Abstract
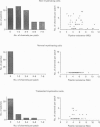
1. Single channel recordings were made of voltage-sensitive sodium channels in outside-out patches excised from the cell body region of Schwann cells. The cells were freshly isolated from sciatic nerves of 10-week-old rabbits and both myelinating and non-myelinating Schwann cells were visually identified for recordings. 2. Sodium channel activities were observed in approximately 75% of patches (n = 41) obtained from cell bodies of non-myelinating Schwann cells. In contrast, sodium channels were not observed in patches (n = 78) obtained from cell bodies of myelinating Schwann cells. 3. Transection of the sciatic nerves and allowing Wallerian degeneration to occur for 5-11 days in vivo prior to recording resulted in the appearance of sodium channel activities in approximately 30% of the patches (n = 33) obtained from the cell body of the myelinating cells. 4. It is interesting that although immunocytochemical and saxitoxin binding experiments indicate the clear presence of sodium channels in the plasmalemma of myelinating Schwann cells (both at the cell body and at the paranodal region), the present study suggests that these channels are absent from the soma region of normal myelinating Schwann cells.
Full text
PDF


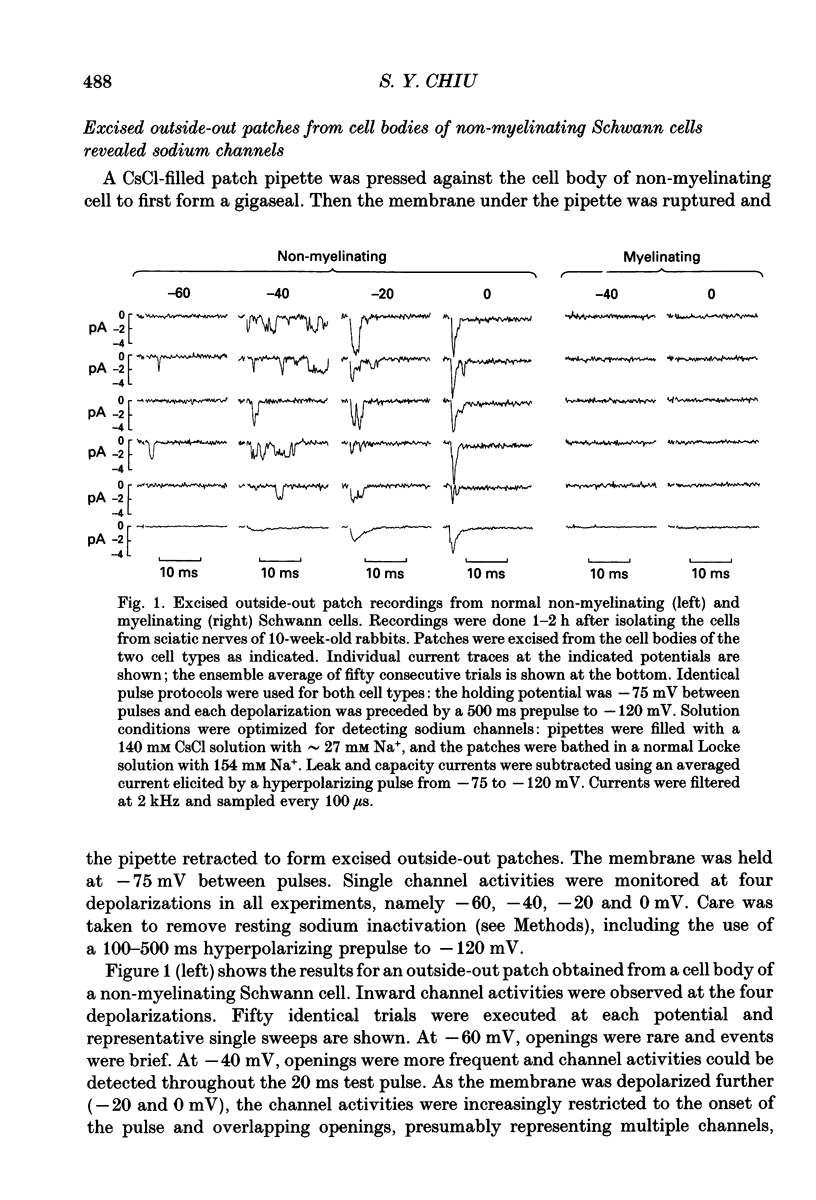

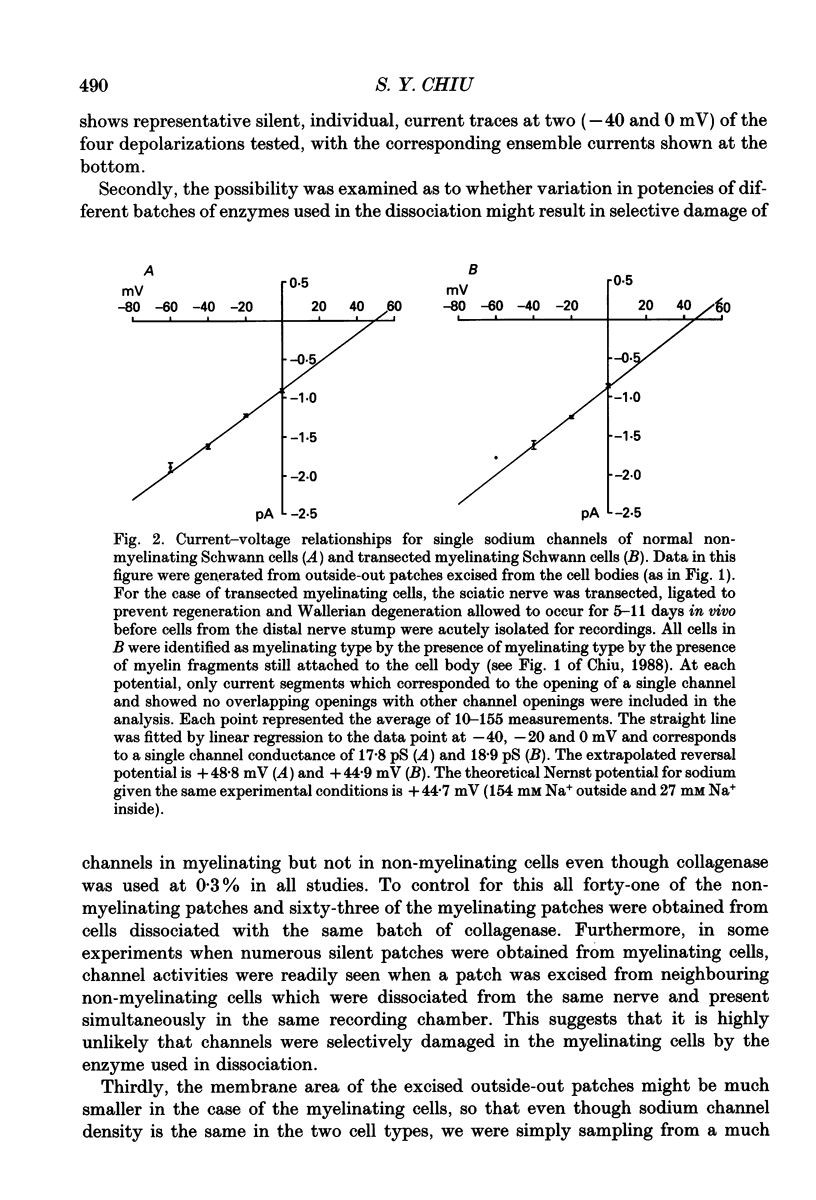
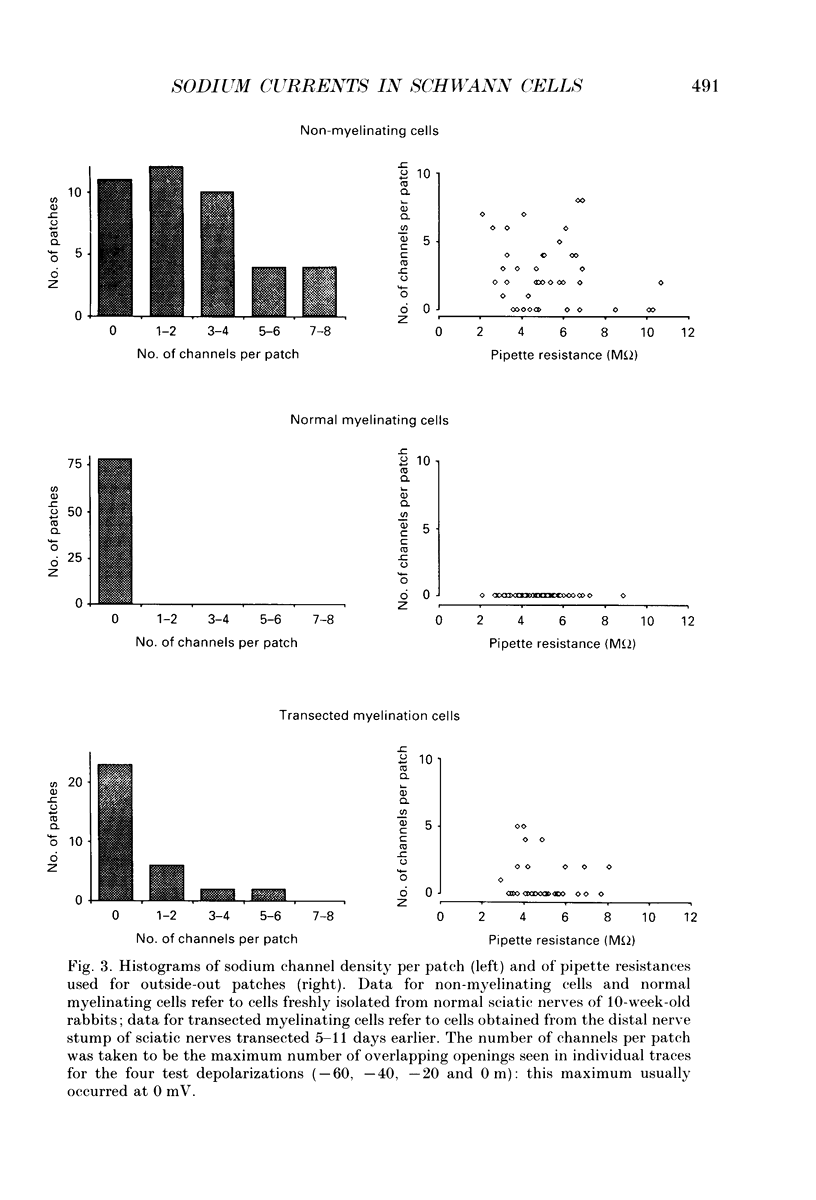
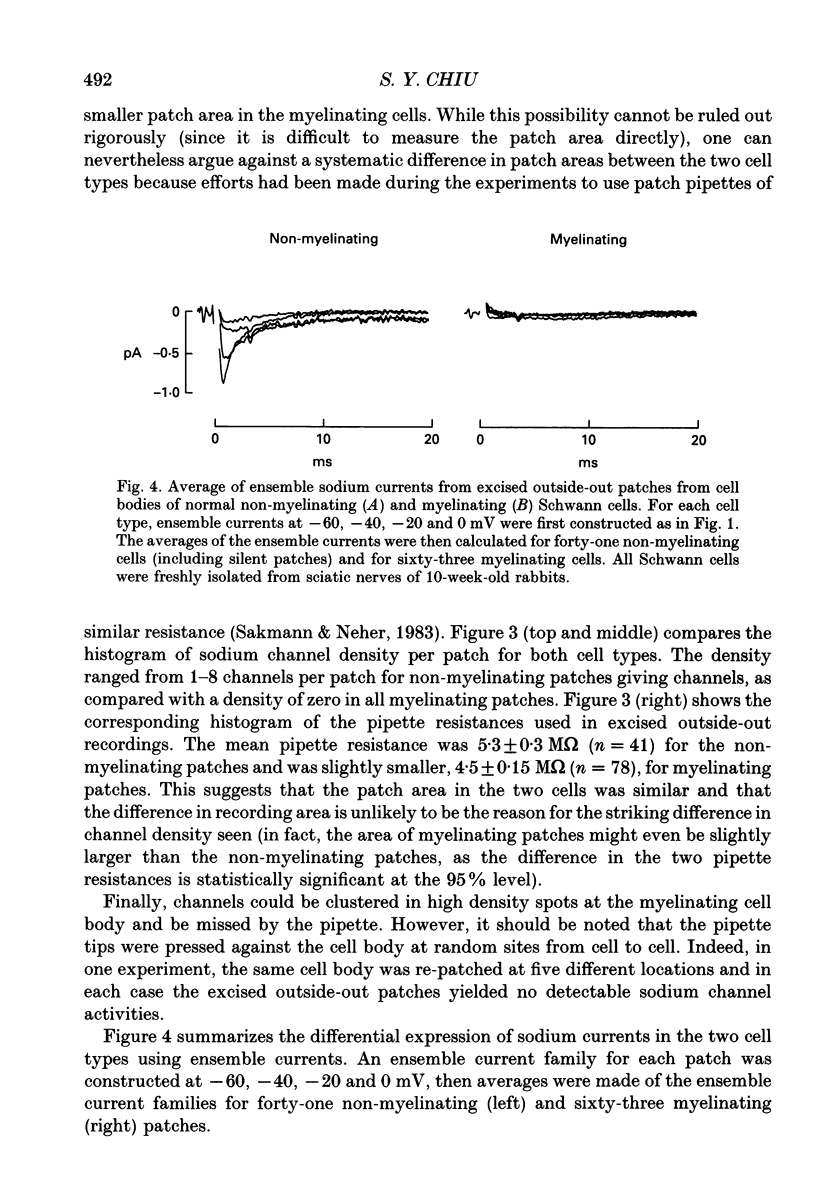
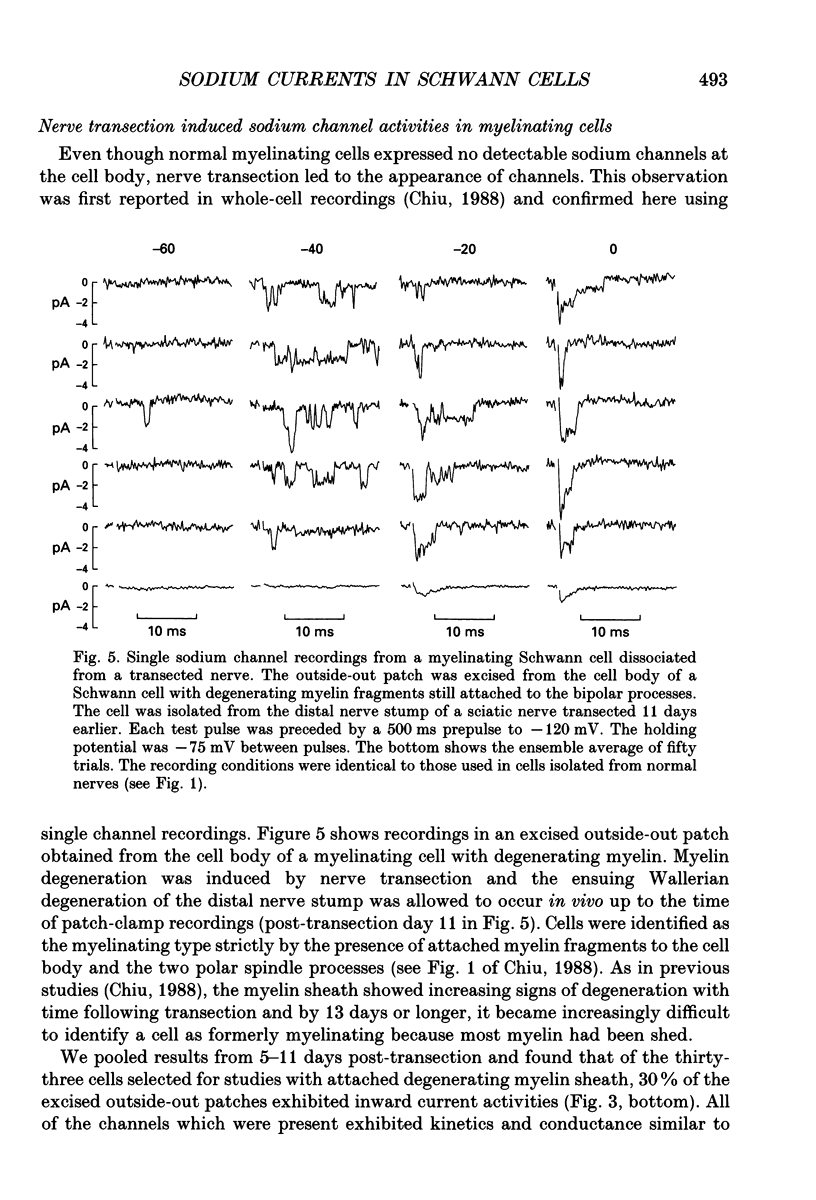






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barres B. A., Chun L. L., Corey D. P. Glial and neuronal forms of the voltage-dependent sodium channel: characteristics and cell-type distribution. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1375–1388. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Chun L. L., Corey D. P. Ion channels in vertebrate glia. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:441–474. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A. New roles for glia. J Neurosci. 1991 Dec;11(12):3685–3694. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-12-03685.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T., Gilly W. F. Synthesis of sodium channels in the cell bodies of squid giant axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1459–1463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Changes in excitable membrane properties in Schwann cells of adult rabbit sciatic nerves following nerve transection. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Functions and distribution of voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels in mammalian Schwann cells. Glia. 1991;4(6):541–558. doi: 10.1002/glia.440040602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Stagg D. A quantitative description of membrane currents in rabbit myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:149–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Schrager P., Ritchie J. M. Neuronal-type Na+ and K+ channels in rabbit cultured Schwann cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):156–157. doi: 10.1038/311156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Schwarz W. Sodium and potassium currents in acutely demyelinated internodes of rabbit sciatic nerves. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:631–649. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Sodium currents in axon-associated Schwann cells from adult rabbits. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:181–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. M. Metabolic organization of the myelinating Schwann cell. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;605:44–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Ritchie J. M. Sodium currents in Schwann cells from myelinated and non-myelinated nerves of neonatal and adult rabbits. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:169–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi T. Dye coupling between mouse Schwann cells. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 29;508(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91121-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke G. Unwrapping the genes of myelin. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R., Catterall W. A., Scheuer T. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):115–118. doi: 10.1126/science.1656525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Black J. A., Waxman S. G., Angelides K. J. Sodium channels in the cytoplasm of Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9290–9294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Ritchie J. M., Rang H. P. Extraneuronal saxitoxin binding sites in rabbit myelinated nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P., Chiu S. Y., Ritchie J. M. Voltage-dependent sodium and potassium channels in mammalian cultured Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):948–952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartanian T., Szuchet S., Dawson G., Campagnoni A. T. Oligodendrocyte adhesion activates protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of myelin basic protein. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1395–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.2431483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. F., Chiu S. Y. Ion channels in axon and Schwann cell membranes at paranodes of mammalian myelinated fibers studied with patch clamp. J Neurosci. 1990 Oct;10(10):3263–3274. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-10-03263.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. F., Chiu S. Y. Mitogenic factors regulate ion channels in Schwann cells cultured from newborn rat sciatic nerve. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:501–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. F., Chiu S. Y. Potassium channel regulation in Schwann cells during early developmental myelinogenesis. J Neurosci. 1990 May;10(5):1615–1625. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-05-01615.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]