Abstract
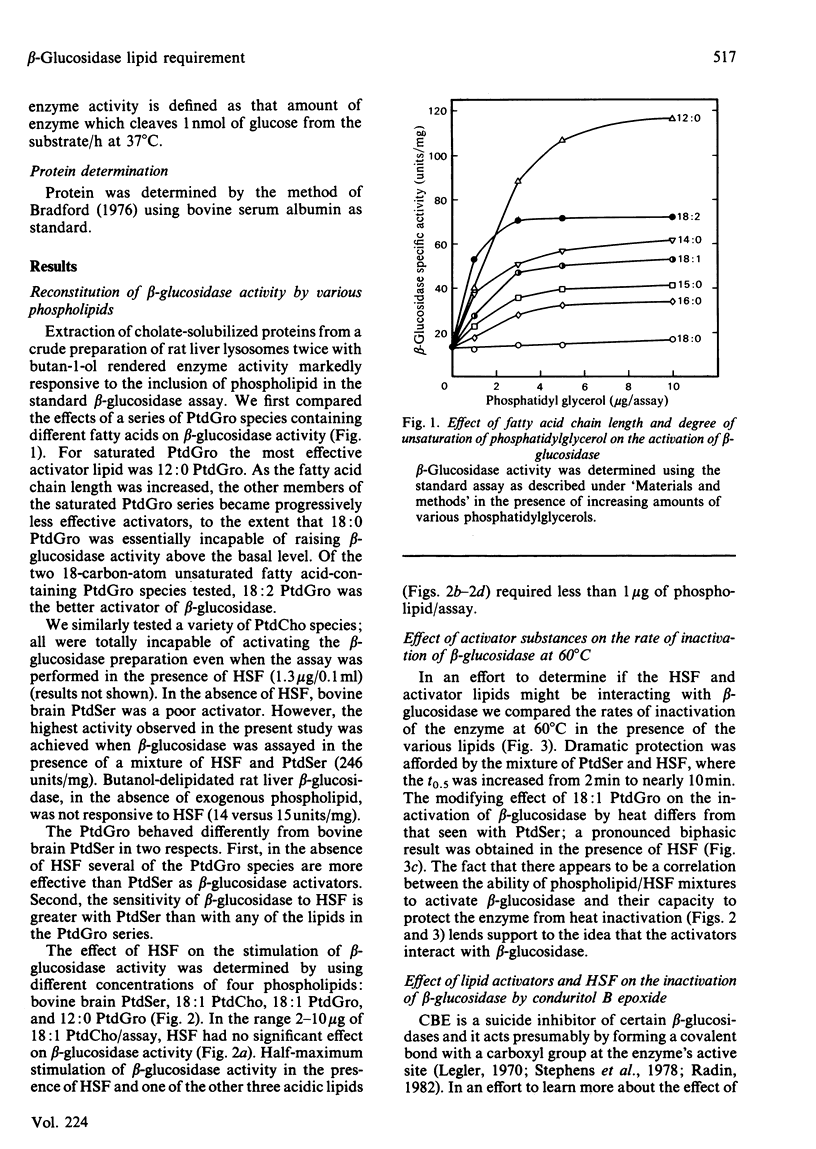
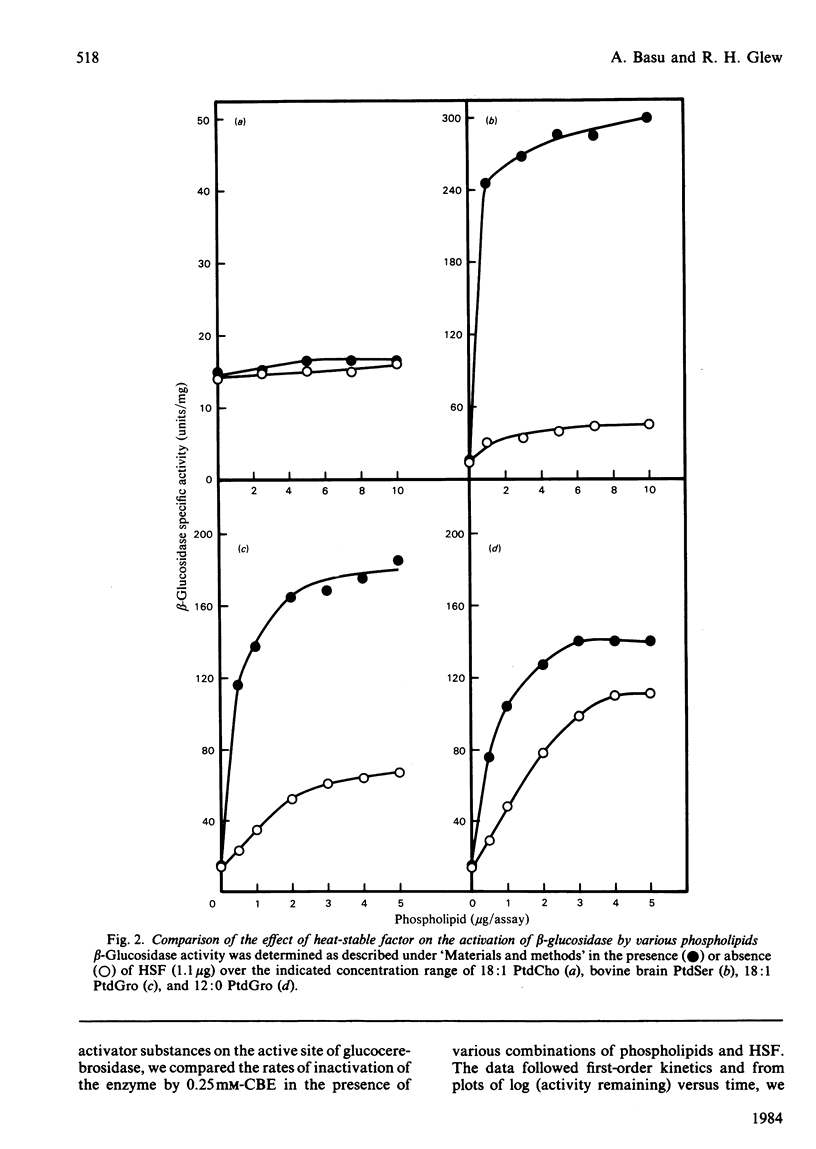
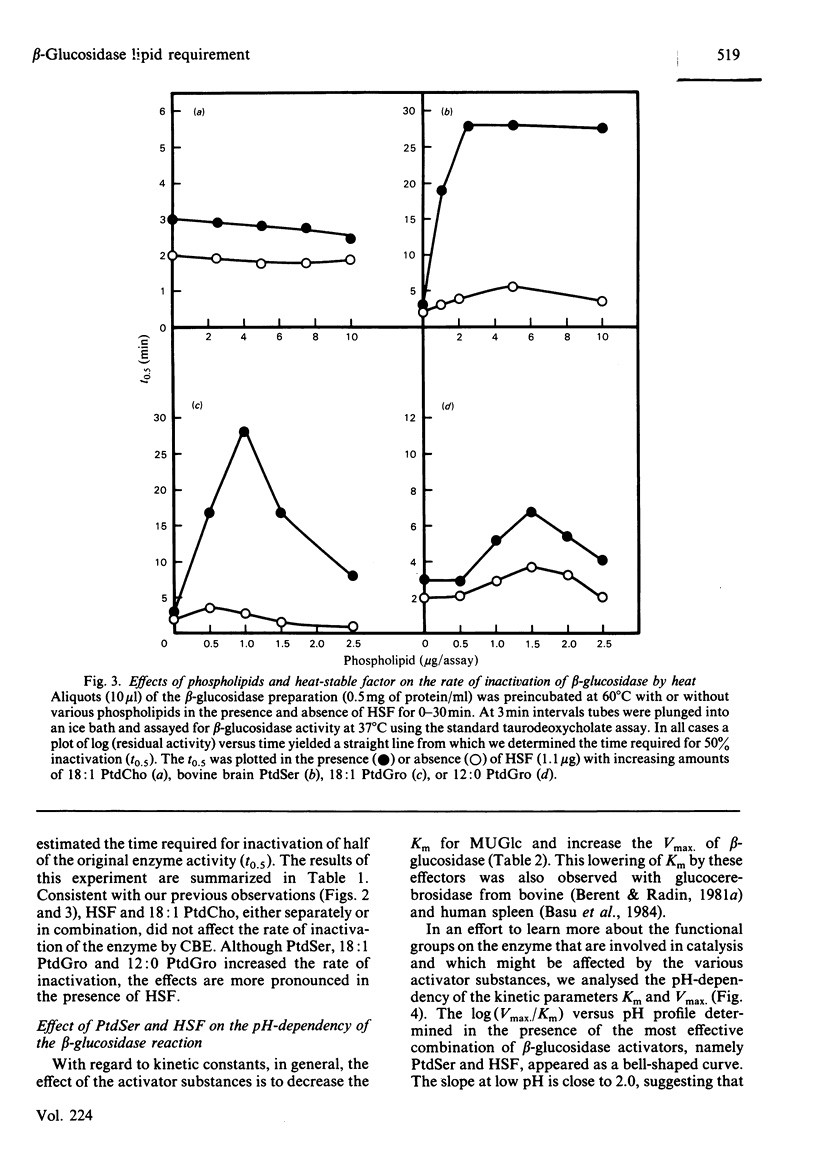
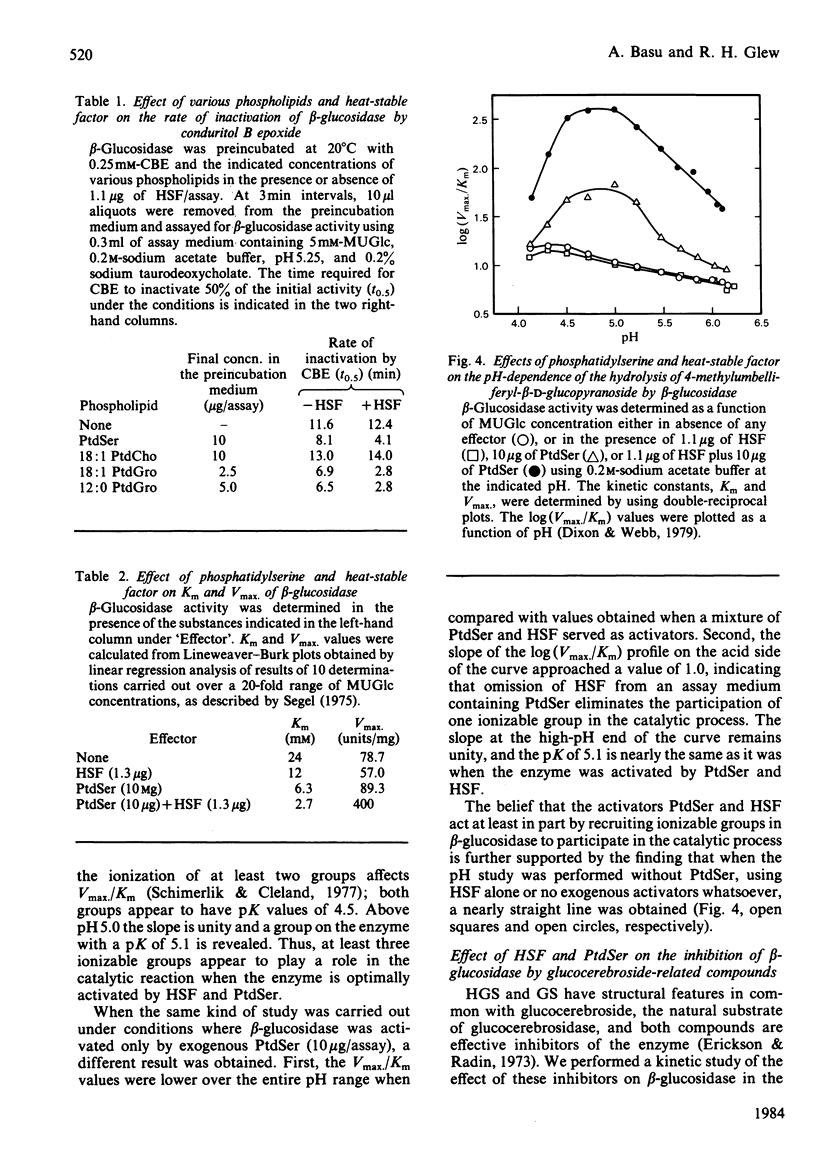
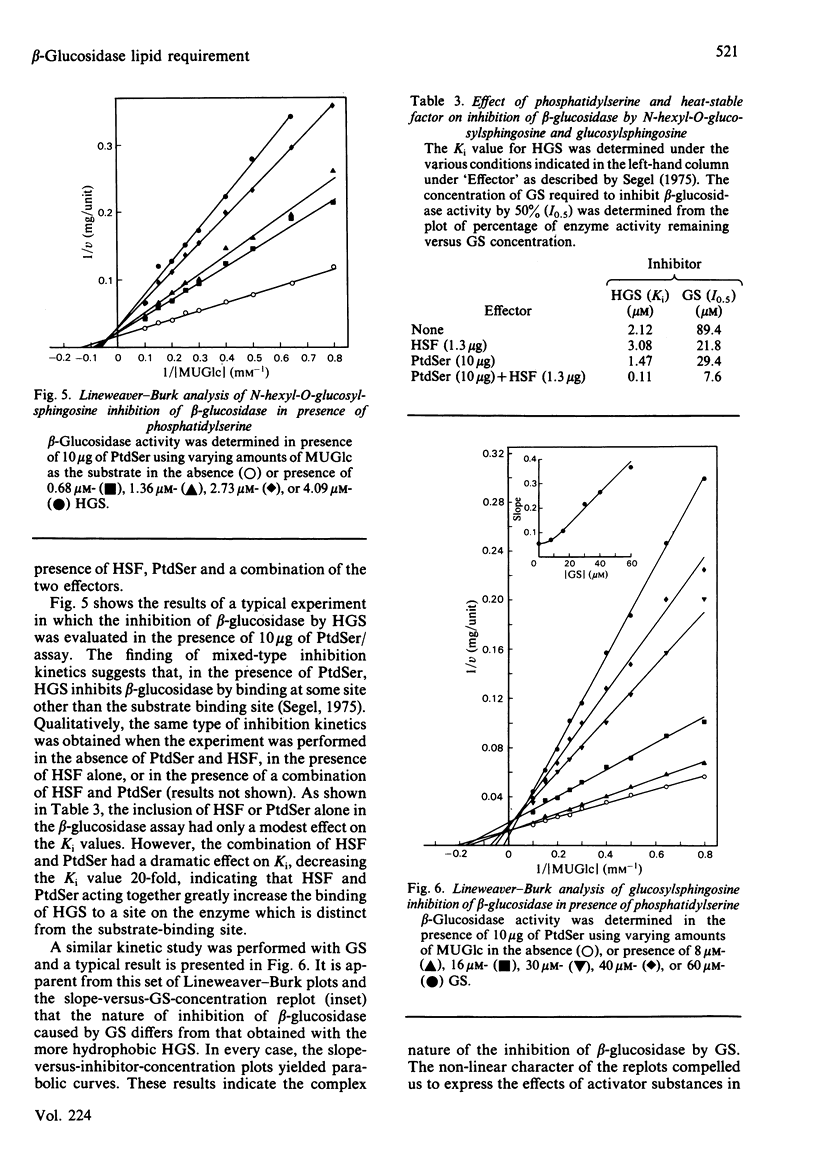
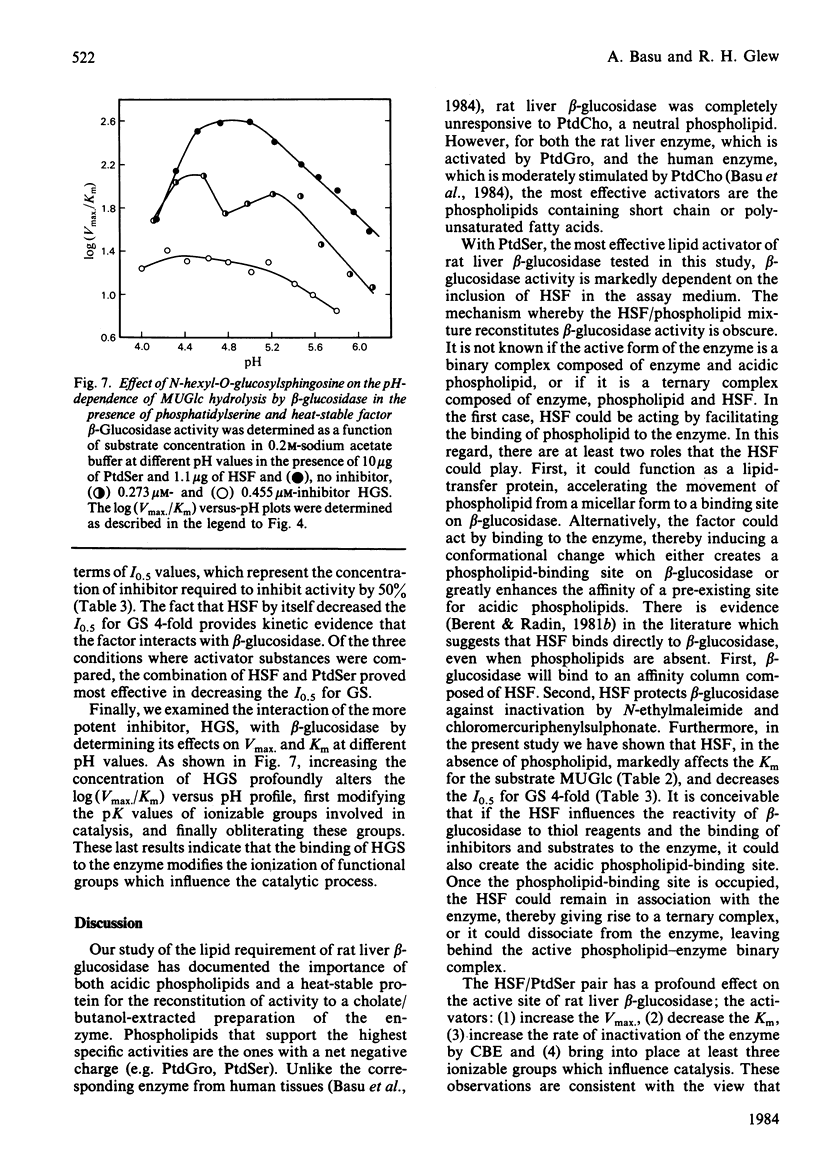
The lipid requirement of membrane-bound rat liver beta-glucosidase was investigated using 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside as the substrate. The enzyme was solubilized and delipidated by sequential extraction of a crude lysosomal fraction from rat liver lysosomes with sodium cholate and ice-cold butan-1-ol. Neither saturated nor unsaturated phosphatidylcholine activated this enzyme. In contrast, acidic phospholipids like phosphatidylglycerol (PtdGro) and phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) were effective activators. For the PtdGro series, fatty acid composition was important, with the shorter chain or unsaturated fatty acid-containing PtdGro species being the best activators. Heat-stable factor (HSF) from Gaucher spleen by itself (1-2 micrograms) had no effect on enzyme activity. However, the same amount of HSF when combined with 10 micrograms of PtdSer markedly stimulated beta-glucosidase activity. In the presence of HSF, di-9-cis-octadecenoyl-PtdGro (1 microgram) or -PtdSer (5 micrograms) provided maximum protection of beta-glucosidase against heat (60 degrees C) inactivation. In the absence of phospholipids, HSF had no effect on the rate of inactivation of the enzyme by the suicide inhibitor conduritol B epoxide (t0.5, 12 +/- 0.5 min); the maximum rate of inactivation was achieved in the presence of a mixture of PtdGro (2.5-5 micrograms) and HSF (t0.5, 2.8 min). The combination of PtdSer (10 micrograms) and HSF (1.3 micrograms) lowered the Km for 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside from 24 to 2.7 mM. Inhibition of the enzyme by the glucocerebrosidase substrate analogues N-hexyl-O-glucosylsphingosine and glucosylsphingosine was influenced by the activator substances. The inclusion of PtdSer and HSF in the beta-glucosidase assay medium lowered the Ki of N-hexyl-O-glucosylsphingosine 20-fold. The same combination of activators decreased the I0.5 of the enzyme for glucosylsphingosine from 89.4 to 7.6 microM. A study of log (Vmax./Km) versus pH indicated that the PtdSer-HSF pair creates the active site of beta-glucosidase, making apparent three ionizable groups on the enzyme with pK values in the range 4.5-5.1.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J. N., SHAPIRO D. METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. II. EVIDENCE OF AN ENZYMATIC DEFICIENCY IN GAUCHER'S DISEASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:221–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90743-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J., SHAPIRO D. THE METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF A GLUCOCEREBROSIDE-CLEAVING ENZYME FROM SPLEEN TISSUE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu A., Glew R. H., Daniels L. B., Clark L. S. Activators of spleen glucocerebrosidase from controls and patients with various forms of Gaucher's disease. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1714–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berent B. L., Radin N. S. beta-Glucosidase activator protein from bovine spleen ("coglucosidase"). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 15;208(1):248–260. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berent S. L., Radin N. S. Mechanism of activation of glucocerebrosidase by co-beta-glucosidase (glucosidase activator protein). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 23;664(3):572–582. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Kuhl W., Trinidad F., Teplitz R., Nadler H. Beta-glucosidase activity in fibroblasts from homozygotes and heterozygotes for Gaucher's disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jan;23(1):62–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H. Ribonucleic acid synthesis by Escherichia coli C3000/L after infection by the ribonucleic acid coliphage ZIK/1, and properties of coliphage-ZIK/1 ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):17–26. doi: 10.1042/bj0970017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blonder E., Klibansky C., de Vries A. Effects of detergents and choline-containing phospholipids on human spleen glucocerebrosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 22;431(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G. L., Villacorte D. G., Beutler E. Solubilization of glucocerebrosidase from human placenta and demonstration of a phospholipid requirement for its catalytic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1048–1053. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L. B., Coyle P. J., Glew R. H., Radin N. S., Labow R. S. Brain glucocerebrosidase in Gaucher's disease. Arch Neurol. 1982 Sep;39(9):550–556. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510210020005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L. B., Glew R. H., Diven W. F., Lee R. E., Radin N. S. An improved fluorometric leukocyte beta-glucosidase assay for Gaucher's disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Sep;115(3):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. S., Radin N. S. N-hexyl-O-glucosyl sphingosine, an inhibitor of glucosyl ceramide -glucosidase. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furbish F. S., Blair H. E., Shiloach J., Pentchev P. G., Brady R. O. Enzyme replacement therapy in Gaucher's disease: large-scale purification of glucocerebrosidase suitable for human administration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3560–3563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginns E. I., Brady R. O., Pirruccello S., Moore C., Sorrell S., Furbish F. S., Murray G. J., Tager J., Barranger J. A. Mutations of glucocerebrosidase: discrimination of neurologic and non-neurologic phenotypes of Gaucher disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5607–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Daniels L. B., Clark L. S., Hoyer S. W. Enzymic differentiation of neurologic and nonneurologic forms of Gaucher's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1982 Nov;41(6):630–641. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198211000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Radin N. S. Destruction and resynthesis of mouse beta-glucosidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 1;582(3):412–422. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. W. Identity of 'acid' beta-glucosidase and glucocerebrosidase in human spleen. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):721–729. doi: 10.1042/bj1360721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. W., Light N. D. Glucocerebrosidase: reconstitution from macromolecular components depends on acidic phospholipids. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):821–823. doi: 10.1042/bj1360821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. W., O'Brien J. S. Gaucher's disease: deficiency of 'acid' -glucosidase and reconstitution of enzyme activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2810–2813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. W., O'Brien J. S., Radin N. S., Erickson J. S. Glucocerebrosidase: reconstitution of activity from macromolecular components. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):173–176. doi: 10.1042/bj1310173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultberg B., Ockerman P. A. Beta-glucosidase activities in human tissues. Findings in Gaucher's disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Apr;28(1):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanfer J. N., Legler G., Sullivan J., Raghavan S. S., Mumford R. A. The Gaucher mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G. Markierung des aktiven Zentrums der beta-Glucosidasen A und B aus dem Süssmandel-Emulsin mit (3H06-Brom-6-desoxy-condurit-B-epoxid. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Jan;351(1):25–31. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1970.351.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maret A., Salvayre R., Negre A., Douste-Blazy L. Propriétés des formes moléculaires de la bêta-glucosidase et de la bêta-glucocérébrosidase de rate humaine normale et de maladie de gaucher. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):455–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matoth Y., Zaizov R., Hoffman J., Klibansky C. Clinical and biochemical aspects of chronic Gaucher's disease. Isr J Med Sci. 1974 Dec;10(12):1523–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mraz W., Fischer G., Jatzkewitz H. Low molecular weight proteins in secondary lysosomes as activators of different sphingolipid hydrolases. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):104–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80879-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller O. T., Rosenberg A. Activation of membrane-bound glucosylceramide: beta-glucosidase in fibroblasts cultured from normal and glucosylceramidotic human skin. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3521–3525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Brady R. O., Blair H. E., Britton D. E., Sorrell S. H. Gaucher disease: isolation and comparison of normal and mutant glucocerebrosidase from human spleen tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3970–3973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Brady R. O., Hibbert S. R., Gal A. E., Shapiro D. Isolation and characterization of glucocerebrosidase from human placental tissue. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5256–5261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S. P., Coyle P., Coffee C. J., Glew R. H. Purification and properties of a heat-stable glucocerebrosidase activating factor from control and Gaucher spleen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):563–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S. P., Coyle P., Glew R. H. Differentiation of beta-glucocerebrosidase from beta-glucosidase in human tissues using sodium taurocholate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Aug;175(2):569–582. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90547-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S. P., Lee R. E., Glew R. H. A microassay for Gaucher's disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 May 1;60(3):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin N. S. Inhibitors and stimulators of glucocerebroside metabolism. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;95:357–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan S. S., Topol J., Kolodny E. H. Leukocyte beta-glucosidase in homozygotes and heterozygotes for Gaucher disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Mar;32(2):158–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimerlik M. I., Cleland W. W. pH variation of the kinetic parameters and the catalytic mechanism of malic enzyme. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):576–583. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens M. C., Bernatsky A., Burachinsky V., Legler G., Kanfer J. N. The Gaucher mouse: differential action of conduritol B epoxide and reversibility of its effects. J Neurochem. 1978 May;30(5):1023–1027. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L., Håkansson G., Dreborg S. Assay of the beta-glucosidase activity with natural labelled and artificial substrates in leukocytes from homozygotes and heterozygotes with the Norrbottnian type (Type 3) of Gaucher disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Sep 25;106(2):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger D. A., Roth S. Homozygote and heterozygote identification. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;95:551–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


