Abstract
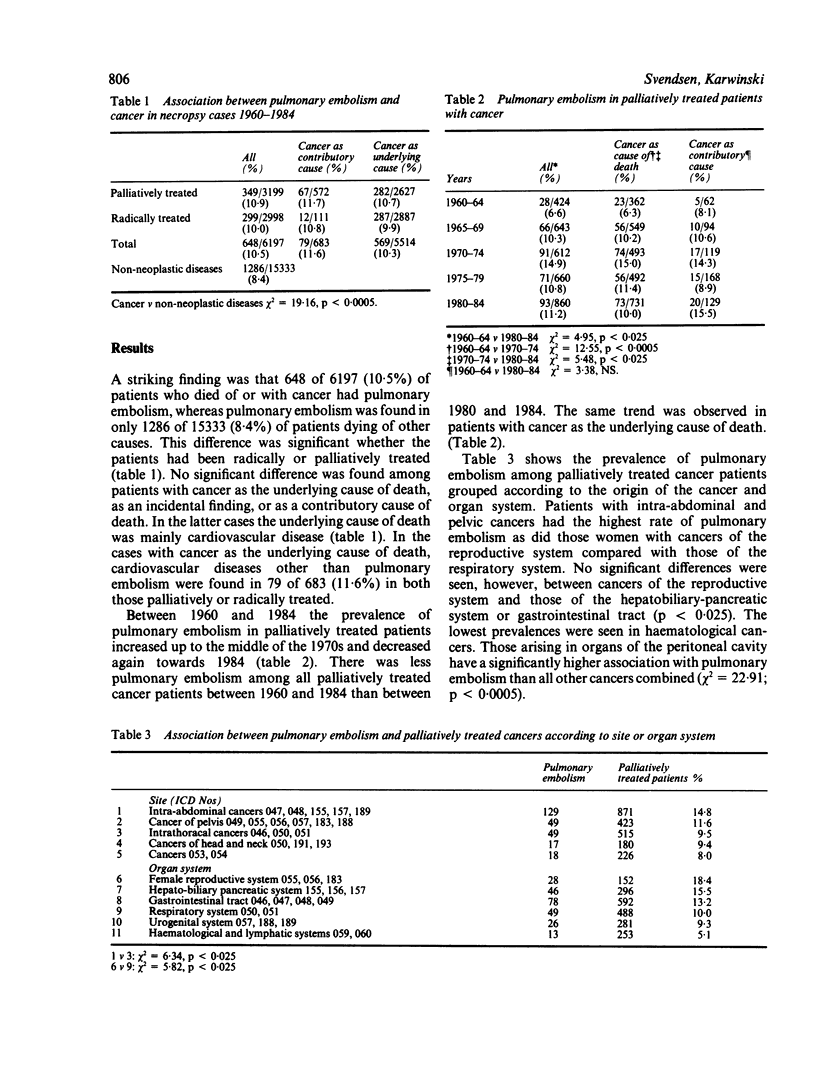
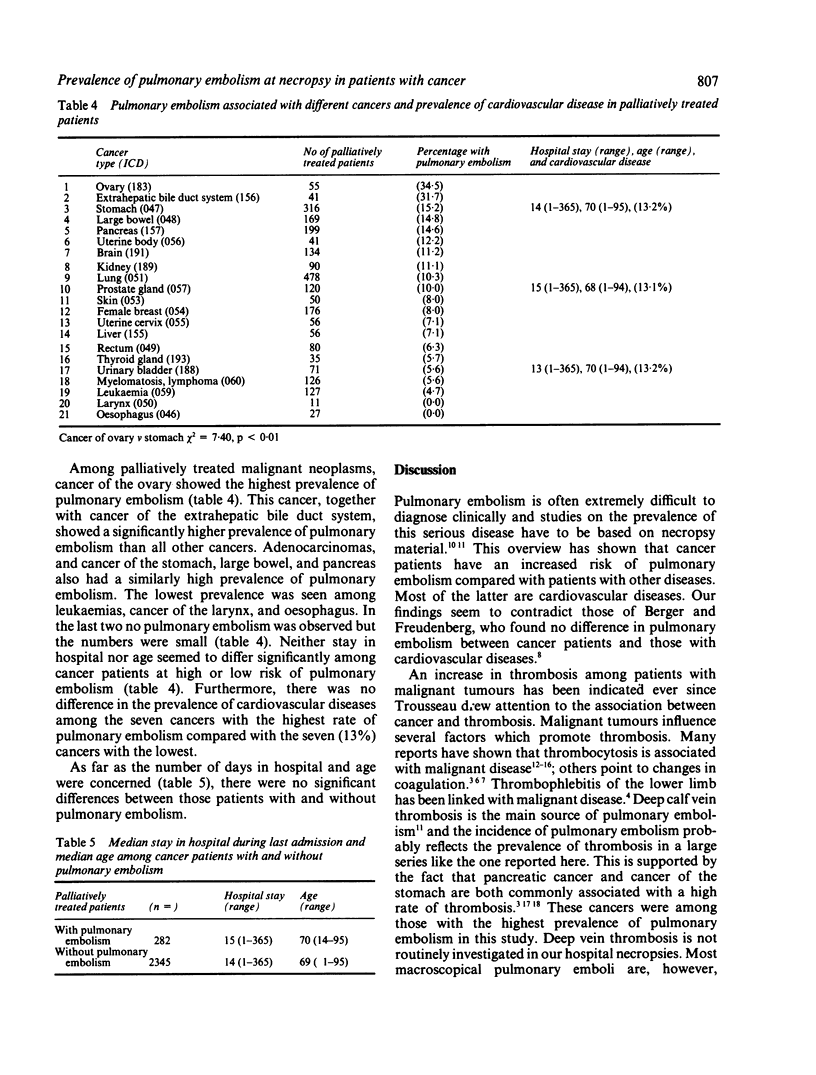
The series studied comprised 6197 patients who had died of or who had cancer at death and represents all patients with cancer from 21,530 necropsies performed at this department from 1960-84. Pulmonary embolism was significantly more common among cancer patients than in those with non-neoplastic diseases. Among those palliatively treated, patients with ovarian cancer, cancer of the extrahepatic bile duct system, and cancer of the stomach had the highest prevalence of pulmonary embolism (34.6%, 31.7%, and 15.2%, respectively). Necropsy patients with cancer of the oesophagus and larynx, together with leukaemia, myelomatosis, and malignant lymphoma had the lowest prevalence (0-5.6%). Palliatively treated cancers in organs of the peritoneal cavity had a significantly higher incidence than all other cancers combined. Cancer of the peritoneal cavity may impede venous drainage from the lower limbs and thus be an important factor in the onset of deep calf vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It is concluded that cancer represents an increased risk factor for onset of pulmonary embolism, in particular in patients with ovarian cancer and cancer of the extrahepatic bile duct system.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belt R. J., Leite C., Haas C. D., Stephens R. L. Incidence of hemorrhagic complications in patients with cancer. JAMA. 1978 Jun 16;239(24):2571–2574. doi: 10.1001/jama.239.24.2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H., Freudenberg N. Todesursachen bei Malignompatienten. Med Welt. 1983 Jan 28;34(4):112–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain M. C., Azzopardi J. G., Baker L. R., Pineo G. F., Roberts P. D., Dacie J. V. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia and mucin-forming adenocarcinoma. Br J Haematol. 1970 Feb;18(2):183–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F. Thrombosis and cancer. Hum Pathol. 1987 Mar;18(3):275–284. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartveit F. Autopsy findings in cases with a clinically uncertain cancer diagnosis. J Pathol. 1979 Nov;129(3):111–119. doi: 10.1002/path.1711290302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karwinski B., Svendsen E. Comparison of clinical and postmortem diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Feb;42(2):135–139. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohanna F. H., Sweeney J., Hussey S., Zacharski L. R., Salzman E. W. Effect of perioperative low-dose heparin administration on the course of colon cancer. Surgery. 1983 Mar;93(3):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN J. S., BORRERO J., URDANETA E., WRIGHT I. S. Thrombophlebitis and cancer. JAMA. 1961 Aug 26;177:542–545. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040340006002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. E., Jr, DeVita V. T., Canellos G. P. Thrombocytosis in chronic granulocytic leukemia: incidence and clinical significance. Blood. 1974 Oct;44(4):483–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr A. C., Dick H. J., Nagel G. A., Senn H. J. Thrombozytose bei malignen Tumoren. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1973 Nov 17;103(46):1626–1629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mählck C. G., Bäckström T., Kjellgren O. Plasma level of estradiol in patients with ovarian malignant tumors. Gynecol Oncol. 1988 Jul;30(3):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(88)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pineo G. F., Brain M. C., Gallus A. S., Hirsh J., Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. Tumors, mucus production, and hypercoagulability. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;230:262–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poller L. Oral contraceptives, blood clotting and thrombosis. Br Med Bull. 1978 May;34(2):151–156. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack G. H., Jr, Levin J., Bell W. R. Trousseau's syndrome and other manifestations of chronic disseminated coagulopathy in patients with neoplasms: clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic features. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Jan;56(1):1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. Tumor, thrombozytose und Thrombosegefährdung. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1988 May 6;113(18):740–746. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1067715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvis S. E., Turkbas N., Doscherholmen A. Thrombocytosis in patients with lung cancer. JAMA. 1970 Mar 16;211(11):1852–1853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spigel S. C., Mooney L. R. Extreme thrombocytosis associated with malignancy. Cancer. 1977 Jan;39(1):339–341. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197701)39:1<339::aid-cncr2820390150>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun N. C., McAfee W. M., Hum G. J., Weiner J. M. Hemostatic abnormalities in malignancy, a prospective study of one hundred eight patients. Part I. Coagulation studies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;71(1):10–16. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON C. M., RODGERS L. R. Analysis of the autopsy records of 157 cases of carcinoma of the pancreas with particular reference to the incidence of thromboembolism. Am J Med Sci. 1952 May;223(5):469–478. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195205000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT I. S. The pathogenesis and treatment of thrombosis. Circulation. 1952 Feb;5(2):161–188. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.5.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


