Abstract
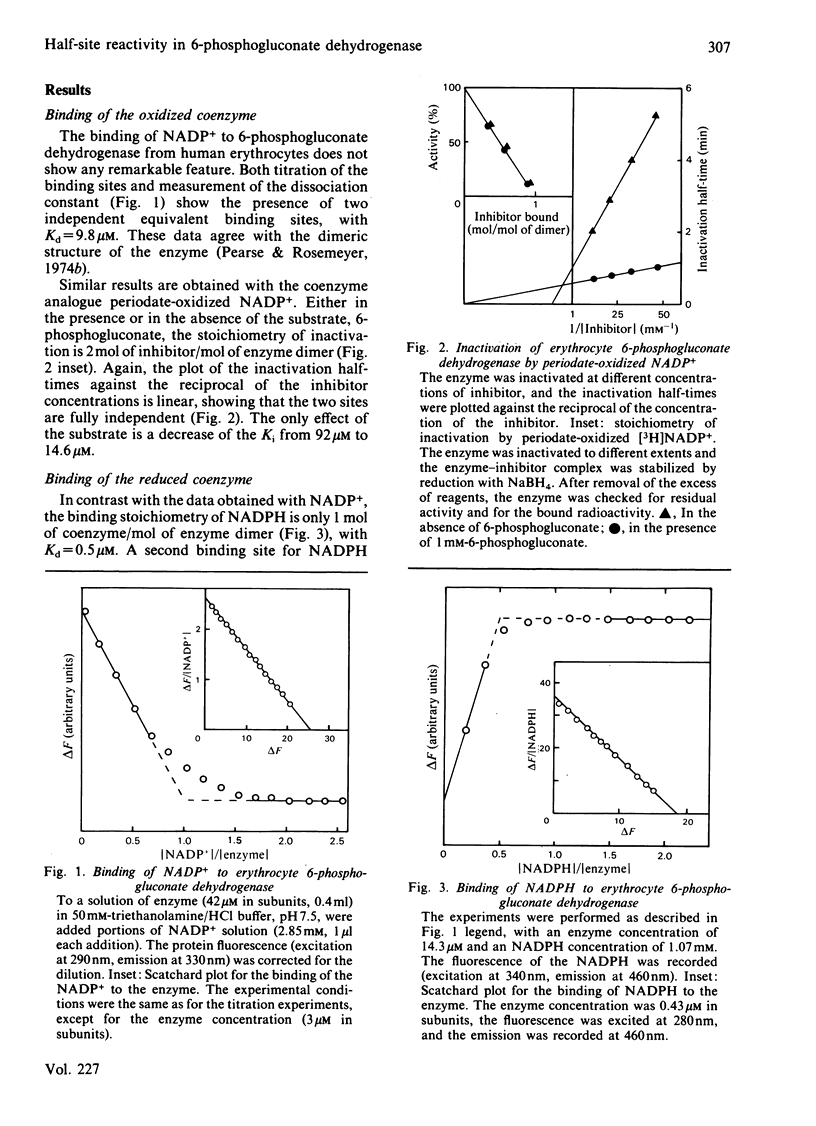
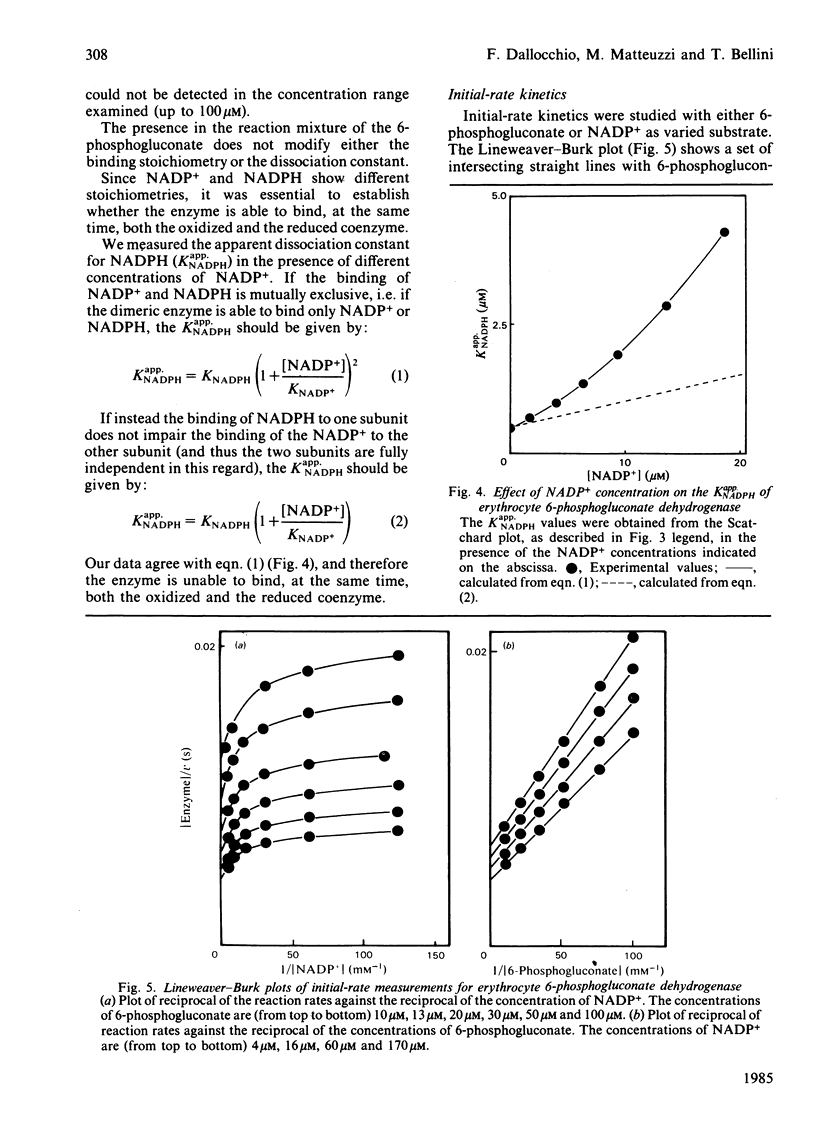
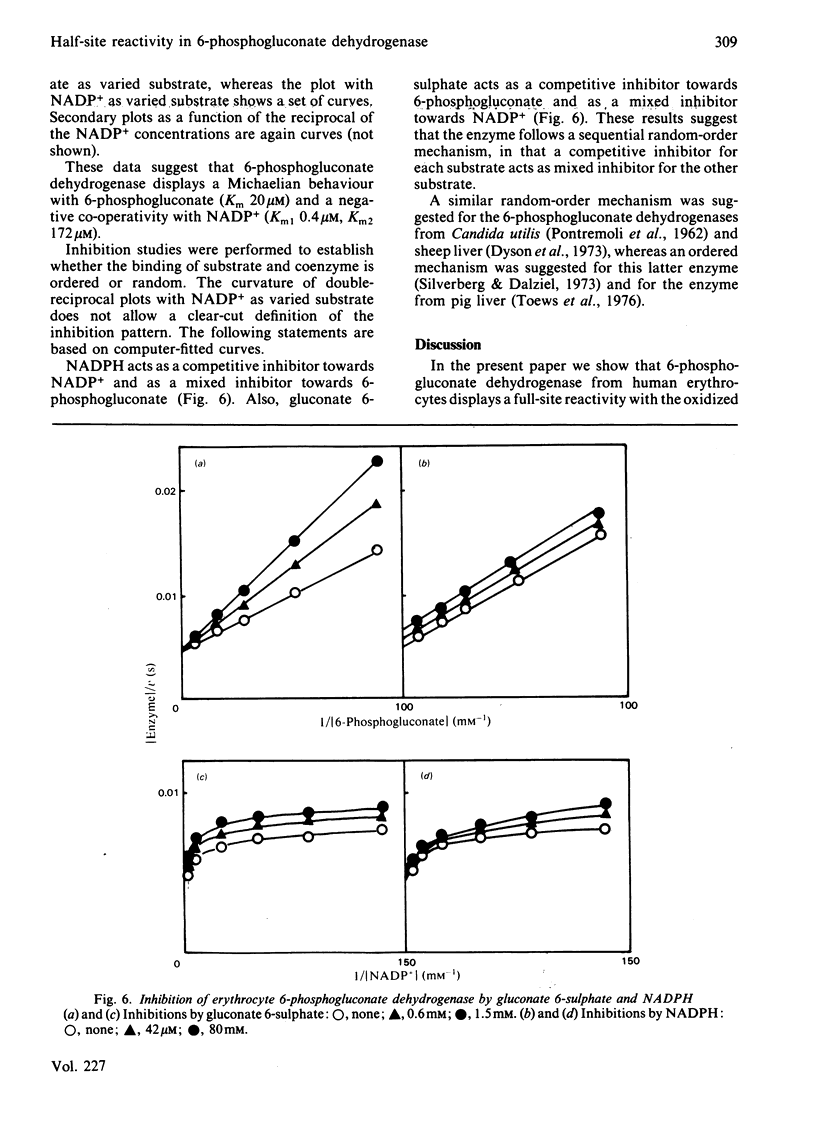
6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from human erythrocytes was purified by an improved procedure. Binding studies showed that the dimeric enzyme binds 2 mol of NADP+/mol but only 1 mol of NADPH/mol, and that the bindings of oxidized and reduced coenzyme are mutually exclusive. From initial-rate kinetics and inhibition studies, a sequential random-order mechanism is proposed. Double-reciprocal plots with NADP+ as varied substrate show a downward curvature, indicating a negative co-operativity. We suggest that the negative co-operativity observed kinetically is a result of the half-site reactivity for the NADPH. The different binding stoichiometries for NADP+ and NADPH generate a non-linear relationship between the apparent dissociation constant for the NADPH and the concentrations of the NADP+, resulting in a regulatory mechanism highly sensitive to the changes in the NADP+/NADPH ratio.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellini T., Signorini M., Dallocchio F., Rippa M. Affinity labelling of the NADP+-binding site of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Candida utilis. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):297–302. doi: 10.1042/bj1830297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallocchio F., Negrini R., Signorini M., Rippa M. Identification of the chemical groups involved in the binding of periodate-oxidized NADP+ to 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel Keith, Engel Paul C. Antagonistic homotropic interactions as a possible explanation of coenzyme activation of glutamate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1968 Oct;1(5):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Flora A., Morelli A., Benatti U., Giuliano F., Molinari M. P. Human erythrocyte glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Interaction with oxidized and reduced coenzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):999–1005. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Flora A., Morelli A., Giuliano F. Human erythrocyte glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Content of bound coenzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 10;59(1):406–413. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson J. E., D'Orazio R. E., Hanson W. H. Sheep liver 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase: isolation procedure and effect of pH, ionic strength, and metal ions on the kinetic parameters. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Feb;154(2):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurganov B. I., Sugrobova N. P., Yakovlev V. A. Estimation of dissociation constant of enzyme-ligand complex from fluorometric data by "difference" method. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 1;19(4):308–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb C. J., Rubery P. H. Inhibition of co-operative enzymes by substrate-analogues: possible implications for the physiological significance of negative co-operativity illustrated by phenylalanine metabolism in higher plants. J Theor Biol. 1976 Aug 7;60(2):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morelli A. Rapid purification of human erythrocyte 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase by means of affinity chromatography. Ital J Biochem. 1979 Jul-Aug;28(4):280–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONTREMOLI S., GRAZI E., DE FLORA A., MANGIAROTTI G. [Kinetic properties of D-gluconate-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and the activating effect of the magnesium ion]. Arch Sci Biol (Bologna) 1962 Jan-Mar;46:83–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Rosemeyer M. A. Human 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Purification of the erythrocyte enzyme and the influence of ions and NADPH on its activity. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):213–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Rosemeyer M. A. The molecular weight and subunit structure of human erythrocyte 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippa M., Signorini M. 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from Candida utilis. Methods Enzymol. 1975;41:237–240. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)41054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Dalziel K. Crystalline 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from sheep liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 5;38(2):229–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Dalziel K. Fluorescence studies of coenzyme binding to 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):646–651. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L., Kanji M. I., Carper W. R. 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Purification and kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7127–7131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


