Abstract
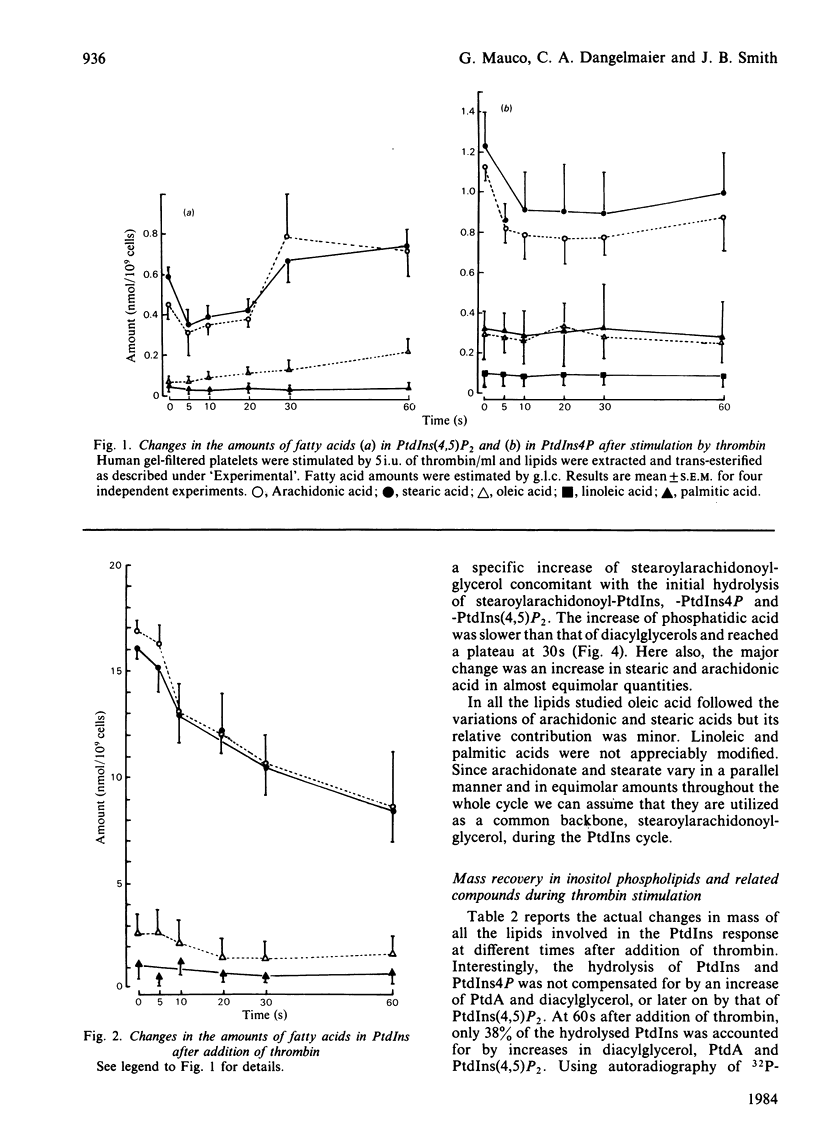
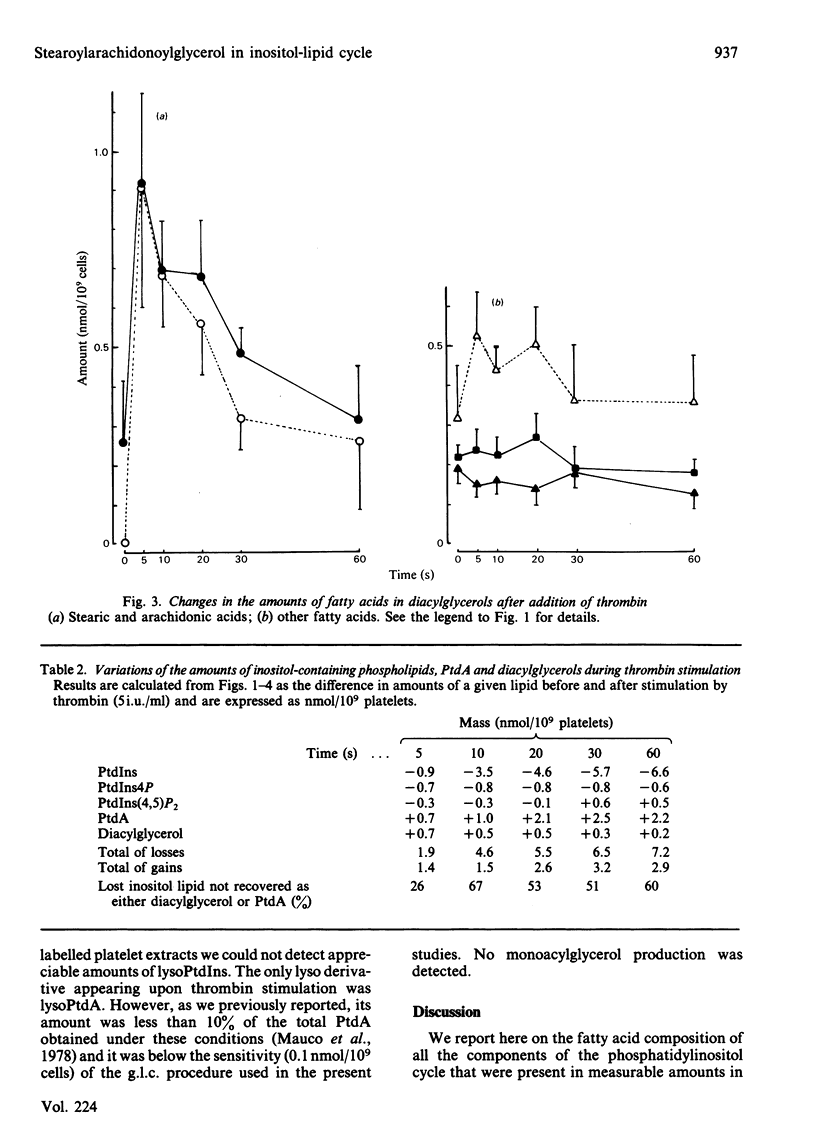
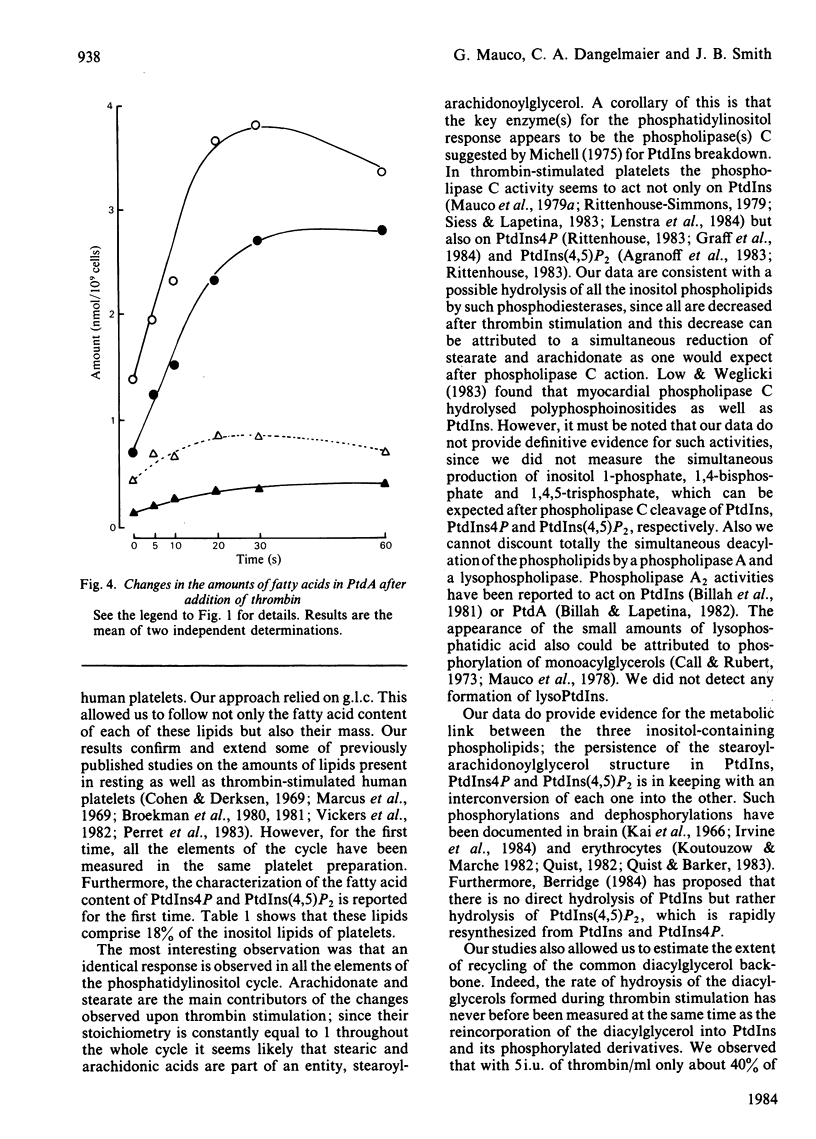
Gel-filtered human platelets were stimulated with 5i.u. of thrombin/ml for times up to 1 min. The fatty acid composition of inositol-containing phospholipids, phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol was determined by g.l.c. in control and thrombin-stimulated platelet suspensions. Inositol phospholipids were found to have similar proportions of stearic and arachidonic acids, the sum of these representing 86.6% of the total fatty acids in phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns), 76.9% in phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) and 85.4% in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2]. However, arachidonic and stearic acids were less abundant in phosphatidic acid (PtdA) and diacylglycerols in non-stimulated platelets. A transient decrease in the mass of PtdIns(4,5)P2 was observed after 5-10s of thrombin stimulation, followed by an increase after 30s. The amounts of PtdIns4P and PtdIns decreased throughout the experiment. A transient accumulation of stearoylarachidonoylglycerol was observed at 5s, whereas stearoylarachidonoylglycerol 3-phosphate (PtdA) was produced in increasing amounts throughout the experiment. The decrease in inositol-containing phospholipids was not fully compensated for by the production of diacylglycerol or PtdA [or PtdIns(4,5)P2] at 1 min. All the changes in inositol phospholipids, as well as those observed in diacylglycerols and PtdA, were due to a parallel reduction or increase in the contents of stearic and arachidonic acids, with a stoichiometry equal to 1. Taken together, this suggests an interconversion of all these lipids with the utilization of a common backbone, stearoylarachidonoylglycerol. The deacylation of this diacylglycerol could account for up to 4-5nmol of arachidonate/10(9) platelets after 1 min stimulation by thrombin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTER R. H., JANDL J. H. PLATELET SEQUESTRATION IN MAN. I. METHODS. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:843–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI104970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis: a multifunctional transducing mechanism. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Nov;24(2):115–140. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 activity specific for phosphatidic acid. A possible mechanism for the production of arachidonic acid in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5399–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Formation of lysophosphatidylinositol in platelets stimulated with thrombin or ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5196–5200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bills T. K., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Selective release of archidonic acid from the phospholipids of human platelets in response to thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI108745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Ward J. W., Marcus A. J. Fatty acid composition of phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidic acid in stimulated platelets. Persistence of arachidonyl-stearyl structure. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8271–8274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Ward J. W., Marcus A. J. Phospholipid metabolism in stimulated human platelets. Changes in phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidic acid, and lysophospholipids. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):275–283. doi: 10.1172/JCI109854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call F. L., 2nd, Rubert M. Diglyceride kinase in human platelets. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jul;14(4):466–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Derksen A. Comparison of phospholipid and fatty acid composition of human erythrocytes and platelets. Br J Haematol. 1969 Oct;17(4):359–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes P., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate: lipids in search of a function. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):467–502. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff G., Nahas N., Nikolopoulou M., Natarajan V., Schmid H. H. Possible regulation of phospholipase C activity in human platelets by phosphatidylinositol 4',5'-bisphosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jan;228(1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser G., Eichberg J. Identification of cytidine diphosphate-diglyceride in the pineal gland of the rat and its accumulation in the presence of DL-propranolol. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Levine L. Inhibition of arachidonic acid release from cells as the biochemical action of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Dawson R. M. Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase and phosphomonoesterase activities of rat brain. Some properties and possible control mechanisms. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):177–185. doi: 10.1042/bj2180177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai M., White G. L., Hawthorne J. N. The phosphatidylinositol kinase of rat brain. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):328–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1010328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutouzov S., Marche P. The Mg2+-activated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-specific phosphomonoesterase of erythrocyte membrane. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 19;144(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lages B., Scrutton M. C., Holmsen H. Studies on gel-filtered human platelets: isolation and characterization in a medium containing no added Ca2+, Mg2+, or K+. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 May;85(5):811–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Stimulation of phosphatidic acid production in platelets precedes the formation of arachidonate and parallels the release of serotonin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 25;573(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra R., Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Studies on enzymes related to diacylglycerol production in activated platelets. I. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C: further characterization using a simple method for determination of activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 9;792(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Mustard J. F. Changes in 32P-content of phosphatidic acid and the phosphoinositides of rabbit platelets during aggregation induced by collagen or thrombin. Br J Haematol. 1974 Feb;26(2):243–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Nishizawa E. E., Haldar J., Mustard J. F. Changes in 32 p-labelling of platelet phospholipids in response to ADP. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):571–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Nishizawa E. E., Joist J. H., Mustard J. F. Effect of ADP-induced aggregation on 32 PO 4 incorporation into phosphatidic acid and the phosphoinositides of rabbit platelets. Br J Haematol. 1973 May;24(5):589–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Weglicki W. B. Resolution of myocardial phospholipase C into several forms with distinct properties. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):325–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2150325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. T., Call F. L., 2nd, Williams W. J. The biosynthesis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1949–1955. doi: 10.1172/JCI106414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., Pollock W. K. Platelet-activating factor stimulates phosphatidylinositol turnover in human platelets. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):433–437. doi: 10.1042/bj2120433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevappa V. G., Holub B. J. The molecular species composition of individual diacyl phospholipids in human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 14;713(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Ullman H. L., Safier L. B. Lipid composition of subcellular particles of human blood platelets. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Characterization and properties of a phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase (phospholipase C) from platelet cytosol. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Platelet activating factor (PAF-acether) promotes an early degradation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate in rabbit platelets. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):361–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80643-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Simon M. F., Douste-Blazy L. Phosphatidic and lysophosphatidic acid production in phospholipase C-and thrombin-treated platelets. Possible involvement of a platelet lipase. Biochimie. 1978 Sep 29;60(6-7):653–661. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80784-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret B. P., Plantavid M., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Are polyphosphoinositides involved in platelet activation? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):660–667. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Majerus P. W. The fatty acid composition of phosphatidylinositol from thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):579–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quist E. E., Barker R. C. Properties of phosphatidylinositol kinase activities in rabbit erythrocyte membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 1;222(1):170–178. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90514-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quist E. E. Polyphosphoinositide synthesis in rabbit erythrocyte membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Nov;219(1):58–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E. Human platelets contain phospholipase C that hydrolyzes polyphosphoinositides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5417–5420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Takai Y., Yamanishi J., Nishizuka Y. A role of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in human platelet activation. Comparison of thrombin and collagen actions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2010–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Properties and distribution of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in human and horse platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 12;752(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Good J. J., Barclay M., Reggio R. B. Quantitative analysis of simple lipid classes by thin-layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 10;152(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Swart C. A., Nijmeyer B., Roelofs J. M., Sixma J. J. Kinetics of intravenously administered heparin in normal humans. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1251–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



