Abstract
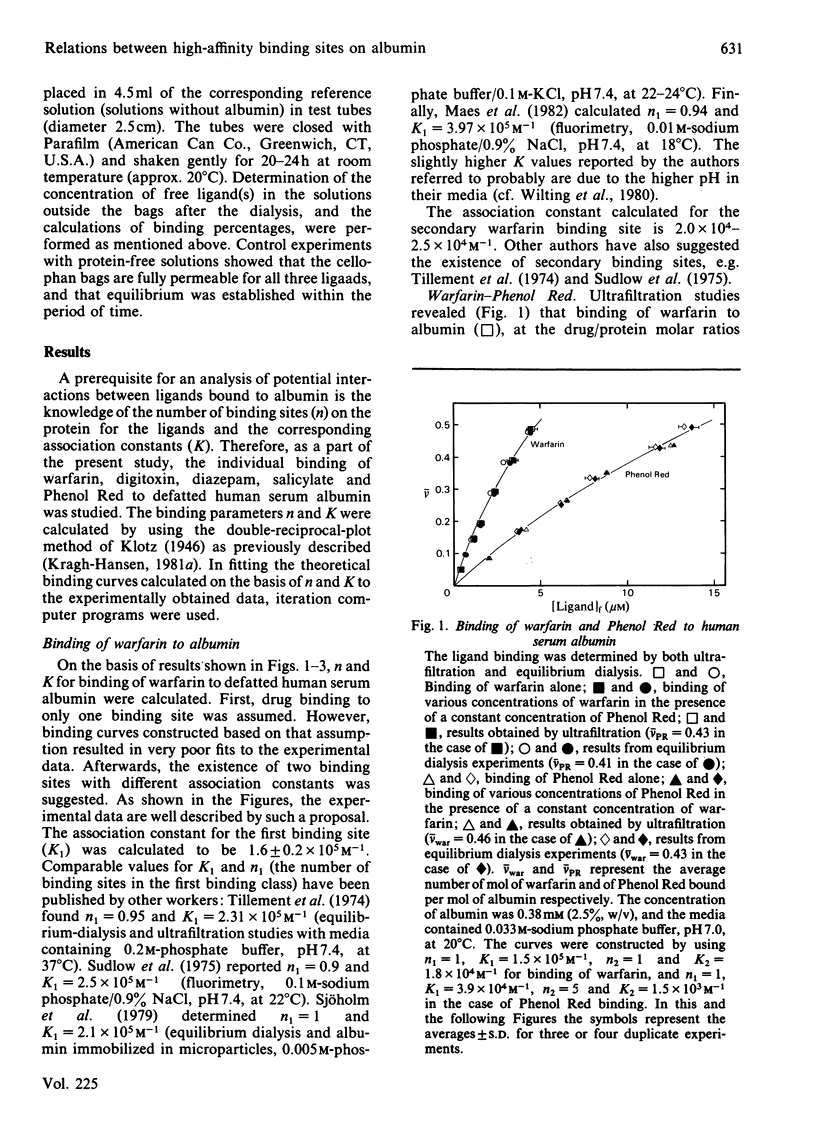
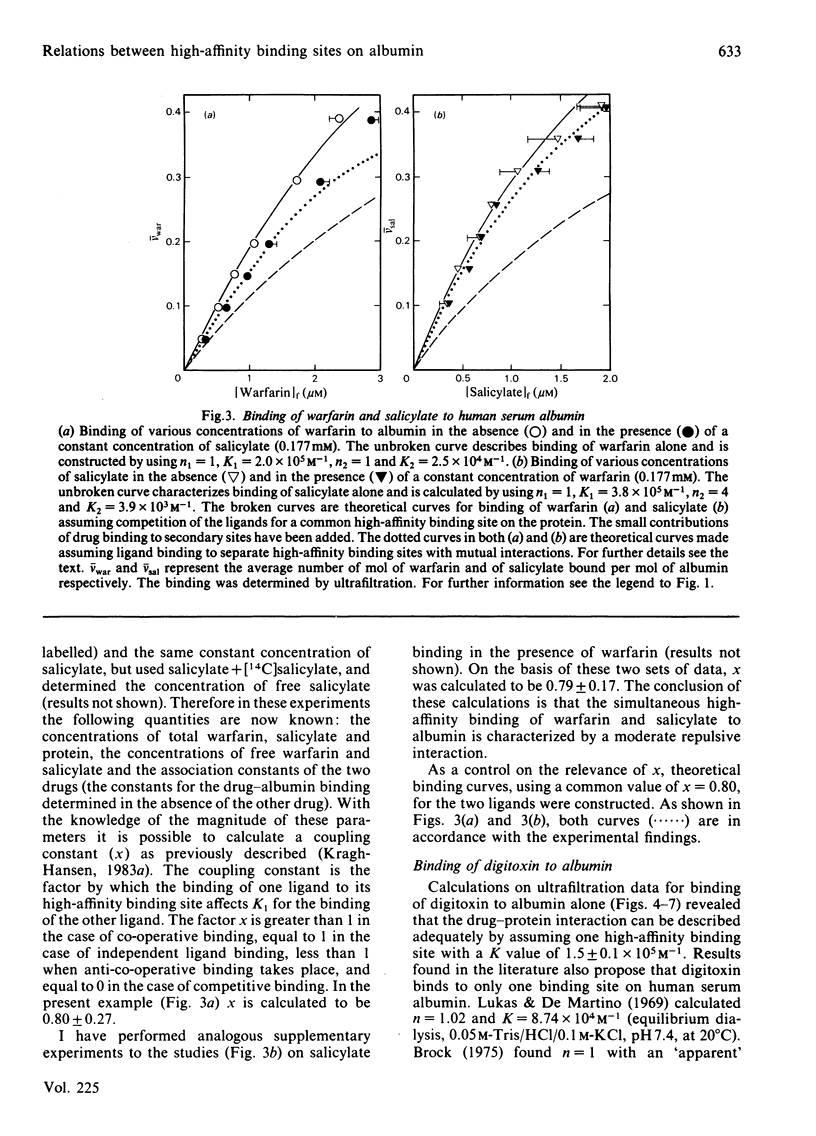
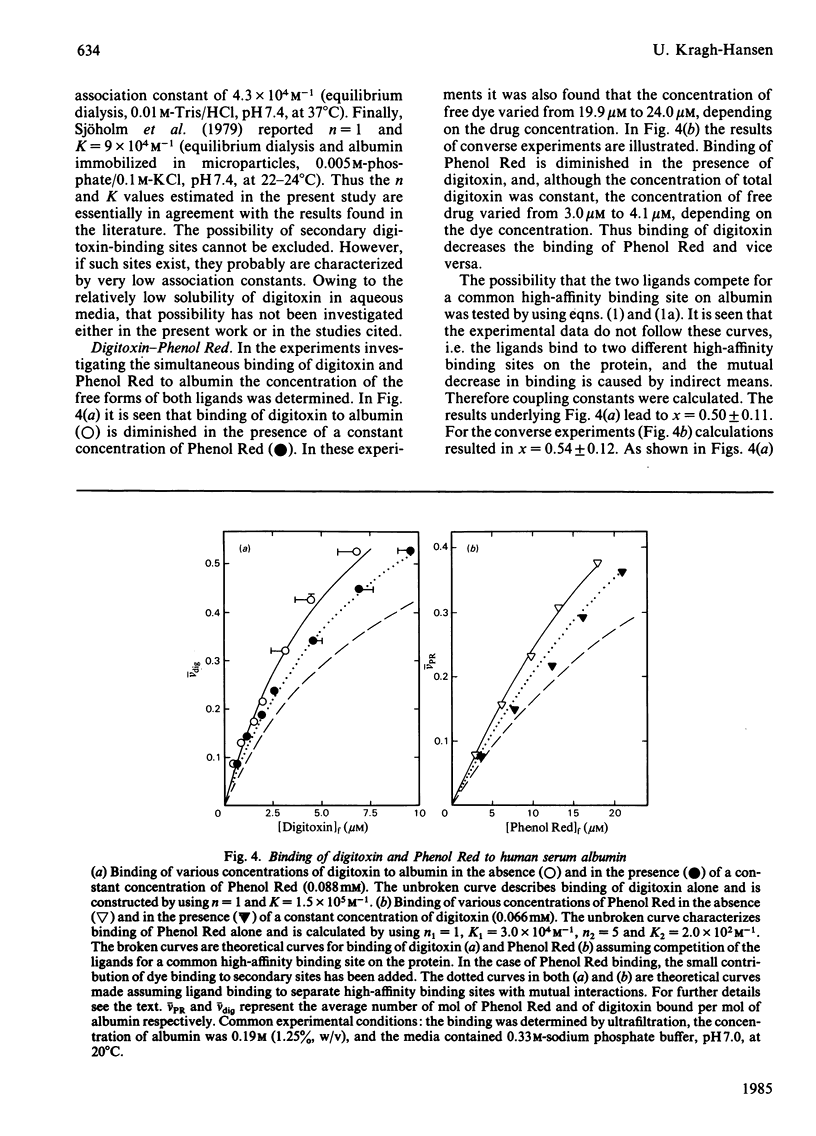
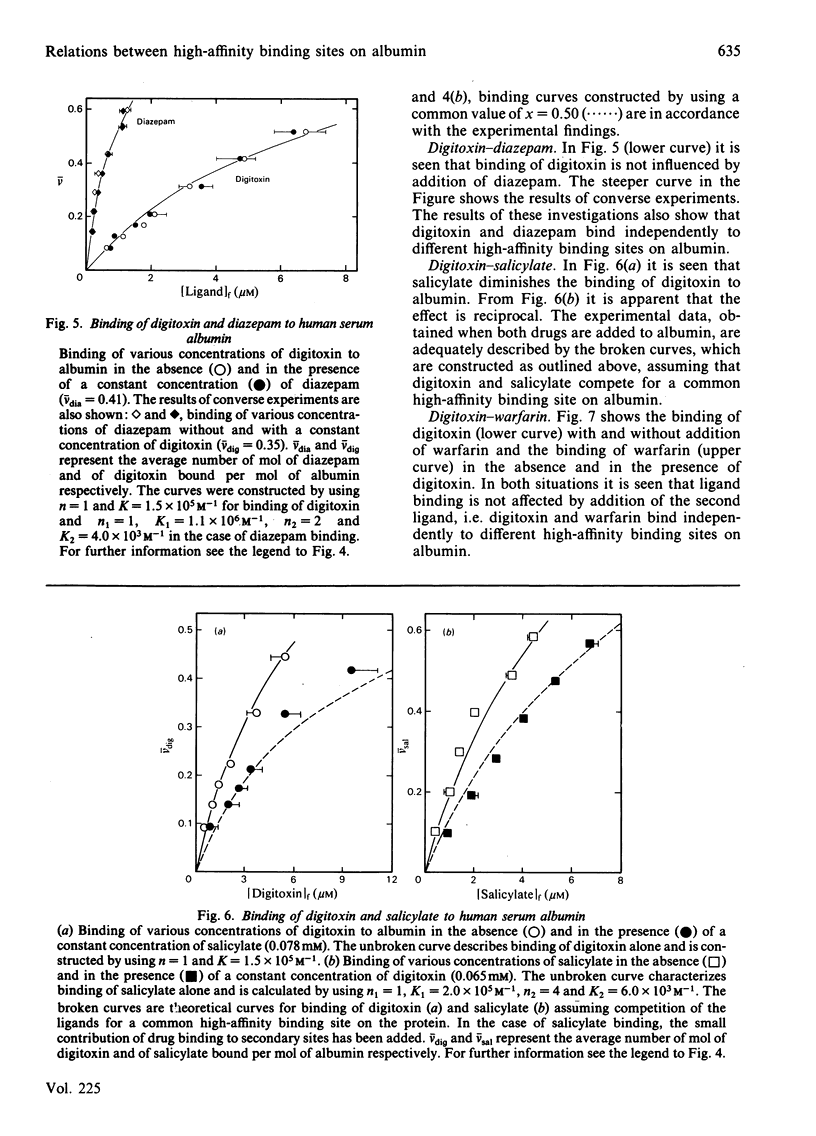
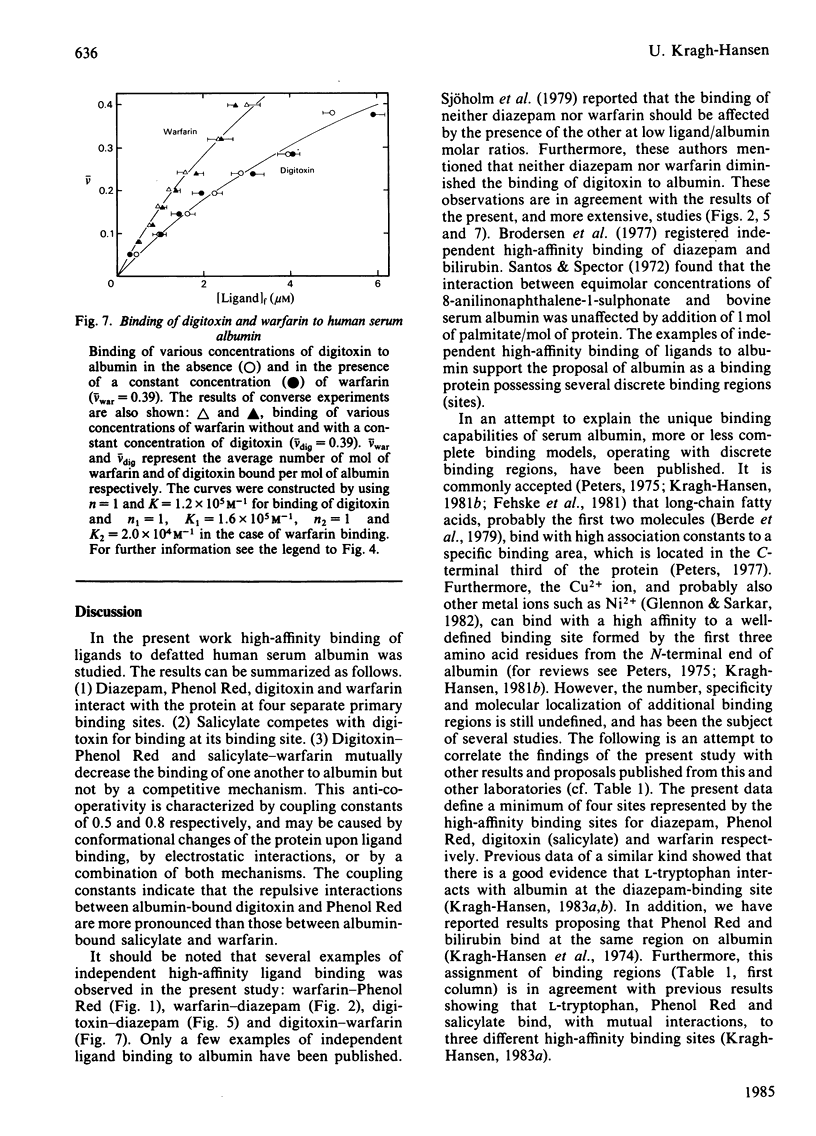
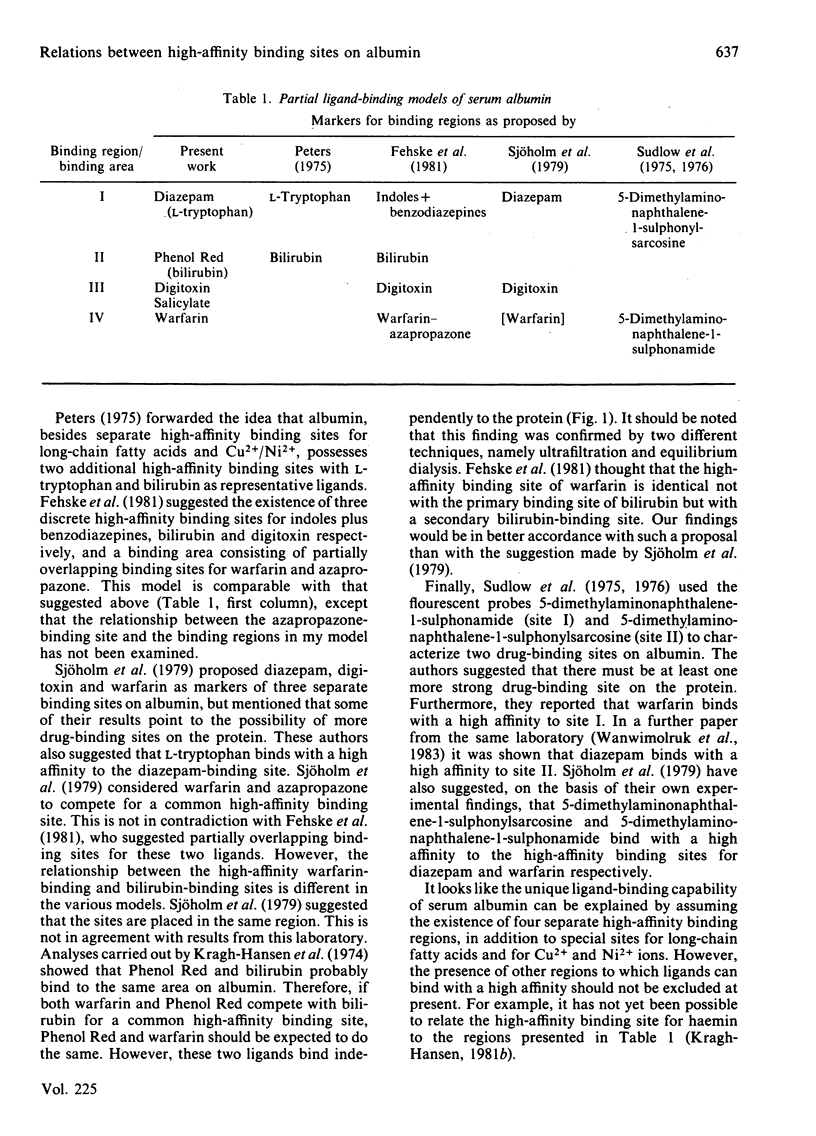
Binding of warfarin, digitoxin, diazepam, salicylate and Phenol Red, individually or in different pair combinations, to defatted human serum albumin at ligand/protein molar ratios less than 1:1 was studied at pH 7.0. The binding was determined by ultrafiltration. Some of the experiments were repeated with the use of equilibrium dialysis in order to strengthen the results. Irrespective of the method used, all ligands bind to one high-affinity binding site with an association constant in the range 10(4)-10(6) M-1. High-affinity binding of the following pair of ligands took place independently: warfarin-Phenol Red, warfarin-diazepam, warfarin-digitoxin and digitoxin-diazepam. Simultaneous binding of warfarin and salicylate led to a mutual decrease in binding of one another, as did simultaneous binding of digitoxin and Phenol Red. Both effects could be accounted for by a coupling constant. The coupling constant is the factor by which the primary association constants are affected; in these examples of anti-co-operativity the factor has a value between 0 and 1. In the first example it was calculated to be 0.8 and in the latter 0.5. Finally, digitoxin and salicylate were found to compete for a common high-affinity binding site. The present findings support the proposal of four separate primary binding sites for warfarin, digitoxin (and salicylate), diazepam and Phenol Red. An attempt to correlate this partial binding model for serum albumin with other models in the literature is made.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berde C. B., Hudson B. S., Simoni R. D., Sklar L. A. Human serum albumin. Spectroscopic studies of binding and proximity relationships for fatty acids and bilirubin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):391–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock A. Binding of digitoxin to human serum proteins: influence of pH on the binding of digitoxin to human albumin. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1975 Jan;36(1):13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1975.tb00767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen R., Sjödin T., Sjöholm I. Independent binding of ligands to human serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5067–5072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehske K. J., Müller W. E., Wollert U. The location of drug binding sites in human serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 1;30(7):687–692. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennon J. D., Sarkar B. Nickel(II) transport in human blood serum. Studies of nickel(II) binding to human albumin and to native-sequence peptide, and ternary-complex formation with L-histidine. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):15–23. doi: 10.1042/bj2030015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen U. Effects of aliphatic fatty acids on the binding of Phenol Red to human serum albumin. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):603–613. doi: 10.1042/bj1950603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen U. Graphical analysis of competitive binding of comparable concentrations of ligand, inhibitor and protein. Ligand binding to serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 15;32(18):2679–2681. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen U. Molecular aspects of ligand binding to serum albumin. Pharmacol Rev. 1981 Mar;33(1):17–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen U., Moller J. V., Sheikh M. I. A spectrophotometric micromethod for the determination of binding of phenol red to plasma proteins of various species. Pflugers Arch. 1972;337(2):163–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00587838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen U. Relations between high-affinity binding sites for L-tryptophan, diazepam, salicylate and Phenol Red on human serum albumin. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):135–142. doi: 10.1042/bj2090135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas D. S., De Martino A. G. Binding of digitoxin and some related cardenolides to human plasma proteins. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1041–1053. doi: 10.1172/JCI106060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maes V., Engelborghs Y., Hoebeke J., Maras Y., Vercruysse A. Fluorimetric analysis of the binding of warfarin to human serum albumin. Equilibrium and kinetic study. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr Serum albumin: recent progress in the understanding of its structure and biosynthesis. Clin Chem. 1977 Jan;23(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E. C., Spector A. A. Effect of fatty acids on the binding of 1-anilino-8-naphthalenesulfonate to bovine serum albumin. Biochemistry. 1972 Jun 6;11(12):2299–2302. doi: 10.1021/bi00762a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm I., Ekman B., Kober A., Ljungstedt-Påhlman I., Seiving B., Sjödin T. Binding of drugs to human serum albumin:XI. The specificity of three binding sites as studied with albumin immobilized in microparticles. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):767–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudlow G., Birkett D. J., Wade D. N. Further characterization of specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):1052–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudlow G., Birkett D. J., Wade D. N. The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Nov;11(6):824–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillement J. P., Zini R., d' Athis P., Vassent G. Binding of certain acidic drugs to human albumin: theoretical and practical estimation of fundamental parameters. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1974 Jul 26;7(4):307–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00560349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanwimolruk S., Birkett D. J., Brooks P. M. Structural requirements for drug binding to site II on human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;24(3):458–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., van der Giesen W. F., Janssen L. H., Weideman M. M., Otagiri M., Perrin J. H. The effect of albumin conformation on the binding of warfarin to human serum albumin. The dependence of the binding of warfarin to human serum albumin on the hydrogen, calcium, and chloride ion concentrations as studied by circular dichroism, fluorescence, and equilibrium dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3032–3037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


