Abstract
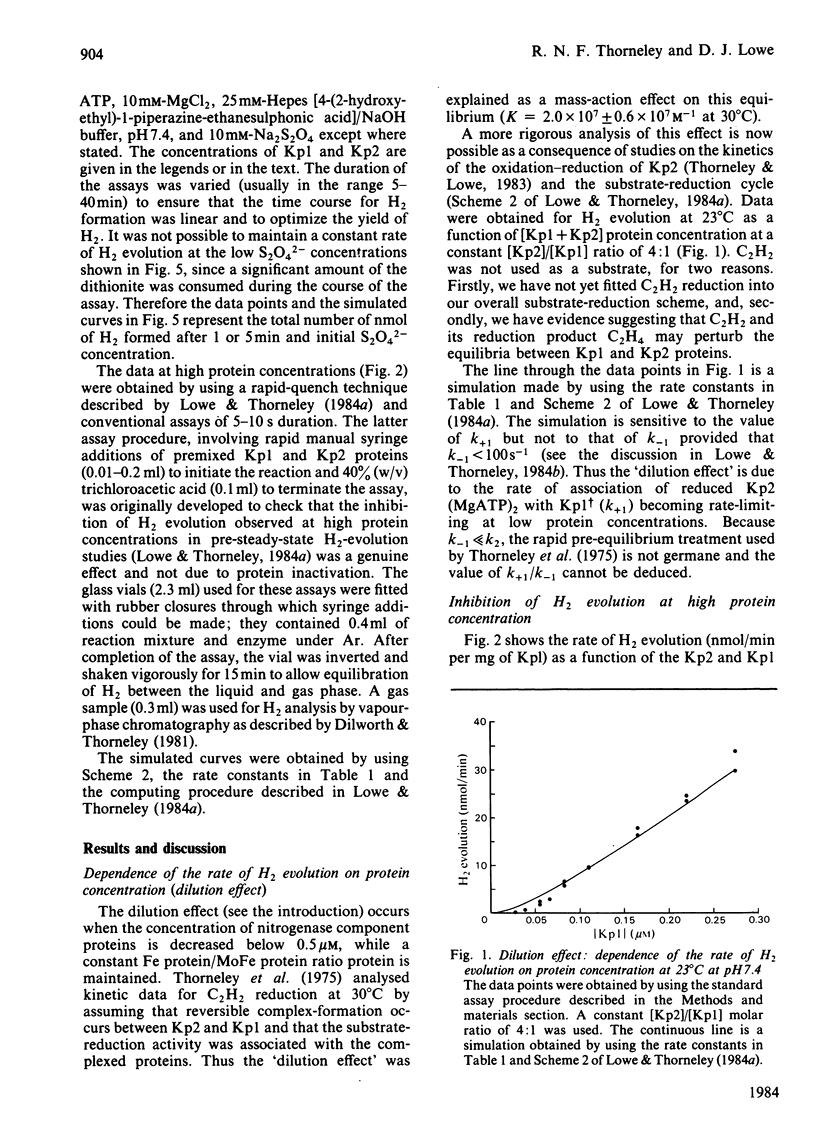
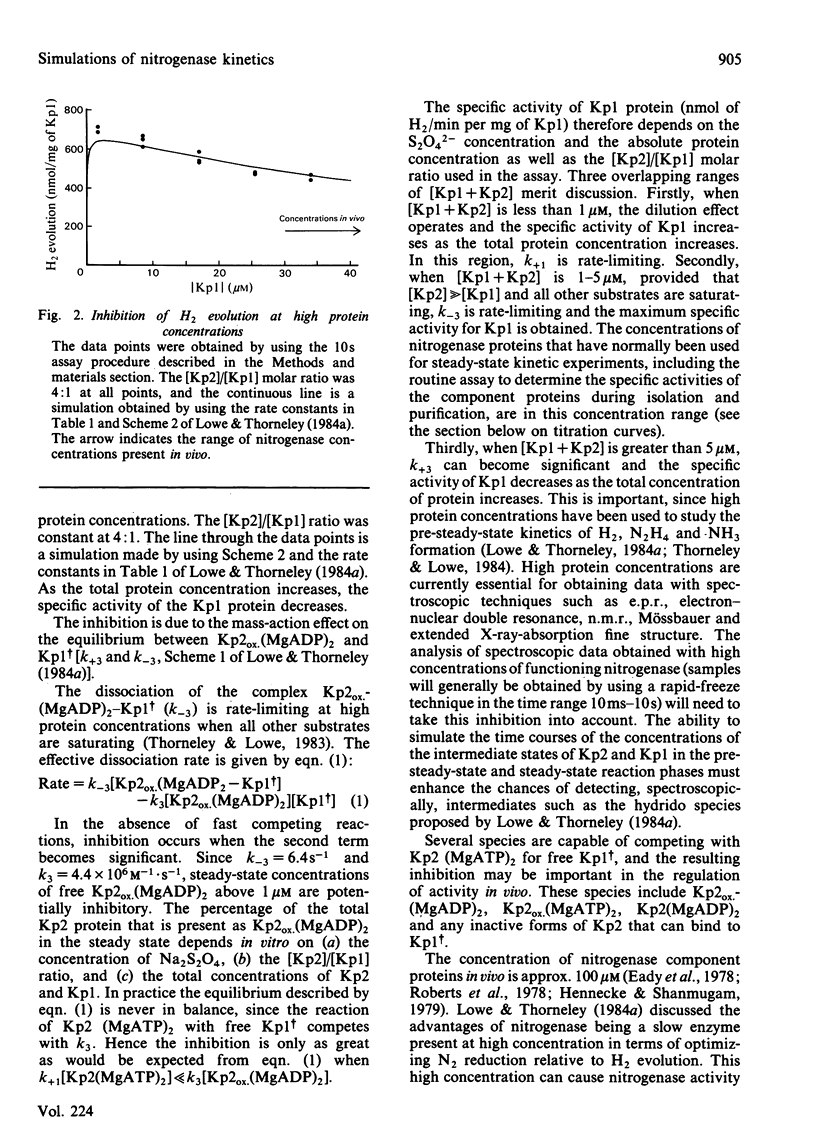
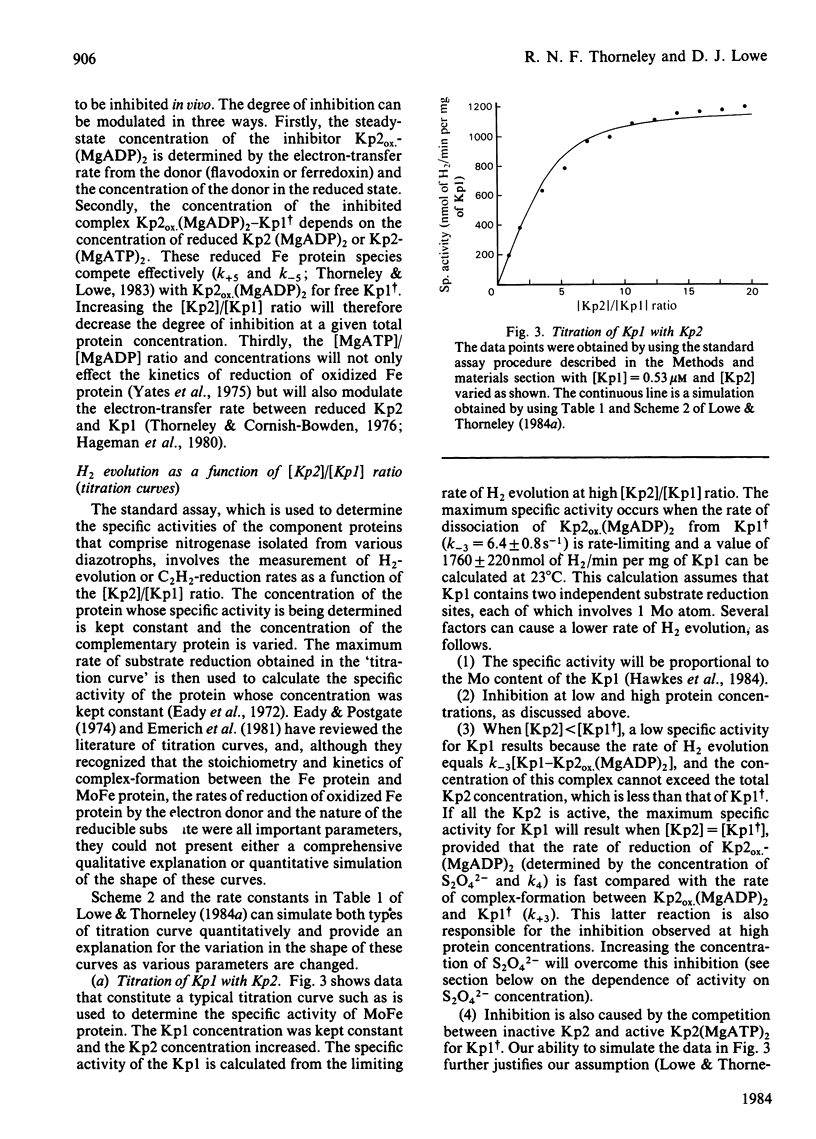
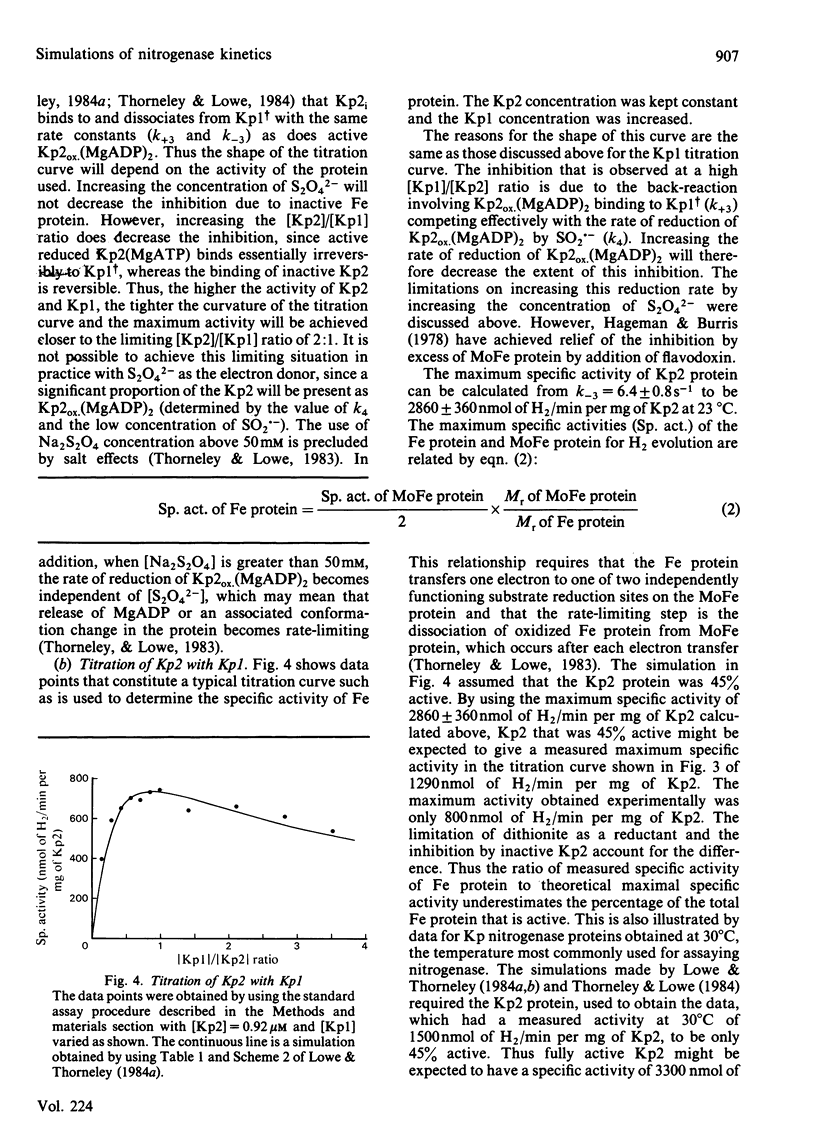
The rate constants from Table 1 and Scheme 2 of Lowe & Thorneley [(1984) Biochem. J. 224, 877-886] were used to simulate the rate of H2 evolution, under various conditions, from nitrogenase isolated from Klebsiella pneumoniae. These rates depend on both the ratio and concentrations of the MoFe protein and Fe protein that comprise nitrogenase. The simulations explain the shapes of 'protein titration' and 'dilution effect' curves. The concept of an apparent Km for the reductant Na2S2O4 is shown to be invalid, since the dependence of H2-evolution rate on the square root of S2O4(2-) concentration is not hyperbolic and depends on the ratio and absolute concentrations of the MoFe protein and Fe protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eady R. R., Issack R., Kennedy C., Postgate J. R., Ratcliffe H. D. Nitrogenase synthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae: comparison of ammonium and oxygen regulation. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):277–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase. Nature. 1974 Jun 28;249(460):805–810. doi: 10.1038/249805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerich D. W., Hageman R. V., Burris R. H. Interactions of dinitrogenase and dinitrogenase reductase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1981;52:1–22. doi: 10.1002/9780470122976.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman R. V., Burris R. H. Kinetic studies on electron transfer and interaction between nitrogenase components from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4117–4124. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman R. V., Orme-Johnson W. H., Burris R. H. Role of magnesium adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the hydrogen evolution reaction catalyzed by nitrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2333–2342. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., McLean P. A., Smith B. E. Nitrogenase from nifV mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae contains an altered form of the iron-molybdenum cofactor. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):317–321. doi: 10.1042/bj2170317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H., Shanmugam K. T. Temperature control of nitrogen fixation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch Microbiol. 1979;123(3):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00406659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. J., Thorneley R. N. The mechanism of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase action. Pre-steady-state kinetics of H2 formation. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):877–886. doi: 10.1042/bj2240877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. J., Thorneley R. N. The mechanism of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase action. The determination of rate constants required for the simulation of the kinetics of N2 reduction and H2 evolution. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):895–901. doi: 10.1042/bj2240895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTENSON L. E. FERREDOXIN AND ATP, REQUIREMENTS FOR NITROGEN FIXATION IN CELL-FREE EXTRACTS OF CLOSTRIDIUM PASTEURIANUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:272–279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Regulation and characterization of protein products coded by the nif (nitrogen fixation) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):267–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.267-279.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Cornish-Bowden A. Kinetics of nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Heterotropic interactions between magnesium-adenosine 5'-diphosphate and magnesium-adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):255–262. doi: 10.1042/bj1650255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R., Yates M. G. Nitrogenases of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Azotobacter chroococum. Complex formation between the component proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 22;403(2):269–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Lowe D. J. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Kinetics of the dissociation of oxidized iron protein from molybdenum-iron protein: identification of the rate-limiting step for substrate reduction. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):393–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2150393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Lowe D. J. The mechanism of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase action. Pre-steady-state kinetics of an enzyme-bound intermediate in N2 reduction and of NH3 formation. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):887–894. doi: 10.1042/bj2240887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt G. D., Burns A. Kinetics of dithionite ion utilization and ATP hydrolysis for reactions catalyzed by the nitrogenase complex from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 25;16(2):264–270. doi: 10.1021/bi00621a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates M. G., Thorneley R. N., Lowe D. J. Nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum: inhibition of ADP of the reduction of oxidised Fe protein by sodium dithionite. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


