Abstract
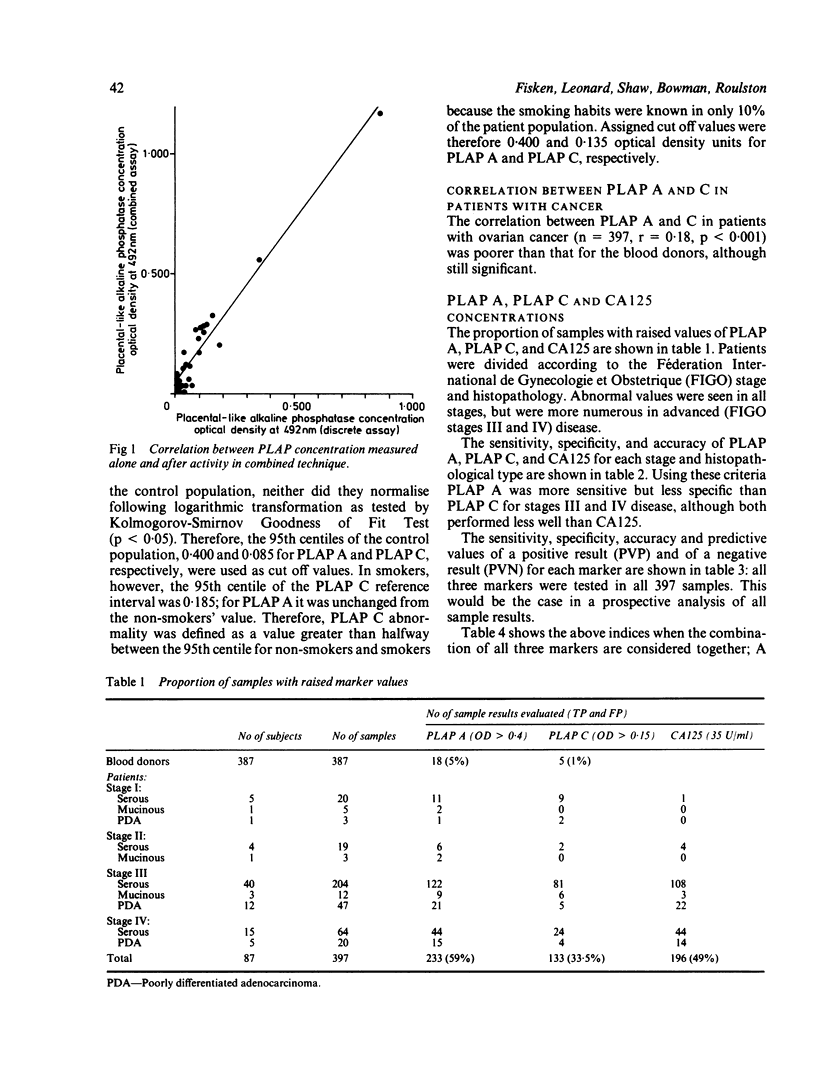
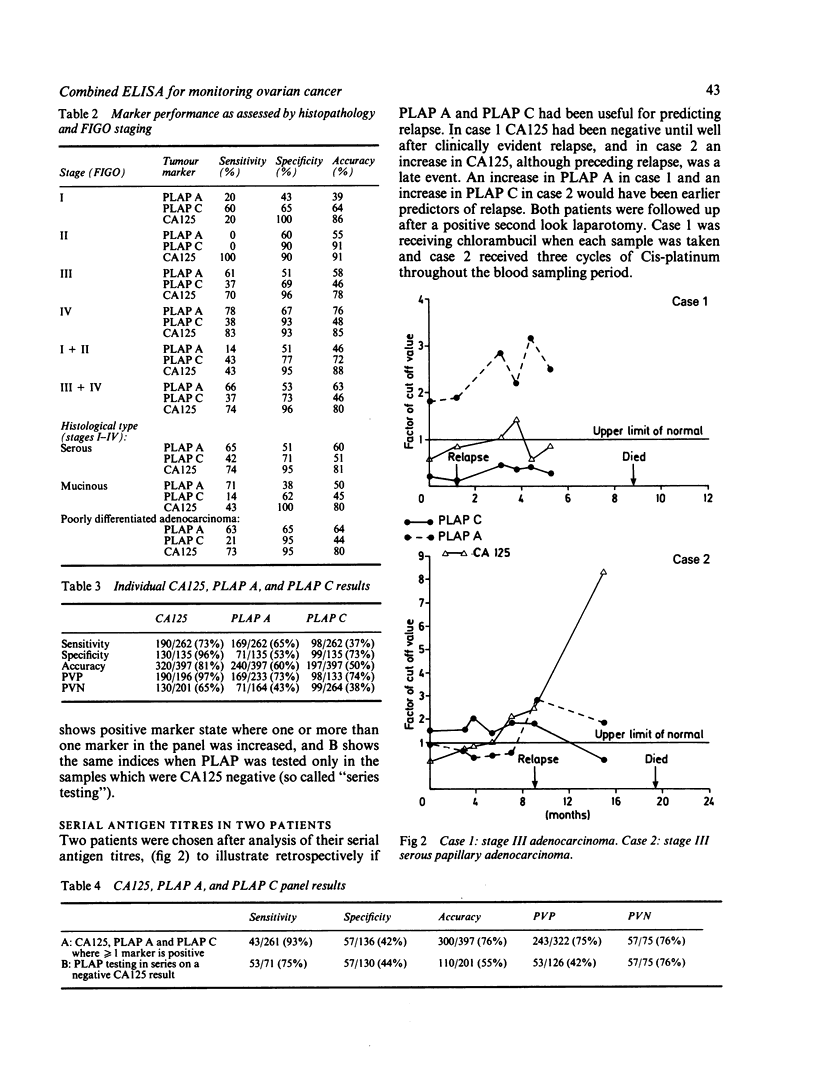
A new combined enzyme linked immunoassay (ELISA) was developed to measure both serum placental-like alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) activity (PLAPA) and concentration (PLAPC) in the same microtitre plate using an Imperial Cancer Research Fund monoclonal antibody, designated H17E2. PLAP A and PLAP C were determined together with an existing marker, CA125 in 397 serial samples from 87 patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Retrospective assessment showed the sensitivity to increase from 73% with CA125 alone, to 88% using CA125 and PLAP A, and to 93% with all three markers in 261 samples from the patients with known active disease at the time of sampling. When the results for all 397 samples were included in the analysis, however, the specificity, sensitivity, accuracy and predictive powers of this monoclonal antibody were not sufficiently high to assist in the prospective follow up of patients with ovarian cancer. This was due to a significant number of false positive and false negative results. Our data indicate that PLAP A or PLAP C estimation with H17E2 may, therefore, only be of value in the management of those patients with known active disease who are already known to be "marker positive" for this antigen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bast R. C., Jr, Klug T. L., St John E., Jenison E., Niloff J. M., Lazarus H., Berkowitz R. S., Leavitt T., Griffiths C. T., Parker L. A radioimmunoassay using a monoclonal antibody to monitor the course of epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 13;309(15):883–887. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310133091503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruickshank D. J., Fullerton W. T., Klopper A. The clinical significance of pre-operative serum CA 125 in ovarian cancer. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1987 Jul;94(7):692–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1987.tb03177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. O., Davies E. R., Howe K., Jackson P., Pitcher E., Randle B., Sadowski C., Stirrat G. M., Sunderland C. A. Practical applications of a monoclonal antibody (NDOG2) against placental alkaline phosphatase in ovarian cancer. J R Soc Med. 1985 Nov;78(11):899–905. doi: 10.1177/014107688507801104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groote G., De Waele P., Van de Voorde A., De Broe M., Fiers W. Use of monoclonal antibodies to detect human placental alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chem. 1983 Jan;29(1):115–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhokia B., Canney P. A., Pectasides D., Munro A. J., Moore M., Wilkinson P. M., Self C., Epenetos A. A. A new immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies HMFG1 and HMFG2 together with an existing marker CA125 for the serological detection and management of epithelial ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 1986 Dec;54(6):891–895. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Inglis N. I., Stolbach L. L., Krant M. J. A serum alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme of human neoplastic cell origin. Cancer Res. 1968 Jan;28(1):150–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haije W. G., van Driel J., van der Burg M. E. Catalytic and immunologic activities of placental-like alkaline phosphatase in clinical studies. The value of PLAP in follow-up of ovarian cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Jun 15;165(2-3):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslow W. C., Muensch H. A., Azama F., Schneider A. S. Sensitive fluorometry of heat-stable alkaline phosphatase (Regan enzyme) activity in serum from smokers and nonsmokers. Clin Chem. 1983 Feb;29(2):260–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin P. J., Gee H., Johnson P. M. Placental-type alkaline phosphatase in pregnancy and malignancy plasma: specific estimation using a monoclonal antibody in a solid phase enzyme immunoassay. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 May 30;130(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L., Stigbrand T. "Sandwich" enzyme immunoassay for placental alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chem. 1981 Dec;27(12):2014–2018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollet D. E., Nouwen E. J., Schelstraete J. B., Renard J., Van de Voorde A., De Broe M. E. Enzyme-antigen immunoassay for human placental alkaline phosphatase in serum and tissue extracts, and its application as a tumor marker. Clin Chem. 1985 Jan;31(1):41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers P., Bodmer W. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against placental alkaline phosphatase and other human trophoblast-associated determinants. Int J Cancer. 1984 May 15;33(5):633–641. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker D. F., Oliver R. T., Travers P., Bodmer W. F. Serum marker potential of placental alkaline phosphatase-like activity in testicular germ cell tumours evaluated by H17E2 monoclonal antibody assay. Br J Cancer. 1985 May;51(5):631–639. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergote I., Onsrud M., Nustad K. Placental alkaline phosphatase as a tumor marker in ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Feb;69(2):228–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. G., Cruickshank D. J., Tucker D. F., Love S. Independent expression in serum of three tumour-associated antigens: CA 125, placental alkaline phosphatase and HMFG2 in ovarian carcinoma. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1987 Jul;94(7):696–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1987.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. H., McLaughlin P. J., Johnson P. M. Tissue origin of serum placental-like alkaline phosphatase in cigarette smokers. Clin Chim Acta. 1986 Mar 28;155(3):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(86)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


