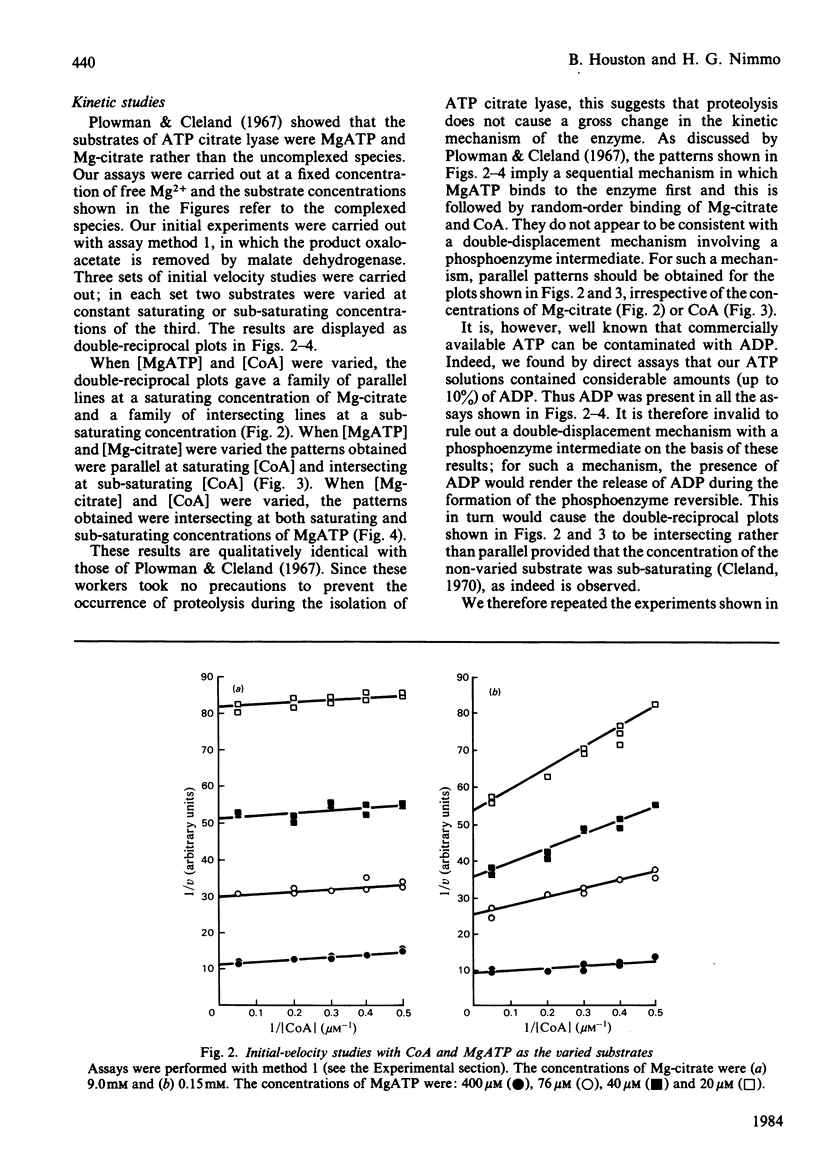
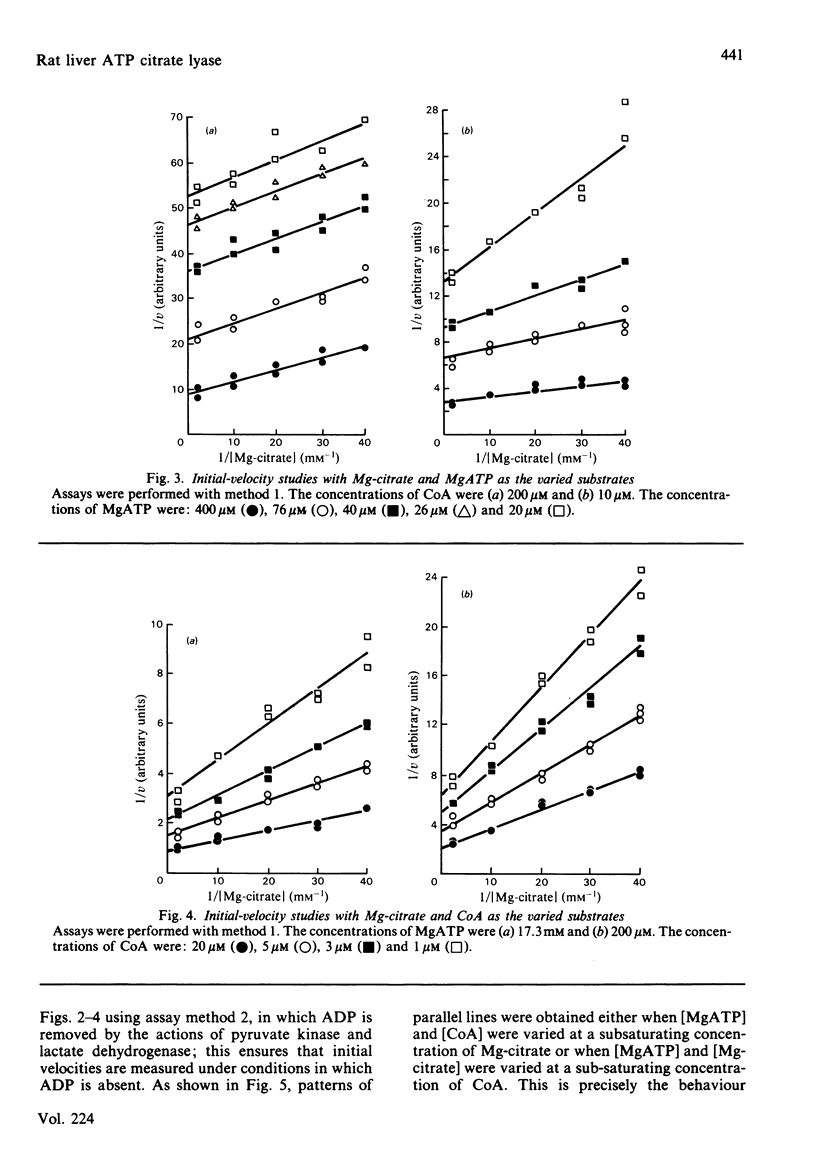
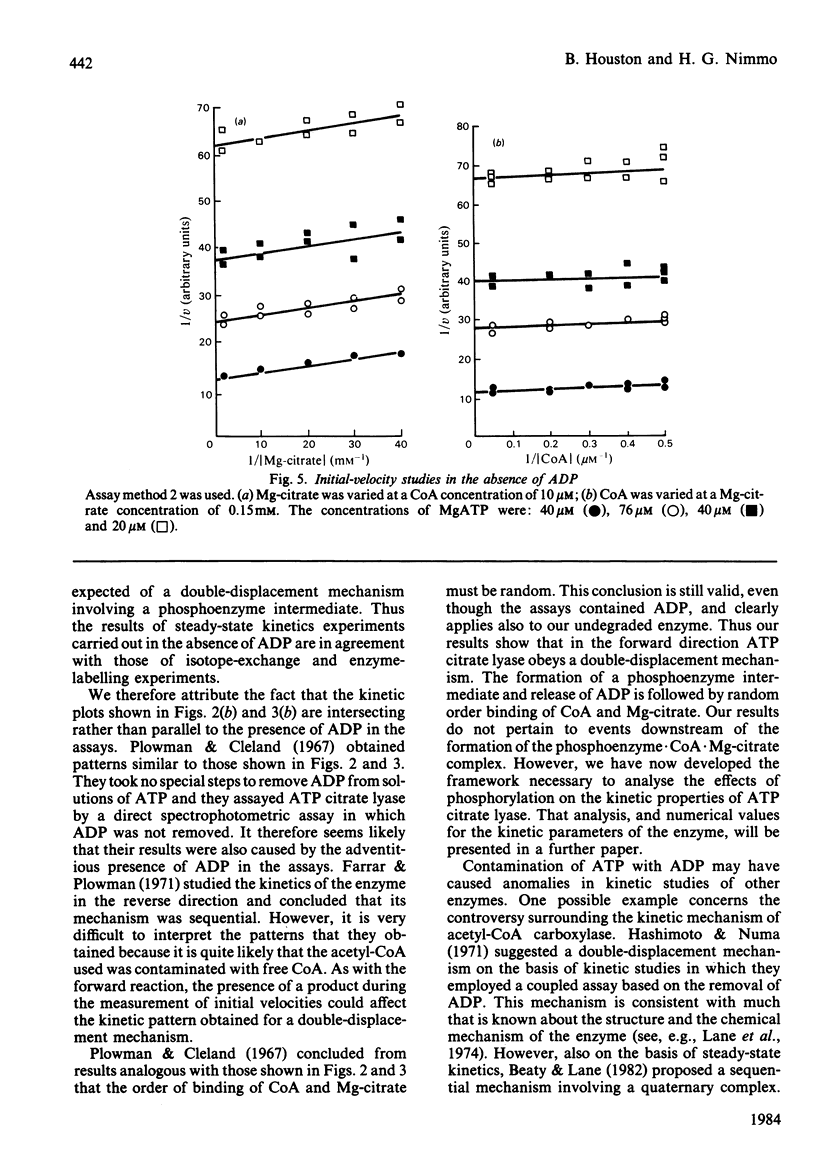
Abstract
A new purification procedure for rat liver ATP citrate lyase is described. The method reproducibly gives homogenous undegraded enzyme. Steady-state kinetic analysis of ATP citrate lyase was complicated by the presence of ADP, a product of the reaction, in solutions of ATP. The kinetic patterns observed were dependent on whether ADP was removed by the assay system. When assays were performed with a method in which ADP was removed, the results showed that the enzyme obeys a double-displacement mechanism with a phosphoenzyme intermediate. This resolves a controversy between the results of previous kinetic studies and those of isotope-exchange and enzyme-labelling experiments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. C., Kowaloff E. M., Witters L. A., Dennihy D. T., Avruch J. Purification of a hepatic 123,000-dalton hormone-stimulated 32P-peptide and its identification as ATP-citrate lyase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8052–8056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty N. B., Lane M. D. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Rapid purification of the chick liver enzyme and steady state kinetic analysis of the carboxylase-catalyzed reaction. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):924–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick A. C., Holms W. H., Nimmo H. G. Isolation of active and inactive forms of isocitrate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli ML 308. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):393–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey E. M., Dils R. Fatty acid biosynthesis. V. Purification and characterisation of fatty acid synthetase from lactating-rabbit mammary gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 8;210(3):371–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottam G. L., Srere P. A. Nature of the phosphorylated residue in citrate clevage enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jun 27;35(6):895–900. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90708-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar Y. J., Plowman K. M. Initial velocity studies of the reverse citrate cleavage reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3777–3782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy P. S., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Purification and physicochemical properties of ATP citrate (pro-3S) lyase from lactating rat mammary gland and studies of its reversible phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):399–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy P. S., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Rat mammary gland ATP-citrate lyase is phosphorylated by cyclic amp-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 14;109(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Cohen P. Purification and physicochemical properties of fatty acid synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):25–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Numa S. Kinetic studies on the reaction mechanism and the citrate activation of liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb 1;18(3):319–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann G. E., Schiessl J., Weiss L. ATP citrate (pro-3S)-lyase in the rat; two-step purification procedure, properties, organ distribution. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Oct;360(10):1445–1451. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1979.360.2.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Suzuki F., Tanioka H., Takeda Y. Studies on ATP citrate lyase of rat liver. 3. The reaction mechanism. J Biochem. 1968 Jan;63(1):89–100. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janski A. M., Srere P. A., Cornell N. W., Veech R. L. Phosphorylation of ATP citrate lyase in response to glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9365–9368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. D., Moss J., Polakis S. E. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):139–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Srere P. A. Identification of ATP citrate lyase as a phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1691–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Nimmo H. G. The interaction of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate with an allosteric site of rat liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80946-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman D. M., Cleland W. W. Purification and kinetic studies of the citrate cleavage enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4239–4247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna S., Benjamin W. B. Fat cell protein phosphorylation. Identification of phosphoprotein-2 as ATP-citrate lyase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9232–9236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna S., Pucci D. L., Benjamin W. B. ATP-citrate lyase kinase and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylate different sites on ATP-citrate lyase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10213–10216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna S., Pucci D. L., Benjamin W. B. Dependence of ATP-citrate lyase kinase activity on the phosphorylation of ATP-citrate lyase by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4950–4956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redshaw J. C., Loten E. G. A rapid purification of hepatic ATP citrate lyase using blue Sepharose. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80303-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart G. D. Influence of polyethylene glycols on the kinetics of rat liver phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10576–10578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M., Richards E. G., Mukherjee A., Srere P. A. Structure of ATP citrate lyase from rat liver. Physicochemical studies and proteolytic modification. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5242–5250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLENFELS K., ZARNITZ M. L., LAULE G., BENDER H., KESER M. [Studies on lactic acid splitting enzyme. III. Purification, crystallization and features of beta-galctosidase of Escherichia coli ML 309]. Biochem Z. 1959;331:459–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. T., Jr, Spector L. B. Citryl phosphate and the mode of action of the citrate cleavage enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4366–4374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]