Abstract
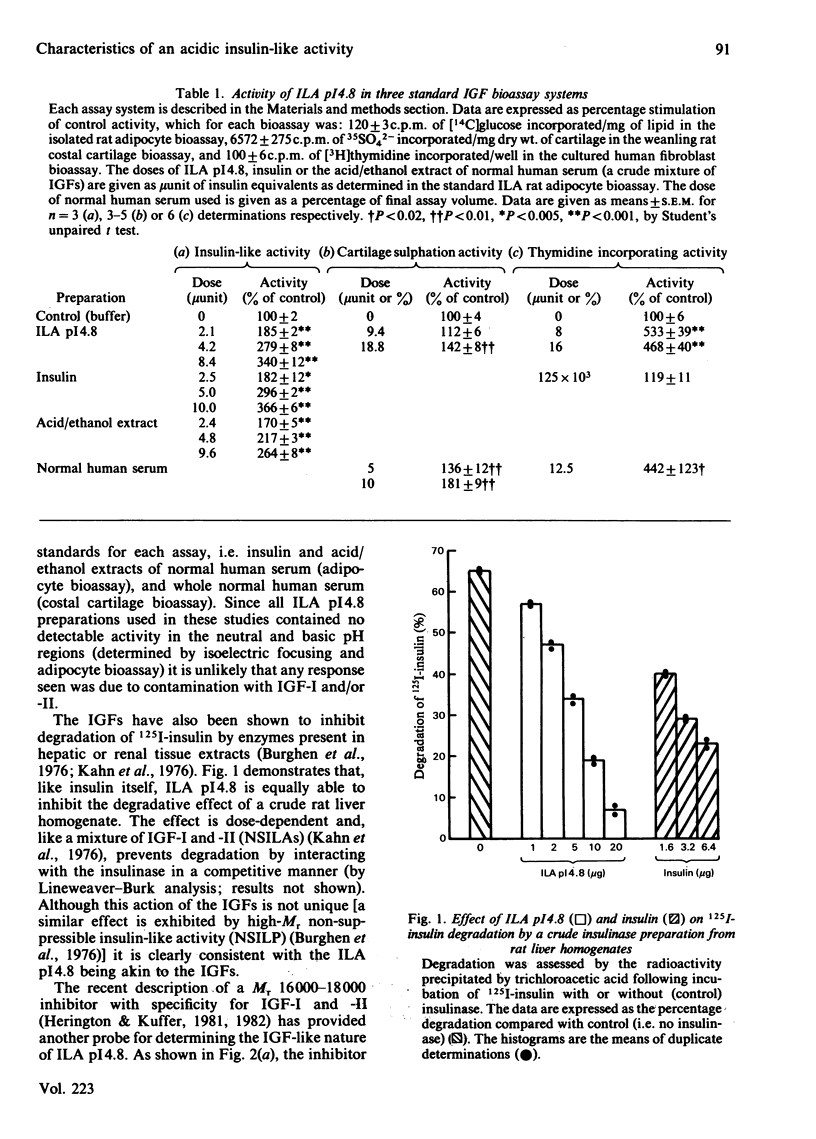
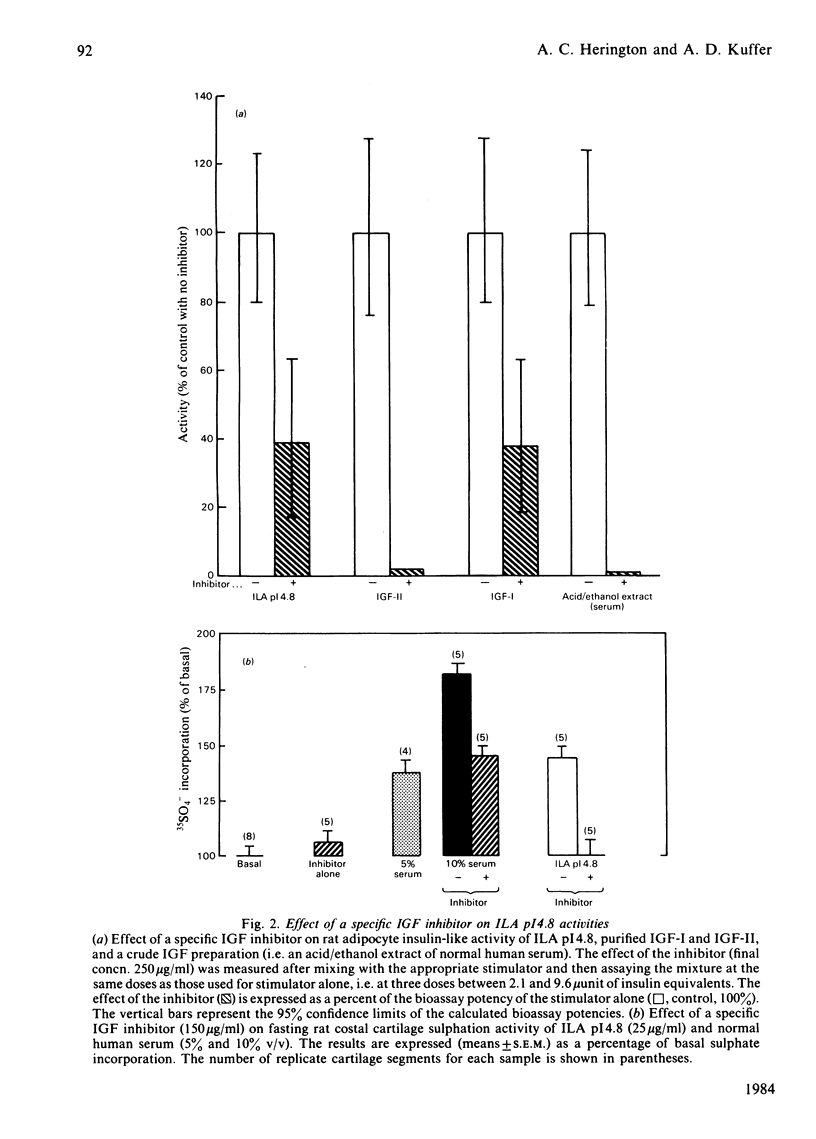
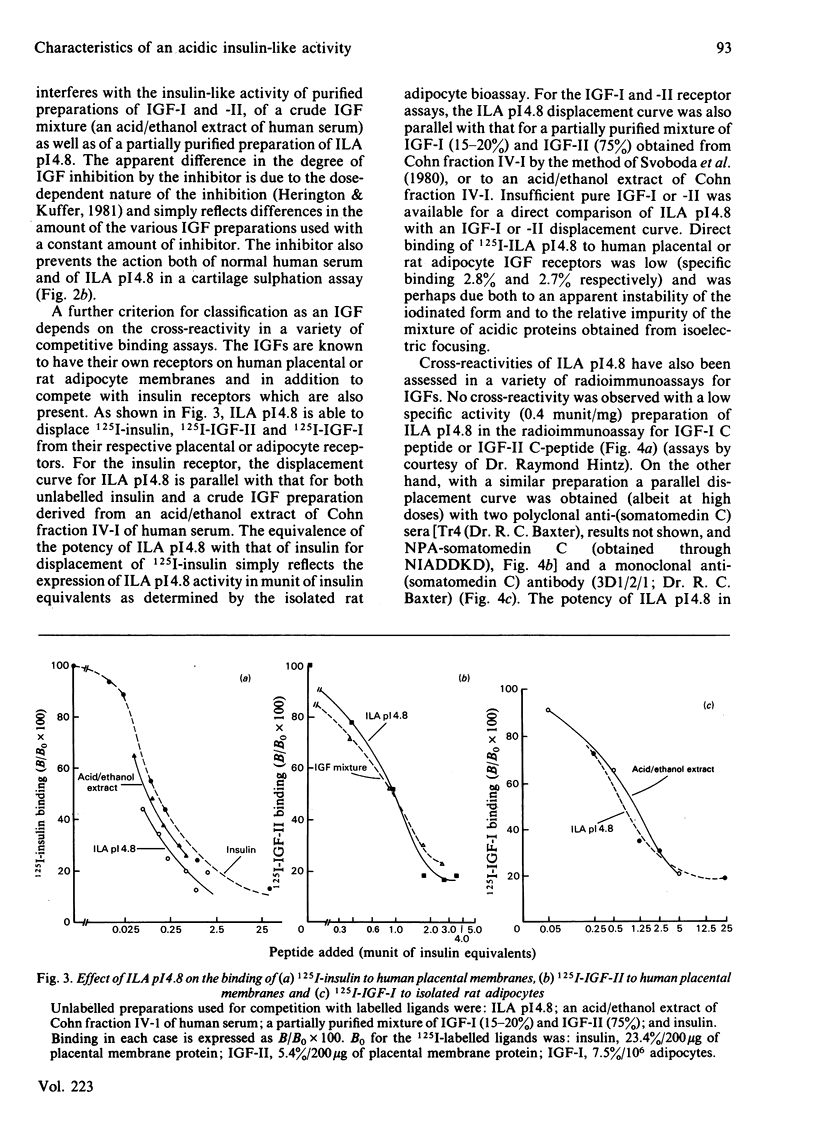
The biological activities of an acidic form of non-suppressible insulin-like activity (ILA pI 4.8) have been studied. ILA pI 4.8 was isolated from Cohn fraction IV-1 of human serum by pH 5.5 ion-exchange chromatography on SP-Sephadex. Carrier-bound ILA was eluted at pH 9.7 and then sequentially gel chromatographed in 1% formic acid on Sephadex G-75 and Bio-Gel P-30. The low-Mr (7000) active material was subjected to flat bed isoelectric focusing. Overall recovery was 87 munit of insulin equivalents/100 g of Cohn fraction IV-1, with a specific activity in the range 4-10 munit/mg of protein, representing a purity of 1-6%. This material has been tested in a variety of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)/somatomedin assay systems. It stimulated, in a dose-related manner, [14C]glucose conversion into lipid by isolated rat adipocytes, 35SO4(2-) incorporation into weanling rat costal cartilage and [3H]thymidine incorporation into DNA of cultured human fibroblasts. Like IGF-I and -II, ILA pI 4.8 was able to inhibit degradation of 125I-insulin by crude homogenates of rat liver. In addition, the biological activity of ILA pI 4.8 was completely suppressible by a recently described inhibitor of IGF-I and IGF-II. ILA pI 4.8 was able to compete, in a parallel manner, with 125I-IGF-I and 125I-IGF-II and, at higher doses, with 125I-insulin in a placental radioreceptor assay. No cross-reactivity was seen in a radioimmunoassay for IGF-I and -II C-peptides, but at higher concentrations parallel displacement was observed in a somatomedin C/IGF-I radioimmunoassay using two different antisera. These data indicate that ILA pI 4.8 does possess many of the biological activities previously reported for the IGFs. Since ILA pI 4.8 does occur naturally in serum, it would appear reasonable to tentatively include it as one of the IGF/somatomedin family.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C., Axiak S., Raison R. L. Monoclonal antibody against human somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-I. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):474–476. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Brown A. S., Turtle J. R. Radioimmunoassay for somatomedin C: comparison with radioreceptor assay in patients with growth-hormone disorders, hypothyroidism, and renal failure. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):488–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghen G., Duckworth W. C., Kitabchi A. E., Solomon S. S., Poffenbarger P. L. Inhibition of insulin degradation by nonsuppressible insulin-like activity. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1089–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI108352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Cornell H. J., Herington A. C. Partial purification of low molecular weight non-suppressible insulin-like activity from human plasma: demonstration of the presence of multiple forms. J Endocrinol. 1980 May;85(2):266–277. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0850267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J. The effect of different isolation procedures on the yields of insulin-like growth factors from human plasma. Prep Biochem. 1982;12(1):57–76. doi: 10.1080/00327488208065550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Phillips L. S., Herington A. C. Measurement of somatomedin by cartilage in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:93–109. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. C., Rennie G. C., Burger H. G., Cameron D. P. A bioassay for NSILA-S in individual serum samples and its relationship to somatotropin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;43(5):1164–1169. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-5-1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herington A. C., Kuffer A. D. Identification of a specific inhibitor of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in a partially purified human serum fraction. Endocrinology. 1981 Nov;109(5):1634–1640. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-5-1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F. A radioimmunoassay for insulin-like growth factor II specific for the C-peptide region. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):442–446. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F., Marshall L. B., Chang D. Interaction of somatomedin-C with an antibody directed against the synthetic C-peptide region of insulin-like growth factor-I. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Feb;50(2):405–407. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Megyesi K., Roth J. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. A potent inhibitor of insulin degradation. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):526–529. doi: 10.1172/JCI108306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Sequence analysis of somatomedin-C: confirmation of identity with insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2215–2217. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffer A. D., Herington A. C. Proteolytic conversion of insulin-like growth factors to an acidic form(s). Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):97–103. doi: 10.1042/bj2230097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. N., Underwood L. E., Voina S. J., Foushee D. B., Van Wyk J. J. Characterization of the insulin and somatomedin-C receptors in human placental cell membranes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Aug;39(2):283–292. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. S., Vassilopoulou-Sellin R. Somatomedins (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 14;302(7):371–380. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002143020704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. S., Vassilopoulou-Sellin R. Somatomedins (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 21;302(8):438–446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002213020805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner B. I., Guyda H. J., Corvol M. T., Rappaport R., Harley C., Goldstein S. Partial purification, characterization, and assay of a slightly acidic insulin-like peptide (ILAs) from human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Dec;47(6):1240–1250. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-6-1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P., Podskalny J. M., Moses A. C., Fryklund L. Identification of a receptor for somatomedin-like polypeptides in human fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 May;44(5):820–831. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-5-820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P. G., Caravaggio T. Isoelectric points and molecular weights of proteins. J Chromatogr. 1976 Apr 21;127(11):1–28. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)98537-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth in hypophysectomized rats. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):252–253. doi: 10.1038/296252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Klapper D. G., Fellows R. E., Grissom F. E., Schlueter R. J. Purification of somatomedin-C from human plasma: chemical and biological properties, partial sequence analysis, and relationship to other somatomedins. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):790–797. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Hall K., Van den Brande J. L., Weaver R. P. Further purification and characterization of sulfation factor and thymidine factor from acromegalic plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Mar;32(3):389–403. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-3-389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Underwood L. E., Hintz R. L., Clemmons D. R., Voina S. J., Weaver R. P. The somatomedins: a family of insulinlike hormones under growth hormone control. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1974;30(0):259–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Kaufmann U., Eigenmann E. J., Froesch E. R. Determination of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in human serum by a sensitive protein-binding assay. Clin Chem. 1977;23(4):677–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) from human serum: recent accomplishments and their physiologic implications. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12):1803–1828. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II: some biological actions and receptor binding characteristics of two purified constituents of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Walter H., Froesch E. R. Radioimmunological determination of insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI110379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


