Abstract
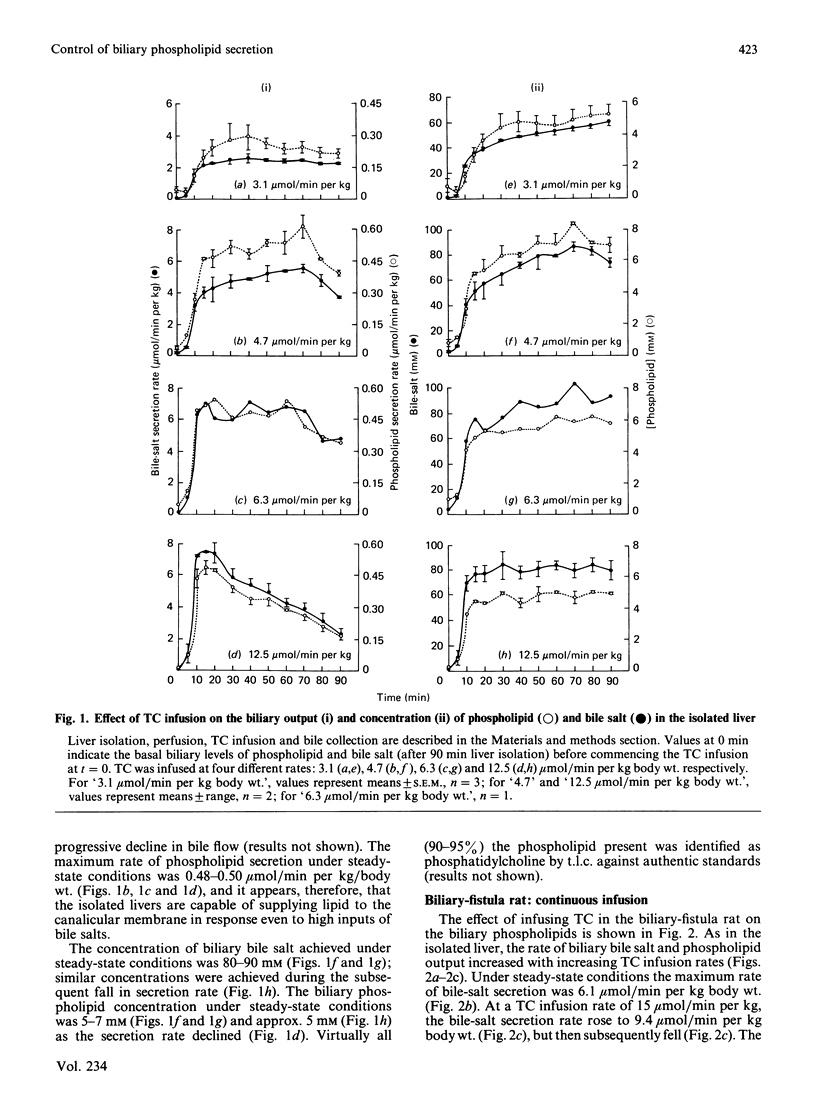
A major determinant of biliary lipid secretion is bile-salt secretion. Taurocholate (TC), a micelle-forming bile salt, was infused continuously at different rates in both isolated perfused livers and biliary-fistula rats. In both of these systems, infusion of TC brought about an elevated secretion of phosphatidylcholine for the duration of the TC infusion period. Initial phospholipid/bile-salt ratios in the bile were higher in the whole-animal model than in isolated livers, but at the higher infusion rates both secreted approx. 6 mol of phospholipid for every 100 mol of bile salt. The secretion of phospholipid, which was maintained even at high rates of bile-salt infusion, suggest a continuous and regulated phospholipid supply and secretion mechanism. In contrast, however, multiple short pulses of TC to the perfused liver, which brought about relatively equal biliary bile-salt output pulses, did not bring about equal phospholipid outputs, since the phospholipid peak size declined with each bile-salt pulse. These experiments taken together suggest either that a threshold (intracellular) bile-salt concentration may be required to 'switch-on' the phospholipid supply and that it may need to be maintained for continuous biliary phospholipid supply to the canalicular membrane.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlberg J., Angelin B., Einarsson K. Hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity and biliary lipid composition in man: relation to cholesterol gallstone disease and effects of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid treatment. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):410–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell S. G., Godfrey P. P., Lowe P. J., Coleman R. Biliary protein output by isolated perfused rat livers. Effects of bile salts. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):549–557. doi: 10.1042/bj2100549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell S. G., Lowe P. J., Coleman R. The effects of colchicine on secretion into bile of bile salts, phospholipids, cholesterol and plasma membrane enzymes: bile salts are secreted unaccompanied by phospholipids and cholesterol. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):723–731. doi: 10.1042/bj2200723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casu A., Cottalasso D., Pronzato M. A., Bassi A. M. Study of proteins, phospholipids and cholesterol of rat bile during chronic drainage. Ital J Biochem. 1981 Sep-Oct;30(5):388–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R., Iqbal S., Godfrey P. P., Billington D. Membranes and bile formation. Composition of several mammalian biles and their membrane-damaging properties. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):201–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1780201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. G., Skibba J. L. Improved in situ rat liver perfusion technique. J Surg Res. 1980 Jan;28(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(80)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronholm T., Curstedt T., Sjövall J. Origin of biliary phosphatidylcholines studied by coenzyme labelling with [1,1-2H2]ethanol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 20;753(2):276–279. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Klaassen C. D. Effects of acute administration of taurocholic and taurochenodeoxycholic acid on biliary lipid excretion in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Jan;151(1):198–202. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Kremmmer T., Culvenor J. G. Role of membranes in bile formation. Comparison of the composition of bile and a liver bile-canalicular plasma-membrane subfraction. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):589–595. doi: 10.1042/bj1540589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L. Mechanisms of hepatic bile formation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:323–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. A., Huling S., Jones A. L. Hepatic handling of bile salts and protein in the rat during intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1983 May;84(5 Pt 1):978–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez M. C., Sutherland E., Simon F. R. Regulation of hepatic transport of bile salt. Effect of protein synthesis inhibition on excretion of bile salts and their binding to liver surface membrane fractions. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):684–694. doi: 10.1172/JCI109351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. The movement of cholesterol within cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Dec;11(6):637–639. doi: 10.1042/bst0110637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory D. H., Vlahcevic Z. R., Schatzki P., Swell L. Mechanism of secretion of biliary lipids. I. Role of bile canalicular and microsomal membranes in the synthesis and transport of biliary lecithin and cholesterol. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):105–114. doi: 10.1172/JCI107900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Apter J. T. Micellar theory of biliary cholesterol excretion. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jan;222(1):61–67. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Hatoff D. E., Miyai K., Weiner R. G. Nature of bile acid maximum secretory rate in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):G337–G343. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.4.G337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems R., Ross B. D., Berry M. N., Krebs H. A. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):284–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1010284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz R., Paumgartner G., Preisig R. Inhibition of bile formation by high doses of taurocholate in the perfused rat liver. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11(7):741–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman R., Norrby S., Sjödahl R., Tiselius H. G., Tagesson C. Altered gallbladder bile composition in gallstone disease. Relation to gallbladder wall permeability. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(5):581–586. doi: 10.3109/00365528009182219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Schmucker D. L., Mooney J. S., Ockner R. K., Adler R. D. Alterations in hepatic pericanalicular cytoplasm during enhanced bile secretory activity. Lab Invest. 1979 Apr;40(4):512–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Schmucker D. L., Renston R. H., Murakami T. The architecture of bile secretion. A morphological perspective of physiology. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Aug;25(8):609–629. doi: 10.1007/BF01318875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Okano G., Akino T. Biosynthesis and turnover of individual molecular species of phosphatidylcholine in liver and bile. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 14;619(1):20–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitani K., Kanai S. Tauroursodeoxycholate prevents taurocholate induced cholestasis. Life Sci. 1982 Feb 7;30(6):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90264-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremmer T., Wisher M. H., Evans W. H. The lipid composition of plasma membrane subfractions originating from the three major functional domains of the rat hepatocyte cell surface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. J., Barnwell S. G., Coleman R. Rapid kinetic analysis of the bile-salt-dependent secretion of phospholipid, cholesterol and a plasma-membrane enzyme into bile. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):631–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2220631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyai K., Price V. M., Fisher M. M. Bile acid metabolism in mammals. Ultrastructural studies on the intrahepatic cholestasis induced by lithocholic and chenodeoxycholic acids in the rat. Lab Invest. 1971 Apr;24(4):292–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Máille E. R., Richards T. G., Short A. H. The influence of conjugation of cholic acid on its uptake and secretion: hepatic extraction of taurocholate and cholate in the dog. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):337–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Le M. Taurocholate, but not taurodehydrocholate, increases biliary permeability to sucrose. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):G651–G655. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.5.G651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Paumgartner G. Uptake of bile acids by perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):734–742. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben A., Howell K. E., Boyer J. L. Effects of taurocholate on the size of mixed lipid micelles and their associations with pigment and proteins in rat bile. J Lipid Res. 1982 Sep;23(7):1039–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. J., Brunengraber H. Origin of biliary cholesterol and lecithin in the rat: contribution of new synthesis and preformed hepatic stores. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):604–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherstén T. Bile acids as a determining factor for synthesis and excretion of human bile lecithin. Helv Med Acta. 1973 Sep;37(2):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. C., Berman M., Vlahcevic Z. R., Halloran L. G., Gregory D. H., Swell L. Multicompartmental analysis of cholesterol metabolism in man. Characterization of the hepatic bile acid and biliary cholesterol precursor sites. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):408–423. doi: 10.1172/JCI108952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. The formation of gallstones. Adv Intern Med. 1970;16:243–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange R. C. Hepatic bile salt transport. A review of subcellular binding sites. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Feb;9(1):170–174. doi: 10.1042/bst0090170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swell L., Bell C. C., Jr, Entenman C. Bile acids and lipid metabolism. 3. Influence of bile acids on phospholipids in liver and bile of the isolated perfused dog liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):278–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swell L., Entenman C., Leong G. F., Holloway R. J. Bile acids and lipid metabolism. IV. Influence of bile acids on biliary and liver organelle phospholipids and cholesterol. Am J Physiol. 1968 Dec;215(6):1390–1396. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.6.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O., King K. K. Biliary excretion of lecithin and cholesterol in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1337–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI106930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O. Secretion of bile acids by the liver and their role in the formation of hepatic bile. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):533–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousef I. M., Bloxam D. L., Phillips M. J., Fisher M. M. Liver cell plasma membrane lipids and the origin of biliary phospholipid. Can J Biochem. 1975 Sep;53(9):989–997. doi: 10.1139/o75-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


