Abstract
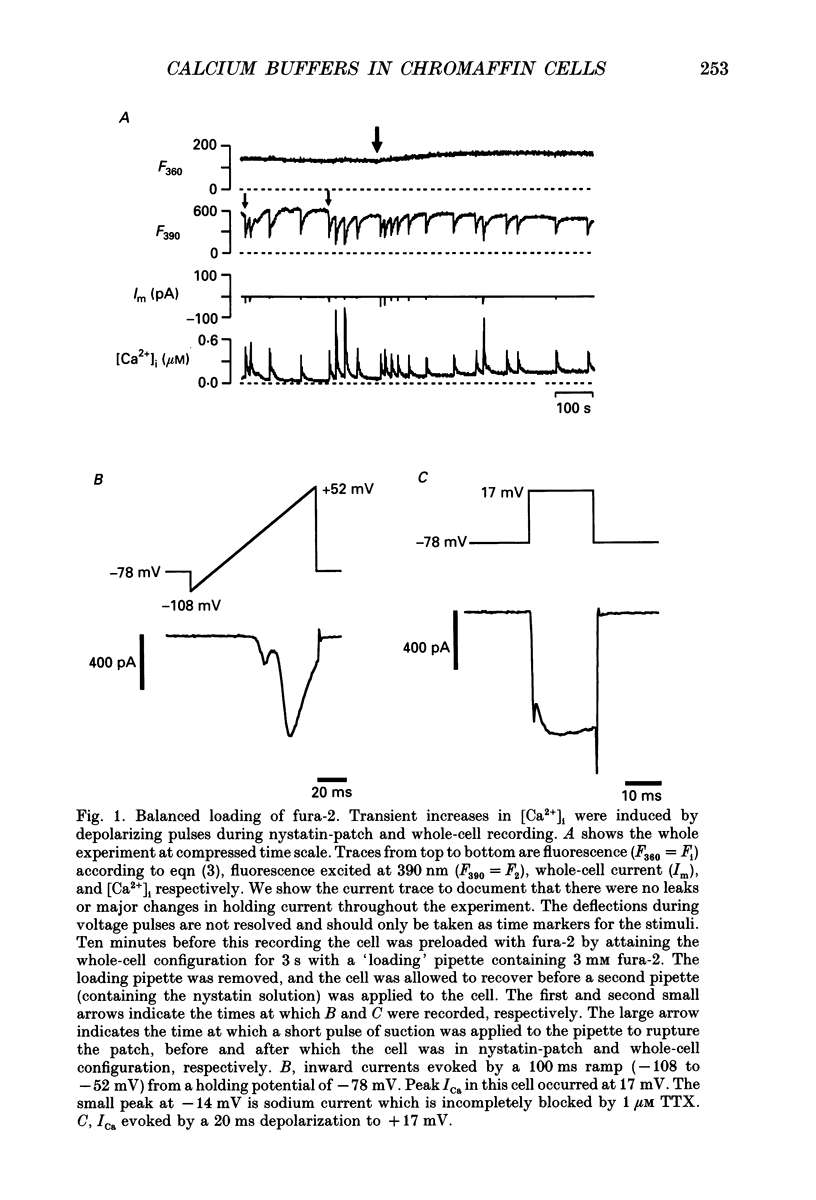
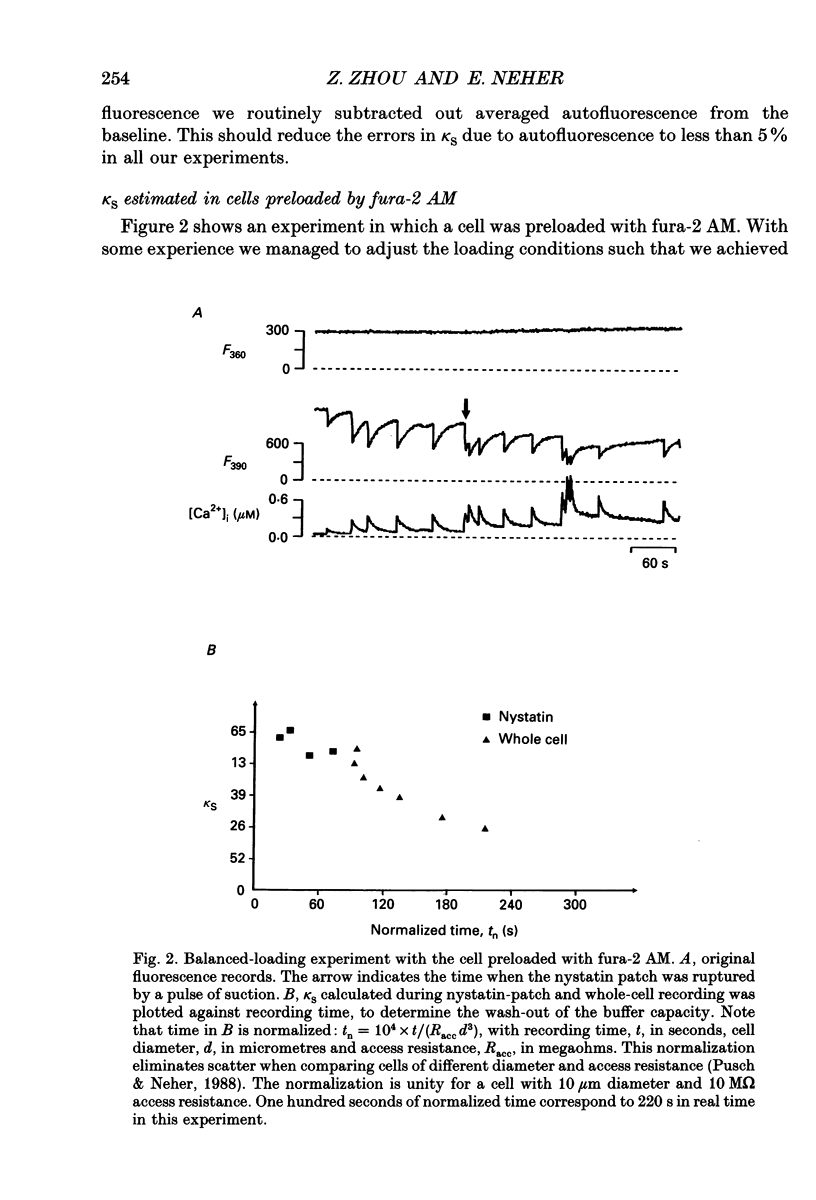
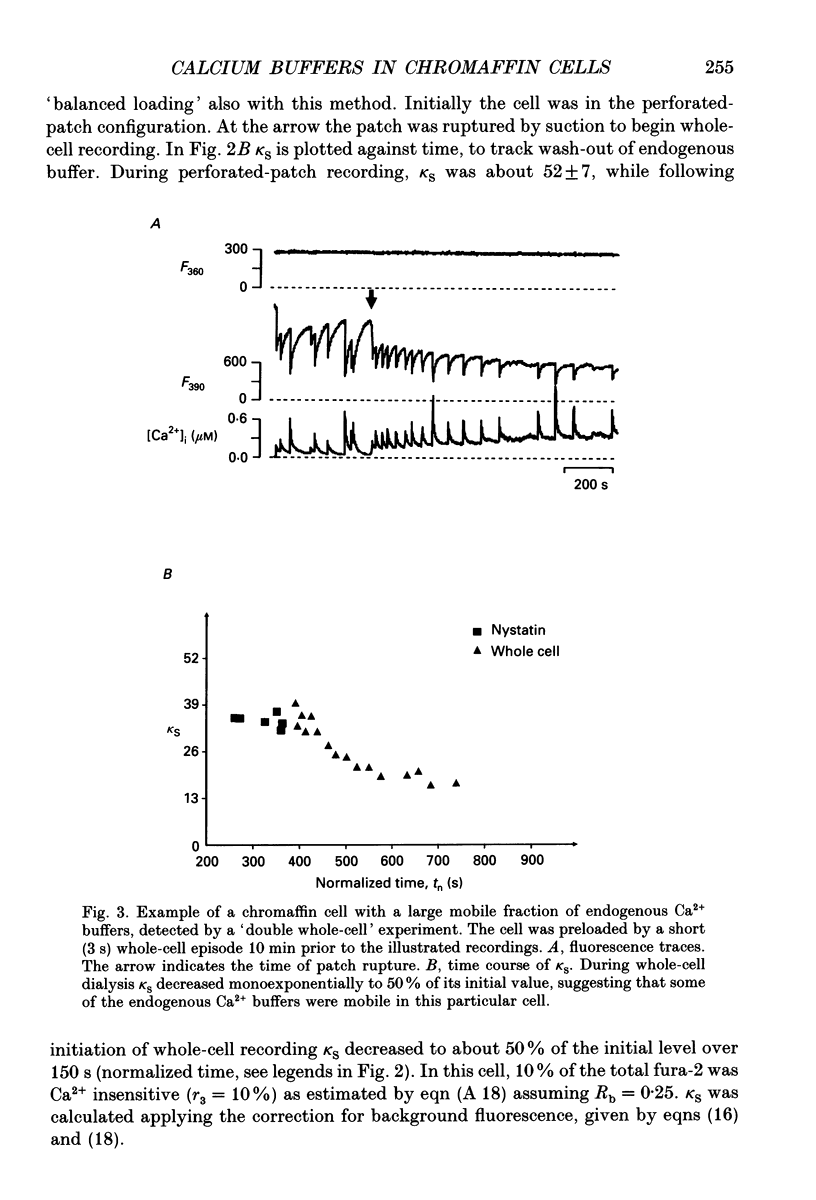
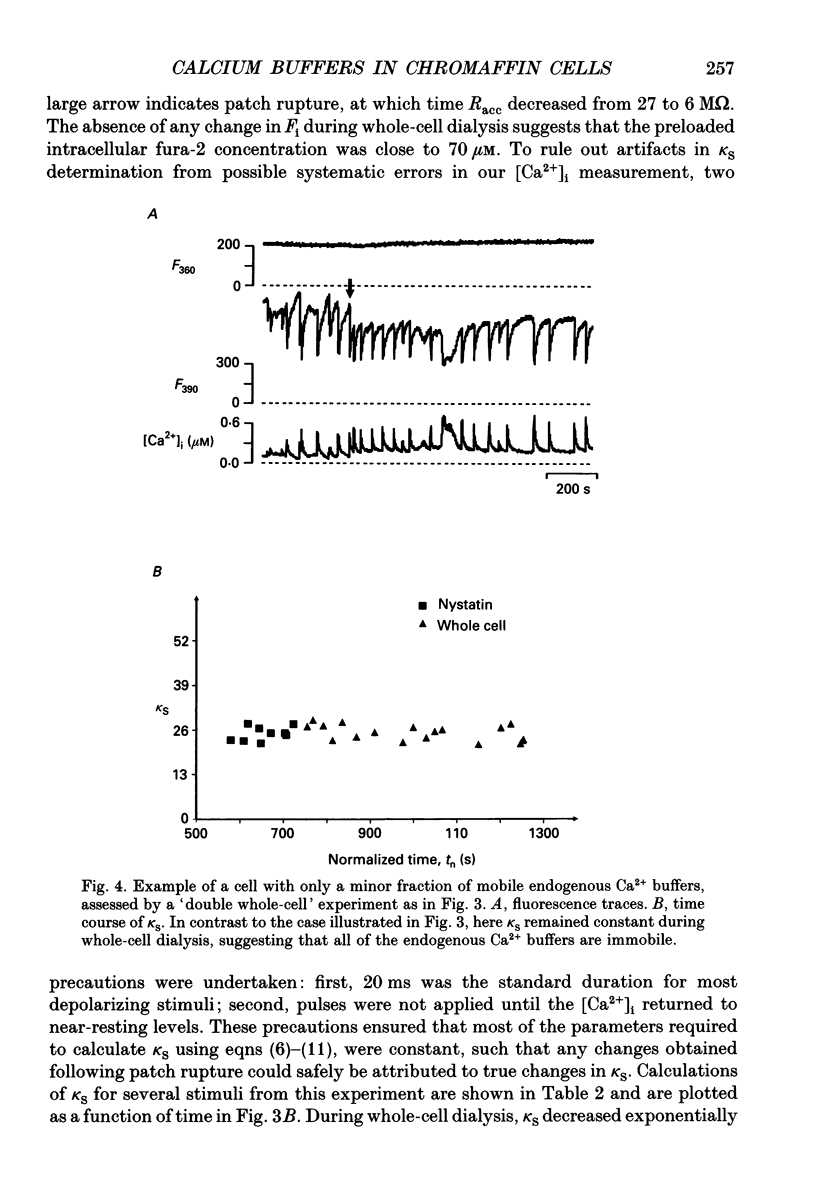
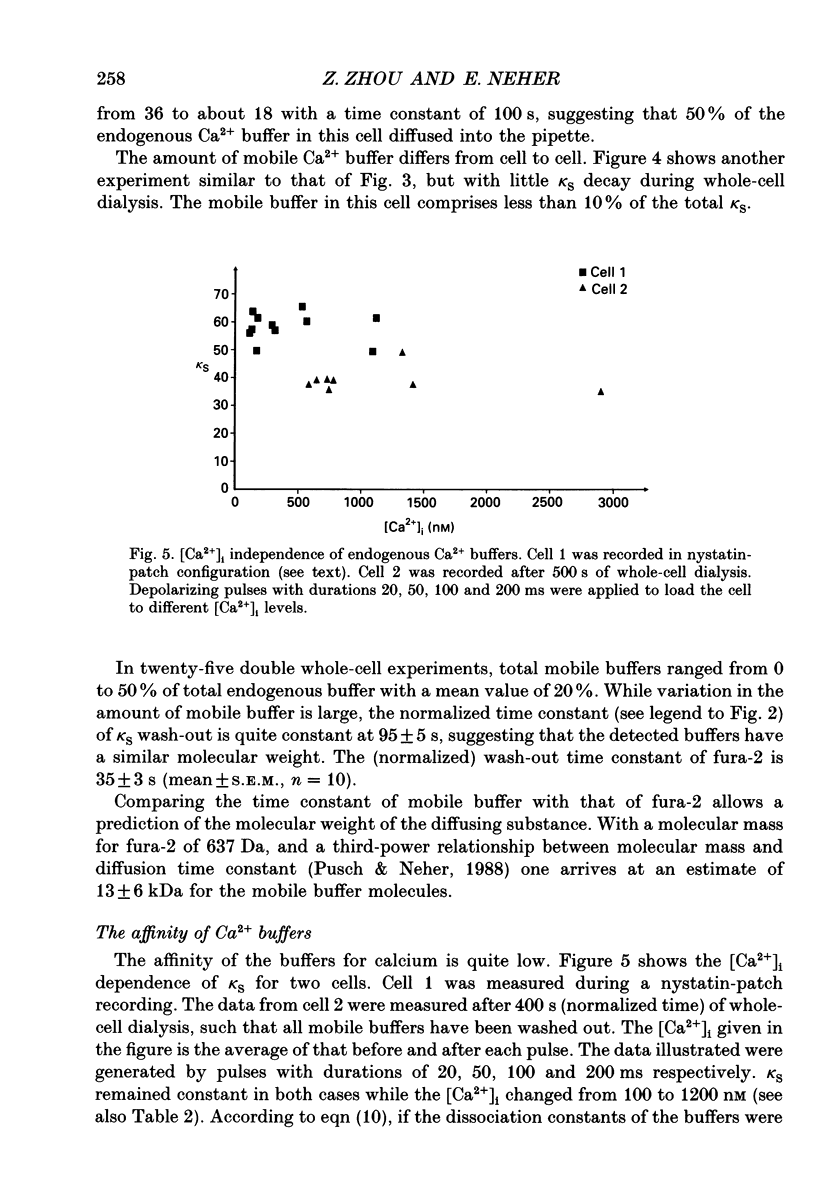
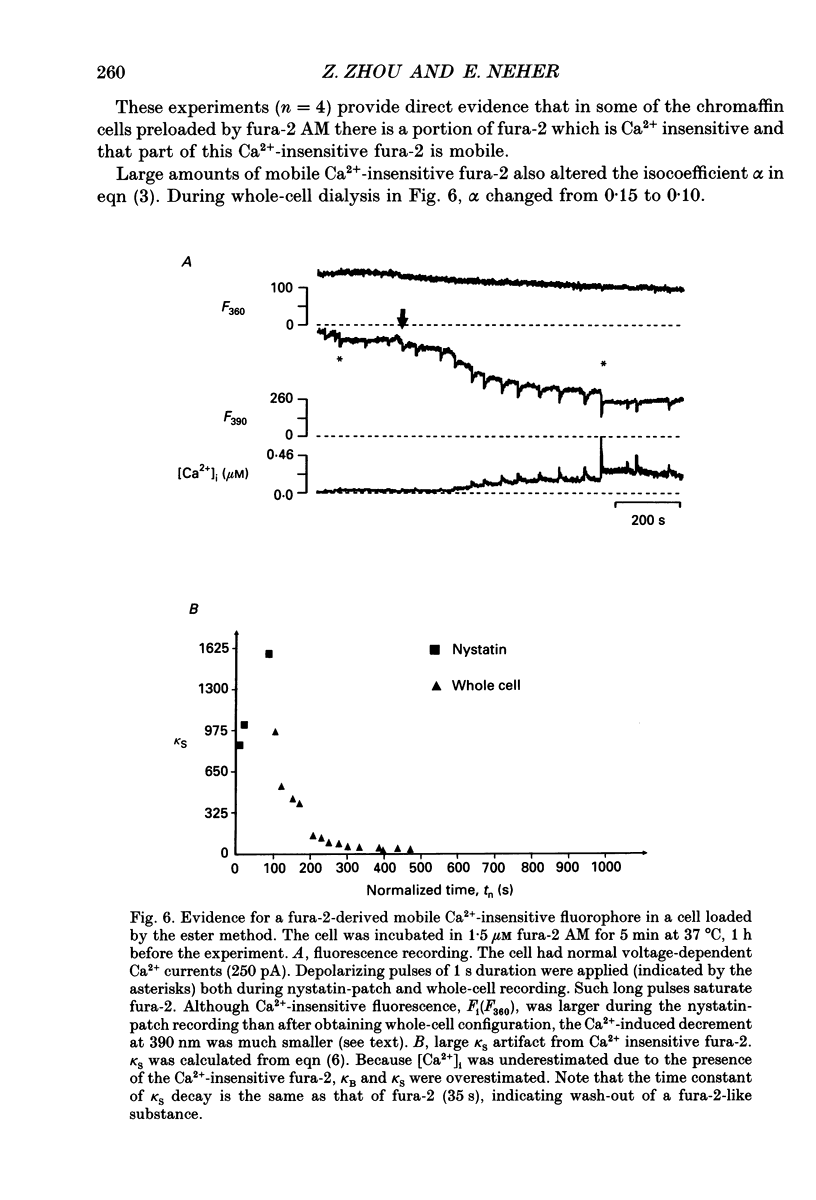
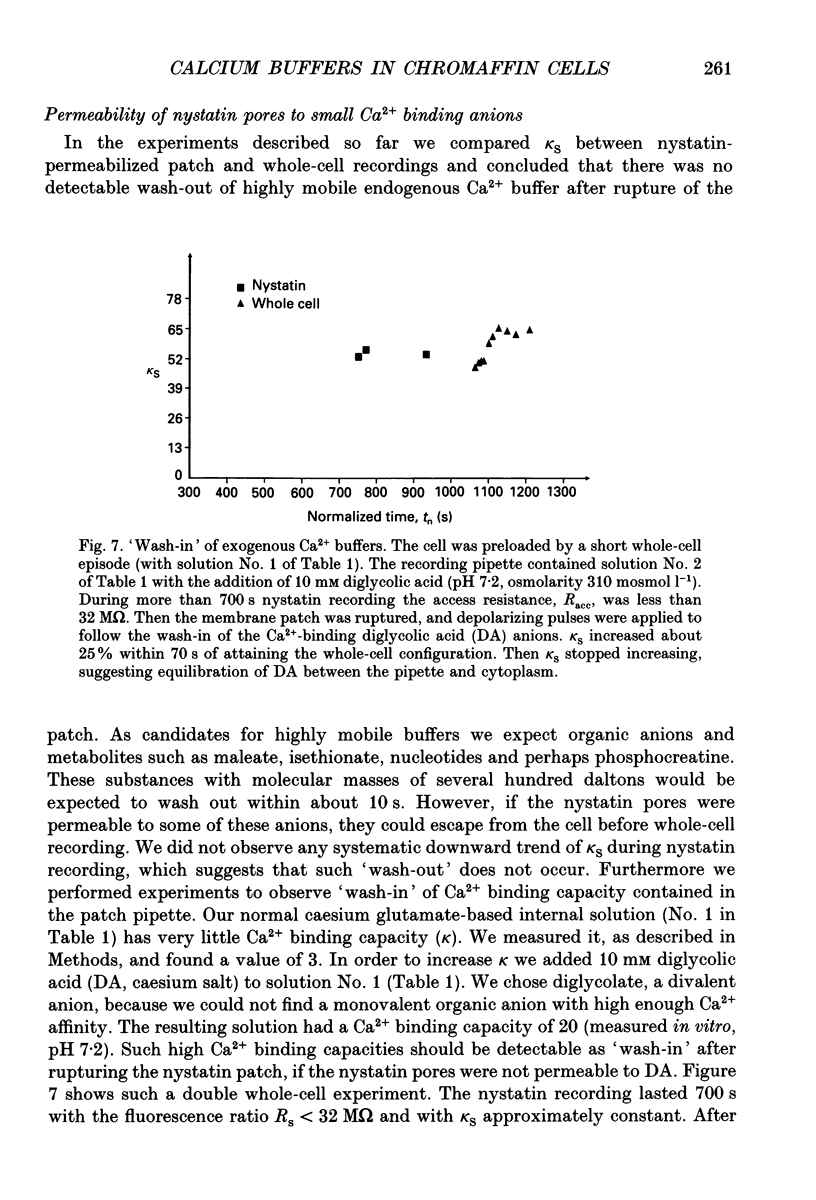
1. The calcium binding capacity (kappa S) of bovine chromaffin cells preloaded with fura-2 was measured during nystatin-perforated-patch recordings. 2. Subsequently, the perforated patch was ruptured to obtain a whole-cell recording situation, and the time course of kappa S was monitored during periods of up to one hour. 3. No rapid change (within 10-20 s) of kappa S was observed upon transition to whole-cell recording, as would be expected, if highly mobile organic anions contributed significantly to calcium buffering. However, approximately half of the cells investigated displayed a drop in kappa S within 2-5 min, indicative of the loss of soluble Ca2+ binding proteins in the range of 7-20 kDa. 4. The average Ca2+ binding capacity (differential ratio of bound calcium over free calcium) was 9 +/- 7 (mean +/- S.E.M.) for the poorly mobile component and 31 +/- 10 for the fixed component. It was concluded that a contribution of 7 from highly mobile buffer would have been detected, if present. Thus, this value can be considered as an upper bound to highly mobile Ca2+ buffer. 5. Both mobile and fixed calcium binding capacity appeared to have relatively low Ca2+ affinity, since kappa S did not change in the range of Ca2+ concentrations between 0.1 and 3 microM. 6. It was found that cellular autofluorescence and contributions to fluorescence of non-hydrolysed or compartmentalized dye contribute a serious error in estimation of kappa S. 'Balanced loading', a degree of fura-2 loading such that the calcium binding capacity of fura-2 equals cellular calcium binding capacity, minimizes these errors. Also, changes in kappa S at the transition from perforated-patch to whole-cell recording can be most faithfully recorded for similar degrees of loading in both situations. 7. Nystatin was found unable to make pores from inside of the plasma membrane of chromaffin cells. With careful preparation and storage the diluted nystatin solution maintained its high activity of membrane perforation for more than one week. 8. An equation for the effective diffusion constant for total cytoplasmic calcium, D'Ca, was derived, which takes into account fixed buffer and poorly mobile buffer as determined, as well as calcium bound to fura-2 and some highly mobile buffers.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler E. M., Augustine G. J., Duffy S. N., Charlton M. P. Alien intracellular calcium chelators attenuate neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1496–1507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01496.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Calcium regulation by and buffer capacity of molluscan neurons during calcium transients. Cell Calcium. 1988 Apr;9(2):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(88)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Mogul D. J., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Three types of bovine chromaffin cell Ca2+ channels: facilitation increases the opening probability of a 27 pS channel. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:213–240. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Neher E. Neuronal Ca2+ signalling takes the local route. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Jun;2(3):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. L., Fay F. S. Photobleaching of fura-2 and its effect on determination of calcium concentrations. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C613–C618. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass A., Finkelstein A., Krespi V. The ion permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):100–124. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feher J. J., Fullmer C. S., Fritzsch G. K. Comparison of the enhanced steady-state diffusion of calcium by calbindin-D9K and calmodulin: possible importance in intestinal calcium absorption. Cell Calcium. 1989 May-Jun;10(4):189–203. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Intracellular calcium accumulation during depolarization in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:259–285. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. M., Bers D. M. The effect of temperature and ionic strength on the apparent Ca-affinity of EGTA and the analogous Ca-chelators BAPTA and dibromo-BAPTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 13;925(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Korn S. J. Prevention of rundown in electrophysiological recording. Methods Enzymol. 1992;207:149–155. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07010-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg M. E., Finkelstein A. Single-length and double-length channels formed by nystatin in lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(3):257–269. doi: 10.1007/BF01868444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Olson A., Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic binding of fura-2 investigated by steady-state fluorescence and absorbance measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1089–1104. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83045-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Podolsky R. J. Ionic mobility in muscle cells. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Finkelstein A. Pores formed in lipid bilayer membranes by nystatin, Differences in its one-sided and two-sided action. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Apr;65(4):515–526. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.4.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Neher E. Potassium channels in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:117–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney R. N., Neering I. R. The measurement of changes in intracellular free calcium during action potentials in mammalian neurones. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Mar;13(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menéndez Robredo A. R., Gonzalvo Rodríguez P., De la Rosa Peña M. L., Llavona Amor J. A., Alvarez Rodríguez A., Celorio Peinado C., Fernández Palacio E. Adenocarcinoma gástrico calcificado. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 1991 Apr;79(4):273–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasi E., Tillotson D. The rate of diffusion of Ca2+ and Ba2+ in a nerve cell body. Biophys J. 1985 May;47(5):735–738. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83972-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Correction for liquid junction potentials in patch clamp experiments. Methods Enzymol. 1992;207:123–131. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Pinter M. J. Time courses of calcium and calcium-bound buffers following calcium influx in a model cell. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81342-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J., Cooper K., Gates P., Watsky M. Low access resistance perforated patch recordings using amphotericin B. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Mar;37(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90017-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reber B. F., Reuter H. Dependence of cytosolic calcium in differentiating rat pheochromocytoma cells on calcium channels and intracellular stores. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:145–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala F., Hernández-Cruz A. Calcium diffusion modeling in a spherical neuron. Relevance of buffering properties. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82533-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon M., Williams D. A., Fay F. S. A Ca2+-insensitive form of fura-2 associated with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Assessment and accurate Ca2+ measurement. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6308–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Aequorin response facilitation and intracellular calcium accumulation in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:167–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman M. P., Ashley C. C. Fura-2 diffusion and its use as an indicator of transient free calcium changes in single striated muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fogarty K. E., Tsien R. Y., Fay F. S. Calcium gradients in single smooth muscle cells revealed by the digital imaging microscope using Fura-2. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):558–561. doi: 10.1038/318558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


