Abstract
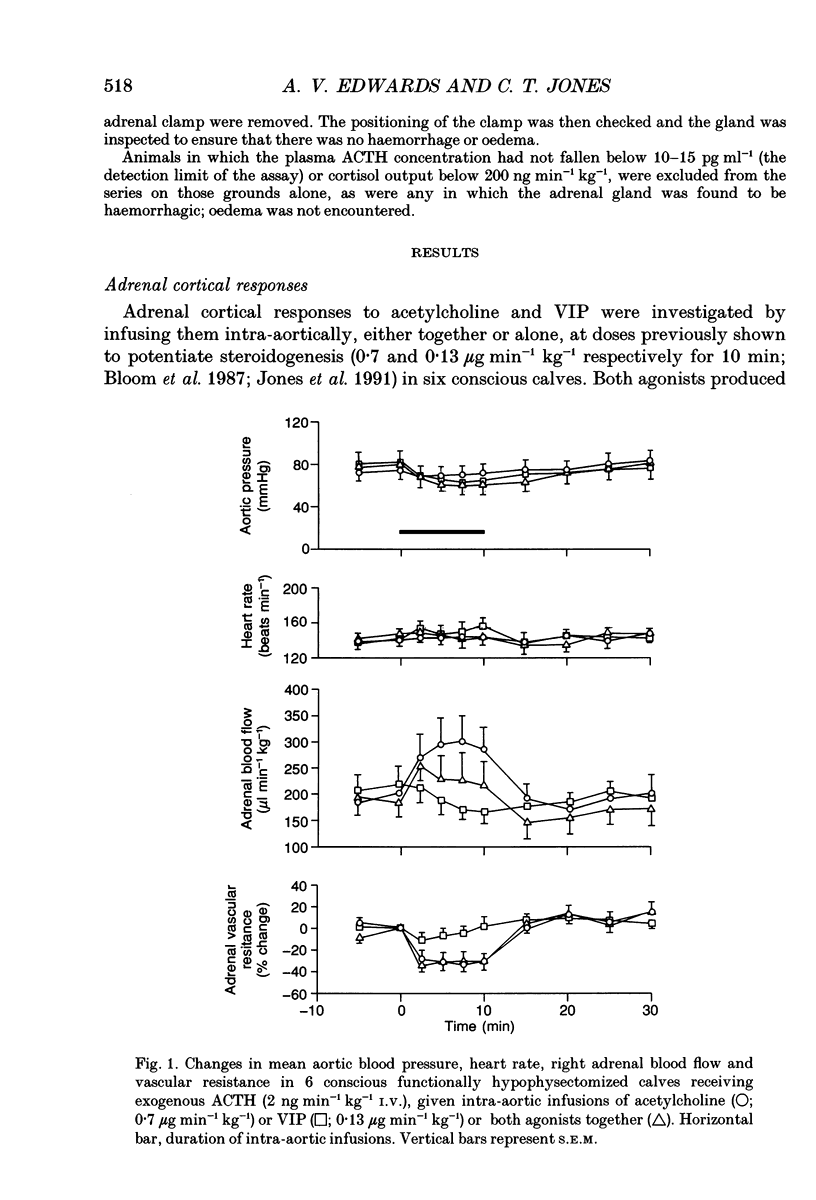
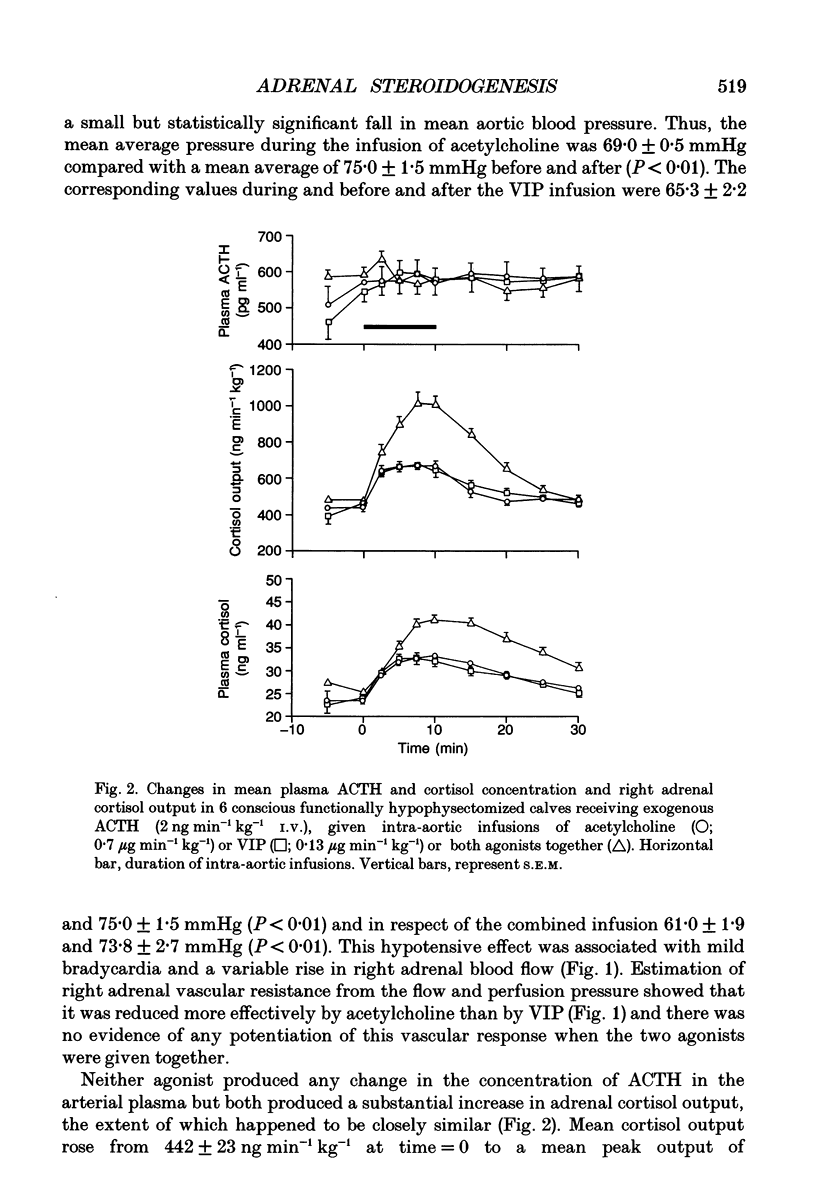
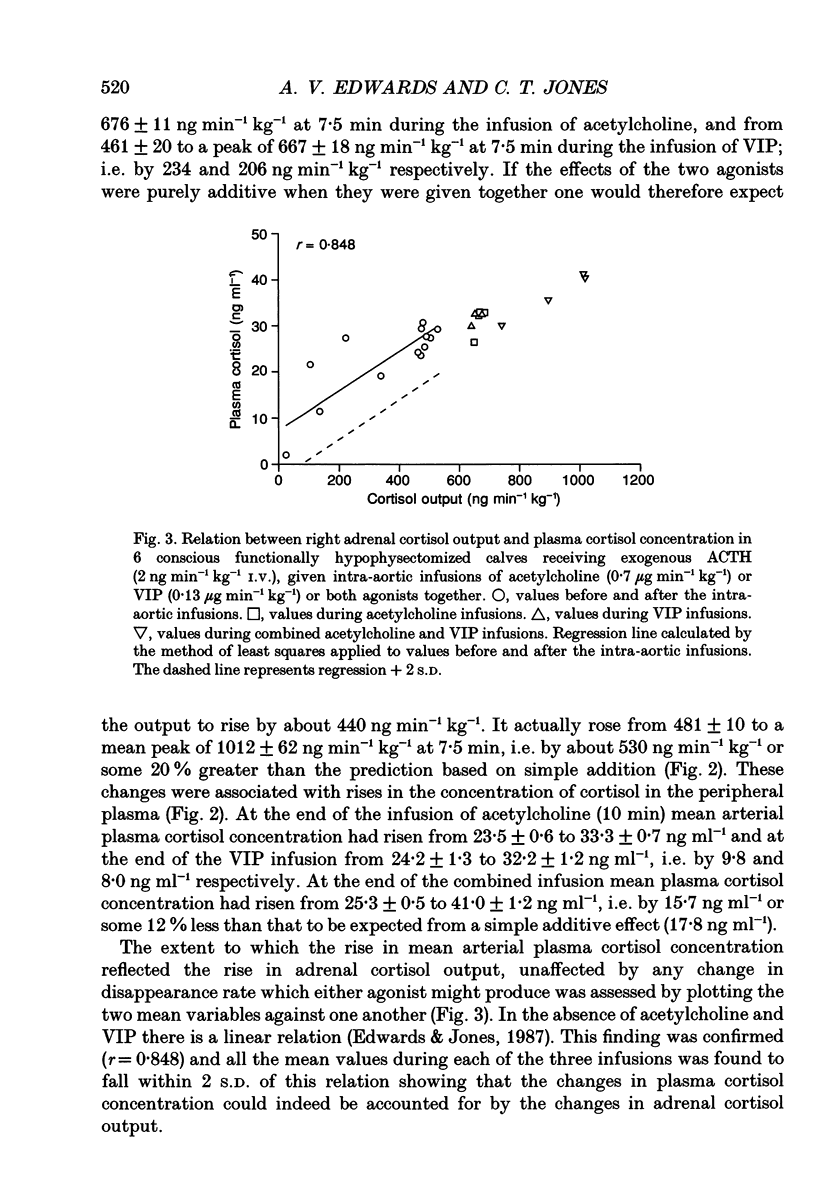
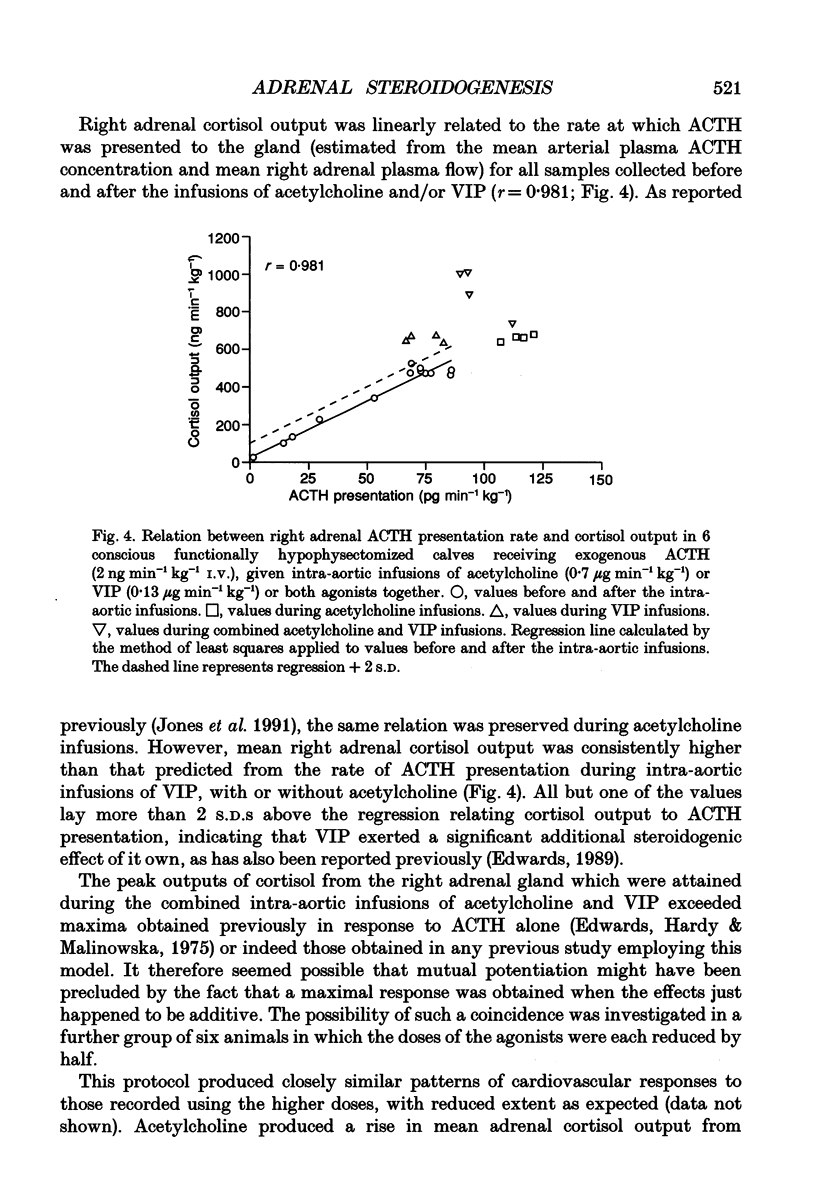
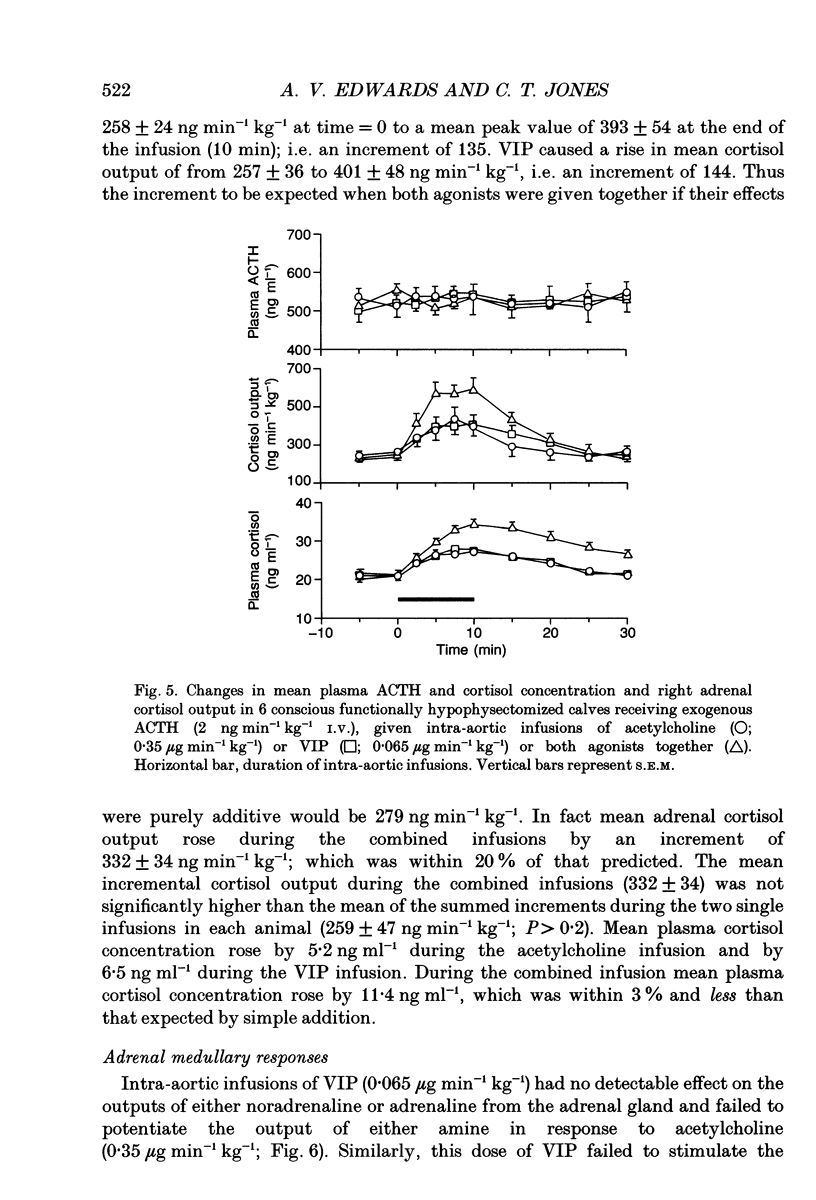
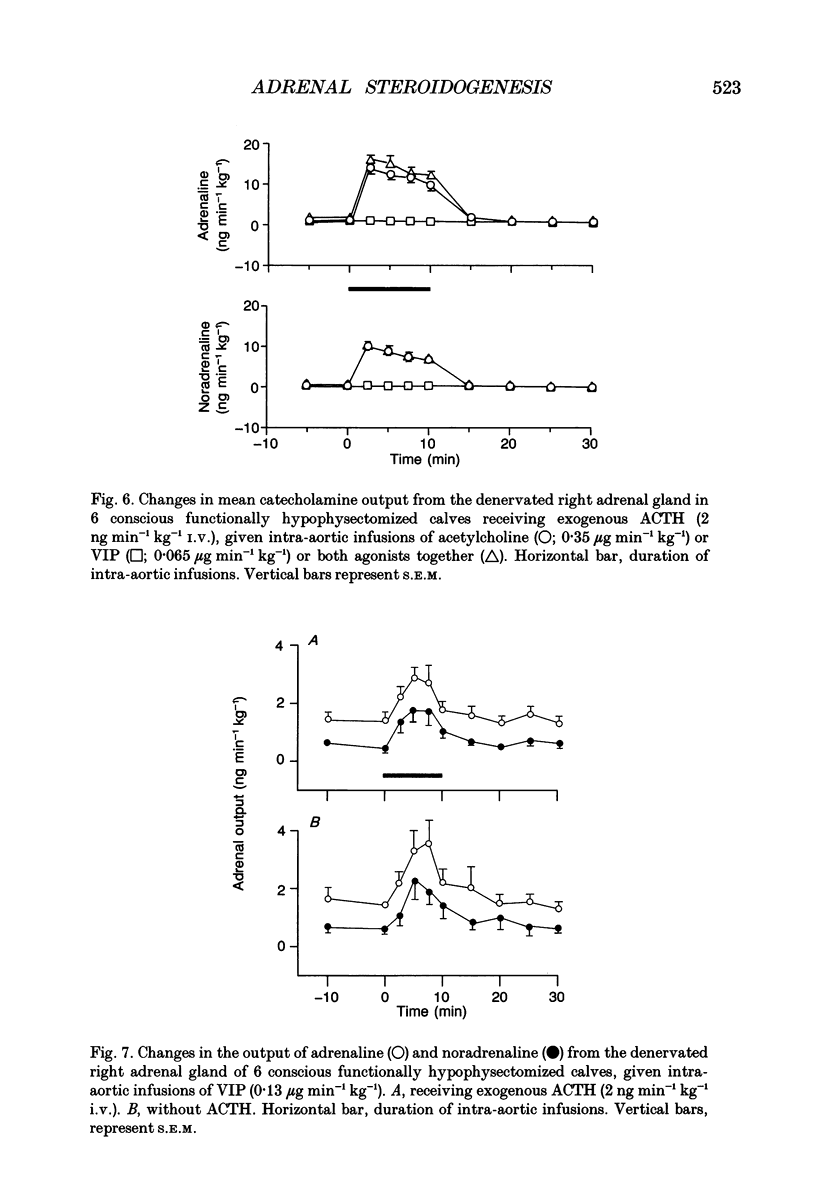
1. Adrenal responses to intra-aortic infusions of acetylcholine and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) have been investigated in functionally hypophysectomized calves given exogenous adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH, 2 ng min-1 kg-1 I.V.). 2. Infusions of VIP at a dose of 0.13 micrograms min-1 kg-1 caused a small, but significant increase in adrenaline and noradrenaline output which was, however, far below the level recorded previously in response to acetylcholine (0.7 micrograms min-1 kg-1). In contrast, these doses of the two agonists produced closely similar rises in adrenal cortisol output. 3. The steroidogenic effects of acetylcholine and VIP were found to be strictly additive and no evidence of potentiation was obtained in relation to either cortical or medullary responses or in the case of any of the cardiovascular responses which were monitored. 4. Intra-aortic infusions of VIP, at a dose which produced a substantial increase in adrenal steroidogenesis (0.065 micrograms min-1 kg-1), had no effect on the output of catecholamines, enkephalin-like immunoreactivity or corticotrophin-releasing factor, either in the presence or absence of acetylcholine. 5. It is concluded that VIP is unlikely to modulate adrenal medullary responses to muscarinic stimulation in this species as it has been claimed to do in the rat and does not potentiate adrenal steroidogenesis in response to acetylcholine as it does to ACTH.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arkinstall S. J., Jones C. T. Regional changes in catecholamine content of the pregnant uterus. J Reprod Fertil. 1985 Mar;73(2):547–557. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0730547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audigier S., Barberis C., Jard S. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide increases inositol phospholipid breakdown in the rat superior cervical ganglion. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 25;376(2):363–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. Adrenal cortical responses to vasoactive intestinal peptide in conscious hypophysectomized calves. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:441–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Vasoactive intestinal peptide in relation to atropine resistant vasodilatation in the submaxillary gland of the cat. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:41–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delarue C., Leboulenger F., Homo-Delarche F., Benyamina M., Lihrmann I., Perroteau I., Vaudry H. Involvement of prostaglandins in the response of frog adrenocortical cells to muscarinic receptor activation. Prostaglandins. 1986 Jul;32(1):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(86)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Furness P. N., Helle K. B. Adrenal medullary responses to stimulation of the splanchnic nerve in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:15–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Hansell D., Jones C. T. Effects of synthetic adrenocorticotrophin on adrenal medullary responses to splanchnic nerve stimulation in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Hansell D., Jones C. T. Effects of synthetic adrenocorticotrophin on adrenal medullary responses to splanchnic nerve stimulation in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K. W. The sensitivity of adrenal responses to synthetic adrenocorticotrophin in the conscious unrestrained calf. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):639–653. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. The effect of splanchnic nerve stimulation on adrenocortical activity in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:385–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart-Bornstein M., Bornstein S. R., Scherbaum W. A., Pfeiffer E. F., Holst J. J. Role of the vasoactive intestinal peptide in a neuroendocrine regulation of the adrenal cortex. Neuroendocrinology. 1991 Dec;54(6):623–628. doi: 10.1159/000125969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando J. C., Abdallah E. A., Evinger M., Forray C., el-Fakahany E. E. The presence of an M4 subtype muscarinic receptor in the bovine adrenal medulla revealed by mRNA and receptor binding analyses. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 14;207(4):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90003-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjian A. J., Ventre R., Chambaz E. M. Cholinergic muscarinic receptors in bovine adrenal cortex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 27;98(4):892–900. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houchi H., Oka M., Misbahuddin M., Morita K., Nakanishi A. Stimulation by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide of catecholamine synthesis in isolated bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Possible involvement of protein kinase C. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 May 1;36(9):1551–1554. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Boddy K., Robinson J. S., Ratcliffe J. G. Developmental changes in the responses of the adrenal glands of foetal sheep to endogenous adrenocorticotrophin, as indicated by hormone responses to hypoxaemia. J Endocrinol. 1977 Mar;72(3):279–292. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0720279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V., Bloom S. R. Endocrine responses to intra-aortic infusions of acetylcholine in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:481–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V. Muscarinic adrenal responses to acetylcholine in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:605–614. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawatani M., Rutigliano M., De Groat W. C. Selective facilitatory effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) on muscarinic firing in vesical ganglia of the cat. Brain Res. 1985 Jun 17;336(2):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90649-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leboulenger F., Benyamina M., Delarue C., Netchitaïlo P., Saint-Pierre S., Vaudry H. Neuronal and paracrine regulation of adrenal steroidogenesis: interactions between acetylcholine, serotonin and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) on corticosteroid production by frog interrenal tissue. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 21;453(1-2):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leboulenger F., Perroteau I., Netchitailo P., Lihrmann I., Leroux P., Delarue C., Coy D. H., Vaudry H. Action of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) on amphibian adrenocortical function, in vitro. Peptides. 1984 Mar-Apr;5(2):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Anggård A., Fahrenkrug J., Hökfelt T., Mutt V. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in cholinergic neurons of exocrine glands: functional significance of coexisting transmitters for vasodilation and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1651–1655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hedlund B., Bartfai T. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide enhances muscarinic ligand binding in cat submandibular salivary gland. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):147–149. doi: 10.1038/295147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra R. K., Wakade A. R. Non-cholinergic component of rat splanchnic nerves predominates at low neuronal activity and is eliminated by naloxone. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:639–652. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra R. K., Wakade A. R. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide stimulates the secretion of catecholamines from the rat adrenal gland. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:285–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra R. K., Wakade T. D., Wakade A. R. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and muscarine mobilize intracellular Ca2+ through breakdown of phosphoinositides to induce catecholamine secretion. Role of IP3 in exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2123–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misbahuddin M., Houchi H., Nakanishi A., Morita K., Oka M. Stimulation by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide of muscarinic receptor-mediated catecholamine secretion from isolated guinea pig adrenal medullary cells. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Dec 23;72(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90533-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Marchi M., Paudice P. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) potentiates the muscarinic stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover in rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 6;133(1):127–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Vaughan J., Yamamoto G., Bruhn T., Douglas C., Dalton D., Rivier C., Rivier J. Assay of corticotropin releasing factor. Methods Enzymol. 1983;103:565–577. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)03040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R. Noncholinergic transmitter(s) maintains secretion of catecholamines from rat adrenal medulla for several hours of continuous stimulation of splanchnic neurons. J Neurochem. 1988 Apr;50(4):1302–1308. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Wakade T. D. Contribution of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in the secretion of catecholamines evoked by endogenous and exogenous acetylcholine. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):973–978. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade T. D., Blank M. A., Malhotra R. K., Pourcho R., Wakade A. R. The peptide VIP is a neurotransmitter in rat adrenal medulla: physiological role in controlling catecholamine secretion. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:349–362. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. W., Strachan M. W., Lightly E. R., Williams B. C., Bird I. M. Acetylcholine stimulates cortisol secretion through the M3 muscarinic receptor linked to a polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in bovine adrenal fasciculata/reticularis cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Sep 10;72(3):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90147-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. W., Strachan M. W., Nicol M., Williams B. C., Bird I. M. Dose-dependent effects of angiotensin II, acetylcholine and vasopressin on the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ in suspension primary cultures of zona fasciculata/reticularis cells from bovine adrenal cortex. J Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;6(2):197–203. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0060197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan D. C., Livett B. G. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulates proenkephalin A mRNA expression in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jun 19;101(2):218–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waymire J. C., Craviso G. L., Lichteig K., Johnston J. P., Baldwin C., Zigmond R. E. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulates catecholamine biosynthesis in isolated adrenal chromaffin cells: evidence for a cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation and activation of tyrosine hydroxylase. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1313–1324. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and substance P increase levels of enkephalin-containing peptides in adrenal chromaffin cells. Life Sci. 1987 Feb 16;40(7):623–628. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P. Vasoactive intestinal peptide elevates cyclic AMP levels and potentiates secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Neuropeptides. 1988 Jan;11(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(88)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


