Abstract
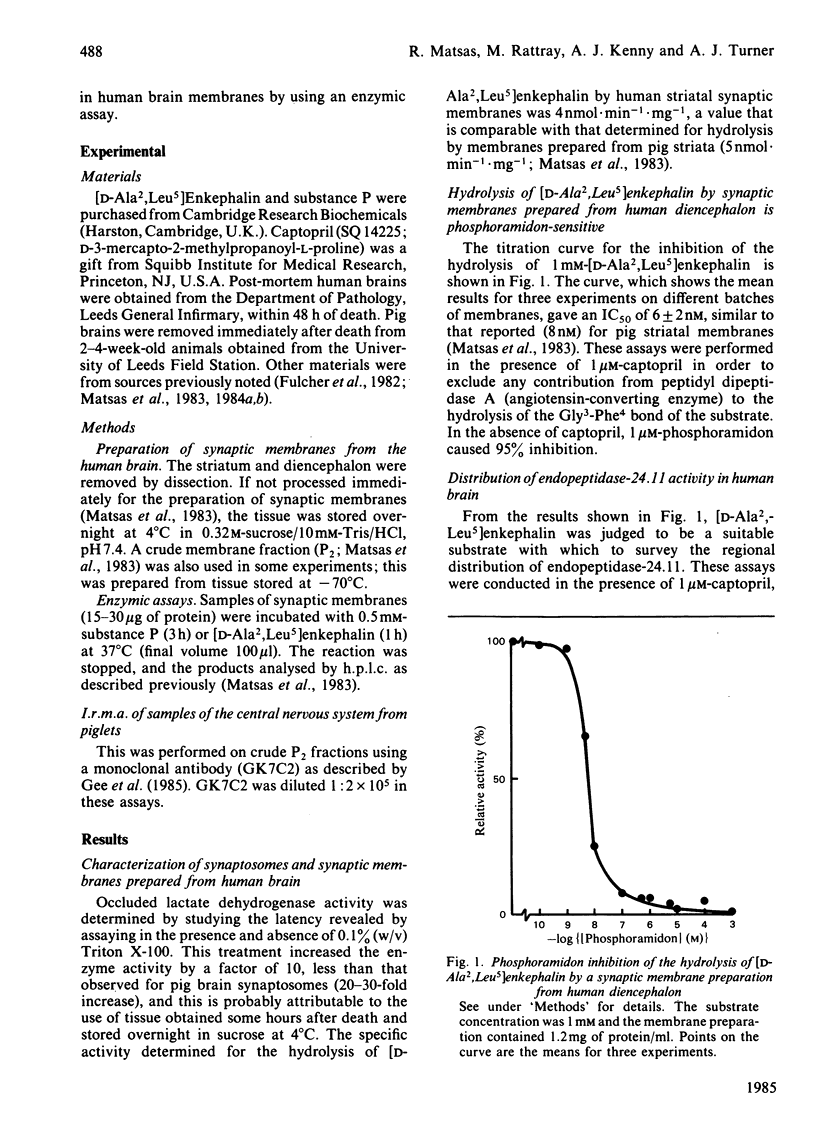
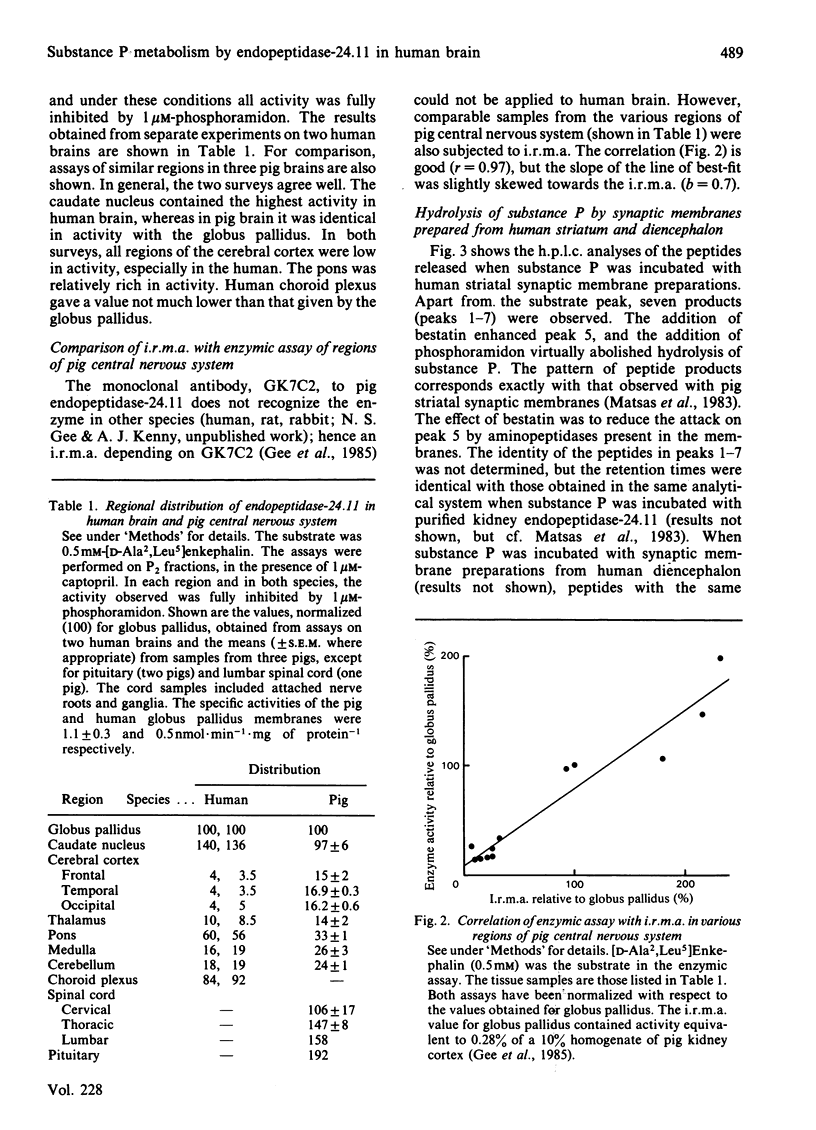
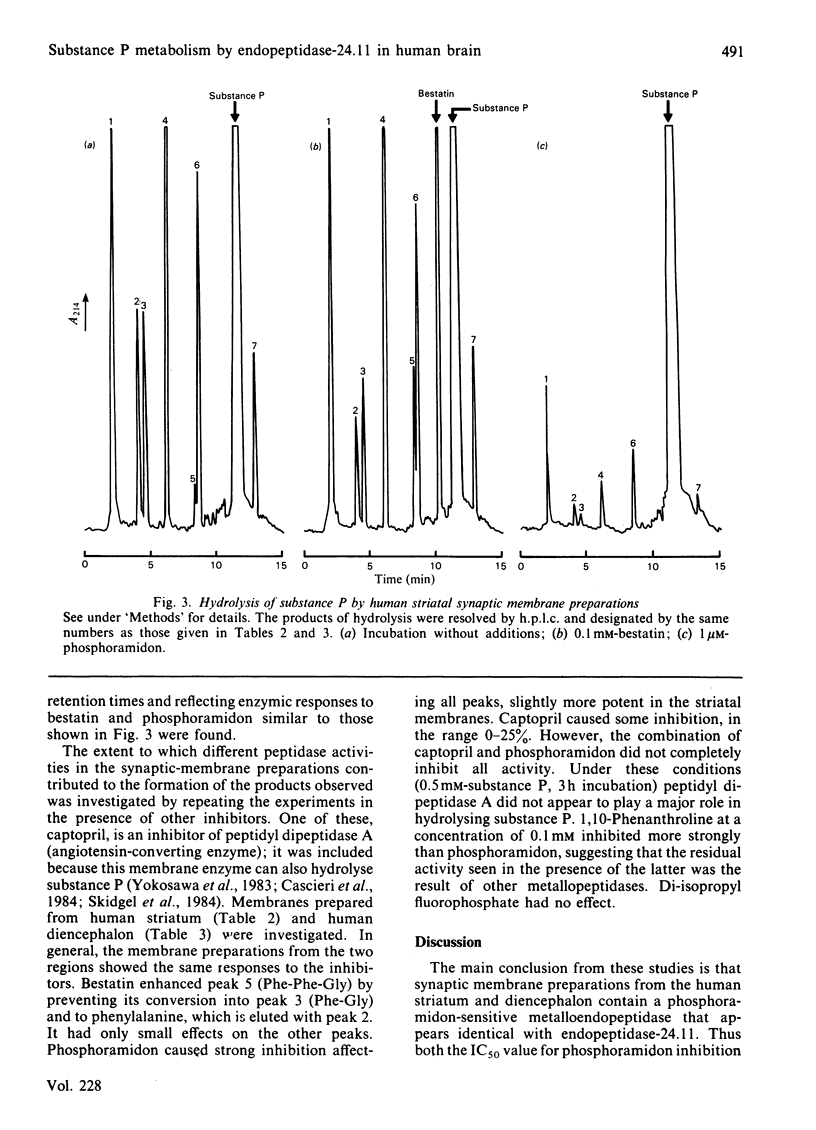
Synaptic membrane preparations from human striatum and human diencephalon were shown to contain a phosphoramidon-sensitive metalloendopeptidase that appeared identical with endopeptidase-24.11. The activity of endopeptidase-24.11 was determined with an enzymic assay employing [D-Ala2,Leu5]enkephalin as substrate, and its distribution in human brain was similar to that in pig brain, with the striatum containing the highest levels. The choroid plexus and pons also contained substantial activity. A good correlation (r = 0.97) was obtained for the distribution of the endopeptidase in pig brain and pituitary by the enzymic assay and by an immunoradiometric assay specific for pig endopeptidase-24.11. Synaptic membrane preparations from human striatum and diencephalon hydrolysed substance P at the same sites as did preparations of pig striatal synaptic membranes, and hydrolysis was substantially abolished by phosphoramidon. These results suggest that endopeptidase-24.11 is the principal enzyme hydrolysing substance P in human synaptic membrane preparations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almenoff J., Orlowski M. Biochemical and immunological properties of a membrane-bound brain metalloendopeptidase: comparison with thermolysin-like kidney neutral metalloendopeptidase. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):151–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Bull H. G., Mumford R. A., Patchett A. A., Thornberry N. A., Liang T. Carboxyl-terminal tripeptidyl hydrolysis of substance P by purified rabbit lung angiotensin-converting enzyme and the potentiation of substance P activity in vivo by captopril and MK-422. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Kidney neutral endopeptidase and the hydrolysis of enkephalin by synaptic membranes show similar sensitivity to inhibitors. Biochem J. 1982 May 1;203(2):519–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2030519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Matsas R., Kenny A. J. A monoclonal antibody to kidney endopeptidase-24.11. Its application in immunoadsorbent purification of the enzyme and immunofluorescent microscopy of kidney and intestine. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):377–386. doi: 10.1042/bj2140377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsthemke B., Leblanc P., Kordon C., Wattiaux-De Coninck S., Wattiaux R., Bauer K. Subcellular distribution of particle-bound neutral peptidases capable of hydrolyzing gonadoliberin, thyroliberin, enkephalin and substance P. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 1;139(2):315–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Sandberg B. E., Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Purification and characterisation of a membrane-bound substance-P-degrading enzyme from human brain. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):315–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Endopeptidase-24.11 and aminopeptidase activity in brain synaptic membranes are jointly responsible for the hydrolysis of cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8). FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80583-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A., Engelbrecht S., Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Hydrolysis of substance p and neurotensin by converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. Peptides. 1984 Jul-Aug;5(4):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa H., Endo S., Ogura Y., Ishii S. A new feature of angiotensin-converting enzyme in the brain: hydrolysis of substance P. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90586-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


