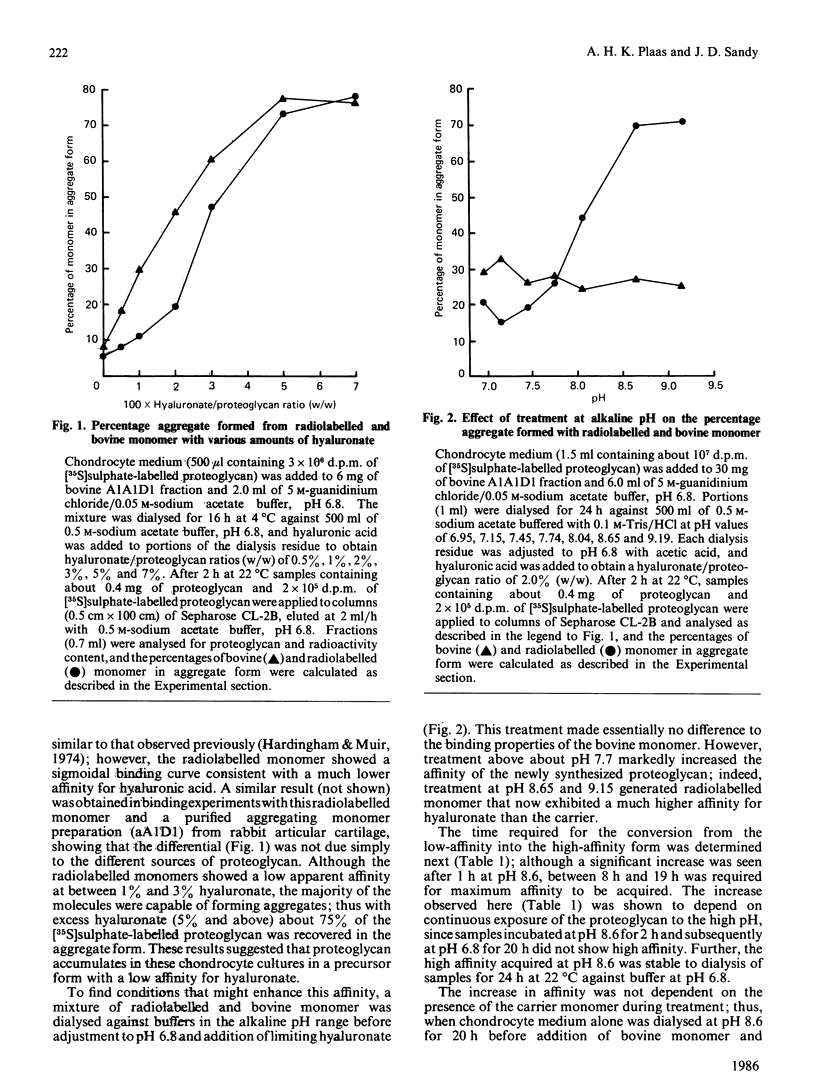
Abstract
The affinities for hyaluronic acid of newly synthesized proteoglycan from post-confluent rabbit chondrocyte cultures and purified bovine proteoglycan monomer were compared. In mixtures prepared at pH 6.8 the newly synthesized proteoglycan had the lower affinity; however, in mixtures incubated at pH 8.5 for 24 h before addition of hyaluronic acid, the newly synthesized proteoglycan exhibited a markedly higher affinity than the bovine monomer. The results suggest that proteoglycan secreted without associated link protein [Plaas, Sandy & Muir (1983) Biochem. J. 214, 855-864] has a low affinity for hyaluronate and that this may be increased during subsequent extracellular processing.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayliss M. T., Ridgway G. D., Ali S. Y. Differences in the rates of aggregation of proteoglycans from human articular cartilage and chondrosarcoma. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):705–708. doi: 10.1042/bj2150705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet F., Dunham D. G., Hardingham T. E. Structure and interactions of cartilage proteoglycan binding region and link protein. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):77–85. doi: 10.1042/bj2280077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. The interaction of link proteins with proteoglycan monomers in the absence of hyaluronic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farndale R. W., Sayers C. A., Barrett A. J. A direct spectrophotometric microassay for sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cartilage cultures. Connect Tissue Res. 1982;9(4):247–248. doi: 10.3109/03008208209160269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Ewins R. J., Muir H. Cartilage proteoglycans. Structure and heterogeneity of the protein core and the effects of specific protein modifications on the binding to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1042/bj1570127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Hyaluronic acid in cartilage and proteoglycan aggregation. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):565–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1390565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Lohmander L. S., Hascall V. C. Studies on the biosynthesis of cartilage proteoglycan in a model system of cultured chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(4):261–278. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Thonar E. J., Hascall V. C., Reiner A., Poole A. R. Identification of core protein, an intermediate in proteoglycan biosynthesis in cultured chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7890–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr Delayed formation of proteoglycan aggregate structures in human articular cartilage disease states. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):583–585. doi: 10.1038/288583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaas A. H., Sandy J. D. Age-related decrease in the link-stability of proteoglycan aggregates formed by articular chondrocytes. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):337–340. doi: 10.1042/bj2200337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaas A. H., Sandy J. D., Muir H. Proteoglycan aggregate formation by articular chondrocytes. Decrease in link-protein synthesis during culture. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 15;214(3):855–864. doi: 10.1042/bj2140855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. D. The assay of xylosyltransferase in cartilage extracts. A modified procedure for preparation of Smith-degraded proteoglycan. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):569–574. doi: 10.1042/bj1770569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetlaufer D. B. Nonenzymatic formation and isomerization of protein disulfides. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:301–304. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


