Abstract
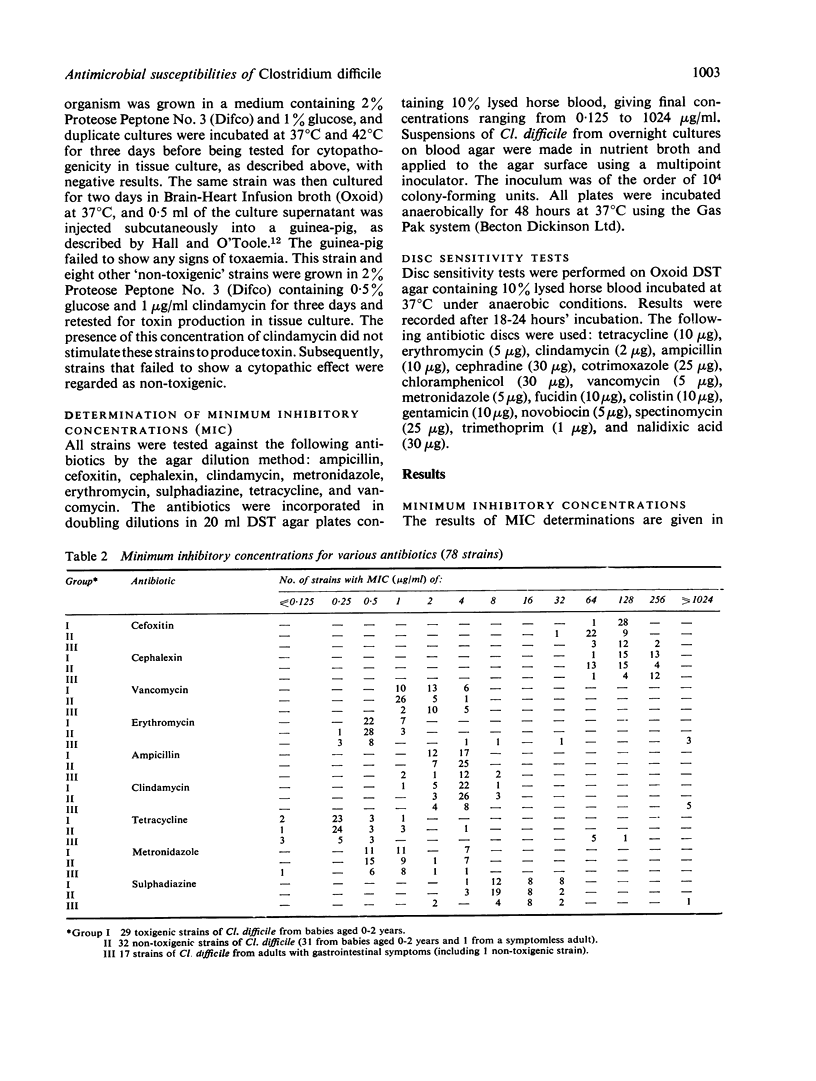
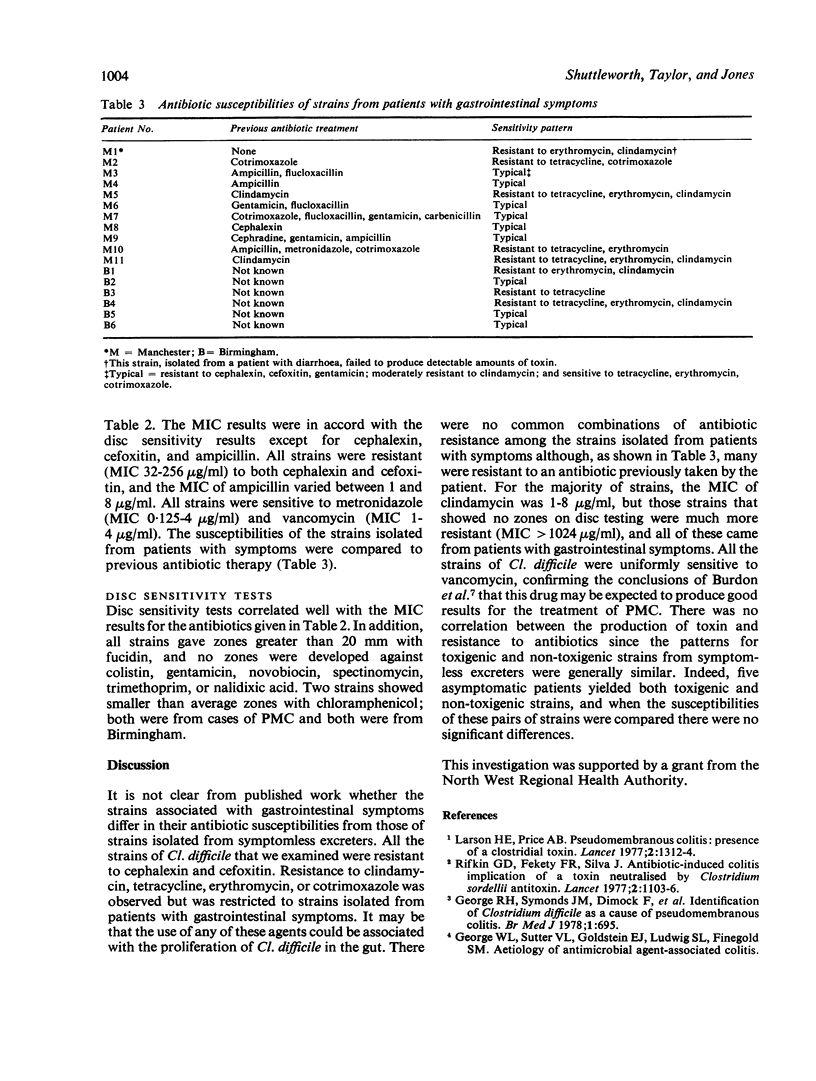
The antimicrobial susceptibilities of 78 strains of Clostridium difficile isolated from patients with and without gastrointestinal symptoms were determined and compared. Strains from patients with symptoms were more likely to show resistance to antibiotics. The antimicrobial susceptibilities of toxigenic and non-toxigenic strains were found to be similar.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G., Moon N., Chang T. W., Taylor N., Onderdonk A. B. Role of Clostridium difficile in antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):778–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon D. W., Brown J. D., Youngs D. J., Arabi Y., Shinagawa N., Alexander-Williams J., Keighley M. R., George R. H. Antibiotic susceptibility of Clostridium difficile. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 May;5(3):307–310. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R. H., Symonds J. M., Dimock F., Brown J. D., Arabi Y., Shinagawa N., Keighley M. R., Alexander-Williams J., Burdon D. W. Identification of Clostridium difficile as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1978 Mar 18;1(6114):695–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6114.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Volpicelli N. A., Stiner D. B., Richman D. D., Liechty E. J., Mok H. Y., Rolfe R. D., Finegold S. M. Relapse of pseudomembranous colitis after vancomycin therapy. N Engl J Med. 1979 Aug 23;301(8):414–415. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197908233010806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keighley M. R., Burdon D. W., Arabi Y., Williams J. A., Thompson H., Youngs D., Johnson M., Bentley S., George R. H., Mogg G. A. Randomised controlled trial of vancomycin for pseudomembranous colitis and postoperative diarrhoea. Br Med J. 1978 Dec 16;2(6153):1667–1669. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6153.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B. Pseudomembranous colitis: Presence of clostridial toxin. Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1312–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B., Trewby P. N., Chase R. A., Mellon P. J., Hanid M. A., Davies M., Langley P. G., Wheeler P. G., Williams R. Treatment of fulminant hepatic failure by polyacrylonitrile-membrane haemodialysis. Lancet. 1977 Jul 2;2(8027):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco F., Markham R., Gurwith M., Christie D., Bartlett J. G. Oral vancomycin for antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1978 Jul 29;2(8083):226–228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91741-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


