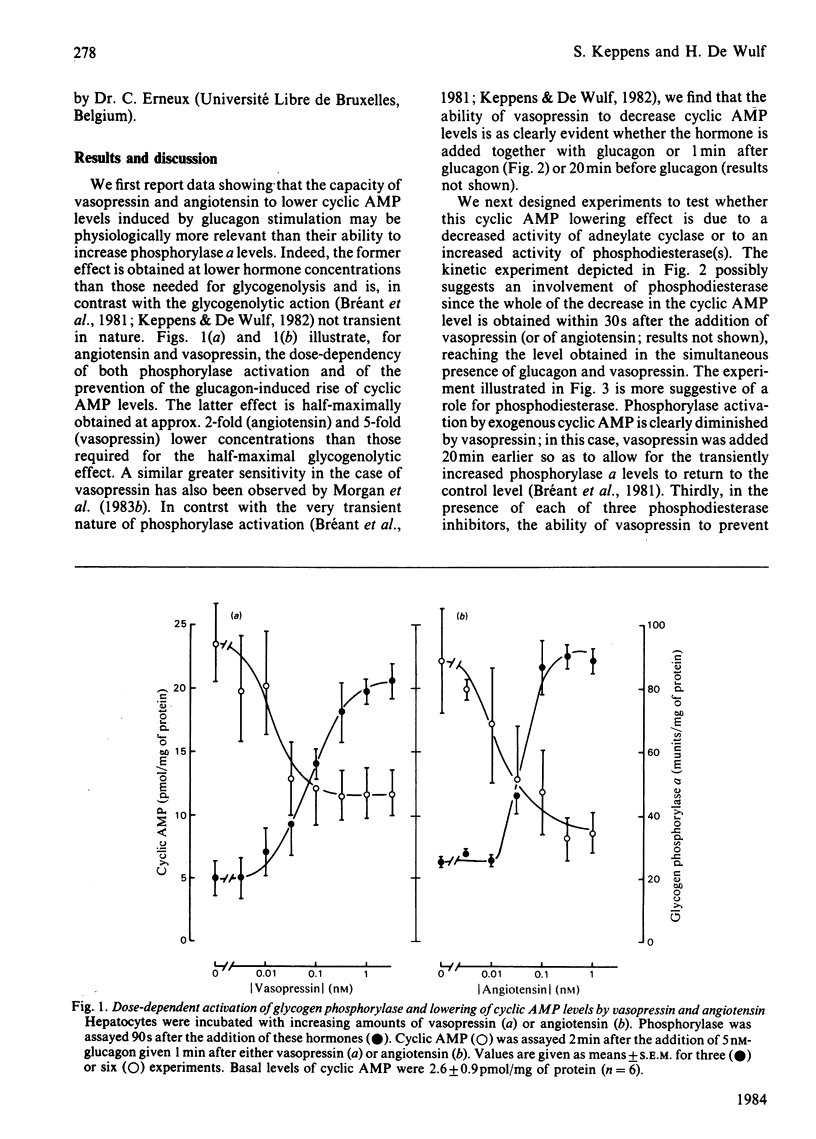
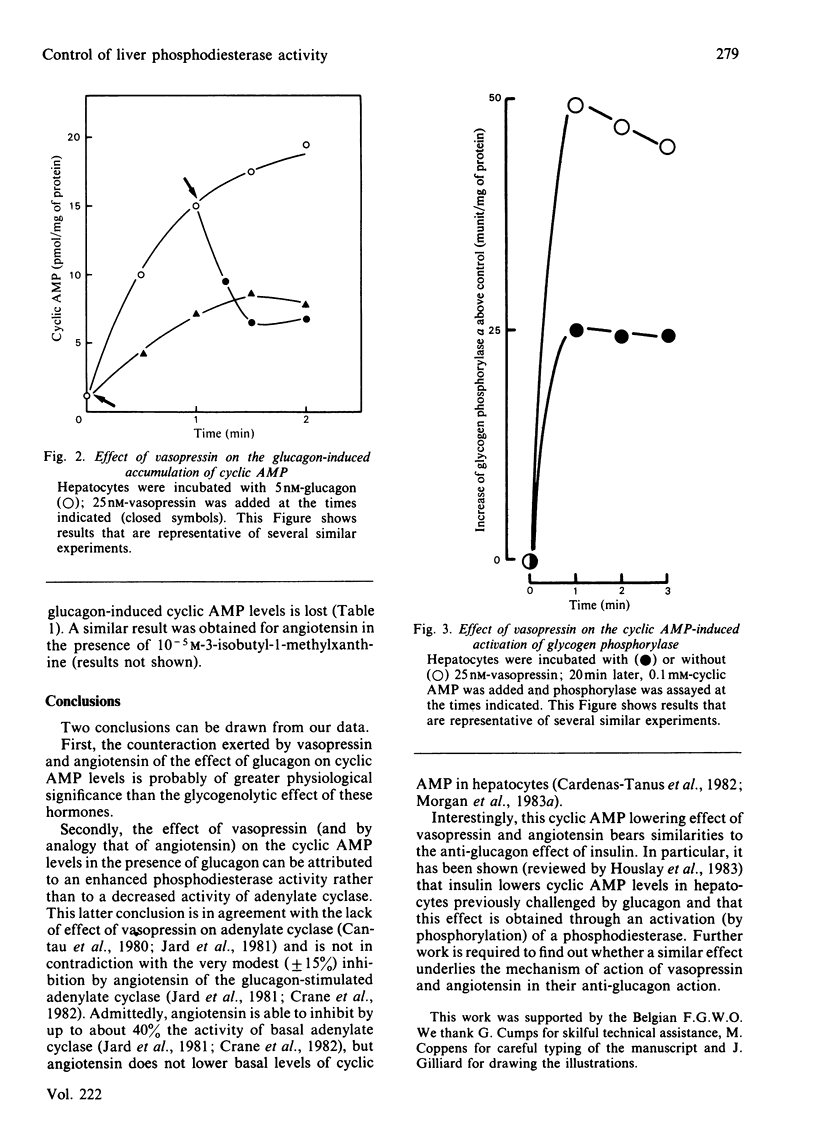
Abstract
Vasopressin and angiotensin are able to lower the glucagon-induced increase of cyclic AMP levels in isolated hepatocytes. Results presented are in favour of an enhanced phosphodiesterase activity to account for this cyclic AMP lowering effect. In particular, vasopressin prevents exogenous cyclic AMP from activating glycogen phosphorylase: in the presence of phosphodiesterase inhibitors, the hormone becomes unable to decrease glucagon-induced cyclic AMP levels. This anti-glucagon effect of vasopressin and angiotensin might be physiologically more important than their glycogenolytic effect; indeed, the latter is very transient in nature and, in addition, requires higher hormone concentrations [Bréant, Keppens & De Wulf (1981) Biochem. J. 200, 509-514] than those needed for the anti-glucagon effect, as reported here.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bréant B., Keppens S., De Wulf H. Heterologous desensitization of the cyclic AMP-independent glycogenolytic response in rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):509–514. doi: 10.1042/bj2000509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantau B., Keppens S., De Wulf H., Jard S. (3H)-vasopressin binding to isolated rat hepatocytes and liver membranes: regulation by GTP and relation to glycogen phosphorylase activation. J Recept Res. 1980;1(2):137–168. doi: 10.3109/10799898009044096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane J. K., Campanile C. P., Garrison J. C. The hepatic angiotensin II receptor. II. Effect of guanine nucleotides and interaction with cyclic AMP production. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4959–4965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas-Tanús R. J., Huerta-Bahena J., García-Sáinz J. A. Angiotensin II inhibits the accumulation of cyclic AMP produced by glucagon but not its metabolic effects. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Wallace A. V., Marchmont R. J., Martin B. R., Heyworth C. M. Insulin controls intracellular cyclic AMP concentrations in hepatocytes by activating specific cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases: phosphorylation of the peripheral plasma membrane enzyme. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;16:159–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jard S., Cantau B., Jakobs K. H. Angiotensin II and alpha-adrenergic agonists inhibit rat liver adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2603–2606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. Characteristics of the desensitization and resensitization of the cyclic AMP-independent glycogenolytic response in rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 15;208(2):317–322. doi: 10.1042/bj2080317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Angiotensin II inhibits hepatic cAMP accumulation induced by glucagon and epinephrine and their metabolic effects. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Shipp C. C., Exton J. H. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of hepatic cAMP accumulation by vasopressin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 14;163(2):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80835-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Keppens S., De Wulf H. The activation of liver phosphorylase b kinase by glucagon. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)81040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


