Abstract
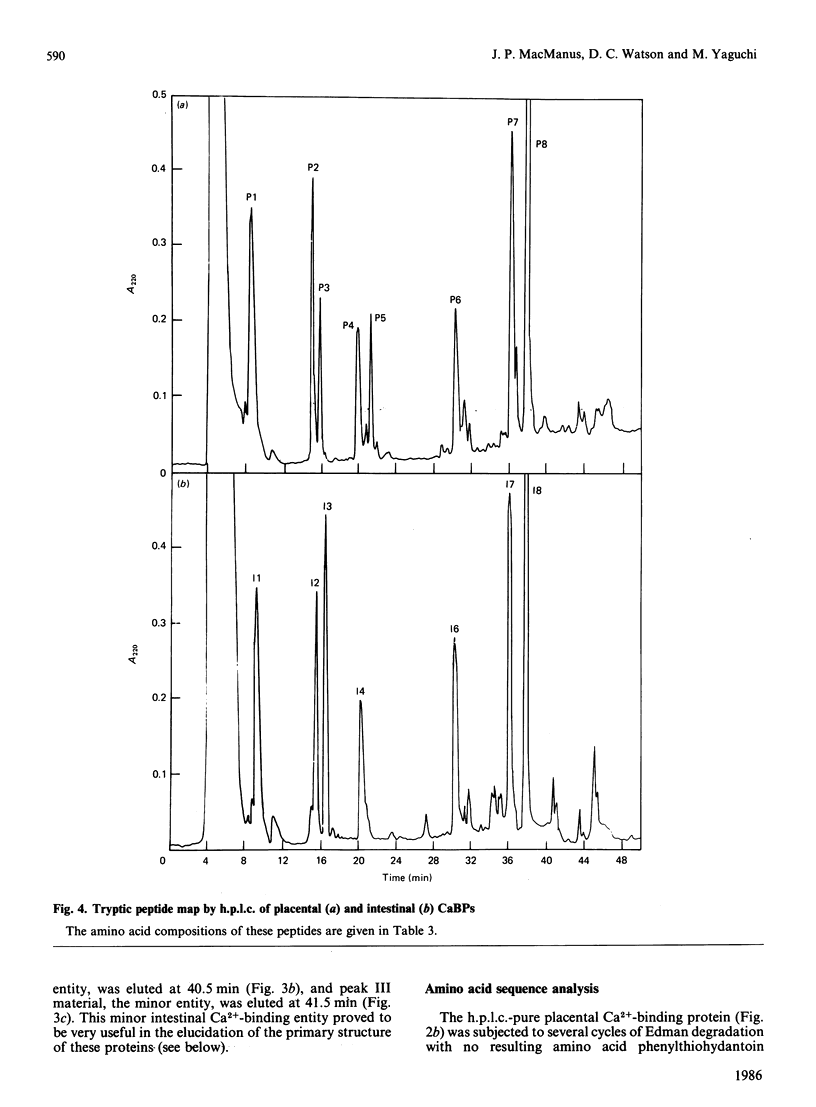
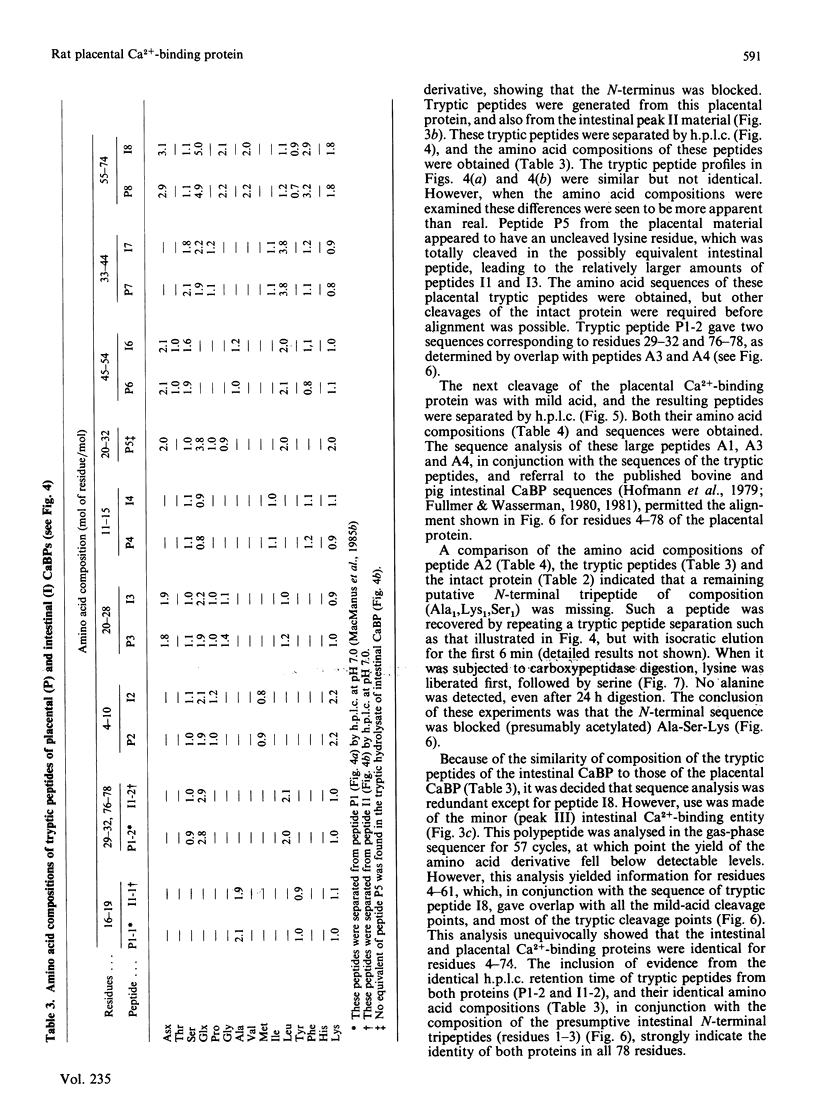
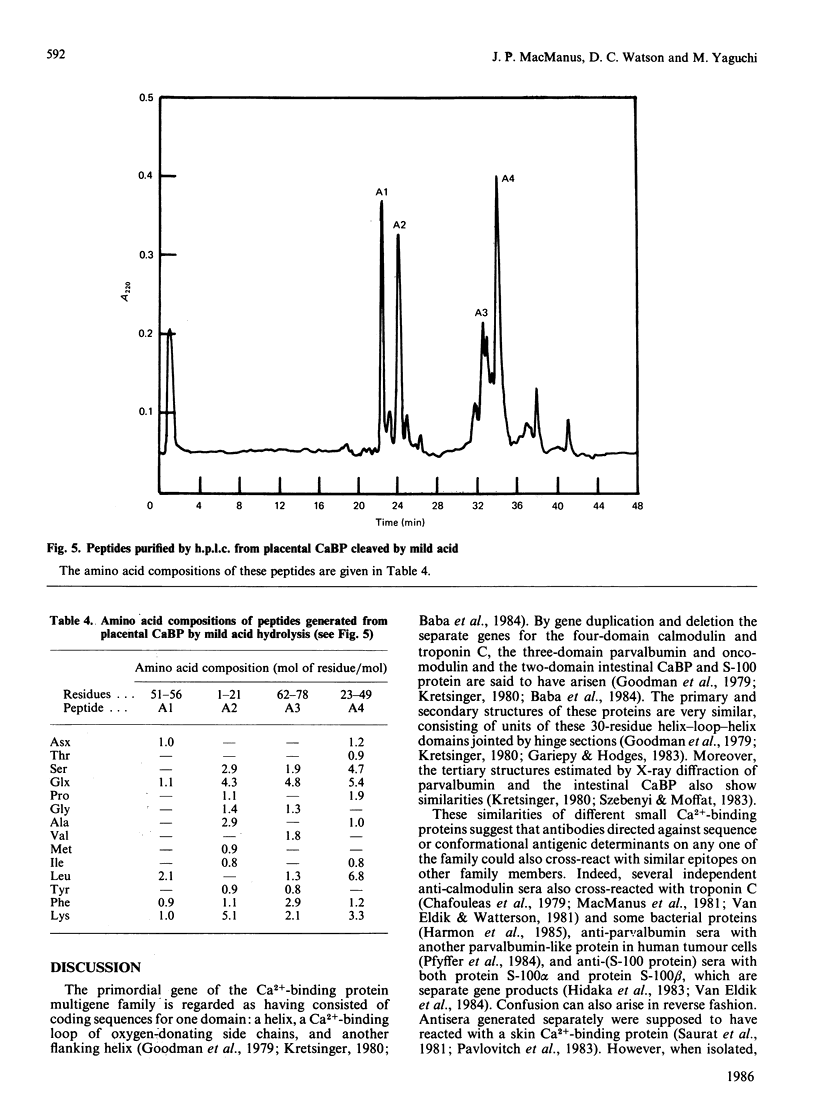
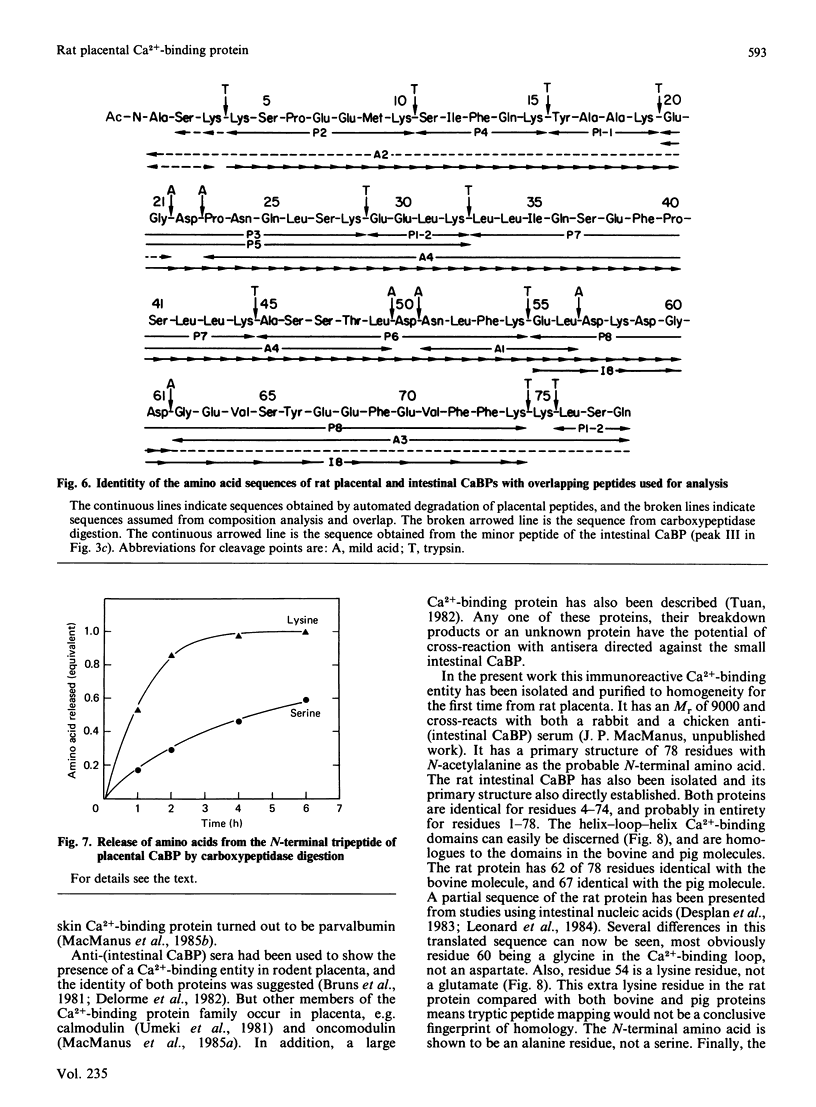
A 9000-Mr Ca2+-binding protein was isolated from rat placenta and purified to homogeneity by h.p.l.c. procedures. The complete amino acid sequence was established for the 78-residue placental protein. A sequence analysis of a minor component of the rat intestinal Ca2+-binding protein (residues 4-78) and a tryptic peptide (residues 55-74), both purified by h.p.l.c., showed both proteins to be identical. Thus this placental 9000-Mr Ca2+-binding protein is the same gene product as the intestinal Ca2+-binding protein whose synthesis is dependent on vitamin D.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba M. L., Goodman M., Berger-Cohn J., Demaille J. G., Matsuda G. The early adaptive evolution of calmodulin. Mol Biol Evol. 1984 Nov;1(6):442–455. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brommage R., DeLuca H. F. Placental transport of calcium and phosphorus is not regulated by vitamin D. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 2):F526–F529. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.4.F526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
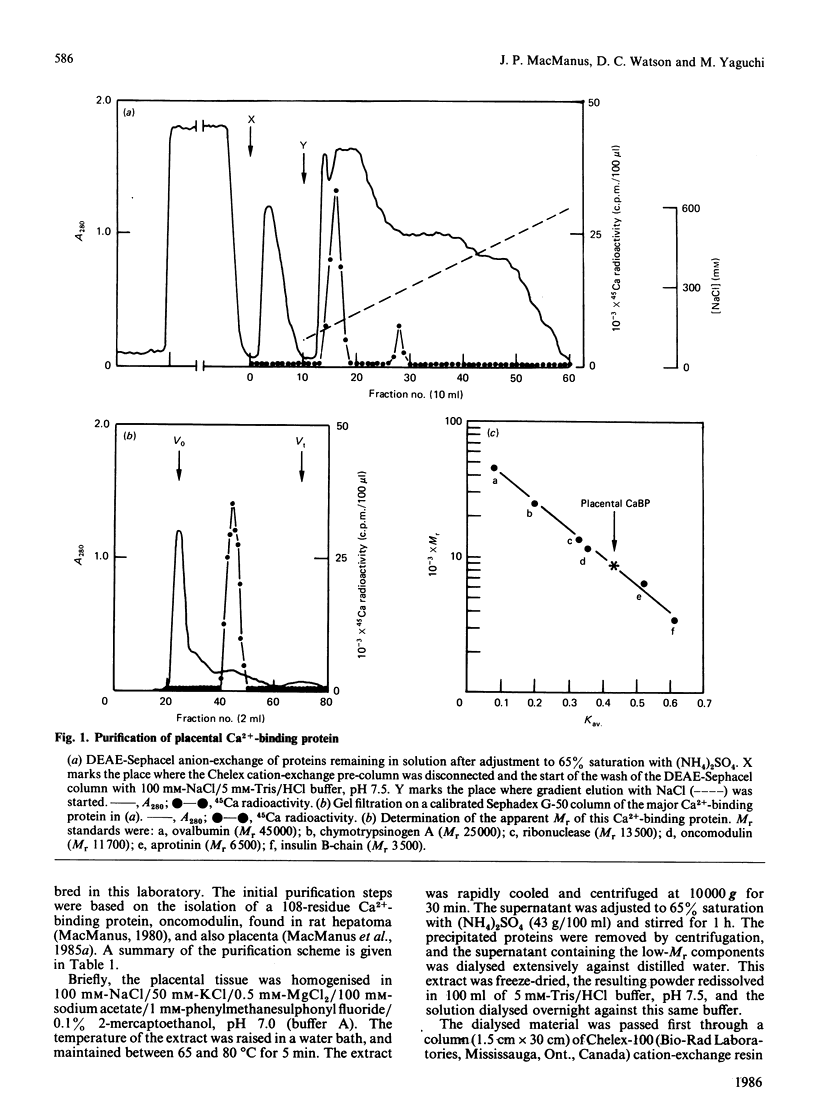
- Bruns M. E., Fausto A., Avioli L. V. Placental calcium binding protein in rats. Apparent identity with vitamin D-dependent calcium binding protein from rat intestine. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3186–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M. E., Fleisher E. B., Avioli L. V. Control of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein in rat intestine by growth and fasting. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4145–4150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M. E., Vollmer S., Wallshein V., Bruns D. E. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Immunochemical studies and synthesis by placental tissue in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4649–4653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M. E., Wallshein V., Bruns D. E. Regulation of calcium-binding protein in mouse placenta and intestine. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):E47–E52. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.242.1.E47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
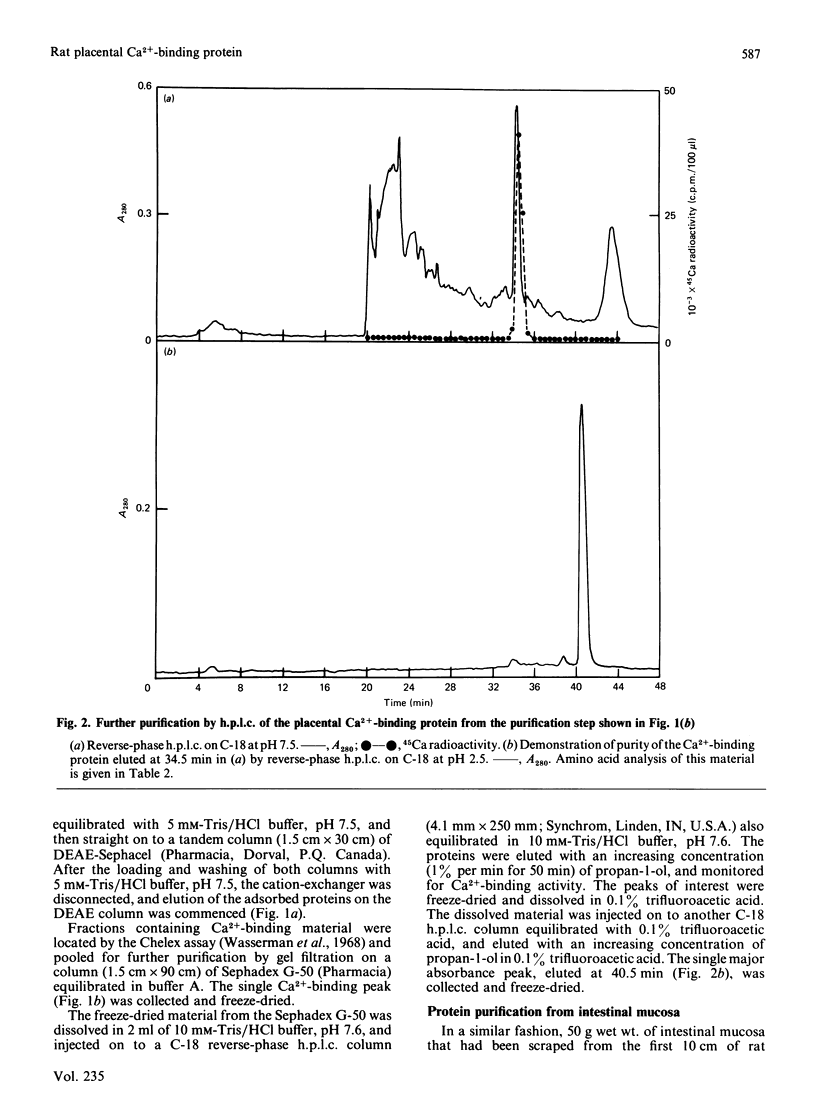
- Chafouleas J. G., Dedman J. R., Munjaal R. P., Means A. R. Calmodulin. Development and application of a sensitive radioimmunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10262–10267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christakos S., Bruns M. E., Mehra A. S., Rhoten W. B., Van Eldik L. J. Calmodulin and rat vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding proteins: biochemical and immunochemical comparison. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 15;231(1):38–47. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie M. Calcium-ion-binding activity in human small-intestinal mucosal cytosol. Purification of two proteins and interrelationship of calcium-binding fractions. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):55–65. doi: 10.1042/bj1970055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delorme A. C., Danan J. L., Mathieu H. Biochemical evidence for the presence of two vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding proteins in mouse kidney. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1878–1884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
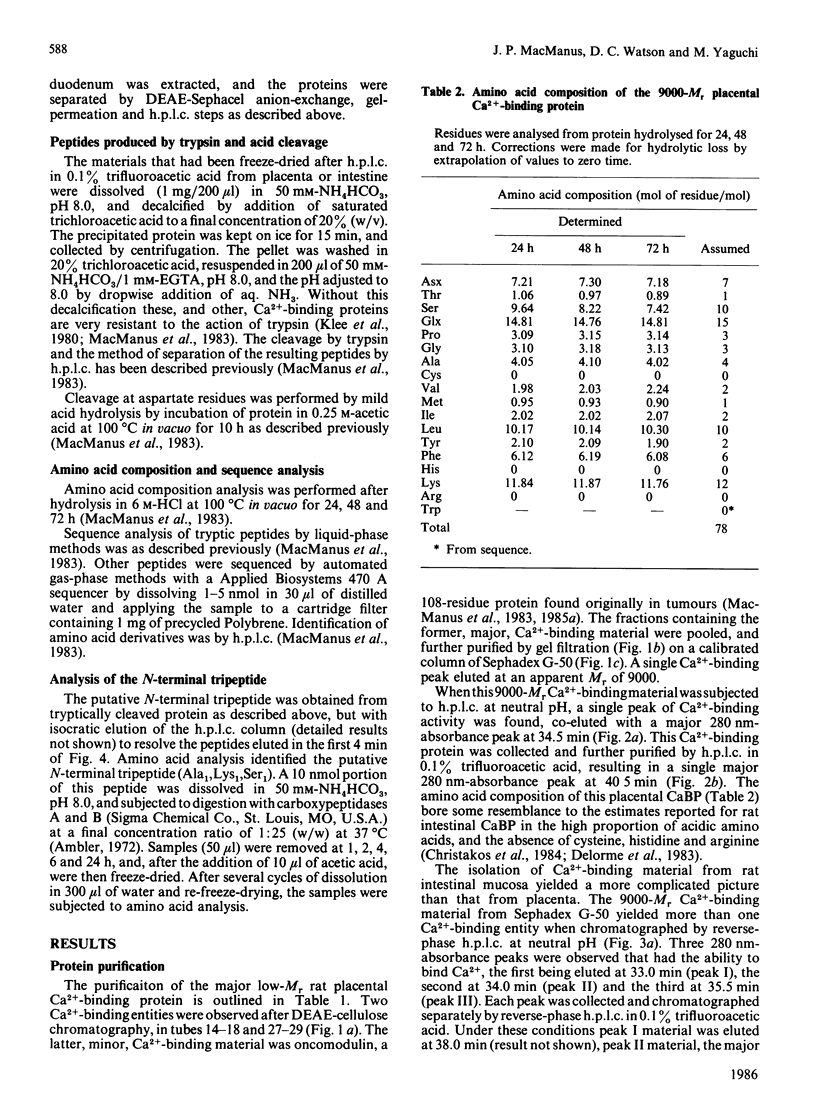
- Delorme A. C., Danan J. L., Ripoche M. A., Mathieu H. Biochemical characterization of mouse vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Evidence for its presence in embryonic life. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 1;205(1):49–57. doi: 10.1042/bj2050049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
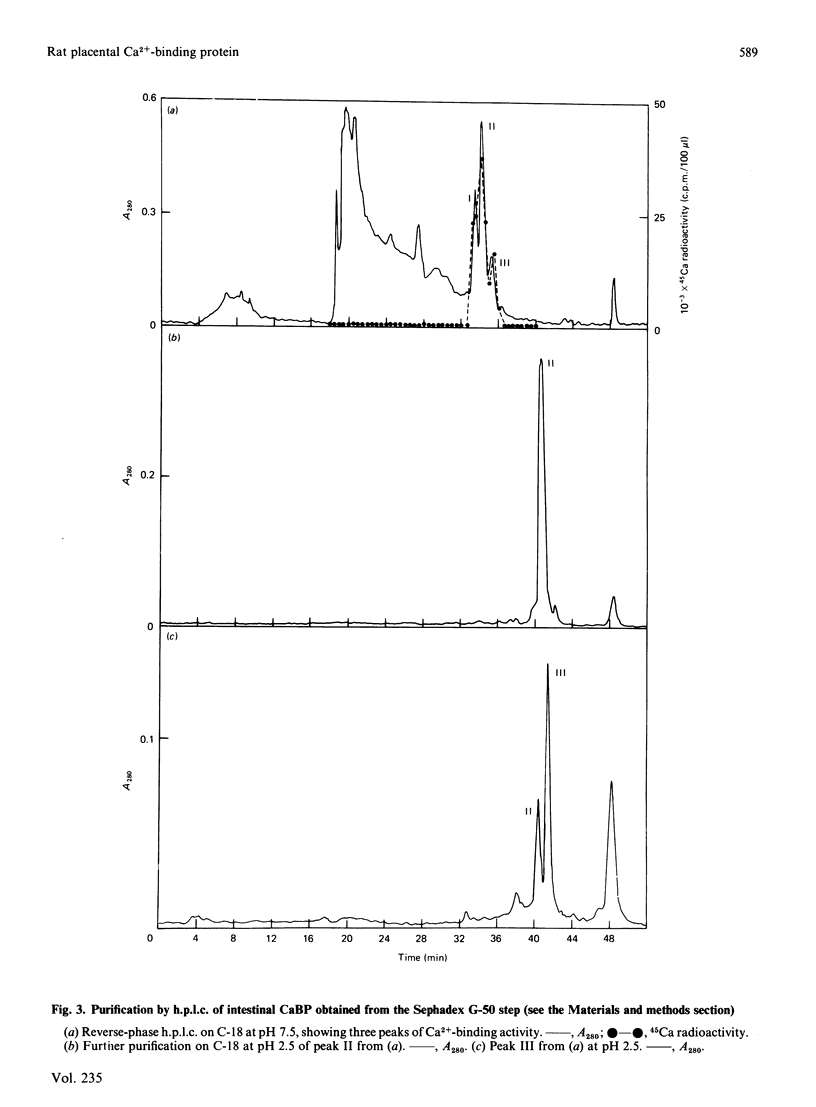
- Delorme A. C., Marche P., Garel J. M. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Changes during gestation, prenatal and postnatal development in rats. J Dev Physiol. 1979 Jun;1(3):181–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Heidmann O., Lillie J. W., Auffray C., Thomasset M. Sequence of rat intestinal vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein derived from a cDNA clone. Evolutionary implications. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13502–13505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. Bovine intestinal calcium-binding proteins. Purification and some properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 12;317(1):172–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. The amino acid sequence of bovine intestinal calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5669–5674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel J. M., Delorme A. C., Marche P., Nguyen T. M., Garabedian M. Vitamin D3 metabolite injections to thyroparathyroidectomized pregnant rats: effects on calcium-binding proteins of maternal duodenum and of fetoplacental unit. Endocrinology. 1981 Jul;109(1):284–289. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-1-284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariépy J., Hodges R. S. Primary sequence analysis and folding behavior of EF hands in relation to the mechanism of action of troponin C and calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80924-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason W. A., Jr, Lankford G. L. Rat intestinal calcium-binding protein: rapid purification with AG MP-1 ion-exchange chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 15;116(2):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90353-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M., Pechère J. F., Haiech J., Demaille J. G. Evolutionary diversification of structure and function in the family of intracellular calcium-binding proteins. J Mol Evol. 1979 Nov;13(4):331–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01731373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon A. C., Prasher D., Cormier M. J. High-affinity calcium-binding proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Endo T., Kawamoto S., Yamada E., Umekawa H., Tanabe K., Hara K. Purification and characterization of adipose tissue S-100b protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2705–2709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchman A. J., Kerr M. K., Harrison J. E. The purification of pig vitamin D-induced intestinal calcium binding protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):221–222. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann T., Kawakami M., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E., Dorrington K. J. The amino acid sequence of porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):737–748. doi: 10.1139/o79-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Structure and evolution of calcium-modulated proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(2):119–174. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Strauss A. W., Go M. F., Alpers D. H., Gordon J. I. Biosynthesis and compartmentalization of rat-intestinal vitamin-D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 15;139(3):561–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P., Braceland B. M., Rixon R. H., Whitfield J. F., Morris H. P. An increase in calmodulin during growth of normal and cancerous liver in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1981 Oct 12;133(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80480-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P., Brewer L. M., Whitfield J. F. The widely-distributed tumour protein, oncomodulin, is a normal constituent of human and rodent placentas. Cancer Lett. 1985 Jun;27(2):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(85)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P. The purification of a unique calcium-binding protein from Morris hepatoma 5123 tc. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 27;621(2):296–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P., Watson D. C., Yaguchi M. Rat skin calcium-binding protein is parvalbumin. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):39–45. doi: 10.1042/bj2290039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P., Watson D. C., Yaguchi M. The complete amino acid sequence of oncomodulin--a parvalbumin-like calcium-binding protein from Morris hepatoma 5123tc. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):9–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marche P., Delorme A., Cuisinier-Gleizes P. Intestinal and placental calcium-binding proteins in vitamin D-deprived or -supplemented rats. Life Sci. 1978 Dec 25;23(26):2555–2561. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansini A. R., Christakos S. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein in rat kidney. Purification and physiocochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9735–9741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovitch J. H., Didierjean L., Rizk M., Balsan S., Saurat J. H. Skin calcium-binding protein: distribution in other tissues. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):C50–C57. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.1.C50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfyffer G. E., Haemmerli G., Heizmann C. W. Calcium-binding proteins in human carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6632–6636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saurat J. H., Didierjean L., Pavlovitch J. H., Laouari D., Balsan S. Skin calcium binding protein is localized in the cytoplasm of the basal layer of the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):221–223. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J., Pansini A. R., Christakos S. Vitamin D-dependent rat renal calcium-binding protein: development of a radioimmunoassay, tissue distribution, and immunologic identification. Endocrinology. 1984 Aug;115(2):640–648. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-2-640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. N., Gleason W. A., Jr, Lankford G. L. Rat intestinal vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein: immunocytochemical localization in incisor ameloblasts. J Dent Res. 1984 Feb;63(2):94–97. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630021701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomasset M., Parkes C. O., Cuisinier-Gleizes P. Rat calcium-binding proteins: distribution, development, and vitamin D dependence. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):E483–E488. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.6.E483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan R. S. Identification and characterization of a calcium-binding protein from human placenta. Placenta. 1982 Apr-Jun;3(2):145–158. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(82)80048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeki S., Nagao S., Nozawa Y. The purification and identification of calmodulin from human placenta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 18;674(3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eldik L. J., Ehrenfried B., Jensen R. A. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies with specificity for the S100 beta polypeptide of brain S100 fractions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6034–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eldik L. J., Watterson D. M. Reproducible production of antiserum against vertebrate calmodulin and determination of the immunoreactive site. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4205–4210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Corradino R. A., Taylor A. N. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3978–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Fullmer C. S. Calcium transport proteins, calcium absorption, and vitamin D. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:375–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


