Abstract
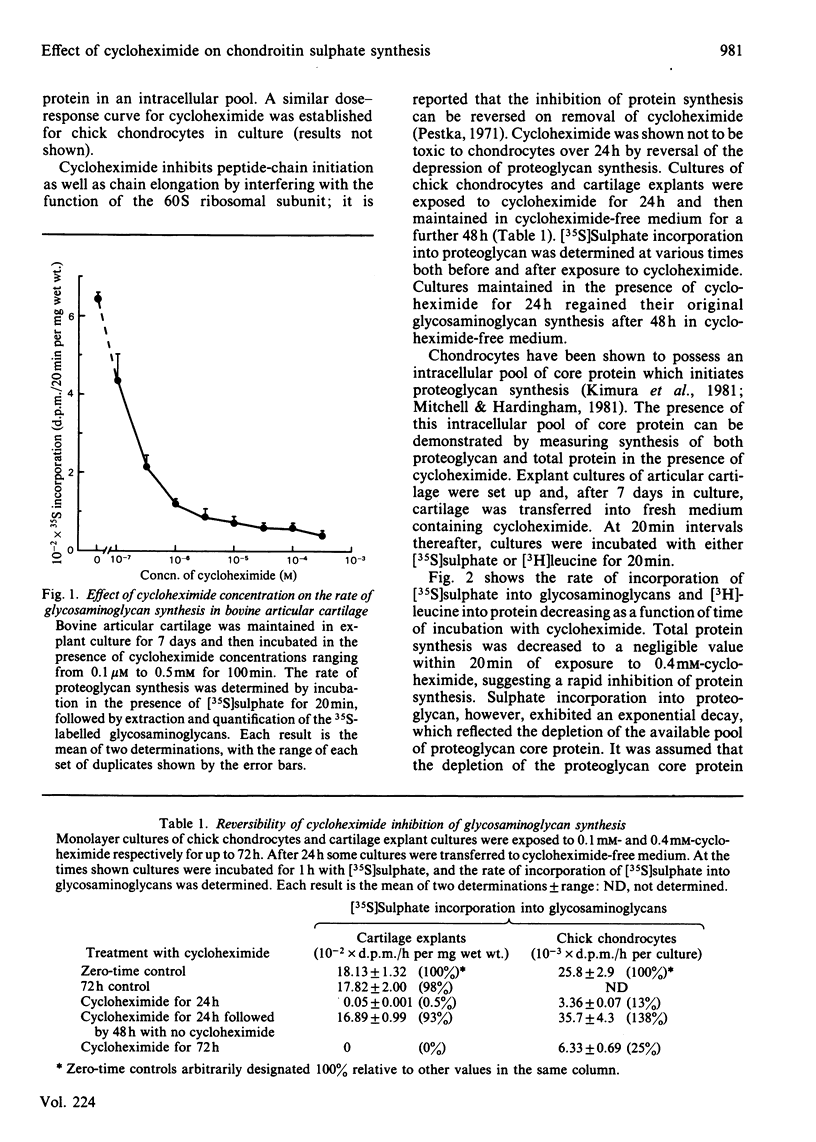
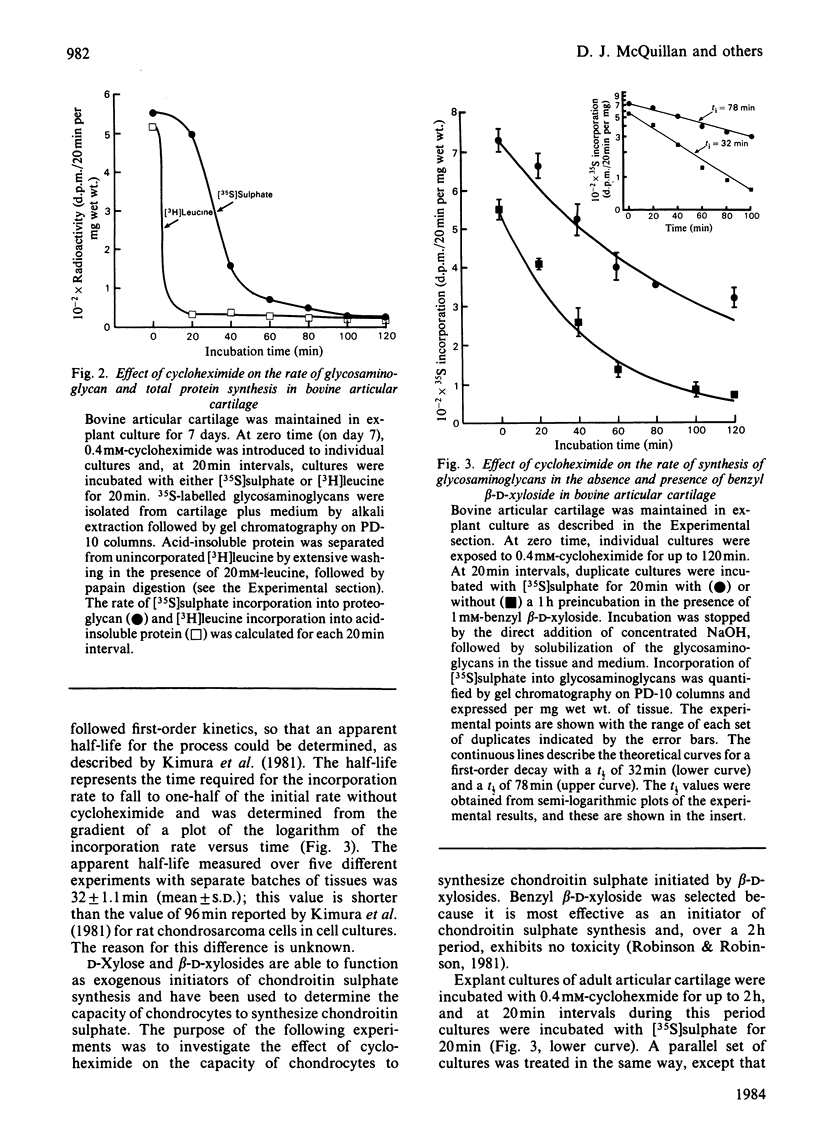
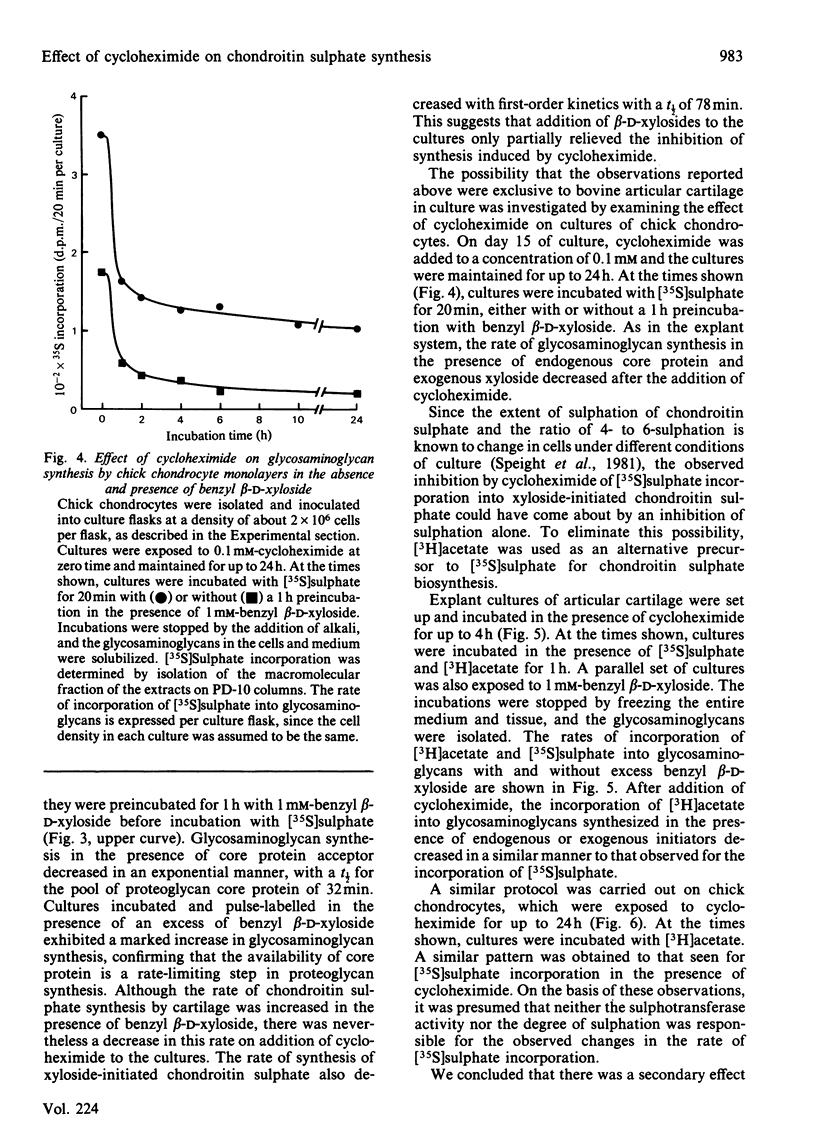
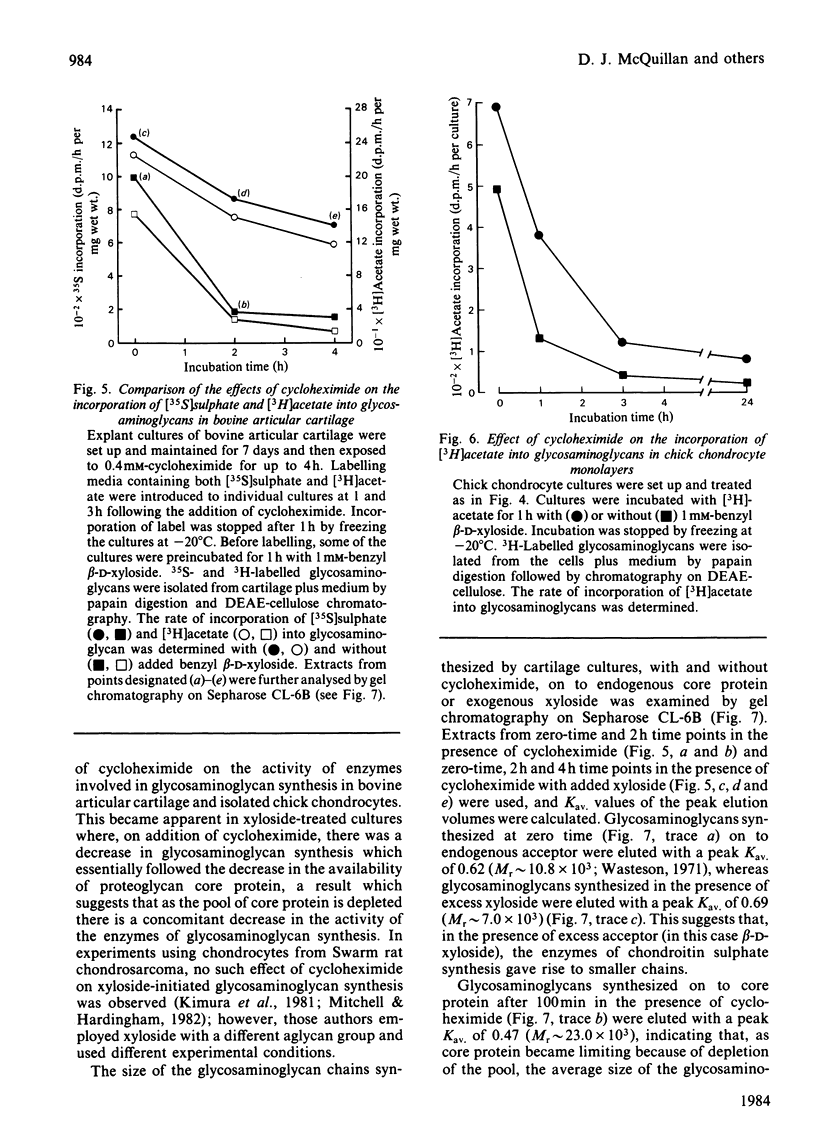
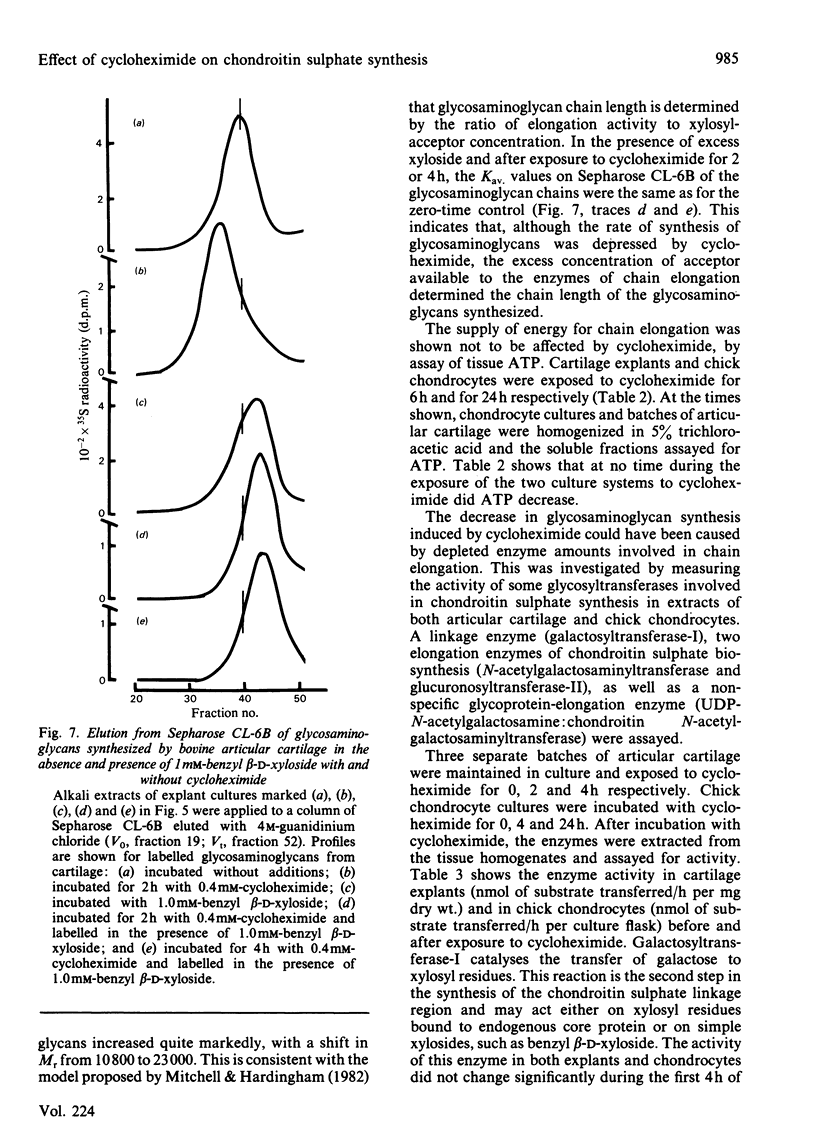
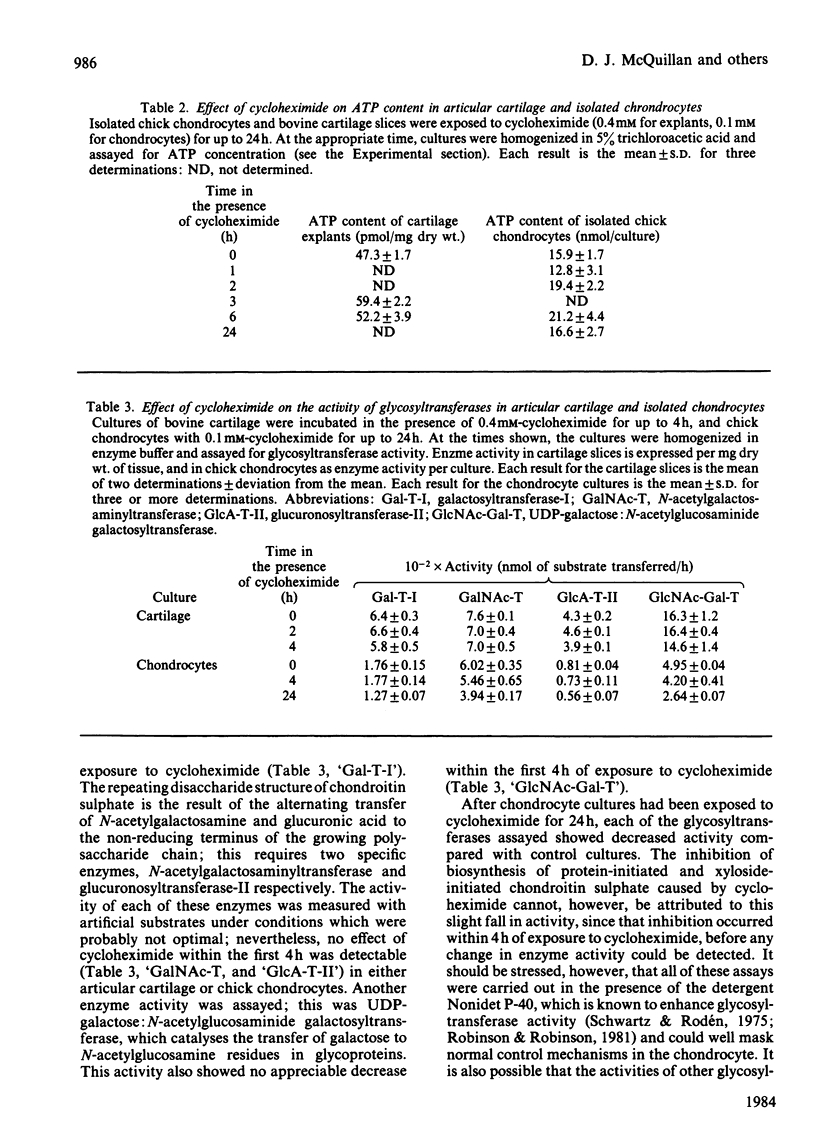
The effect of cycloheximide on chondroitin sulphate biosynthesis was studied in bovine articular cartilage maintained in culture. Addition of 0.4 mM-cycloheximide to the culture medium was followed, over the next 4h, by a first-order decrease in the rate of incorporation of [35S]sulphate into glycosaminoglycan (half-life, t 1/2 = 32 min), which is consistent with the depletion of a pool of proteoglycan core protein. Addition of 1.0 mM-benzyl beta-D-xyloside increased the rate of incorporation of [35S]sulphate and [3H]acetate into glycosaminoglycan, but this elevated rate was also diminished by cycloheximide. It was concluded that cycloheximide exerted two effects on the tissue; not only did it inhibit the synthesis of the core protein, but it also lowered the tissue's capacity for chondroitin sulphate chain synthesis. Similar results were obtained with chick chondrocytes grown in high-density cultures. Although the exact mechanism of this secondary effect of cycloheximide is not known, it was shown that there was no detectable change in cellular ATP concentration or in the amount of three glycosyltransferases (galactosyltransferase-I, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase and glucuronosyltransferase-II) involved in chondroitin sulphate chain synthesis. The sizes of the glycosaminoglycan chains formed in the presence of cycloheximide were larger than those formed in control cultures, whereas those synthesized in the presence of benzyl beta-D-xyloside were consistently smaller, irrespective of the presence of cycloheximide. These results suggest that beta-D-xylosides must be used with caution to study chondroitin sulphate biosynthesis as an event entirely independent of proteoglycan core-protein synthesis, and they also indicate a possible involvement of the core protein in the activation of the enzymes of chondroitin sulphate synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Luca S., Caplan A. I., Hascall V. C. Biosynthesis of proteoglycans by chick limb bud chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4713–4720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellini S. A., Hascall V. C., Kimura J. H. Localization of proteoglycan core protein in subcellular fractions isolated from rat chondrosarcoma chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4634–4641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galligani L., Hopwood J., Schwartz N. B., Dorfman A. Stimulation of synthesis of free chondroitin sulfate chains by beta-D-xylosides in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5400–5406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley C. J., Bateman J. F., Oakes B. W., Lowther D. A. Characterization of the collagen synthesized by cultured cartilage cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 29;386(2):444–450. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley C. J., Lowther D. A. Extracellular matrix metabolism by chondrocytes. III. Modulation of proteoglycan synthesis by extracellular levels of proteoglycan in cartilage cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 7;500(1):132–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley C. J., Lowther D. A. Inhibition of proteoglycan biosynthesis by hyaluronic acid in chondrocytes in cell culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 24;444(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Handley C. J., McQuillan D. J., Hascall G. K., Robinson H. C., Lowther D. A. The effect of serum on biosynthesis of proteoglycans by bovine articular cartilage in culture. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 1;224(1):206–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Caputo C. B., Hascall V. C. The effect of cycloheximide on synthesis of proteoglycans by cultured chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4368–4376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Hardingham T. E., Hascall V. C., Solursh M. Biosynthesis of proteoglycans and their assembly into aggregates in cultures of chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2600–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D., Hardingham T. The control of chondroitin sulphate biosynthesis and its influence on the structure of cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 15;202(2):387–395. doi: 10.1042/bj2020387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D., Hardingham T. The effects of cycloheximide on the biosynthesis and secretion of proteoglycans by chondrocytes in culture. Biochem J. 1981 May 15;196(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1960521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Inhibitors of ribosome functions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:487–562. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. C., Brett M. J., Tralaggan P. J., Lowther D. A., Okayama M. The effect of D-xylose, beta-D-xylosides and beta-D-galactosides on chondroitin sulphate biosynthesis in embryonic chicken cartilage. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;148(1):25–34. doi: 10.1042/bj1480025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. A., Robinson H. C. Control of chondroitin sulphate biosynthesis. beta-D-Xylopyranosides as substrates for UDP-galactose: D-xylose transferase from embryonic-chicken cartilage. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):839–846. doi: 10.1042/bj1940839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz N. B., Galligani L., Ho P. L., Dorfman A. Stimulation of synthesis of free chondroitin sulfate chains by beta-D-xylosides in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4047–4051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz N. B., Rodén L. Biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate. Solubilization of chondroitin sulfate glycosyltransferases and partial purification of uridine diphosphate-D-galactose:D-xylose galactosyltrans. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5200–5207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speight G., Handley C. J., Lowther D. A. Effect of dibutyryl cyclic AMP on the sulphation of proteoglycans by chondrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 7;672(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolmiller A. C., Horwitz A. L., Dorfman A. Biosynthesis of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. Purification and properties of xylosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3525–3532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Pollak J. K. The increasing adenine nucleotide concentration and the maturation of rat liver mitochondria during neonatal development. Differentiation. 1978 Nov 15;12(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb00985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telser A., Robinson H. C., Dorfman A. The biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):458–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telser A., Robinson H. C., Dorfman A. The biosynthesis of chondroitin-sulfate protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):912–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thonar E. J., Lohmander L. S., Kimura J. H., Fellini S. A., Yanagishita M., Hascall V. C. Biosynthesis of O-linked oligosaccharides on proteoglycans by chondrocytes from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11564–11570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B., Vertel B. M., Dorfman A. Translation and characterization of messenger RNAs in differentiating chicken cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4847–4851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A. A method for the determination of the molecular weight and molecular-weight distribution of chondroitin sulphate. J Chromatogr. 1971 Jul 8;59(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D. A., Smith D. F., Drzeniek Z., Tsai C. M., Ginburg V. Affinity purification of antibodies using oligosaccharide-phenethylamine derivaties coupled to Sepharose. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:171–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


