Abstract
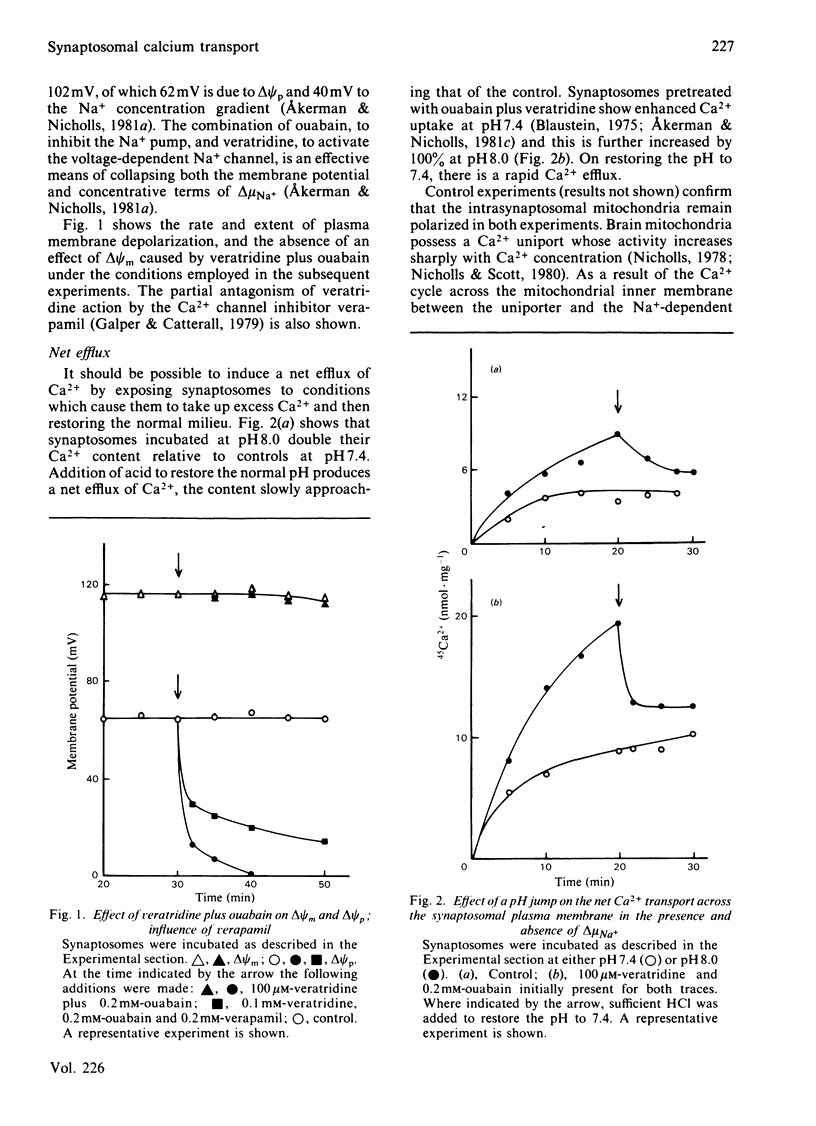
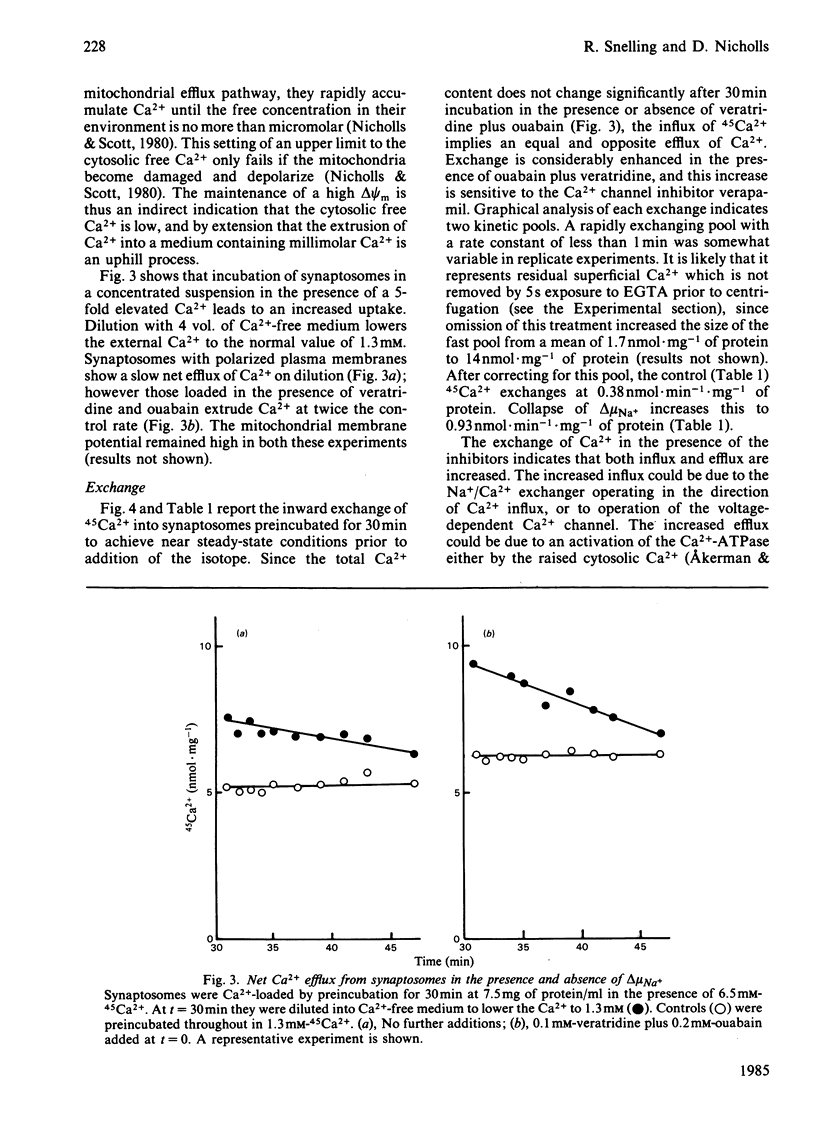
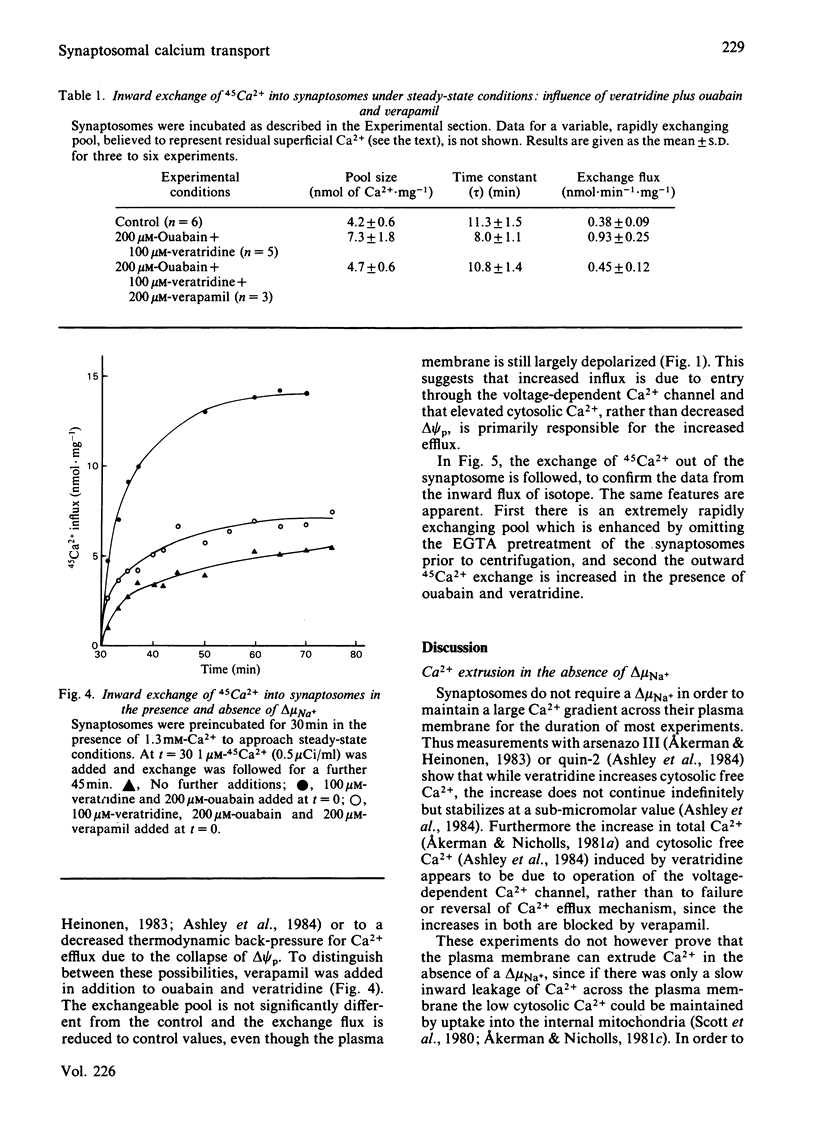
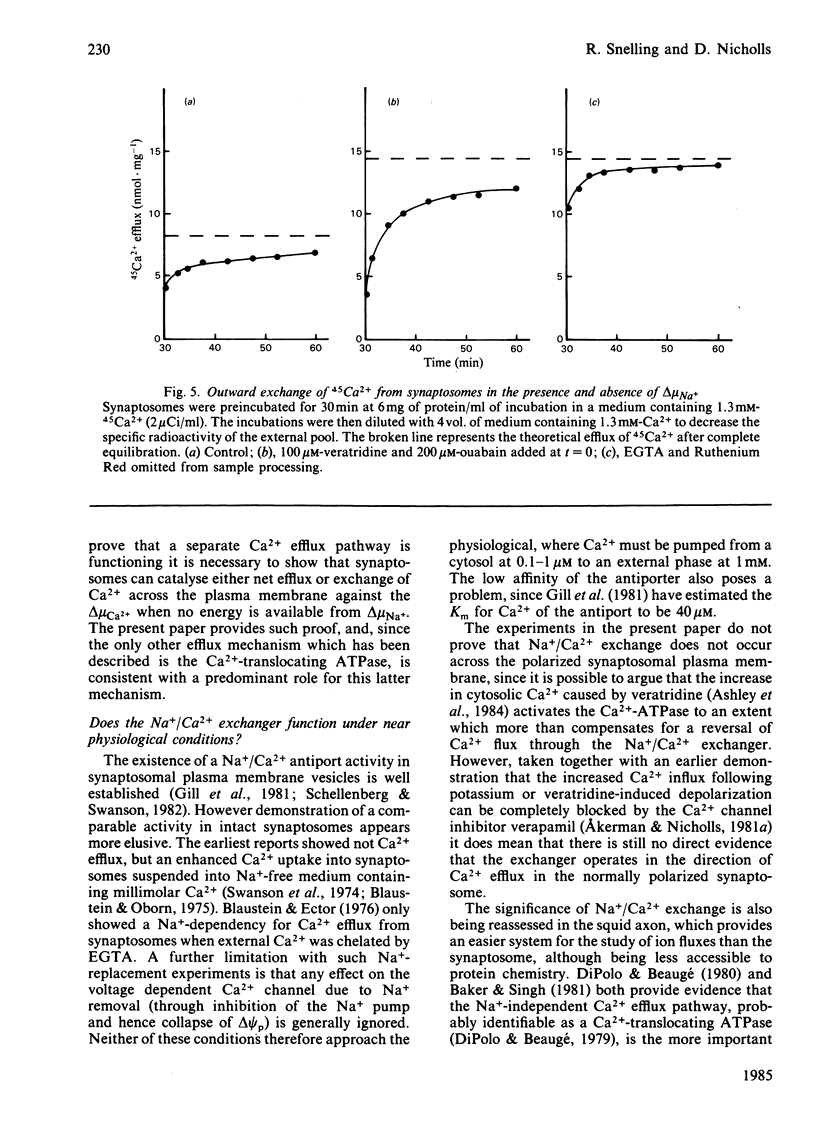
Ca2+ efflux from intact synaptosomes is investigated. Net efflux can be induced by returning synaptosomes from media with elevated Ca2+ or high pH to a normal medium. Net Ca2+ efflux is accelerated when the Na+ electrochemical potential gradient is collapsed by veratridine plus ouabain. Under steady-state conditions at 30 degrees C, Ca2+ cycles across the plasma membrane at 0.38 nmol . min-1 . mg-1 of protein. Exchange is increased by 145% by veratridine plus ouabain, both influx and efflux being increased. Increased influx is probably due to activation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels, since it is abolished by verapamil. The results indicate that, at least under conditions of low Na+ electrochemical gradient, some pathway other than a Na+/Ca2+ exchange must operate in the plasma membrane to expel Ca2+.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerman K. E., Heinonen E. Qualitative measurements of cytosolic calcium ion concentration within isolated guinea pig nerve endings using entrapped arsenazo III. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 13;732(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. ATP depletion increases Ca2+ uptake by synaptosomes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80979-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. Ca2+ transport by intact synaptosomes: the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel and a re-evaluation of the role of sodium/calcium exchange. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(3):491–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. Intrasynaptosomal compartmentation of calcium during depolarization-induced calcium uptake across the plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 6;645(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley R. H., Brammer M. J., Marchbanks R. Measurement of intrasynaptosomal free calcium by using the fluorescent indicator quin-2. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):149–158. doi: 10.1042/bj2190149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ector A. C. Carrier-mediated sodium-dependent and calcium-dependent calcium efflux from pinched-off presynaptic nerve terminals (synaptosomes) in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Effects of potassium, veratridine, and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):617–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Oborn C. J. The influence of sodium on calcium fluxes in pinched-off nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):657–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Kendrick N. C., Schweitzer E. S. Calcium buffering in presynaptic nerve terminals. I. Evidence for involvement of a nonmitochondrial ATP-dependent sequestration mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jul;72(1):15–41. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Schweitzer E. S. Calcium buffering in presynaptic nerve terminals. II. Kinetic properties of the nonmitochondrial Ca sequestration mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jul;72(1):43–66. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Villani F., Carafoli E. The cardiotoxic antibiotic doxorubicin inhibits the Na+/Ca2+ exchange of dog heart sarcolemmal vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 3;130(2):184–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPolo R., Beaugé L. Physiological role of ATP-driven calcium pump in squid axon. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):271–273. doi: 10.1038/278271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. J. Properties of the Ca(2+)-ATPase activity of mammalian synaptic membrane preparations. J Neurochem. 1976 Nov;27(5):1277–1279. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb00344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORNALL A. G., BARDAWILL C. J., DAVID M. M. Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem. 1949 Feb;177(2):751–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galper J. B., Catterall W. A. Inhibition of sodium channels by D600. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;15(1):174–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichida S., Kuo C. H., Matsuda T., Yoshida H. Effects of La+++, Mn++ and ruthenium red on Mg-Ca-ATPase activity and ATP-dependent Ca-binding of the synaptic plasma membrane. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1976 Feb;(1):39–43. doi: 10.1254/jjp.26.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. Calcium transport and porton electrochemical potential gradient in mitochondria from guinea-pig cerebral cortex and rat heart. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):511–522. doi: 10.1042/bj1700511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Scott I. D. The regulation of brain mitochondrial calcium-ion transport. The role of ATP in the discrimination between kinetic and membrane-potential-dependent calcium-ion efflux mechanisms. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):833–839. doi: 10.1042/bj1860833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D., Akerman K. Mitochondrial calcium transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 1;683(1):57–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff H., Abramovitz E. Calcium transport in a vesicular membrane preparation from rat brain synaptosomes. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D. Vanadate inhibition of brain (Ca + Mg)-ATPase. Neurochem Res. 1981 Mar;6(3):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00964038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Swanson P. D. Solubilization and reconstitution of membranes containing the Na+ -Ca2+ exchange carrier from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 25;690(1):133–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott I. D., Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. Calcium-ion transport by intact synaptosomes. Intrasynaptosomal compartmentation and the role of the mitochondrial membrane potential. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):873–880. doi: 10.1042/bj1920873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott I. D., Nicholls D. G. Energy transduction in intact synaptosomes. Influence of plasma-membrane depolarization on the respiration and membrane potential of internal mitochondria determined in situ. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):21–33. doi: 10.1042/bj1860021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobue K., Ichida S., Yoshida H., Yamazaki R., Kakiuchi S. Occurrence of a Ca2+- and modulator protein-activatable ATPase in the synaptic plasma membranes of brain. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 1;99(1):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson P. D., Anderson L., Stahl W. L. Uptake of calcium ions by synaptosomes from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 31;356(2):174–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


