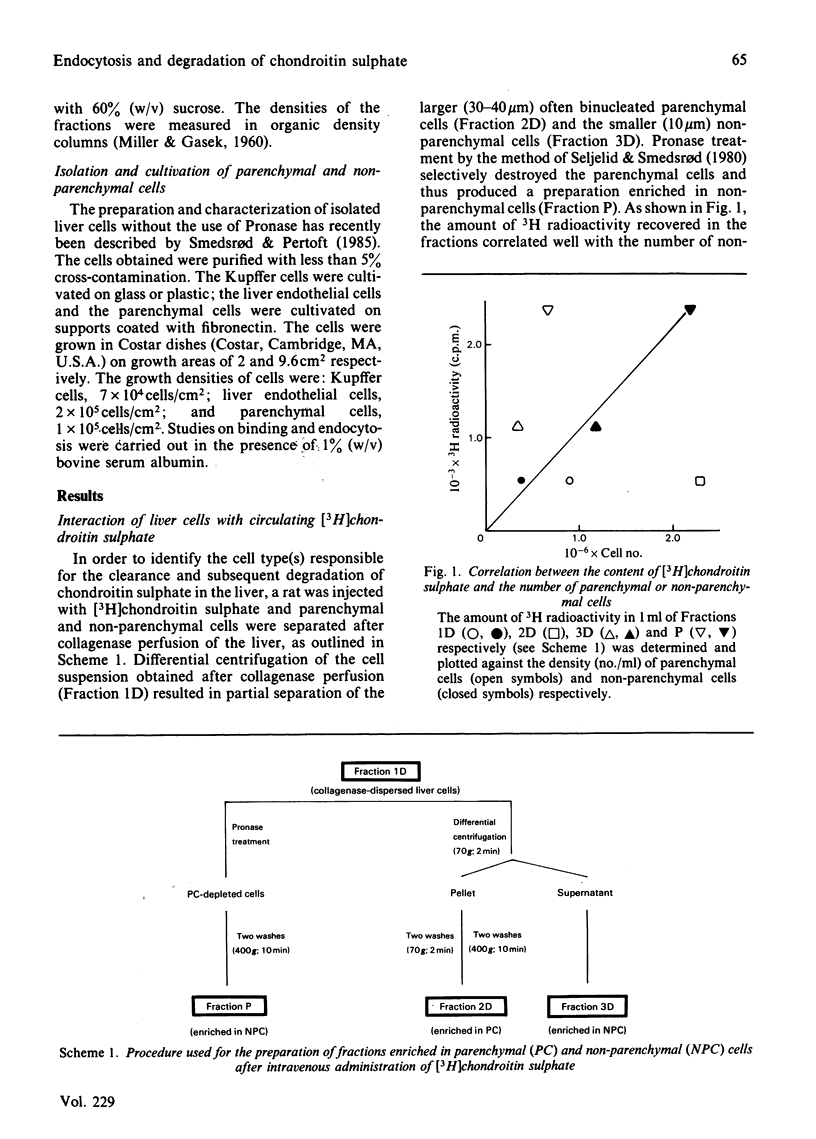
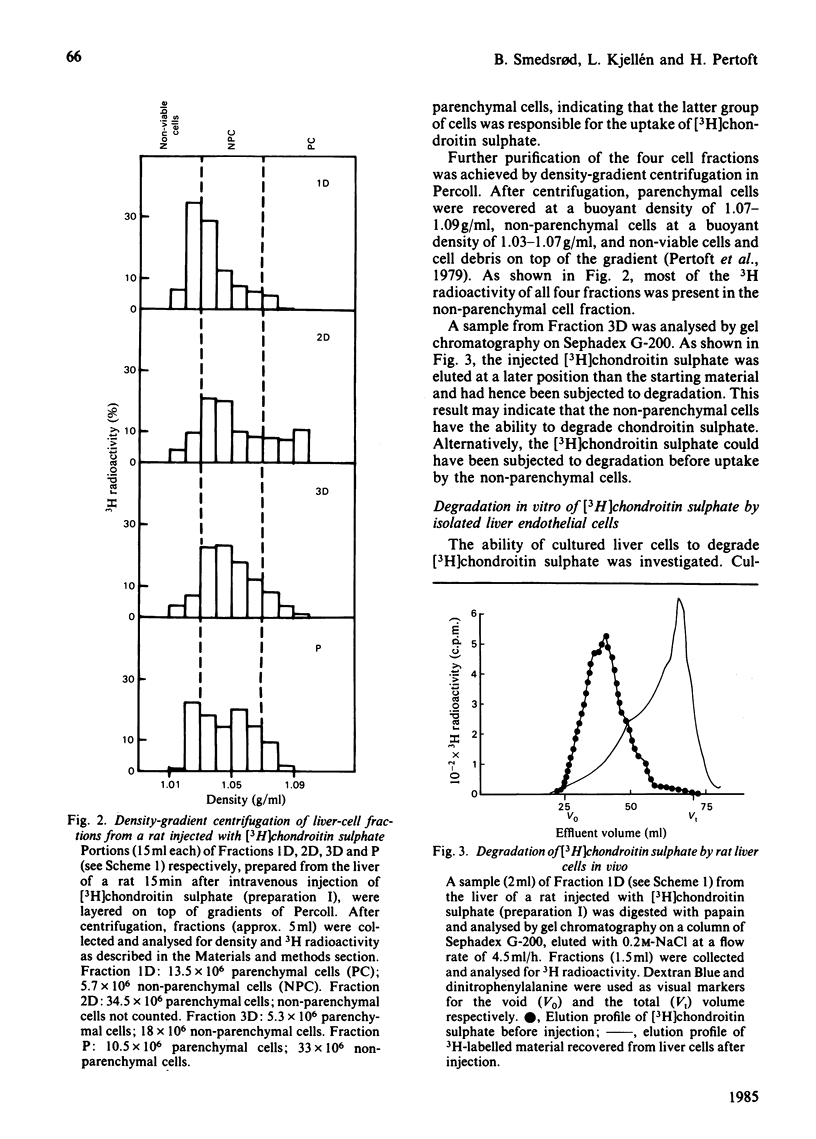
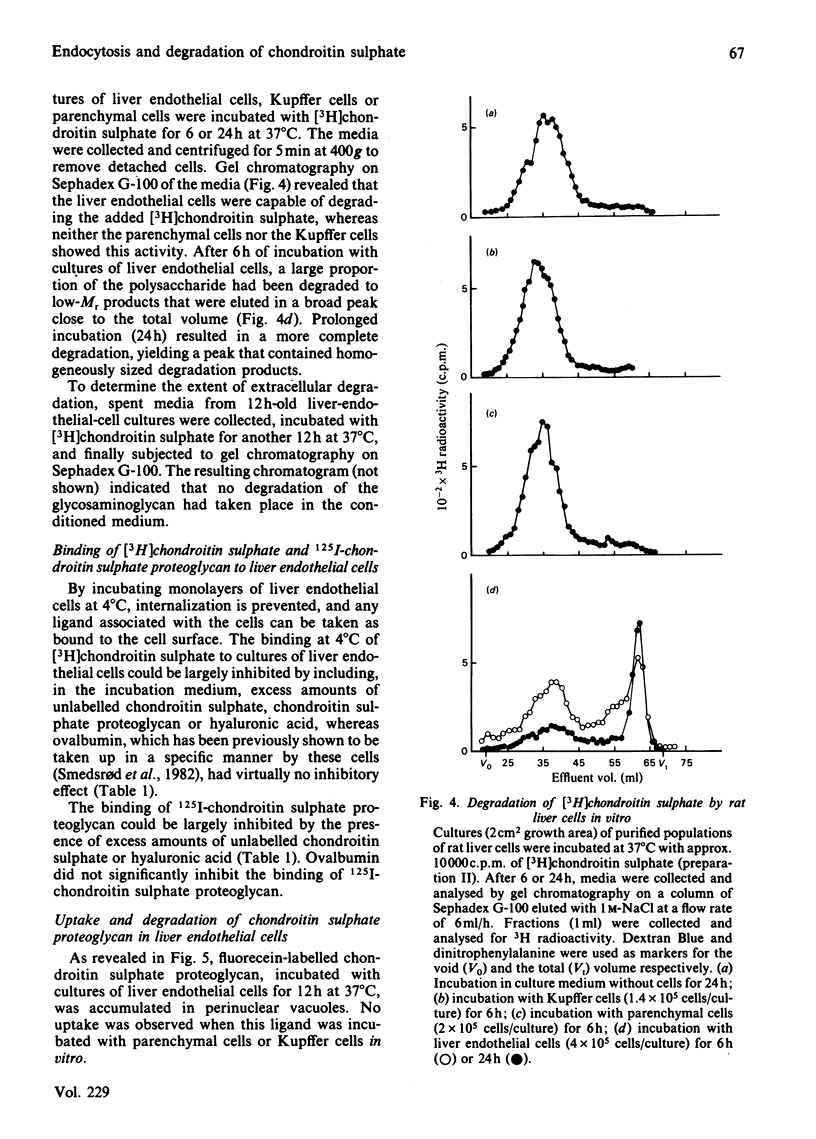
Abstract
Intravenously administered chondroitin sulphate, chemically labelled by [3H]acetylation of partially deacetylated polysaccharide, was taken up and degraded by the non-parenchymal cells of the liver. Studies using primary monolayer cultures of pure Kupffer cells, liver endothelial cells and parenchymal cells revealed that [3H]chondroitin sulphate was taken up and degraded by the liver endothelial cells only. Binding studies at 4 degrees C with [3H]chondroitin sulphate and 125I-chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan indicated that the glycosaminoglycan and the proteoglycan are recognized by the same binding sites on the liver endothelial cells. The ability of hyaluronic acid to compete with the labelled ligands for binding suggested that the binding site is identical with the recently described hyaluronate receptor on the liver endothelial cells [Smedsrød, Pertoft, Eriksson, Fraser & Laurent (1984) Biochem. J. 223, 617-626]. Fluorescein-labelled chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan accumulated in perinuclear vesicles of the liver endothelial cells, indicating that the proteoglycan is internalized and transported to the lysosomes. The finding that [3H]chondroitin sulphate and 125I-chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan were degraded by the liver endothelial cells to low-molecular-mass radioactive products suggested that both the polysaccharide chain and the core protein were catabolized by the cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calatroni A., Donnelly P. V., Di Ferrante N. The glycosaminoglycans of human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):332–343. doi: 10.1172/JCI105989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Riesenfeld J., Lindahl U. N-[3H]Acetyl-labeling, a convenient method for radiolabeling of glycosaminoglycans. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):236–245. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90580-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolset S. O., Kjellén L., Seljelid R., Lindahl U. Changes in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis during differentiation in vitro of human monocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):661–667. doi: 10.1042/bj2100661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse H., Tekolf W., von Figura K., Buddecke E. Metabolism of sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cultivated bovine arterial cells. II. Quantitative studies on the uptake of 35SO4-labeled proteoglycans. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Jun;356(6):943–952. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.s1.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse H., Truppe W. Untersuchungen zur Pinozytose von Proteoglykanen und Glykosaminoglykanen. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1978 Mar 17;90(6):188–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER G. L., GASEK J. M. Drift of drops in density gradient columns. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:78–87. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B. Hepatocyte--collagen adhesion. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):513–529. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz R., Schwermann J., Buddecke E., von Figura K. Endocytosis of sulphated proteoglycans by cultured skin fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):671–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1760671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Uzman B. G. Uptake of chondroitin sulfate by mammalian cells in culture. II. Kinetics of uptake and autoradiography. Exp Cell Res. 1971 May;66(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. D., Brown H. L., Lowther D. A. Degradation of proteoglycan in articular cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):536–544. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Pertoft H., Eriksson S., Fraser J. R., Laurent T. C. Studies in vitro on the uptake and degradation of sodium hyaluronate in rat liver endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):617–626. doi: 10.1042/bj2230617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truppe W., Kresse H. Uptake of proteoglycans and sulfated glycosaminoglycans by cultured skin fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A., Lindahl U., Hallén A. Mode of degradation of the chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan in rat costal cartilage. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):729–738. doi: 10.1042/bj1300729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. M., Curtis C. G., Powell G. M., Wusteman F. S. The metabolic fate of intravenously injected peptide-bound chondroitin sulphate in the rat. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 15;158(1):39–46. doi: 10.1042/bj1580039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. M., Wusteman F. S., Curtis C. G. The degradation of intravenously injected chondroitin 4-sulphate in the rat. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1009–1013. doi: 10.1042/bj1341009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]