Abstract
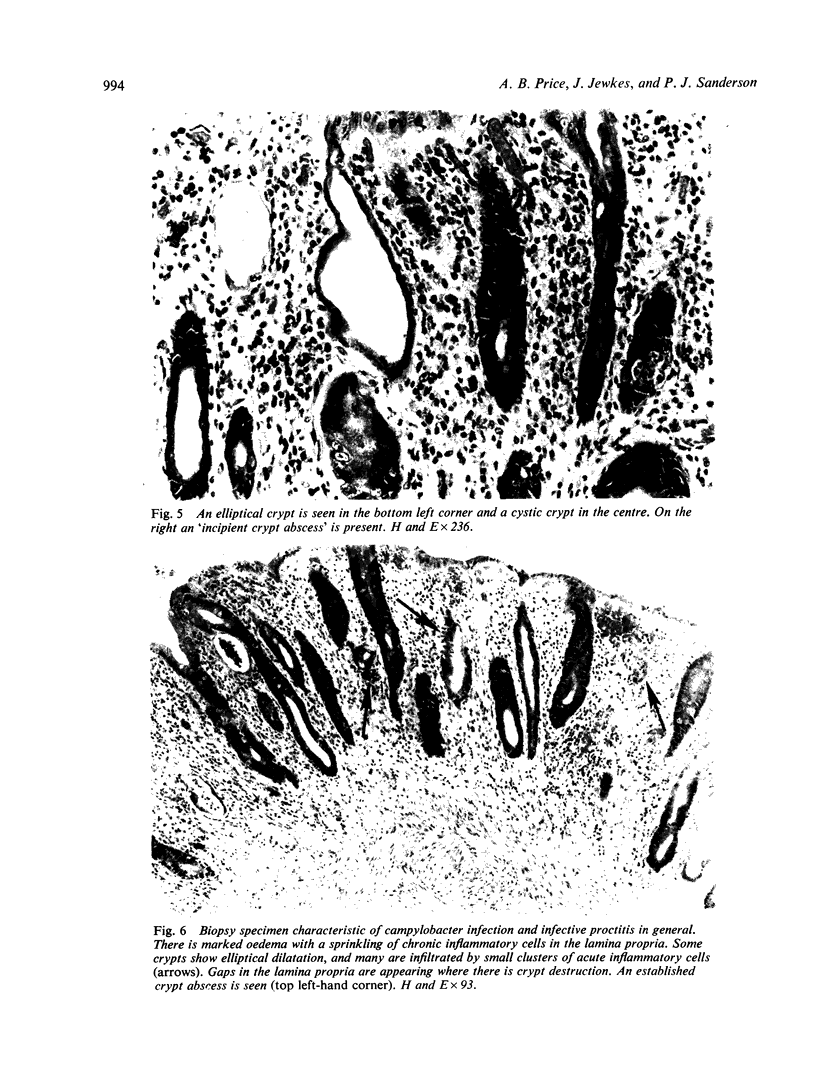
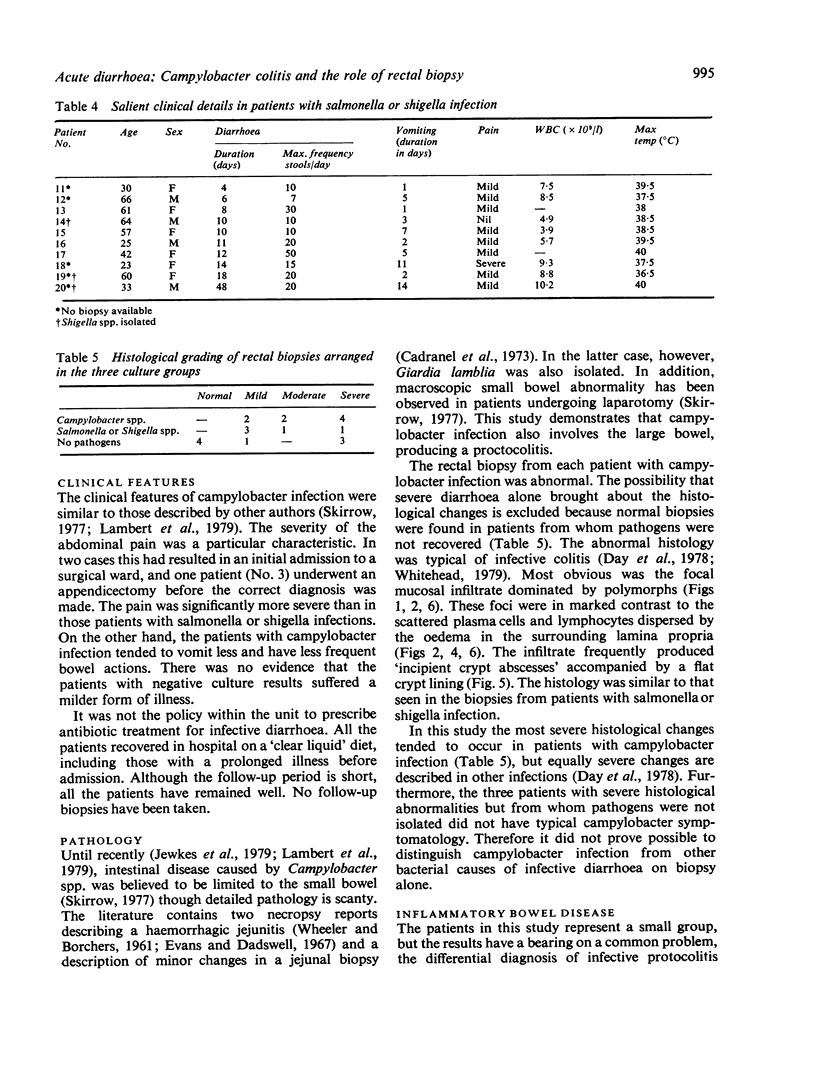
Campylobacter spp. were the organisms isolated most frequently from 29 consecutive patients admitted with acute diarrhoea to an infectious disease unit. Rectal biopsies taken from 21 of the patients were abnormal in all but four, and in the patients with campylobacter infection there was a characteristic proctocolitis in each case. The histopathology was similar to that described for salmonella and shigella infections but clearly different from typical ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Therefore in patients with acute diarrhoea we suggest that selective culture for Campylobacter spp. should be made a routine and that rectal biopsy has an important diagnostic role, particularly in patients with negative cultures.
Full text
PDF
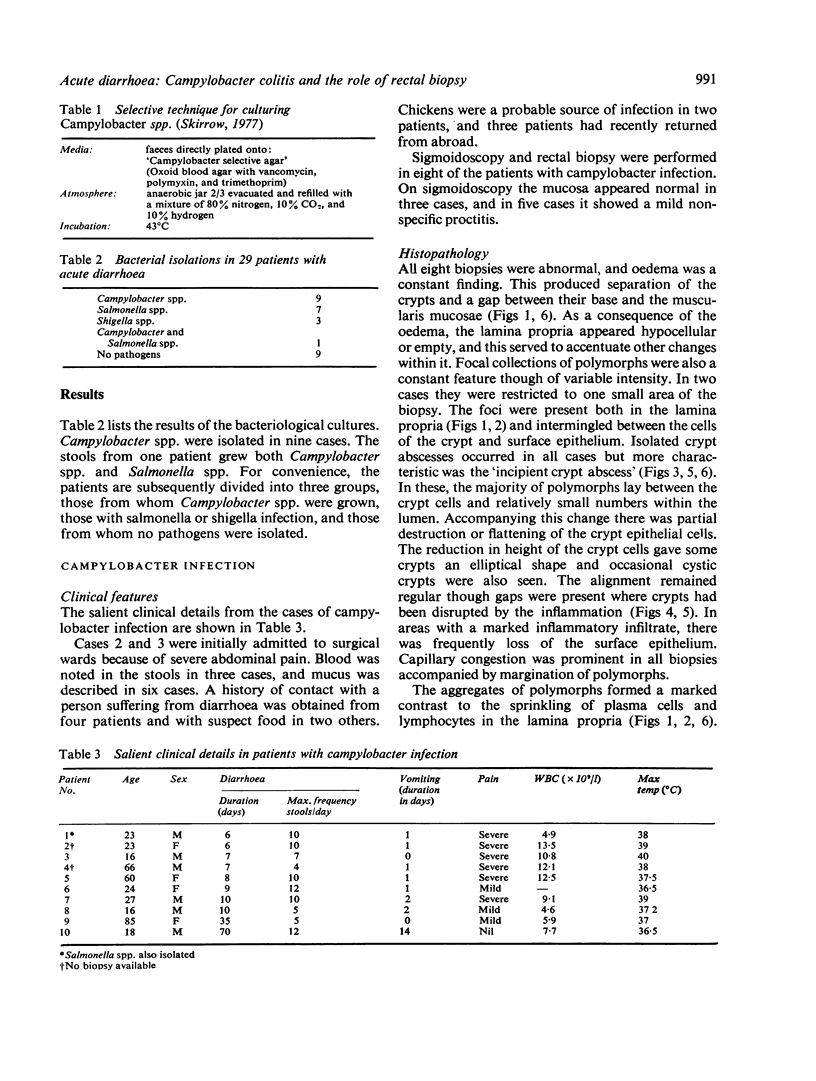
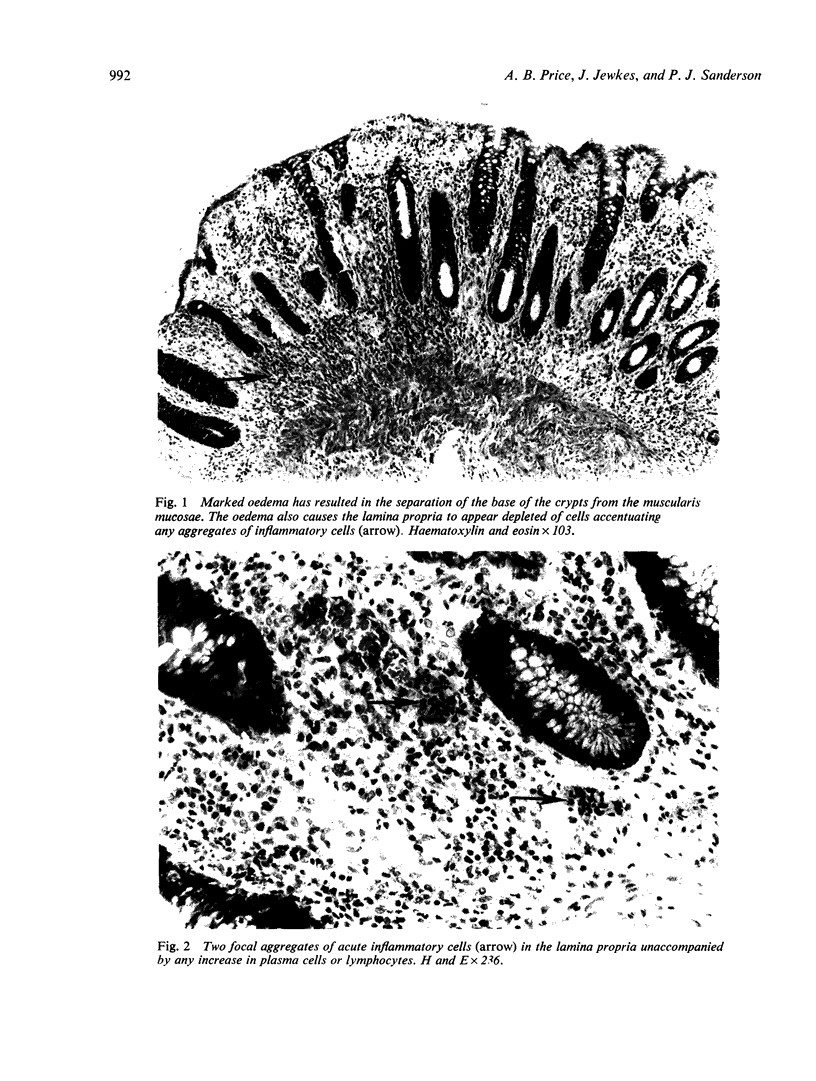
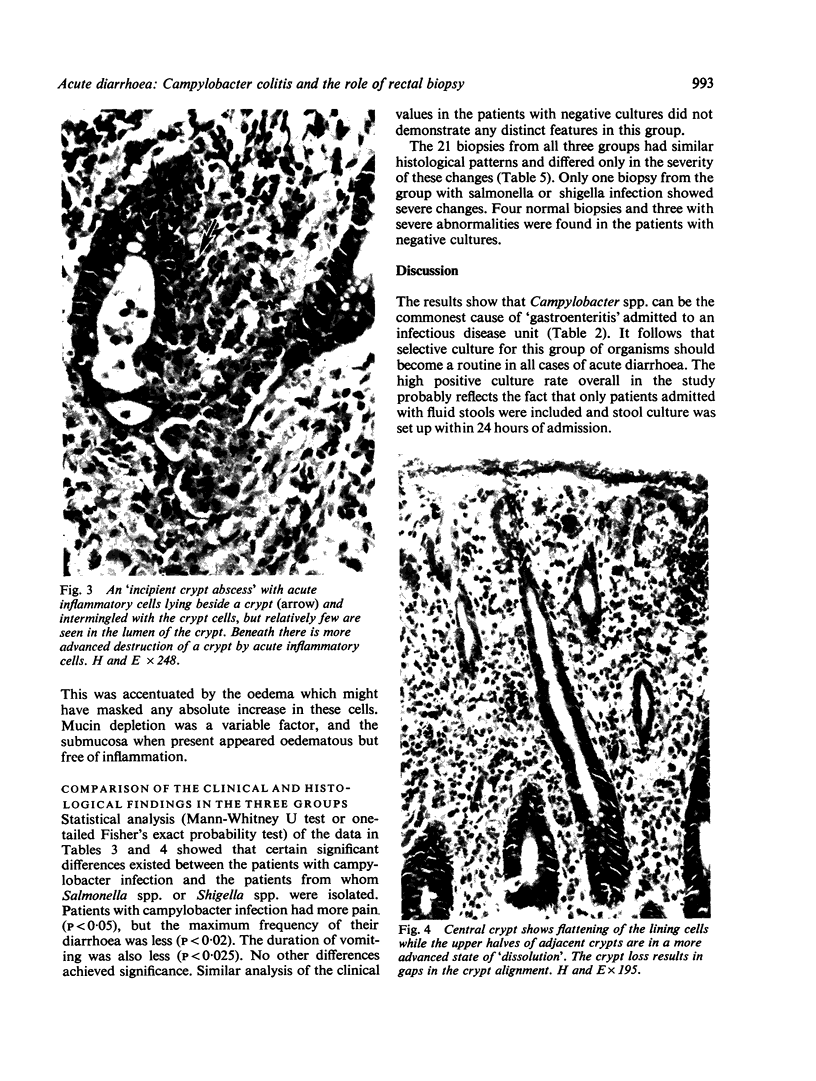


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cadranel S., Rodesch P., Butzler J. P., Dekeyser P. Enteritis due to "related vibrio" in children. Am J Dis Child. 1973 Aug;126(2):152–155. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1973.02110190134004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day D. W., Mandal B. K., Morson B. C. The rectal biopsy appearances in Salmonella colitis. Histopathology. 1978 Mar;2(2):117–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1978.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekeyser P., Gossuin-Detrain M., Butzler J. P., Sternon J. Acute enteritis due to related vibrio: first positive stool cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):390–392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson R. J., Gilmour H. M., McClelland D. B. Rectal biopsy in patients presenting to an infectious disease unit with diarrhoeal disease. Gut. 1979 Feb;20(2):141–148. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O. Human infections with Vibrio fetus and a closely related vibrio. J Infect Dis. 1957 Sep-Oct;101(2):119–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/101.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. E., Schofield P. F., Ironside A. G., Mandal B. K. Campylobacter colitis. Br Med J. 1979 Mar 31;1(6167):857–859. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6167.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton A. Imported diseases in general practice. Gastrointestinal disorders. Br Med J. 1974 Nov 30;4(5943):522–524. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5943.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEBALD M., VERON M. TENEUR EN BASES DE L'ADN ET CLASSIFICATION DES VIBRIONS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Nov;105:897–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER W. E., BORCHERS J. Vibrionic enteritis in infants. Am J Dis Child. 1961 Jan;101:60–66. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1961.04020020062010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]