122(3):129–136. doi: 10.1002/path.1711220303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat M., Rossino P., Bussolati G., Morra I., Comoglio P. M. Production of monoclonal antibodies for the immunohistochemical detection of gastric carcinomas. Cancer Detect Prev. 1987;10(3-4):293–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp W., Windisch M., Peschke P., Wurster K. Purification of human intestinal goblet cell antigen (GOA), its immunohistological demonstration in the intestine and in mucus producing gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1979 May 31;382(2):163–177. doi: 10.1007/BF01102872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Garavito M. Enhancement of structural preservation and immunocytochemical staining in low temperature embedded pancreatic tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 May;29(5):663–671. doi: 10.1177/29.5.6166664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasano N., Nakamura K., Arai M., Akazaki K. Ultrastructural cell patterns in human gastric carcinoma compared with non-neoplastic gastric mucosa--histogenetic analysis of carcinoma by mucin histochemistry. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Oct;43(4):783–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuddin A. M., Phelps P. C., Trump B. F. Human large intestinal epithelium: light microscopy, histochemistry, and ultrastructure. Hum Pathol. 1982 Sep;13(9):790–803. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., Mukherjee T. M., Hecker R. C bodies and R bodies in the epithelial cells of normal and diseased human rectum. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1977 Aug;101(8):437–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toner P. G. Cytology of intestinal epithelial cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1968;24:233–343. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61401-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trier J. S., Rubin C. E. Electron microscopy of the small intestine: a review. Gastroenterology. 1965 Nov;49(5):574–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTENBERG L. W. Histochemical study of aminopeptidase in metaplasia and carcinoma of the stomach. AMA Arch Pathol. 1959 Mar;67(3):281–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer W. G., Forsyth A., Nairn R. C. Gastric antigens in health and disease. Behaviour in early development, senescence, metaplasia, and cancer. Br Med J. 1969 Jul 12;3(5662):93–94. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5662.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]