Abstract
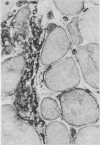
Muscle biopsy specimens with a pronounced inflammatory component were evaluated for myocyte expression of class II histocompatibility antigens (HLA-DR) by immunohistochemical techniques. All 15 cases of polymyositis were positive; six cases of muscular dystrophy (two Duchenne, four facio-scapulo-humeral), and one case of acute denervation (motor neurone disease) were negative, despite having a comparably intense mononuclear infiltrate. Twelve entirely normal biopsy specimens were also negative for HLA-DR expression. Expression of this membrane glycoprotein may have a clinically important aetiological role in polymyositis, and demonstration of its presence may prove useful as a marker for this disorder in selected problematic biopsy specimens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arahata K., Engel A. G. Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. I: Quantitation of subsets according to diagnosis and sites of accumulation and demonstration and counts of muscle fibers invaded by T cells. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballardini G., Mirakian R., Bianchi F. B., Pisi E., Doniach D., Bottazzo G. F. Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigens on bileduct epithelium in primary biliary cirrhosis: relevance to pathogenesis. Lancet. 1984 Nov 3;2(8410):1009–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan W. M., Behan P. O. Immunological features of polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1985;8(3):267–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00197300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. Significance and biological function of class II MHC molecules. Rous-Whipple Award lecture 1985. Am J Pathol. 1985 Sep;120(3):334–343. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collings L. A., Poulter L. W., Janossy G. The demonstration of cell surface antigens on T cells, B cells and accessory cells in paraffin-embedded human tissues. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Dec 31;75(2):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of HLA-A, B, C antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):287–292. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of MHC Class II antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta J. D., Cemach K., Dubey D. P., Yunis E. J., Amos D. B. The role of class I histocompatibility antigens in the regulation of T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1094–1098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins R. L., Mastaglia F. L. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity to muscle in polymyositis. Effect of immunosuppression. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 1;288(9):434–438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303012880903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Arahata K. Mononuclear cells in myopathies: quantitation of functionally distinct subsets, recognition of antigen-specific cell-mediated cytotoxicity in some diseases, and implications for the pathogenesis of the different inflammatory myopathies. Hum Pathol. 1986 Jul;17(7):704–721. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K. C. L. Oakley lecture (1987). The pathogenesis of beta cell destruction in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. J Pathol. 1987 Jul;152(3):141–148. doi: 10.1002/path.1711520302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K. Class II major histocompatibility complex and organ specific autoimmunity in man. J Pathol. 1986 Sep;150(1):5–11. doi: 10.1002/path.1711500103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorno R., Barden M. T., Kohler P. F., Ringel S. P. Immunohistochemical characterization of the mononuclear cells infiltrating muscle of patients with inflammatory and noninflammatory myopathies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Mar;30(3):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran P. F., Wadgymar A., Autenried P. The regulation of expression of major histocompatibility complex products. Transplantation. 1986 Apr;41(4):413–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffner R. R., Jr, Barron S. A., Jenis E. H., Valeski J. E. Skeletal muscle in polymyositis. Immunohistochemical study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1979 Jun;103(6):310–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallenberg C. G., Schilizzi B. M., Beaumont F., De Leij L., Poppema S., The T. H. Expression of class II major histocompatibility complex antigens on alveolar epithelium in interstitial lung disease: relevance to pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jul;40(7):725–733. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.7.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine N. R., Ryan J. F., Cox E. L., Mayston V., Revell P. A., Swash M. Immunohistochemical analysis of mononuclear cell subsets in inflammatory and non-inflammatory myopathies. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Mar;39(3):271–274. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald G. B., Jewell D. P. Class II antigen (HLA-DR) expression by intestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory diseases of colon. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;40(3):312–317. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.3.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L., Piper D., Cancilla P., Mednick J. Inflammatory myopathy with facioscapulohumeral distribution. Neurology. 1972 Apr;22(4):335–347. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.4.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxenhandler R., Adelstein E. H., Hart M. N. Immunopathology of skeletal muscle. The value of direct immunofluorescence in the diagnosis of connective tissue disease. Hum Pathol. 1977 May;8(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(77)80029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Hollema H., Visser L., Vos H. Monoclonal antibodies (MT1, MT2, MB1, MB2, MB3) reactive with leukocyte subsets in paraffin-embedded tissue sections. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jun;127(3):418–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. J., Isenberg D. A., McDougall J., Beverley P. C. Characterization of polymyositis infiltrates using monoclonal antibodies to human leucocyte antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Aug;45(2):290–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D., Isenberg D. A., Beverley P. C. Monoclonal antibodies to human leucocyte antigens in polymyositis and muscular dystrophy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Nov;54(2):327–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsby E. Structure and function of HLA molecules. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. Comment on the finding of Ia expression in nonlymphoid cells. Lab Invest. 1986 Aug;55(2):123–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. P., Warford A., Fray L., Allen M., Campbell A. C., Lauder I. The demonstration of B-cell, T-cell and myeloid antigens in paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1986 Oct;150(2):89–101. doi: 10.1002/path.1711500203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N. Inflammatory myopathy: a review of etiologic and pathogenetic factors. Muscle Nerve. 1982 Oct;5(8):573–592. doi: 10.1002/mus.880050802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]