Abstract
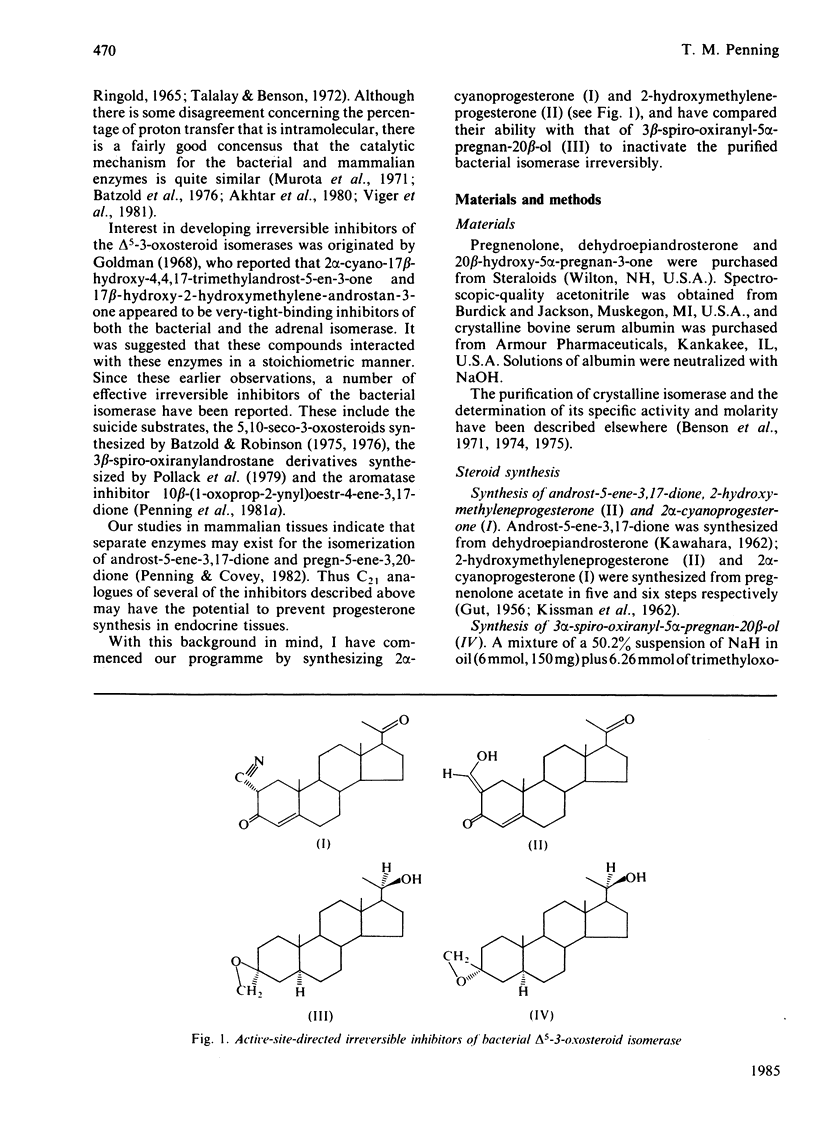
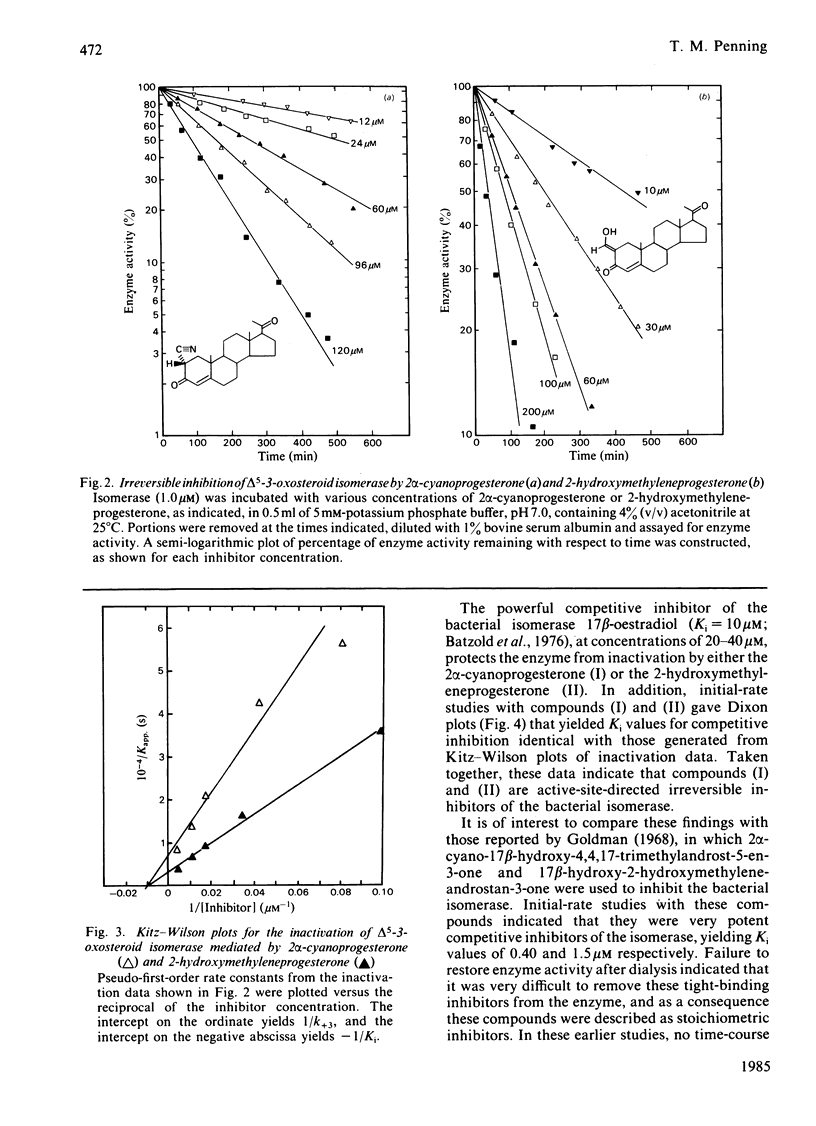
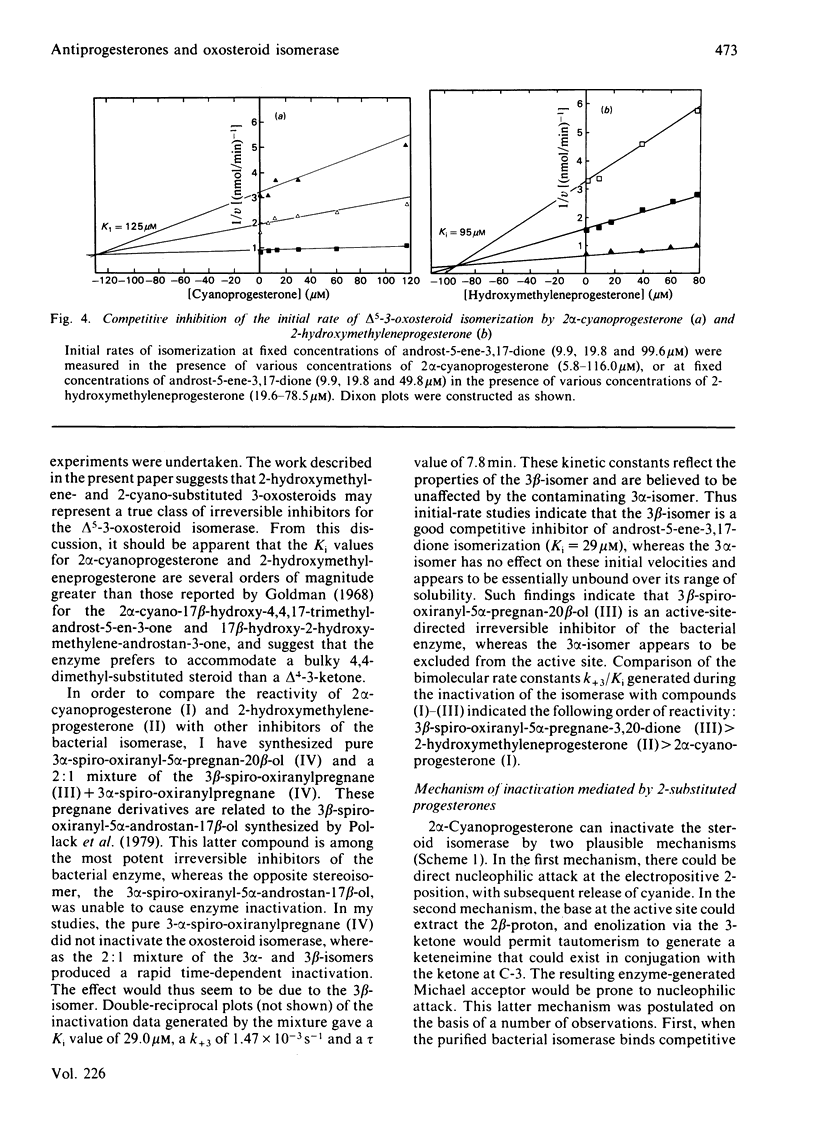
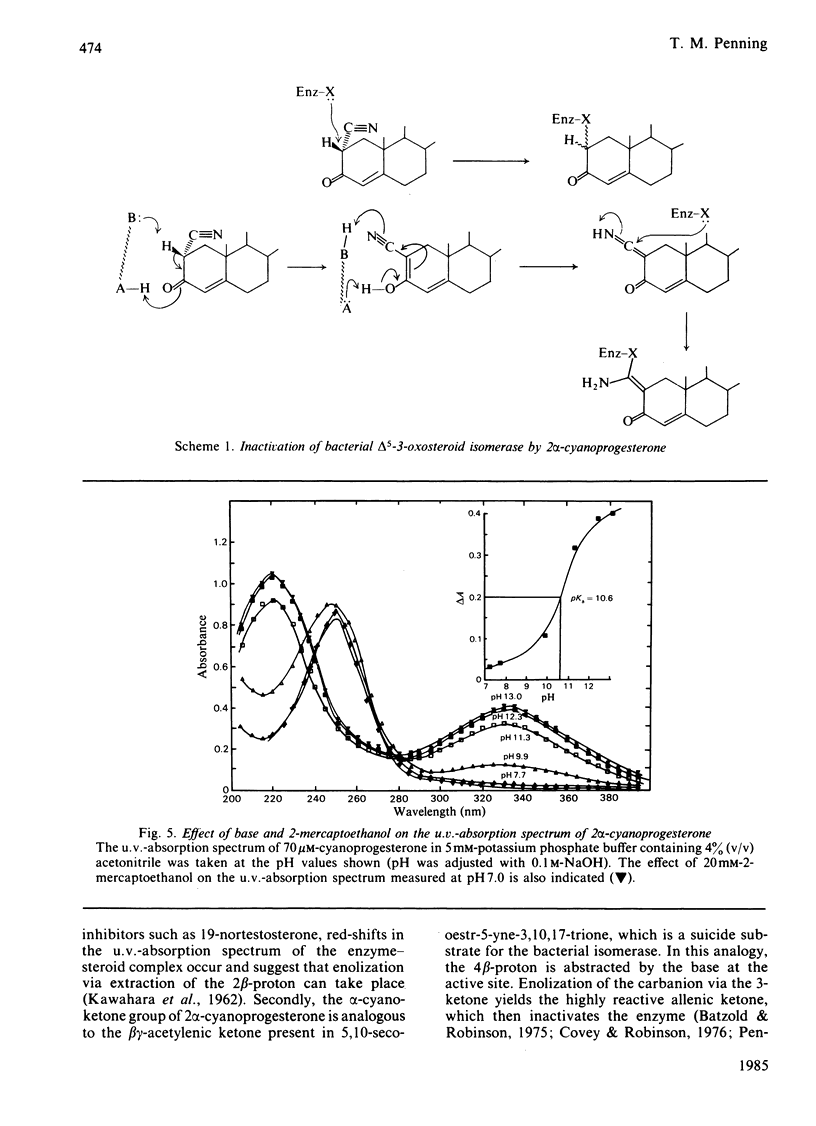
2 alpha-Cyanoprogesterone (I) and 2-hydroxymethyleneprogesterone (II) were synthesized and screened as irreversible active-site-directed inhibitors of the delta 5-3-oxosteroid isomerase (EC 5.3.3.1) from Pseudomonas testosteroni. Both compounds were found to inhibit the purified bacterial enzyme in a time-dependent manner. In either case the inactivated enzyme could be dialysed without return of activity, indicating that a stable covalent bond had formed between the inhibitor and the enzyme. Inactivation mediated by compounds (I) and (II) followed pseudo-first-order kinetics, and at higher inhibitor concentrations saturation was observed. The competitive inhibitor 17 beta-oestradiol offered protection against the inactivation mediated by both compounds, and initial-rate studies indicated that compounds (I) and (II) can also act as competitive inhibitors yielding Ki values identical with those generated during inactivation experiments. 2 alpha-Cyanoprogesterone (I) and 2-hydroxymethyleneprogesterone (II) thus appear to be active-site-directed. To compare the reactivity of these 2-substituted progesterones with other irreversible inhibitors of the isomerase, 3 beta-spiro-oxiranyl-5 alpha-pregnan-20 beta-ol (III) was synthesized as the C21 analogue of 3 beta-spiro-oxiranyl-5 alpha-androstan-17 beta-ol, which is a potent inactivator of the isomerase [Pollack, Kayser & Bevins (1979) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 91, 783-790]. Comparison of the bimolecular rate constants for inactivation (k+3/Ki) mediated by compounds (I)-(III) indicated the following order of reactivity: (III) greater than (II) greater than (I). 2-Mercaptoethanol offers complete protection against the inactivation of the isomerase mediated by 2 alpha-cyanoprogesterone (I). Under the conditions of inactivation compound (I) appears to be completely stable, and no evidence could be obtained for enolate ion formation in the presence or absence of enzyme. It is suggested that cyanoprogesterone inactivates the isomerase after direct nucleophilic attack at the electropositive 2-position, and that tautomerization plays no role in the inactivation event. By contrast, 2-mercaptoethanol offers no protection against the inactivation mediated by 2-hydroxymethyleneprogesterone, and under the conditions of inactivation this compound appears to exist in the semi-enolized form.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar M., Calder M., Smith T., Wright J. N. Mechanistic and stereochemical studies on 3-oxo steroid delta 4-delta 5-isomerase from human placenta. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 1;185(2):411–421. doi: 10.1042/bj1850411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alston T. A. Suicide substrates for mitochondrial enzymes. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;12(1):1–41. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzold F. H., Benson A. M., Covey D. F., Robinson C. H., Talalay P. The delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase reaction: catalytic mechanism, specificity and inhibition. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1976;14:243–267. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(76)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzold F. H., Robinson C. H. Letter: Irreversible inhibition of delta-5-3-ketosteroid isomerase by 5,10-secosteroids. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Apr 30;97(9):2576–2578. doi: 10.1021/ja00842a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzold F. H., Robinson C. H. Synthesis of beta,gamma-acetylenic 3-oxo steroids of the 5,10-seco series. J Org Chem. 1976 Jan 23;41(2):313–317. doi: 10.1021/jo00864a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. M., Jarabak R., Talalay P. The amino acid sequence of 5 -3-ketosteroid isomerase of Pseudomonas testosteroni. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7514–7525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. M., Suruda A. J., Shaw R., Talalay P. Affinity chromatography of 3-oxosteroid delta4--delta5-isomerase of Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 29;348(2):317–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. M., Suruda A. J., Talalay P. Concentration-dependent association of delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase of Pseudomonas testosteroni. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):276–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey D. F., Robinson C. H. Letter: Conjugated allenic 3-oxo-5,10-secosteroids. Irreversible inhibitors of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Aug 4;98(16):5038–5040. doi: 10.1021/ja00432a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman A. S. Further studies of steoidal inhibitors of delpha5, 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and delta5-delta4, 3-ketosteroid isomerase in Pseudomonas testosteroni and in bovine adrenals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Nov;28(11):1539–1546. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-11-1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAWAHARA F. S., WANG S. F., TALALAY P. The preparation and properties of crystalline delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1500–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITZ R., WILSON I. B. Esters of methanesulfonic acid as irreversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3245–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murota S., Fenselau C. C., Talalay P. Partial purification of a beef adrenal delta-5-3-ketosteroid isomerase and studies of its mechanism of action. Steroids. 1971 Jan;17(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(71)80113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Covey D. F. Inactivation of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase(s) from beef adrenal cortex by acetylenic ketosteroids. J Steroid Biochem. 1982 May;16(5):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(82)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Covey D. F., Talalay P. Inactivation of delta 5-3-oxo steroid isomerase with active-site-directed acetylenic steroids. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1930217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Covey D. F., Talalay P. Irreversible inactivation of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase of Pseudomonas testosteroni by acetylenic suicide substrates. Mechanism of formation and properties of the steroid-enzyme adduct. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6842–6850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack R. M., Kayser R. H., Bevins C. L. An active-site-directed irreversible inhibitor of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91948-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Riordan J. F. Chemical approaches to the properties of active sites of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:733–794. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


