Abstract
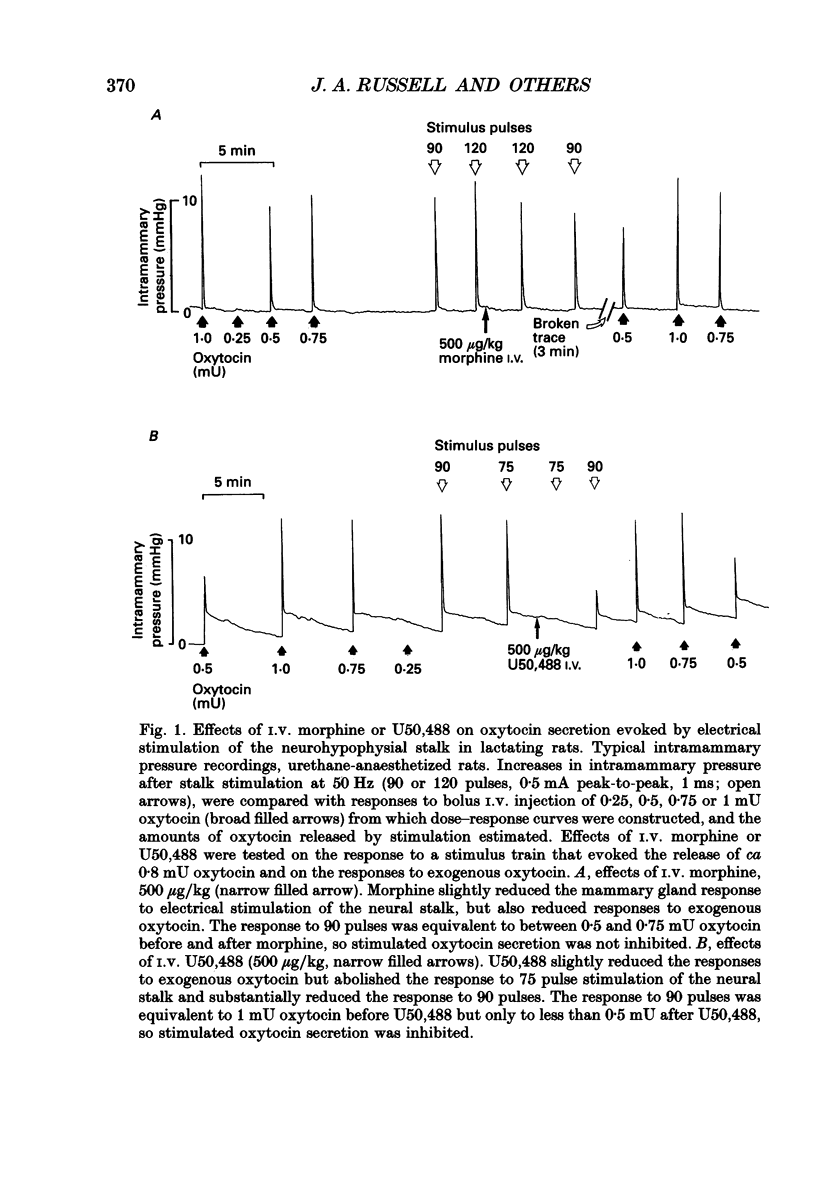
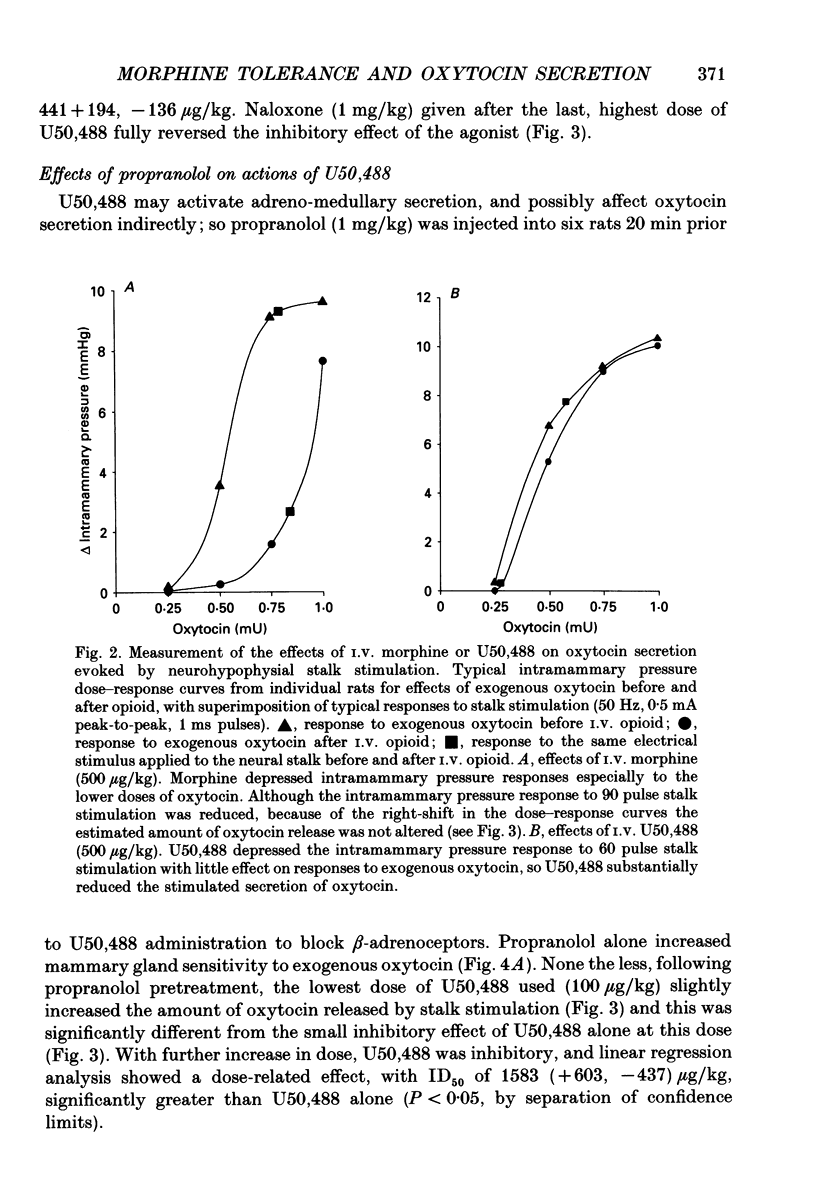
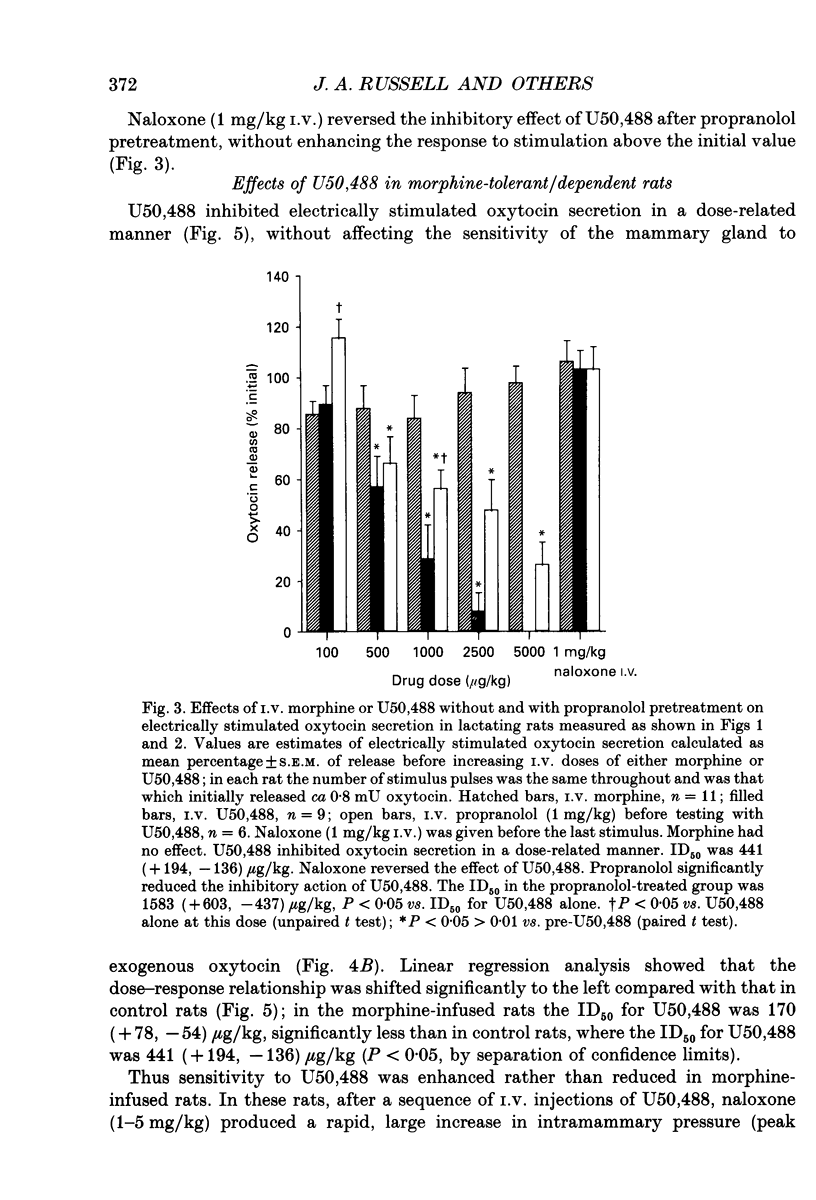
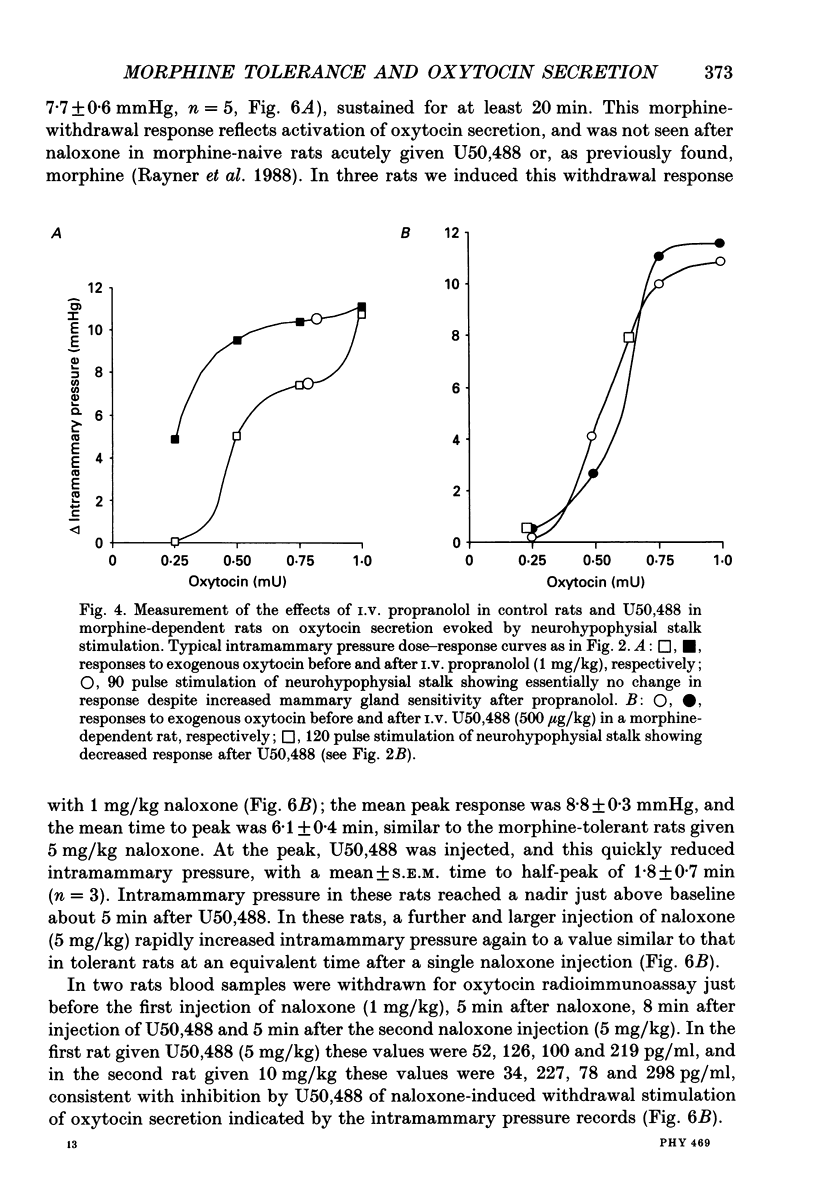
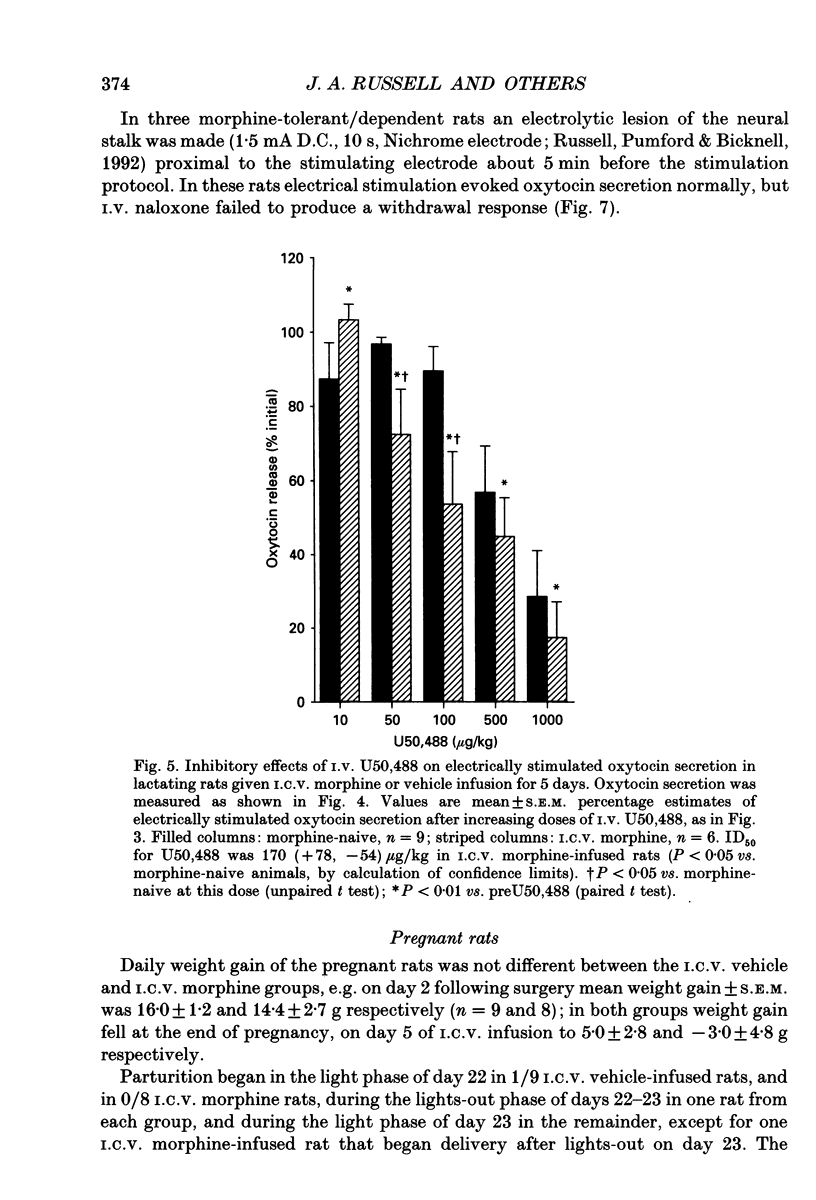
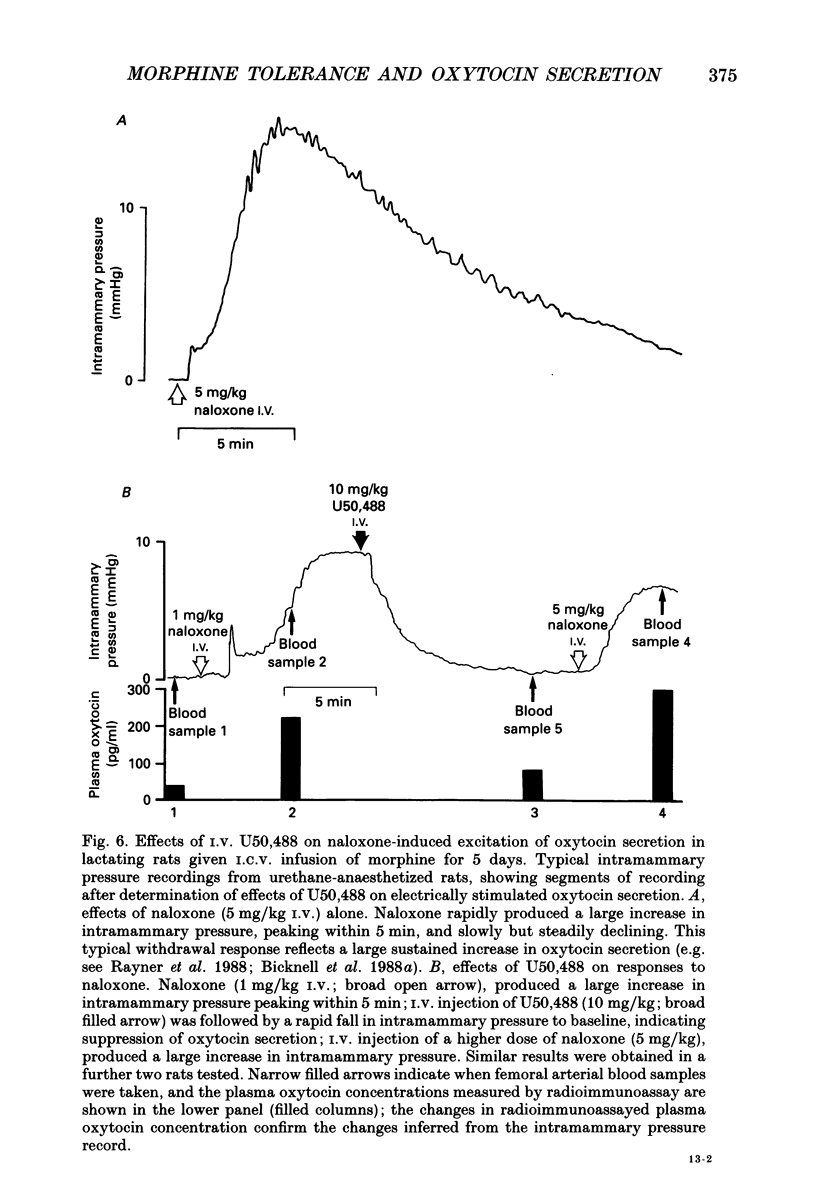
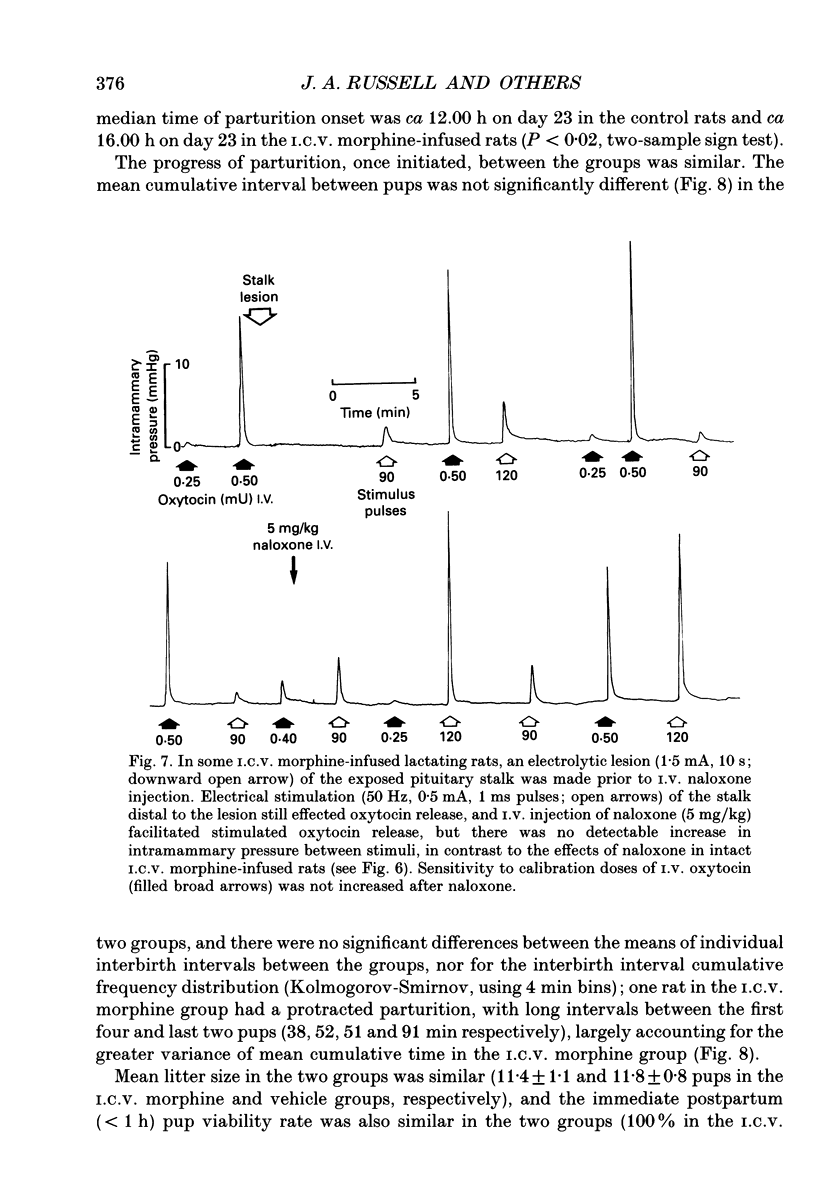
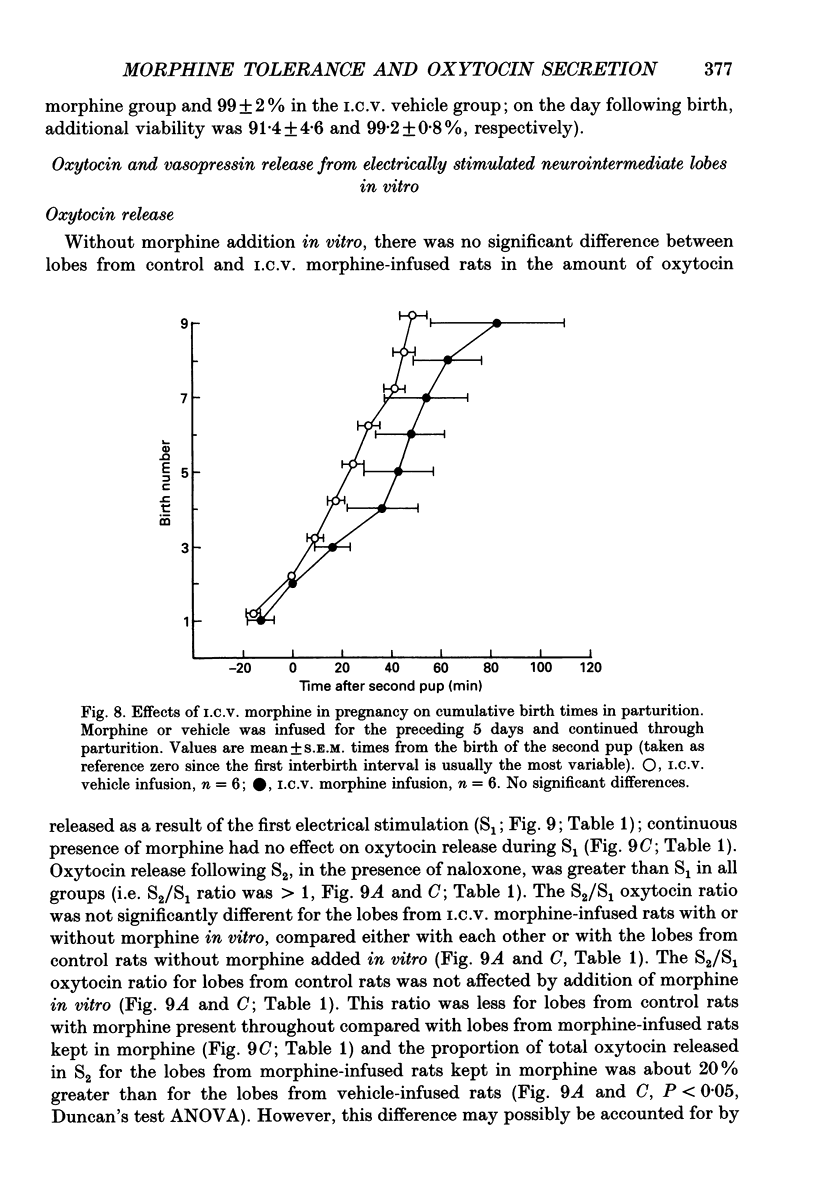
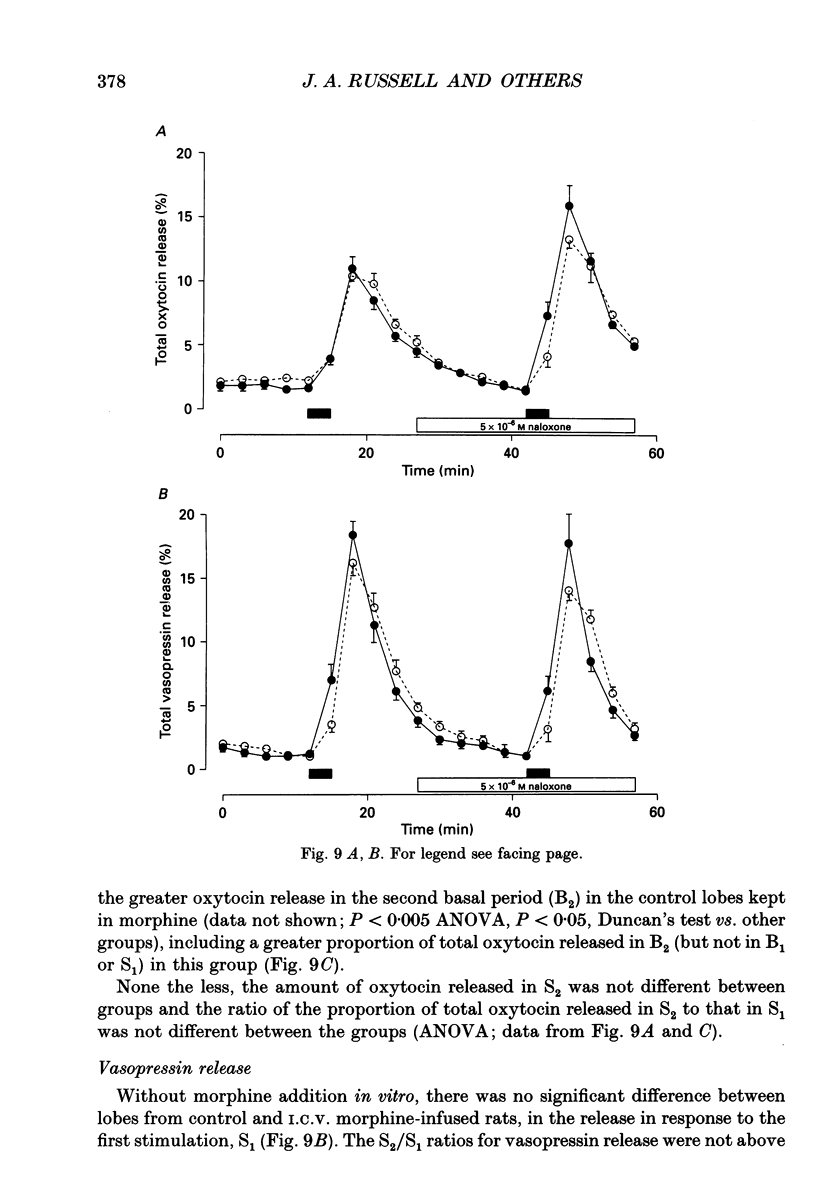
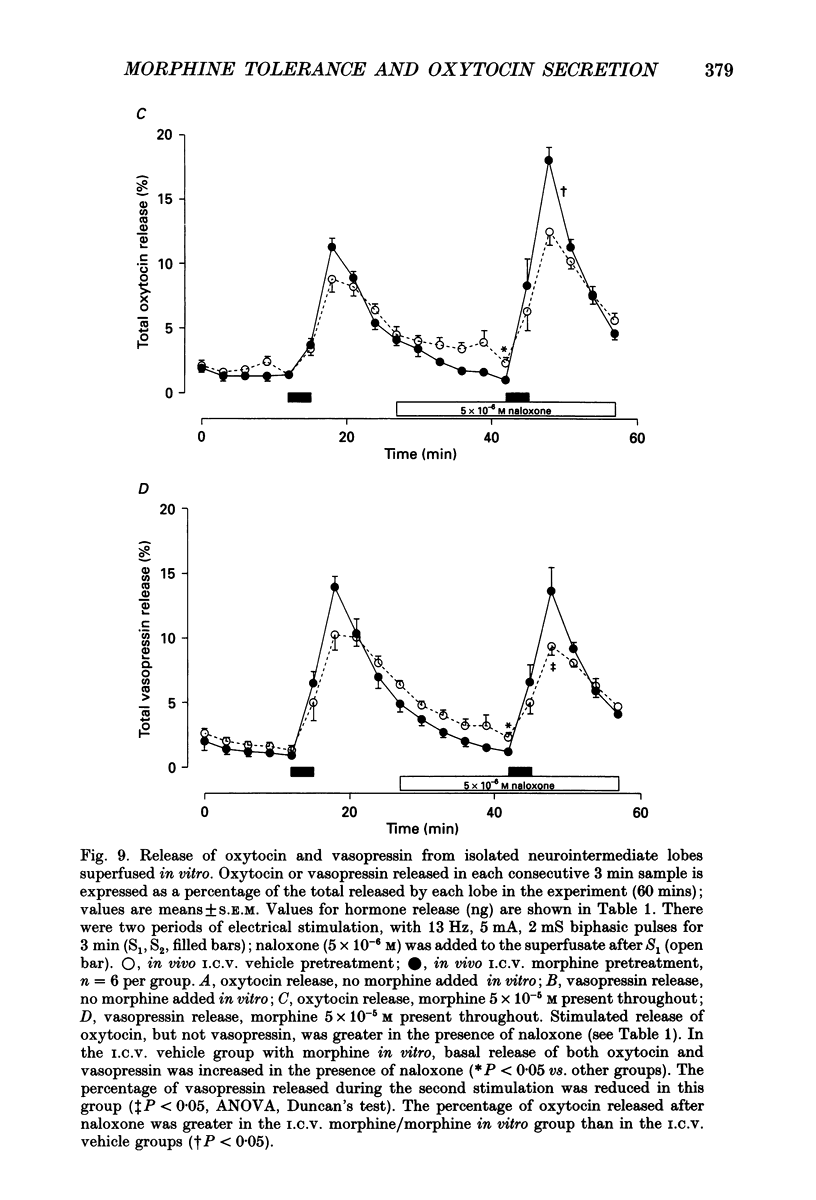
1. The present study investigated the mechanisms by which endogenous opioids regulate oxytocin secretion at the level of the posterior pituitary gland. Effects of the selective kappa-agonist U50,488 on oxytocin secretion were studied in urethane-anaesthetized lactating rats. Oxytocin secretion in response to electrical stimulation (0.5 mA, matched biphasic 1 ms pulses, 50 Hz, 60-180 pulses) of the neurohypophysial stalk was bioassayed on-line by measuring increases in intramammary pressure, calibrated with exogenous oxytocin. Intravenous (I.V.) U50,488 inhibited electrically stimulated oxytocin secretion, without affecting mammary gland sensitivity to oxytocin. The inhibition was dose related, with an ID50 of 441 (+194, -136) micrograms/kg and was naloxone reversible. Antagonism of endogenous beta-adrenoceptor activation by propranolol (1 mg/kg) reduced the potency of U50,488. The selective mu-agonist morphine (up to 5 mg/kg), had no effect on electrically stimulated oxytocin secretion, but depressed the mammary response to oxytocin. 2. In lactating rats given intracerebroventricular (I.C.V.) morphine infusion for 5 days to induce tolerance and dependence, I.V. U50,488 still inhibited electrically stimulated oxytocin secretion, but the ID50 was reduced to 170 (+78, -54) micrograms/kg; thus at the posterior pituitary the sensitivity of kappa-receptors is enhanced rather than reduced in morphine-tolerant rats, indicating the absence of cross-tolerance. In these rats, naloxone produced a large, sustained, fluctuating increase in intramammary pressure indicating morphine-withdrawal excitation of oxytocin secretion; I.V. U50,488 diminished this response, confirmed by radioimmunoassay, demonstrating the independence of mu- and kappa-receptors regulating oxytocin secretion. 3. In pregnant rats, I.C.V. infusion of morphine from day 17-18 of pregnancy delayed the start of parturition by 4 h, but did not significantly affect the progress of parturition once established, indicating tolerance to the inhibitory actions of morphine on oxytocin secretion in parturition, and lack of cross-tolerance to endogenous opioids restraining oxytocin in parturition. 4. Neurointermediate lobes from control and I.C.V. morphine-infused virgin rats were impaled on electrodes and perifused in vitro. Vasopressin and oxytocin release from the glands was measured by radioimmunoassay. Each gland was exposed to two periods of electrical stimulation (13 Hz, for 3 min). Naloxone (5 x 10(-6) M) was added before the second stimulation; half the lobes from each I.C.V. treatment were exposed to 5 x 10(-5) M morphine throughout.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Hisano S., Daikoku S. Intragranular colocalization of immunoreactive methionine-enkephalin and oxytocin within the nerve terminals in the posterior pituitary. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Sep;33(9):891–899. doi: 10.1177/33.9.4020100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anhut H., Knepel W. Release of dynorphin-like immunoreactivity of rat neurohypophysis in comparison to vasopressin after various stimuli in vitro and in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Aug 16;31(2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R. J., Leng G. Endogenous opiates regulate oxytocin but not vasopressin secretion from the neurohypophysis. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):161–162. doi: 10.1038/298161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R. J., Leng G., Lincoln D. W., Russell J. A. Naloxone excites oxytocin neurones in the supraoptic nucleus of lactating rats after chronic morphine treatment. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:297–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R. J., Leng G., Russell J. A., Dyer R. G., Mansfield S., Zhao B. G. Hypothalamic opioid mechanisms controlling oxytocin neurones during parturition. Brain Res Bull. 1988 Jun;20(6):743–749. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(88)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C. A., Gainer H., Russell J. T. Dynorphin A inhibits and naloxone increases the electrically stimulated release of oxytocin but not vasopressin from the terminals of the neural lobe. Endocrinology. 1988 Apr;122(4):1321–1327. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-4-1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castanas E., Bourhim N., Giraud P., Boudouresque F., Cantau P., Oliver C. Interaction of opiates with opioid binding sites in the bovine adrenal medulla: II. Interaction with kappa sites. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):688–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. A., Pasternak G. W. U50,488: a kappa-selective agent with poor affinity for mu1 opiate binding sites. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Mar;27(3):331–332. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G., Patrick G. Differential inhibitory action by morphine on the release of oxytocin and vasopressin from the isolated neural lobe. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Aug 29;39(2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G., Wood P., Merrick L., Lincoln D. W. Opiate inhibition of peptide release from the neurohumoral terminals of hypothalamic neurones. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):746–748. doi: 10.1038/282746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. G., Olley J. E., Rice G. E., Abrahams J. M. Effects of subacute opioid administration during late pregnancy in the rat on the initiation, duration and outcome of parturition and maternal levels of oxytocin and arginine vasopressin. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1989 Mar;16(3):169–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1989.tb01541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. G., Olley J. E., Rice G. E., Abrahams J. M. mu- and K-opiate receptor agonists reduce plasma neurohypophysial hormone concentrations in water-deprived and normally hydrated rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1989 Mar;16(3):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1989.tb01544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. G., Rice G. E., Olley J. E. Studies of the effects of subacute treatment with N-(cyclopropylmethyl)-19-isopentylnororvinol (M320) on timing of parturition in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):777–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaymann W., Martin R. A re-examination of the localization of immunoreactive dynorphin(1-8), [Leu]enkephalin and [Met]enkephalin in the rat neurohypophysis. Neuroscience. 1987 Mar;20(3):1069–1080. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90264-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstberger R., Barden N. Dynorphin 1-8 binds to opiate kappa receptors in the neurohypophysis. Neuroendocrinology. 1986;42(5):376–382. doi: 10.1159/000124475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell S., Christensen J. D., Fjalland B. The influence of morphine and naloxone on plasma oxytocin concentration in the rat. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988 Oct;63(4):274–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1988.tb00953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Rice K. C., Jacobson A. E., Rothman R. B. Opiate receptors in rat pituitary are confined to the neural lobe and are exclusively kappa. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 24;382(2):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi T., Honda K., Fukuoka T., Negoro H., Wakabayashi K. Release of oxytocin during suckling and parturition in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1985 Jun;105(3):339–346. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1050339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi T., Tadokoro Y., Honda K., Negoro H. Detailed analysis of blood oxytocin levels during suckling and parturition in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1986 Aug;110(2):251–256. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1100251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar S., Kim H. S., Wood P. L. Mu-, delta-, kappa- and epsilon-opioid receptor modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis: subchronic tolerance studies of endogenous opioid peptides. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 1;435(1-2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91604-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W. The Wellcome Foundation lecture, 1982. Opioid peptides and their receptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jul 22;225(1238):27–40. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Dyball R. E., Way S. A. Naloxone potentiates the release of oxytocin induced by systemic administration of cholecystokinin without enhancing the electrical activity of supraoptic oxytocin neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1992;88(2):321–325. doi: 10.1007/BF02259107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Mansfield S., Bicknell R. J., Blackburn R. E., Brown D., Chapman C., Dyer R. G., Hollingsworth S., Shibuki K., Yates J. O. Endogenous opioid actions and effects of environmental disturbance on parturition and oxytocin secretion in rats. J Reprod Fertil. 1988 Sep;84(1):345–356. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0840345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G. Rat supraoptic neurones: the effects of locally applied hypertonic saline. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:405–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Russell J. A., Grossmann R. Sensitivity of magnocellular oxytocin neurones to opioid antagonists in rats treated chronically with intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) morphine. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 10;484(1-2):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Corticotrophin-releasing factor, vasopressin and pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA responses to stress and opiates in the rat. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:511–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln D. W., Wakerley J. B. Factors governing the periodic activation of supraoptic and paraventricular neurosecretory cells during suckling in the rat. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(2):443–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnan J., Paterson S. J., Tavani A., Kosterlitz H. W. The binding spectrum of narcotic analgesic drugs with different agonist and antagonist properties. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;319(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00495865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister B., Villar M. J., Ceccatelli S., Hökfelt T. Localization of chemical messengers in magnocellular neurons of the hypothalamic supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei: an immunohistochemical study using experimental manipulations. Neuroscience. 1990;37(3):603–633. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90094-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumford K. M., Leng G., Russell J. A. Morphine actions on supraoptic oxytocin neurones in anaesthetized rats: tolerance after i.c.v. morphine infusion. J Physiol. 1991;440:437–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner V. C., Robinson I. C., Russell J. A. Chronic intracerebroventricular morphine and lactation in rats: dependence and tolerance in relation to oxytocin neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:319–347. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Gosden R. G., Humphreys E. M., Cutting R., Fitzsimons N., Johnston V., Liddle S., Scott S., Stirland J. A. Interruption of parturition in rats by morphine: a result of inhibition of oxytocin secretion. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jun;121(3):521–536. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1210521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Leng G., Coombes J. E., Crockett S. A., Douglas A. J., Murray I., Way S. Pethidine (meperidine) inhibition of oxytocin secretion and action in parturient rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):R358–R368. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.261.2.R358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Pumford K. M., Bicknell R. J. Contribution of the region anterior and ventral to the third ventricle to opiate withdrawal excitation of oxytocin secretion. Neuroendocrinology. 1992 Feb;55(2):183–192. doi: 10.1159/000126113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick E. L., Flint A. P. Circulating concentrations of oxytocin during the estrous cycle and early pregnancy in sheep. Prostaglandins. 1981 Oct;22(4):631–636. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheward W. J., Coombes J. E., Bicknell R. J., Fink G., Russell J. A. Release of oxytocin but not corticotrophin-releasing factor-41 into rat hypophysial portal vessel blood can be made opiate dependent. J Endocrinol. 1990 Jan;124(1):141–150. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1240141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner B. E., Coombes J. E., Pumford K. M., Russell J. A. Opioid receptor subtypes in the supraoptic nucleus and posterior pituitary gland of morphine-tolerant rats. Neuroscience. 1990;37(3):635–645. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90095-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakerley J. B., Noble R., Clarke G. Effects of morphine and D-Ala, D-Leu enkephalin on the electrical activity of supraoptic neurosecretory cells in vitro. Neuroscience. 1983 Sep;10(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnall M. H., Gainer H., Cox B. M., Molineaux C. J. Dynorphin-A-(1-8) is contained within vasopressin neurosecretory vesicles in rat pituitary. Science. 1983 Dec 9;222(4628):1137–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.6648526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ohno M., Ueki S. A selective kappa-opioid agonist, U-50,488H, blocks the development of tolerance to morphine analgesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 26;156(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B. G., Chapman C., Bicknell R. J. Functional kappa-opioid receptors on oxytocin and vasopressin nerve terminals isolated from the rat neurohypophysis. Brain Res. 1988 Oct 11;462(1):62–66. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90585-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B. G., Chapman C., Bicknell R. J. Opioid-noradrenergic interactions in the neurohypophysis. I. Differential opioid receptor regulation of oxytocin, vasopressin, and noradrenaline release. Neuroendocrinology. 1988 Jul;48(1):16–24. doi: 10.1159/000124984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B. G., Chapman C., Brown D., Bicknell R. J. Opioid-noradrenergic interactions in the neurohypophysis. II. Does noradrenaline mediate the actions of endogenous opioids on oxytocin and vasopressin release? Neuroendocrinology. 1988 Jul;48(1):25–31. doi: 10.1159/000124985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


