Abstract
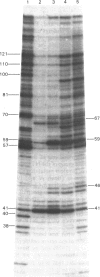
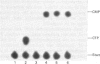
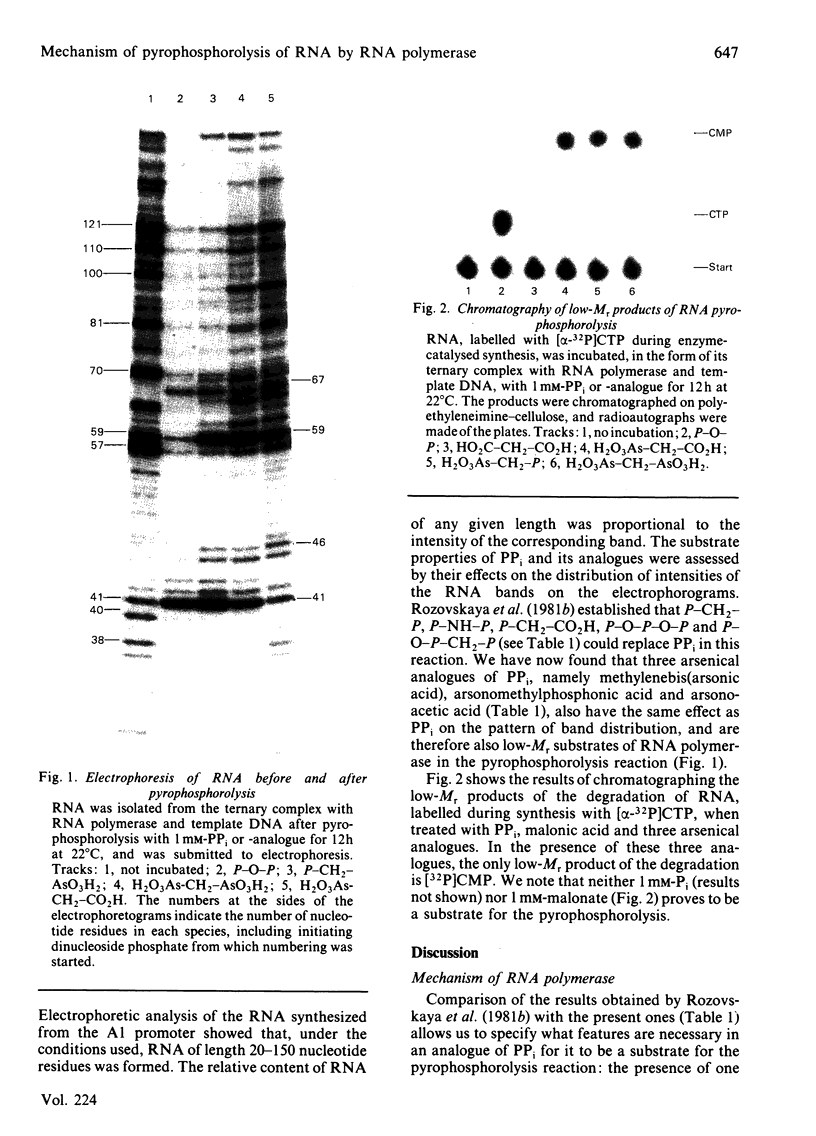
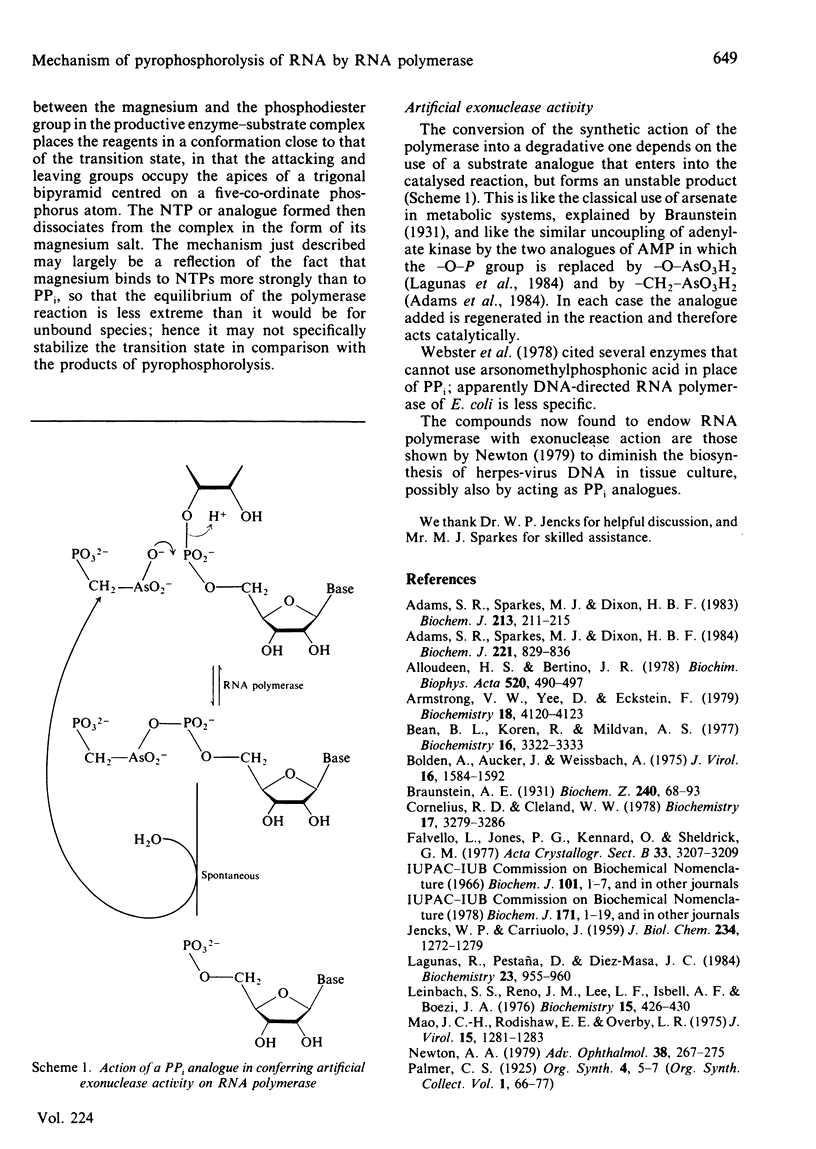
DNA-directed RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli can break down RNA by catalysing the reverse of the reaction: NTP + (RNA)n = (RNA)n+1 + PPi where n indicates the number of nucleotide residues in the RNA molecule, to yield nucleoside triphosphates. This reaction requires the ternary complex of the polymerase with template DNA and the RNA that it has synthesized. It is now shown that methylenebis(arsonic acid) [CH2(AsO3H2)2], arsonomethylphosphonic acid (H2O3As-CH2-PO3H2) and arsonoacetic acid (H2O3As-CH2-CO2H) can replace pyrophosphate in this reaction. When they do so, the low-Mr products of the reaction prove to be nucleoside 5'-phosphates, so that the arsenical compounds endow the polymerase with an artificial exonuclease activity, an effect previously found by Rozovskaya, Chenchik, Tarusova, Bibilashvili & Khomutov [(1981) Mol. Biol. (Moscow) 15, 636-652] for phosphonoacetic acid (H2O3P-CH2-CO2H). This is explained by instability of the analogues of nucleoside triphosphates believed to be the initial products. Specificity of recognition of pyrophosphate is discussed in terms of the sites, beta and gamma, for the -PO3H2 groups of pyrophosphate that will yield P-beta and P-gamma of the nascent nucleoside triphosphate. Site gamma can accept -AsO3H2 in place of -PO3H2, but less well; site beta can accept both, and also -CO2H. We suggest that partial transfer of an Mg2+ ion from the attacking pyrophosphate to the phosphate of the internucleotide bond of the RNA may increase the nucleophilic reactivity of the pyrophosphate and the electrophilicity of the diester, so that the reaction is assisted.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. R., Sparkes M. J., Dixon H. B. The arsonomethyl analogue of 3-phosphoglycerate. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 1;213(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2130211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. R., Sparkes M. J., Dixon H. B. The arsonomethyl analogue of adenosine 5'-phosphate. An uncoupler of adenylate kinase. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):829–836. doi: 10.1042/bj2210829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaudeen H. S., Bertino J. R. Inhibition of activities of DNA polymerase alpha, beta, gamma, and reverse transcriptase of L1210 cells by phosphonoacetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 24;520(3):490–497. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong V. W., Yee D., Eckstein F. Mechanistic studies on deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli using phosphorothioate analogues. 2. The elongation reaction. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4120–4123. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. L., Koren R., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance studies of the conformation of enzyme-bound adenylyl(3' leads to 5')uridine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate on RNA polymerase from Esherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 26;16(15):3322–3333. doi: 10.1021/bi00634a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A., Aucker J., Weissbach A. Synthesis of herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and adenovirus DNA in isolated HeLa cell nuclei. I. Effect of viral-specific antisera and phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1584–1592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1584-1592.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius R. D., Cleland W. W. Substrate activity of (adenosine triphosphato)tetraamminecobalt(III) with yeast hexokinase and separation of diastereomers using the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3279–3286. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENCKS W. P., CARRIUOLO J. Imidazole catalysis. II. Acyl transfer and the reactions of acetyl imidazole with water and oxygen anions. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1272–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunas R., Pestaña D., Diez-Masa J. C. Arsenic mononucleotides. Separation by high-performance liquid chromatography and identification with myokinase and adenylate deaminase. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):955–960. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Isbell A. F., Boezi J. A. Mechanism of phosphonoacetate inhibition of herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):426–430. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E., Overby L. R. Inhibition of DNA polymerase from herpes simplex virus-infected wi-38 cells by phosphonoacetic Acid. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1281–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1281-1283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A. A. Inhibition of the replication of herpes viruses by phosphonoacetate and related compounds. Adv Ophthalmol. 1979;38:267–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozovskaia T. A., Chenchik A. A., Bibilashvili R. Sh. Reaktsiia pirofosforoliza, kataliziruemaia RNK-polimerazoi Escherichia coli. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1981 May-Jun;15(3):636–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozovskaia T. A., Chenchik A. A., Tarusova N. B., Bibilashvili R. Sh, Khomutov R. M. Analogi pirofosfata v reaktsii pirofosforoliza, kataliziruemoi RNK-polimerazoi Escherichia coli. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1981 Nov-Dec;15(6):1205–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L., Myers T., Mednieks M. The enzymatic synthesis of polyribonucleotides using 5'-adenylylmethylenediphosphonate: a phosphonic acid analog of adenosine triphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 8;103(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. J., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance and kinetic studies of initiator-substrate distances on RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2675–2684. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E., MORGAN D. M. Detection of phosphate esters on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1953 Mar 21;171(4351):529–530. doi: 10.1038/171529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster D., Sparkes M. J., Dixon H. B. An arsenical analogue of adenosine diphosphate. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):239–244. doi: 10.1042/bj1690239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]