Abstract
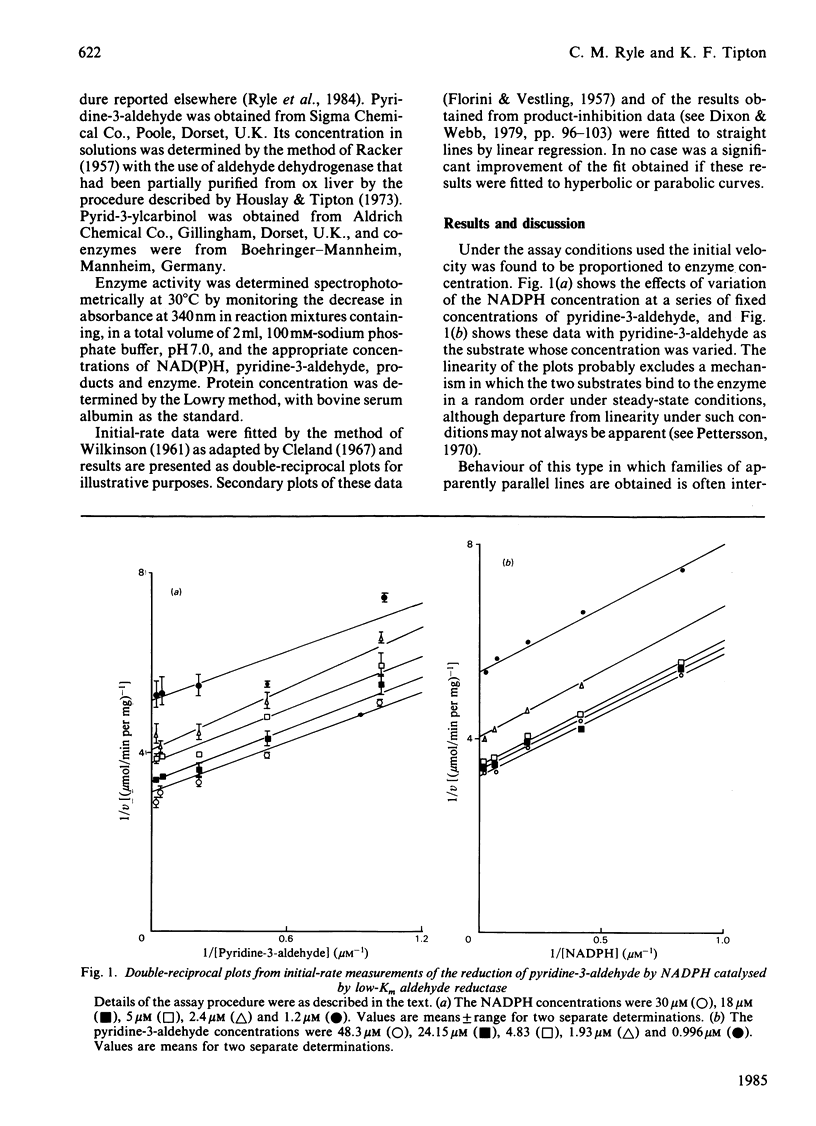
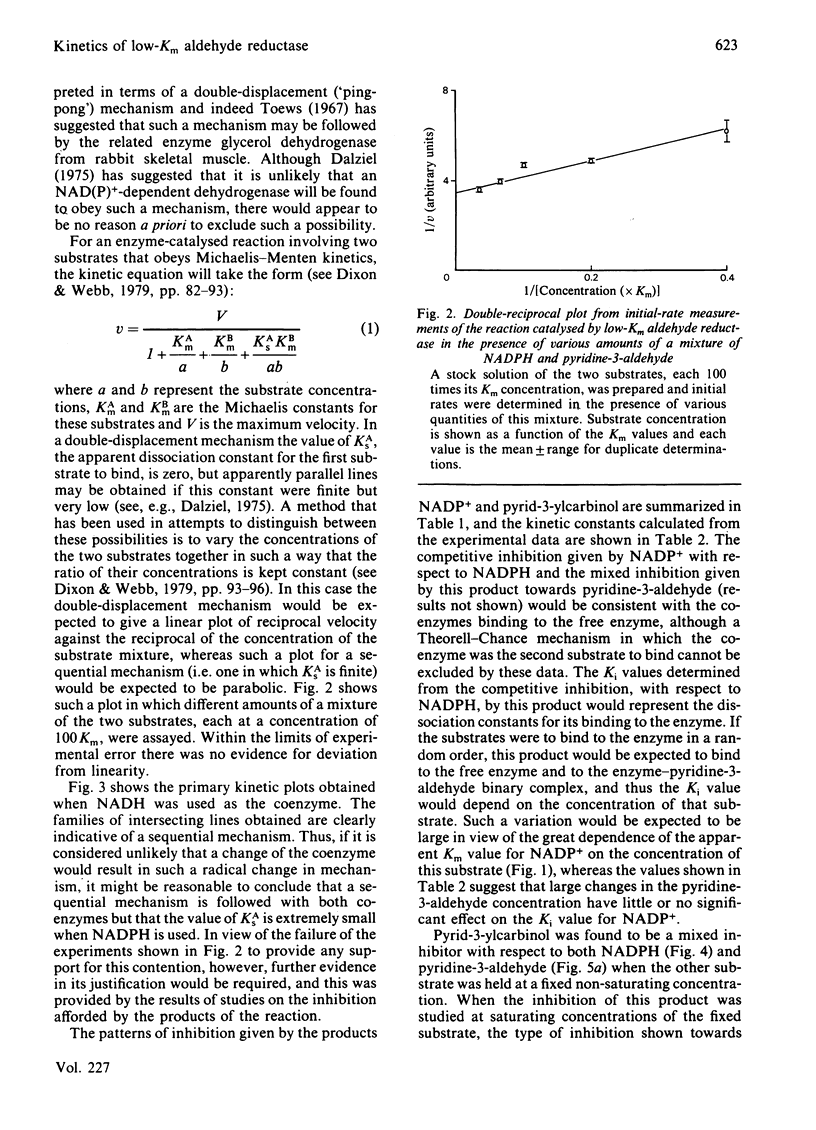
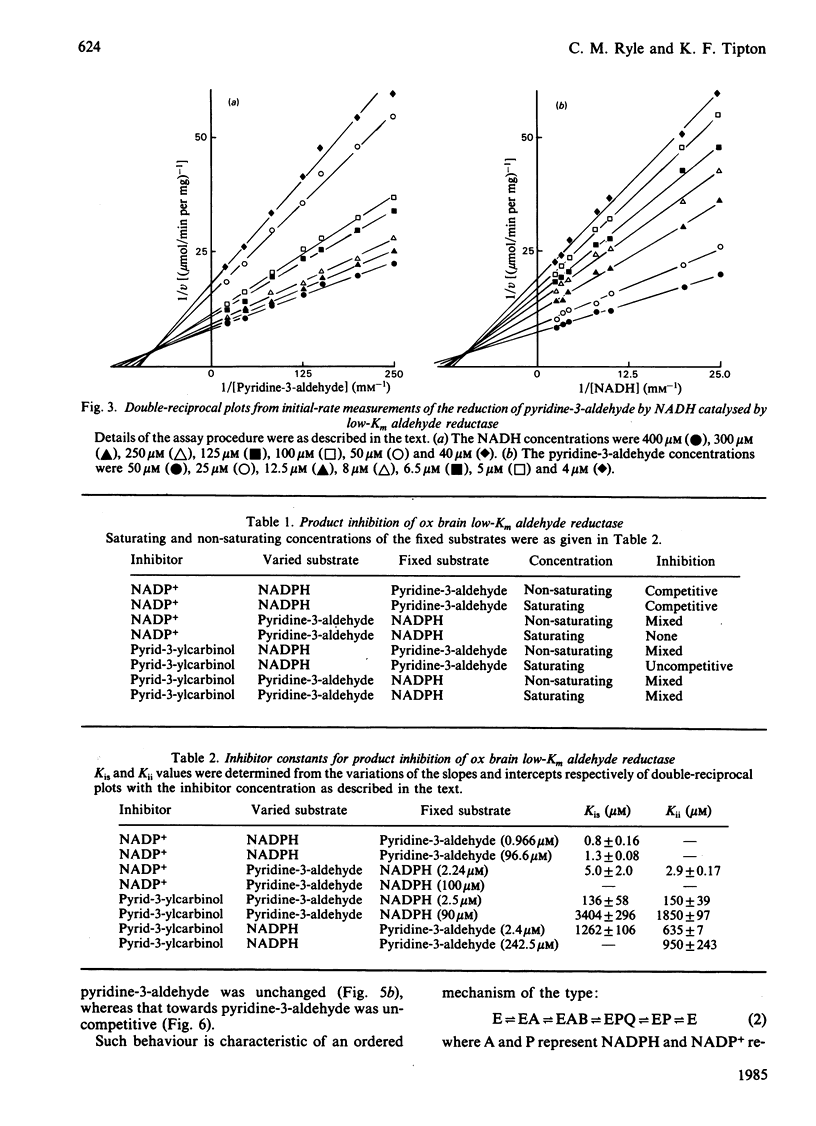
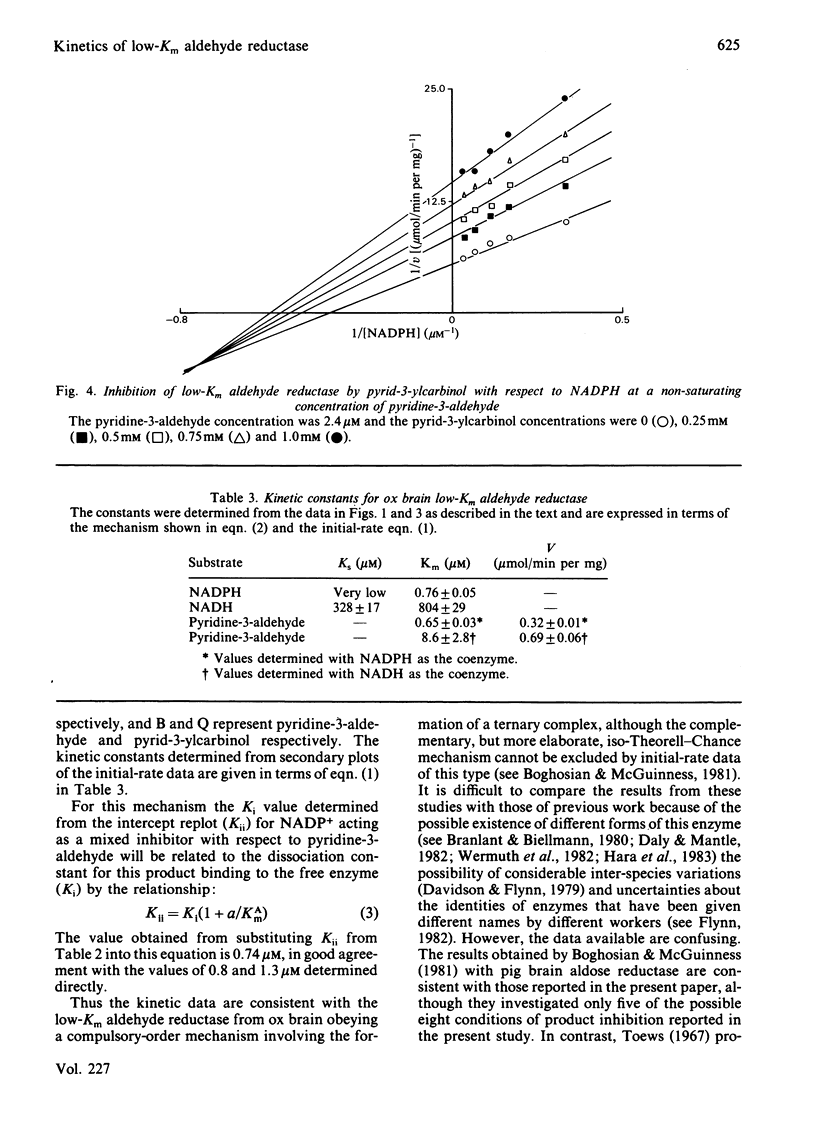
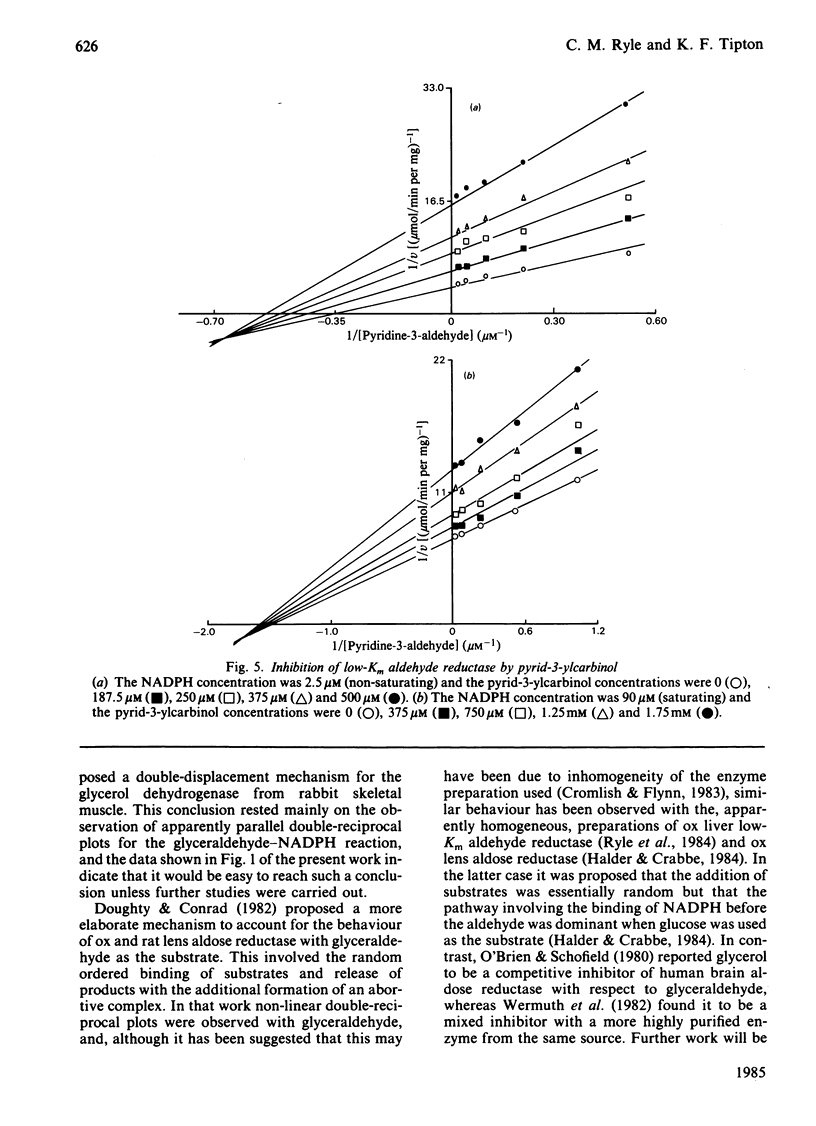
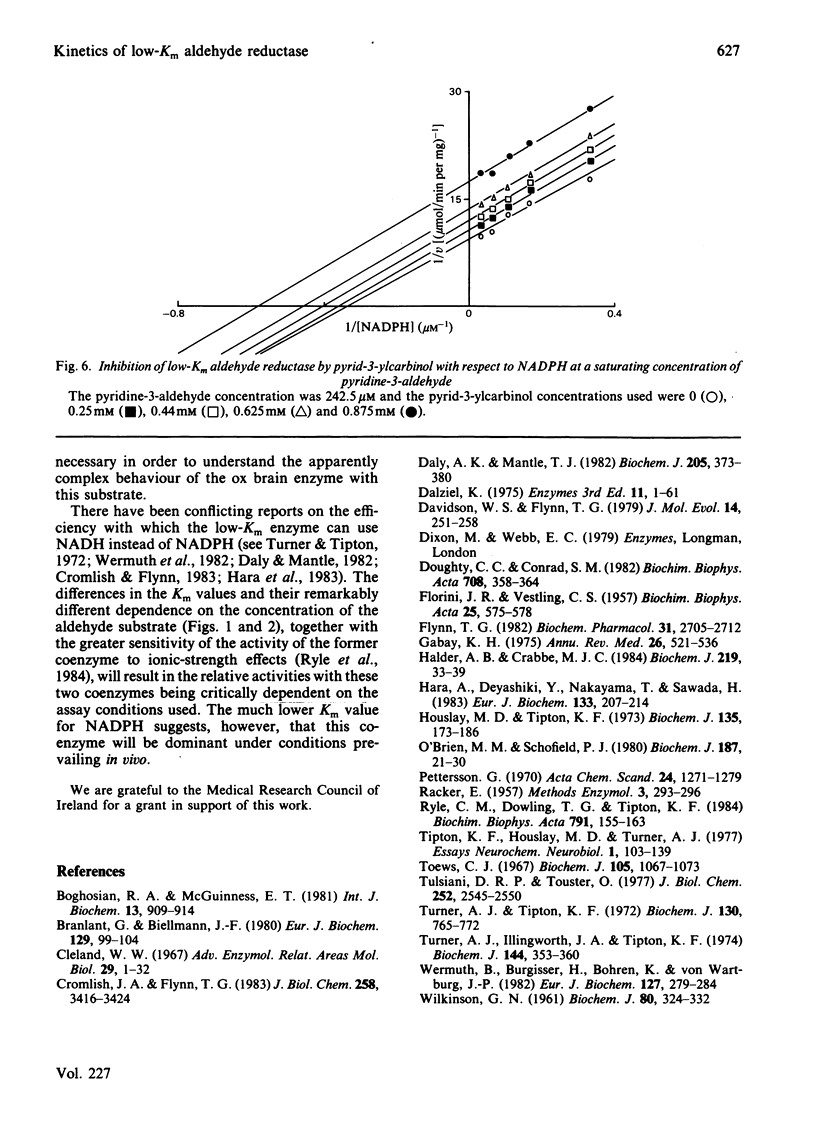
Initial-rate studies of the low-Km aldehyde reductase-catalysed reduction of pyridine-3-aldehyde by NADPH gave families of parallel double-reciprocal plots, consistent with a double-displacement mechanism being obeyed. Studies on the variation of the initial velocity with the concentration of a mixture of the two substrates were also consistent with a double-displacement mechanism. In contrast, the initial-rate data indicated that a sequential mechanism was followed when NADH was used as the coenzyme. Product-inhibition studies, however, indicated that a compulsory-order mechanism was followed in which NADPH bound before pyridine-3-aldehyde with a ternary complex being formed and the release of pyrid-3-ylcarbinol before NADP+. The apparently parallel double-reciprocal plots obtained in the initial-rate studies with NADPH and pyridine-3-aldehyde were thus attributed to the apparent dissociation constant for the binary complex between the enzyme and coenzyme being finite but very low.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boghosian R. A., McGuinness E. T. Pig brain aldose reductase: a kinetic study using the centrifugal fast analyzer. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(8):909–914. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant G. Properties of an aldose reductase from pig lens. Comparative studies of an aldehyde reductase from pig lens. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromlish J. A., Flynn T. G. Purification and characterization of two aldose reductase isoenzymes from rabbit muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3416–3424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly A. K., Mantle T. J. Purification and characterization of the multiple forms of aldehyde reductase in ox kidney. Biochem J. 1982 Aug 1;205(2):373–380. doi: 10.1042/bj2050373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. S., Flynn T. G. Compositional relatedness of aldehyde reductases from several species. J Mol Evol. 1979 Dec;14(4):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF01732492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty C. C., Conrad S. M. A reaction mechanism for aldose reductase from lens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 19;708(3):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90449-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLORINI J. R., VESTLING C. S. Graphical determination of the dissociation constants for two-substrate enzyme systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):575–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90529-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. G. Aldehyde reductases: monomeric NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases with multifunctional potential. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Sep 1;31(17):2705–2712. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H. Hyperglycemia, polyol metabolism, and complications of diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:521–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.002513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halder A. B., Crabbe M. J. Bovine lens aldehyde reductase (aldose reductase). Purification, kinetics and mechanism. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):33–39. doi: 10.1042/bj2190033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Deyashiki Y., Nakayama T., Sawada H. Isolation and characterization of multiforms of aldehyde reductase in chicken kidney. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Tipton K. F. The nature of the electrophoretically separable multiple forms of rat liver monoamine oxidase. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):173–186. doi: 10.1042/bj1350173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. M., Schofield P. J. Polyol-pathway enzymes of human brain. Partial purification and properties of aldose reductase and hexonate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):21–30. doi: 10.1042/bj1870021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson G. Asymptotic properties of enzymatic rate equations of the Wong-Hanes type. Acta Chem Scand. 1970;24(4):1271–1274. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.24-1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryle C. M., Dowling T. G., Tipton K. F. Purification and properties of low-Km aldehyde reductase from ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 7;791(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipton K. F., Houslay M. D., Turner A. J. Metabolism of aldehydes in brain. Essays Neurochem Neuropharmacol. 1977;1:103–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews C. J. The kinetics and reaction mechanism of the nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific glycerol dehydrogenase of rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1067–1073. doi: 10.1042/bj1051067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Touster Resolution and partial characterization of two aldehyde reductases of mammalian liver. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2545–2550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. J., Illingworth J. A., Tipton K. F. Simulation of biogenic amine metabolism in the brain. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):353–360. doi: 10.1042/bj1440353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. J., Tipton K. F. The characterization of two reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked aldehyde reductases from pig brain. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):765–772. doi: 10.1042/bj1300765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wermuth B., Bürgisser H., Bohren K., von Wartburg J. P. Purification and characterization of human-brain aldose reductase. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):279–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


