Abstract
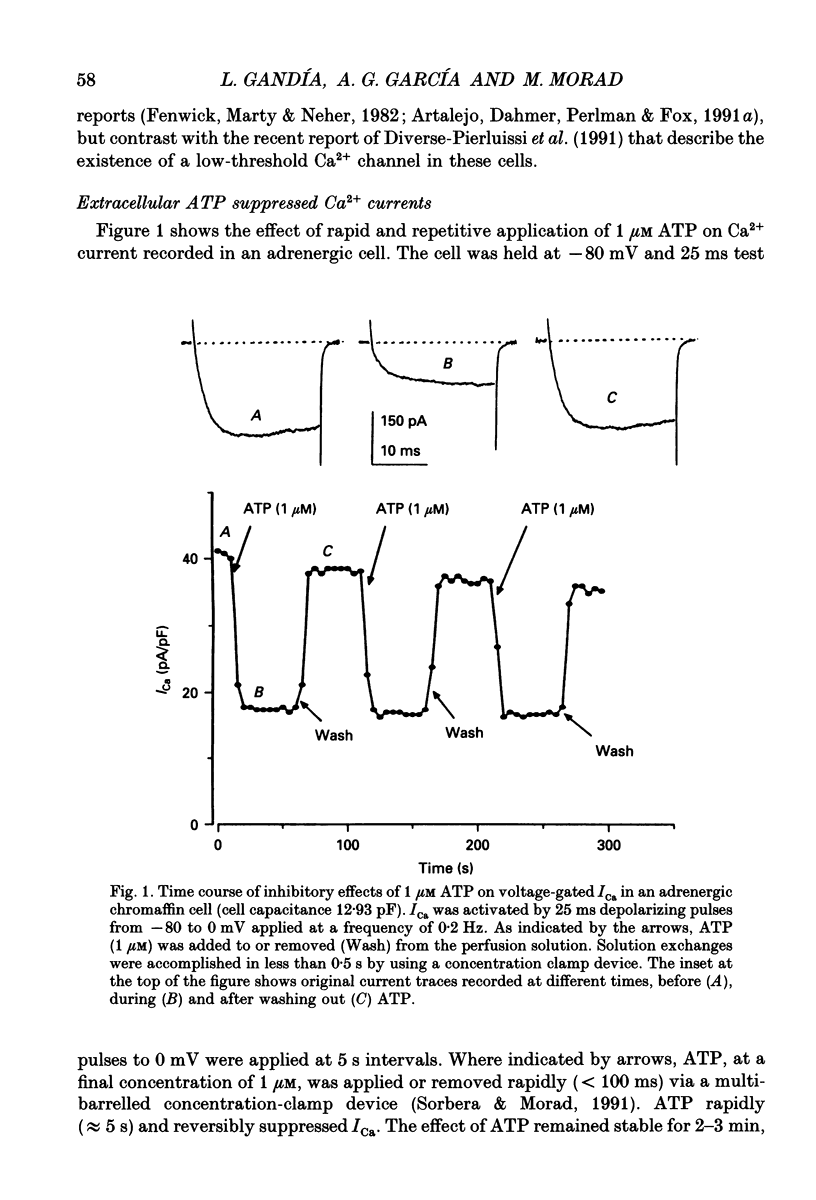
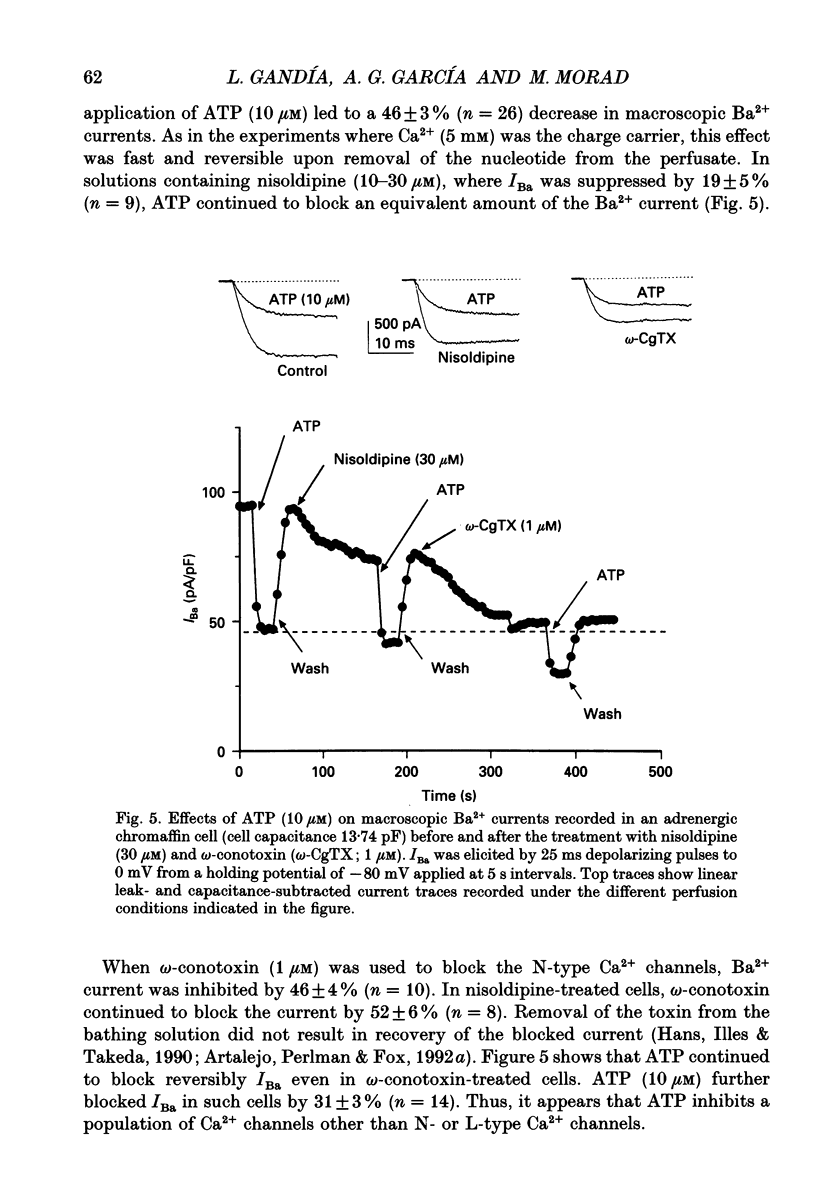
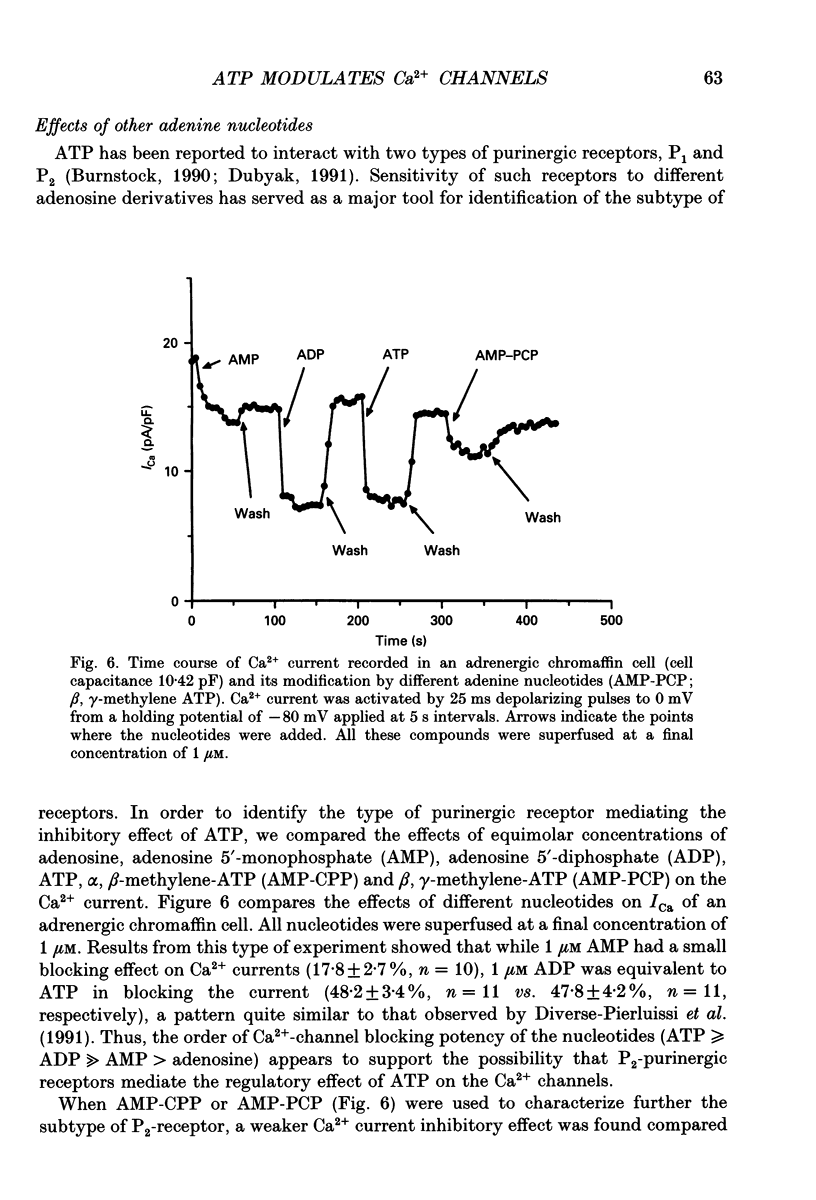
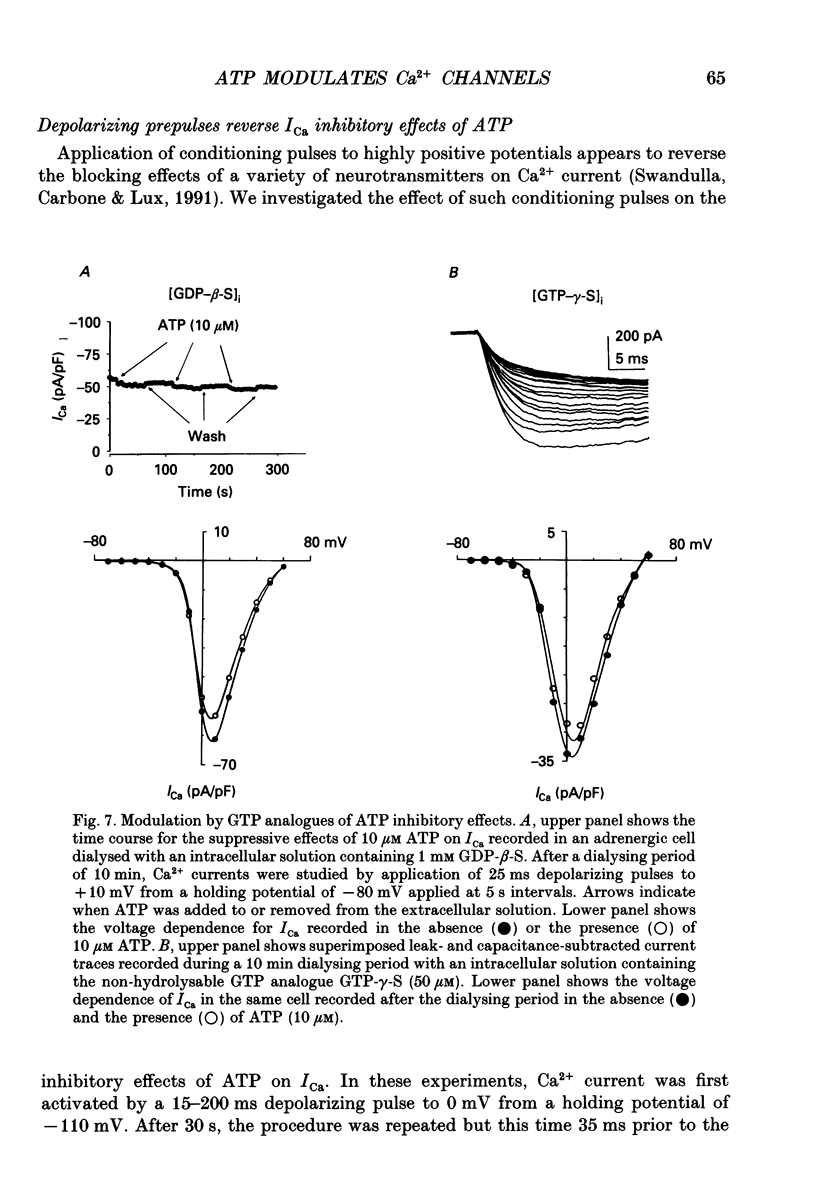
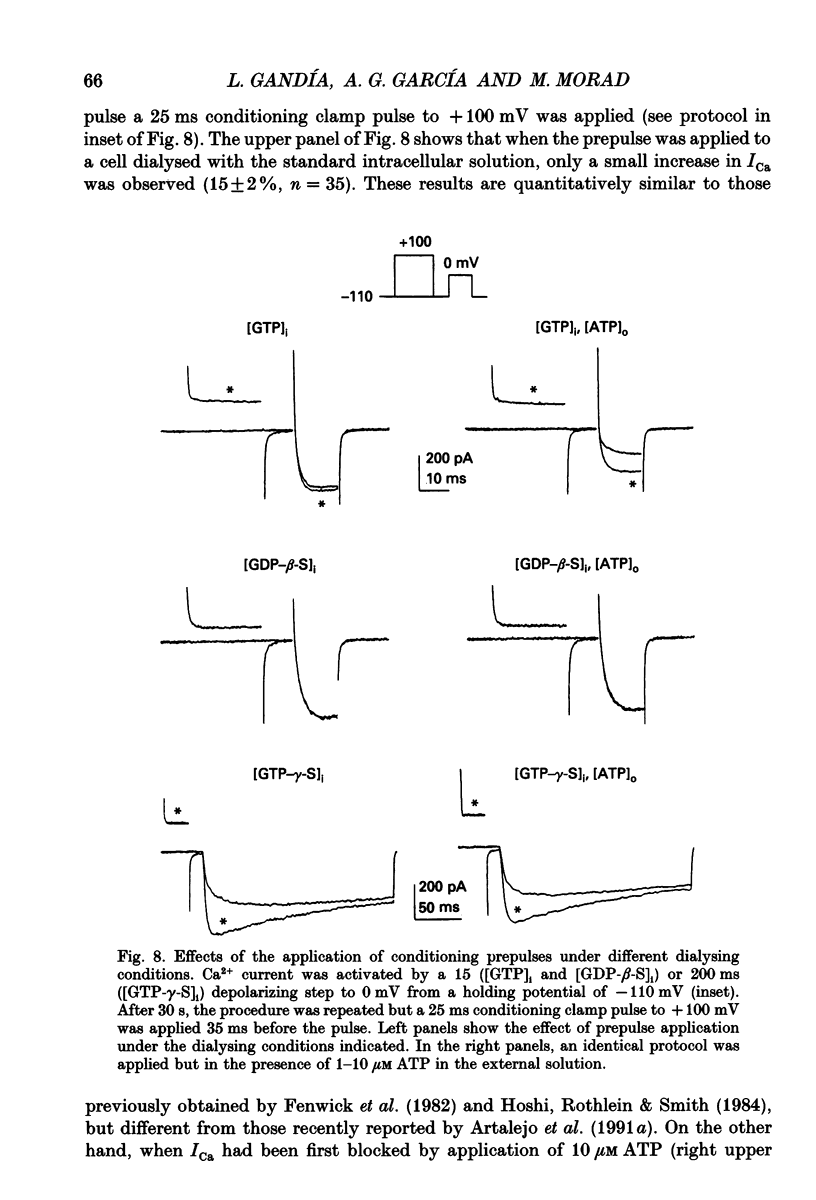
1. The effects of externally applied micromolar concentrations of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) on Ca2+ currents (ICa) were studied in whole-cell clamped adrenaline-secreting chromaffin cells. 2. Ca2+ currents in chromaffin cells activated at about -40 mV, reached a maximum at 0 mV and had an apparent reversal potential at +50 to +60 mV, indicating the existence of only high voltage-activated Ca2+ channels. 3. ATP blocked Ca2+ current rapidly, reversibly and in a concentration-dependent manner (10(-9)-10(-4) M). 4. ATP did not completely block Ca2+ current even at the highest concentrations used (100 microM). The remaining component of Ca2+ current was characterized by slower activation and inactivation kinetics. 5. ATP blocked ICa even in the presence of nisoldipine and/or omega-conotoxin GVIA, suggesting that its modulatory role is not specific for L- and/or N-type Ca2+ channels. 6. Other adenine nucleotides also blocked the Ca2+ current partially. The order of potencies was ATP > or = ADP > AMP >> adenosine, indicating that the ATP effects are most probably mediated by a P2-type purinergic receptor. 7. Dialysis of the cells with an intracellular solution containing 1 mM guanosine 5'-O-thiodiphosphate (GDP-beta-S) or pre-incubation of the cells with pertussis toxin (PTX) blocked the inhibitory effects of ATP. 8. Intracellular application of the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue guanosine 5'-O-(3'-thiotriphosphate) (GTP-gamma-S; 50 microM) also decreased ICa in a manner similar to that seen for ATP and significantly reduced the ATP inhibitory effect. 9. Conditioning pulses to potentials positive to +80 mV partly reversed the inhibitory effects of ATP on the Ca2+ current. The prepulse-induced enhancement of ICa depended on [GTP]i-related G protein activity such that concentrations larger than 200 microM GTP, or GTP-gamma-S (50 microM) were required for significant prepulse potentiation of the Ca2+ current, while dialysis with GDP-beta-S prevented it. 10. We conclude that the ATP, co-released with catecholamines in the intact adrenal gland, may inhibit the secretory process by down-regulating the Ca2+ channel via a P2-type purinergic receptor coupled to a PTX-sensitive G protein.
Full text
PDF


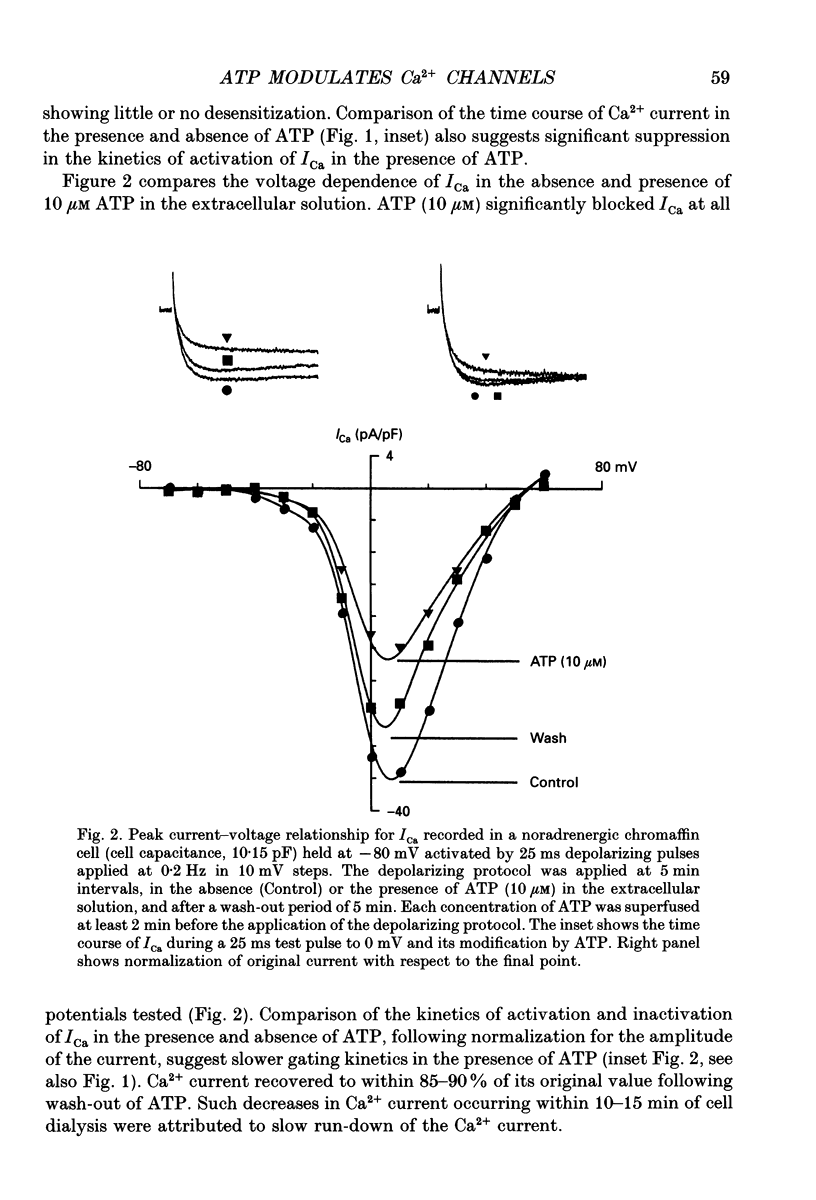
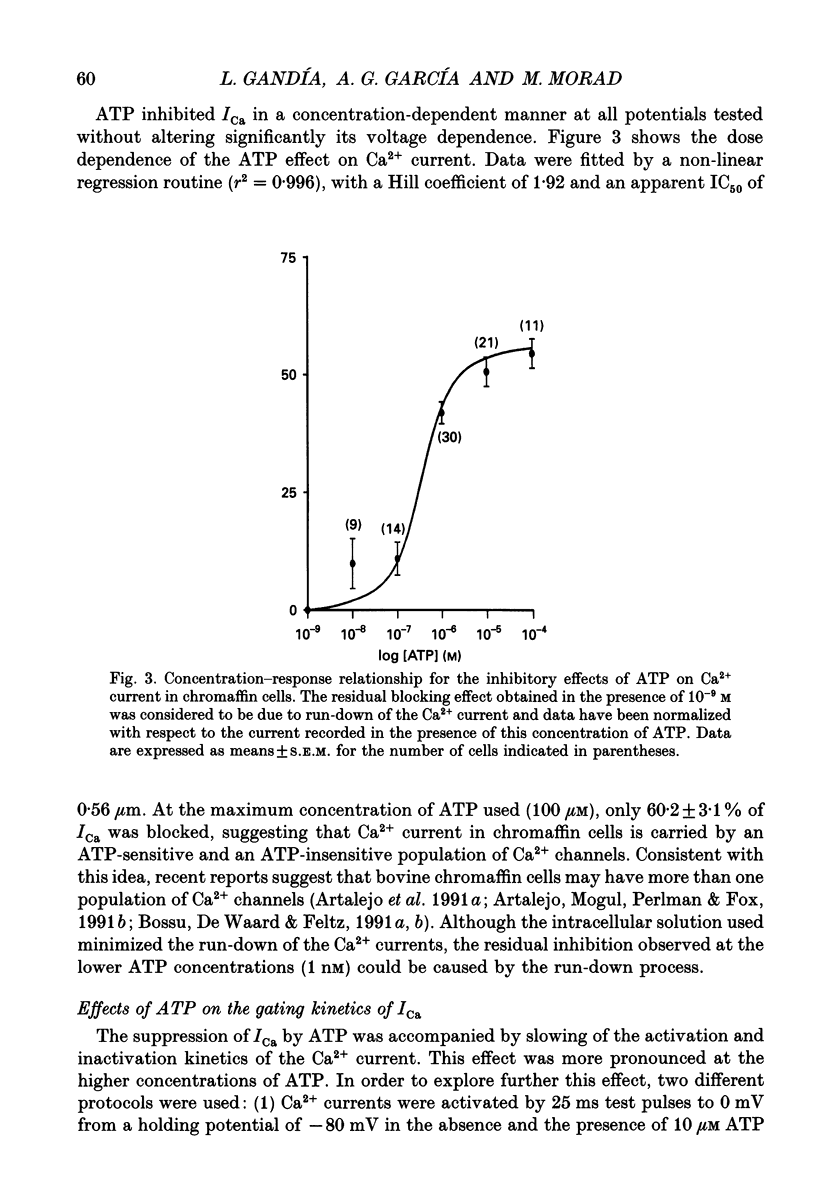
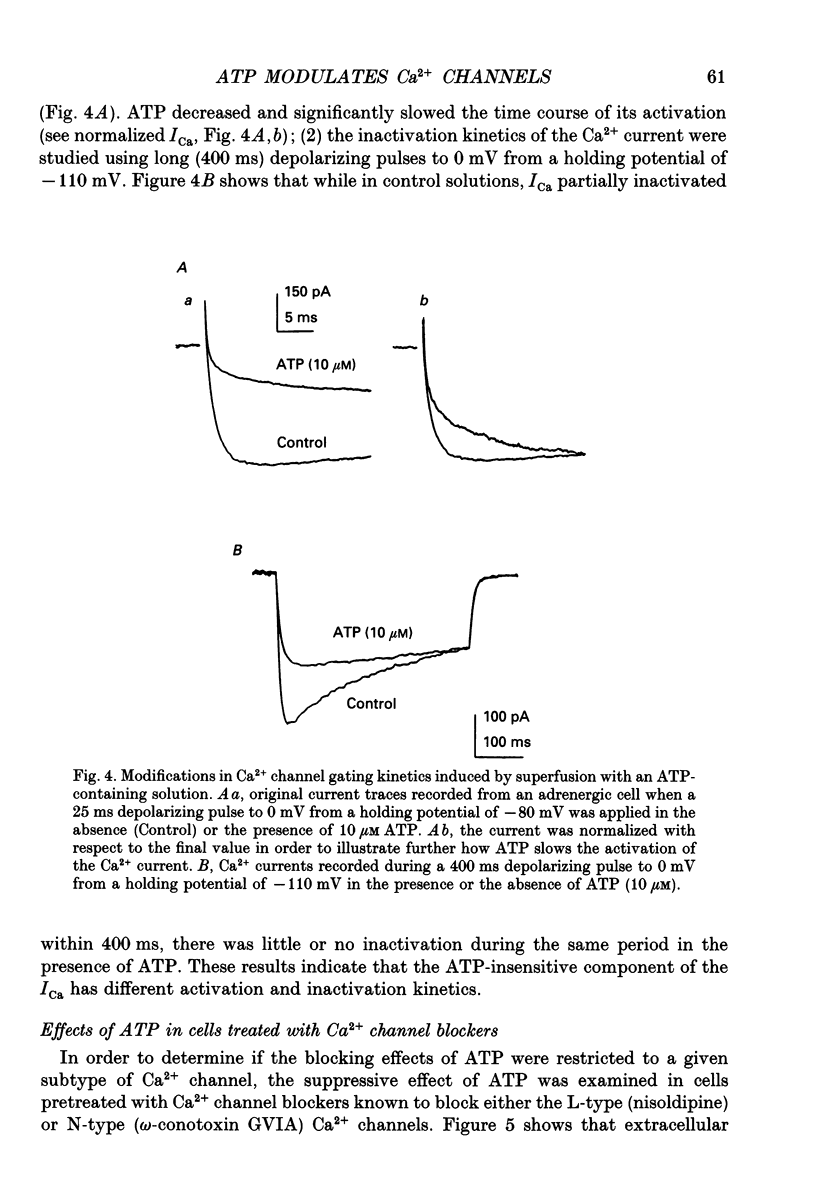







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aicardi G., Pollo A., Sher E., Carbone E. Noradrenergic inhibition and voltage-dependent facilitation of omega-conotoxin-sensitive Ca channels in insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80393-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Dahmer M. K., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Two types of Ca2+ currents are found in bovine chromaffin cells: facilitation is due to the recruitment of one type. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:681–707. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Mogul D. J., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Three types of bovine chromaffin cell Ca2+ channels: facilitation increases the opening probability of a 27 pS channel. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:213–240. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Omega-conotoxin GVIA blocks a Ca2+ current in bovine chromaffin cells that is not of the "classic" N type. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90110-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Rossie S., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Voltage-dependent phosphorylation may recruit Ca2+ current facilitation in chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):63–66. doi: 10.1038/358063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Pharmacology and electrophysiology of ATP-activated ion channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., De Waard M., Feltz A. Inactivation characteristics reveal two calcium currents in adult bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:603–620. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Overview. Purinergic mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert G., Johnson R. G., Morad M. Regulation of the secretory response in bovine chromaffin cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 1):C851–C860. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.4.C851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo C. J., Moro M. A., Del Valle M., Sillero A., García A. G., Sillero M. A. Diadenosine tetraphosphate is co-released with ATP and catecholamines from bovine adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1992 Aug;59(2):723–732. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceña V., Brocklehurst K. W., Pollard H. B., Rojas E. Pertussis toxin stimulation of catecholamine release from adrenal medullary chromaffin cells: mechanism may be by direct activation of L-type and G-type calcium channels. J Membr Biol. 1991 May;122(1):23–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01872736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chern Y. J., Herrera M., Kao L. S., Westhead E. W. Inhibition of catecholamine secretion from bovine chromaffin cells by adenine nucleotides and adenosine. J Neurochem. 1987 May;48(5):1573–1576. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chern Y. J., Kim K. T., Slakey L. L., Westhead E. W. Adenosine receptors activate adenylate cyclase and enhance secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells in the presence of forskolin. J Neurochem. 1988 May;50(5):1484–1493. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diverse-Pierluissi M., Dunlap K., Westhead E. W. Multiple actions of extracellular ATP on calcium currents in cultured bovine chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1261–1265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Poisner A. M., Rubin R. P. Efflux of adenine nucleotides from perfused adrenal glands exposed to nicotine and other chromaffin cell stimulants. J Physiol. 1965 Jul;179(1):130–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R. Signal transduction by P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;4(4):295–300. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.4.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandía L., Casado L. F., López M. G., García A. G. Separation of two pathways for calcium entry into chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1073–1078. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12302.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi F., Lux H. D. Voltage-dependent GABA-induced modulation of calcium currents in chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 23;105(1-2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hans M., Illes P., Takeda K. The blocking effects of omega-conotoxin on Ca current in bovine chromaffin cells. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jun 22;114(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90429-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Rothlein J., Smith S. J. Facilitation of Ca2+-channel currents in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5871–5875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Smith S. J. Large depolarization induces long openings of voltage-dependent calcium channels in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):571–580. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00571.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Jr Proton pumps and chemiosmotic coupling as a generalized mechanism for neurotransmitter and hormone transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:162–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Aosaki T. Modulation of Ca-channel current by an adenosine analog mediated by a GTP-binding protein in chick sensory neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00580956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. T., Westhead E. W. Cellular responses to Ca2+ from extracellular and intracellular sources are different as shown by simultaneous measurements of cytosolic Ca2+ and secretion from bovine chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9881–9885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Ewel C., Rosenthal W., Schultz G., Wittig B. Assignment of G-protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):43–48. doi: 10.1038/353043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Kongsamut S., Tsien R. W. Alpha-adrenergic inhibition of sympathetic neurotransmitter release mediated by modulation of N-type calcium-channel gating. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):639–642. doi: 10.1038/340639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez H. S., Brown A. M. Correlation between G protein activation and reblocking kinetics of Ca2+ channel currents in rat sensory neurons. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):1061–1068. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moro M. A., López M. G., Gandía L., Michelena P., García A. G. Separation and culture of living adrenaline- and noradrenaline-containing cells from bovine adrenal medullae. Anal Biochem. 1990 Mar;185(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90287-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A., Inoue K. An ATP-activated conductance in pheochromocytoma cells and its suppression by extracellular calcium. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:257–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Inoue K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A. ATP-activated single-channel currents recorded from cell-free patches of pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Oct 30;119(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90741-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Torres M., Castro E., Miras-Portugal M. T. Characterization of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) binding sites in cultured chromaffin cells: evidence for a P2y site. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1980–1984. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P., Jaanus S. D. The release of nucleotide from the adrenal medulla by indirectly acting sympathomimetic amines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Jun;16(6):1007–1012. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Dolphin A. C. Regulation of calcium currents by a GTP analogue: potentiation of (-)-baclofen-mediated inhibition. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Aug 15;69(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90414-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorbera L. A., Morad M. Modulation of cardiac sodium channels by cAMP receptors on the myocyte surface. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1286–1289. doi: 10.1126/science.1653970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Robinson R. L., Van Dyke K., Stitxel R. Synthesis, storage and drug-induced release of atp-8-3h in the perfused bovine adrenal gland. Pharmacology. 1975;13(1):40–55. doi: 10.1159/000136883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swandulla D., Carbone E., Lux H. D. Do calcium channel classifications account for neuronal calcium channel diversity? Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):46–51. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90018-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Westhead E. The molecular organization of adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1980;5(11):1803–1823. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


