Abstract
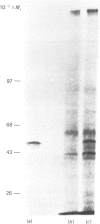
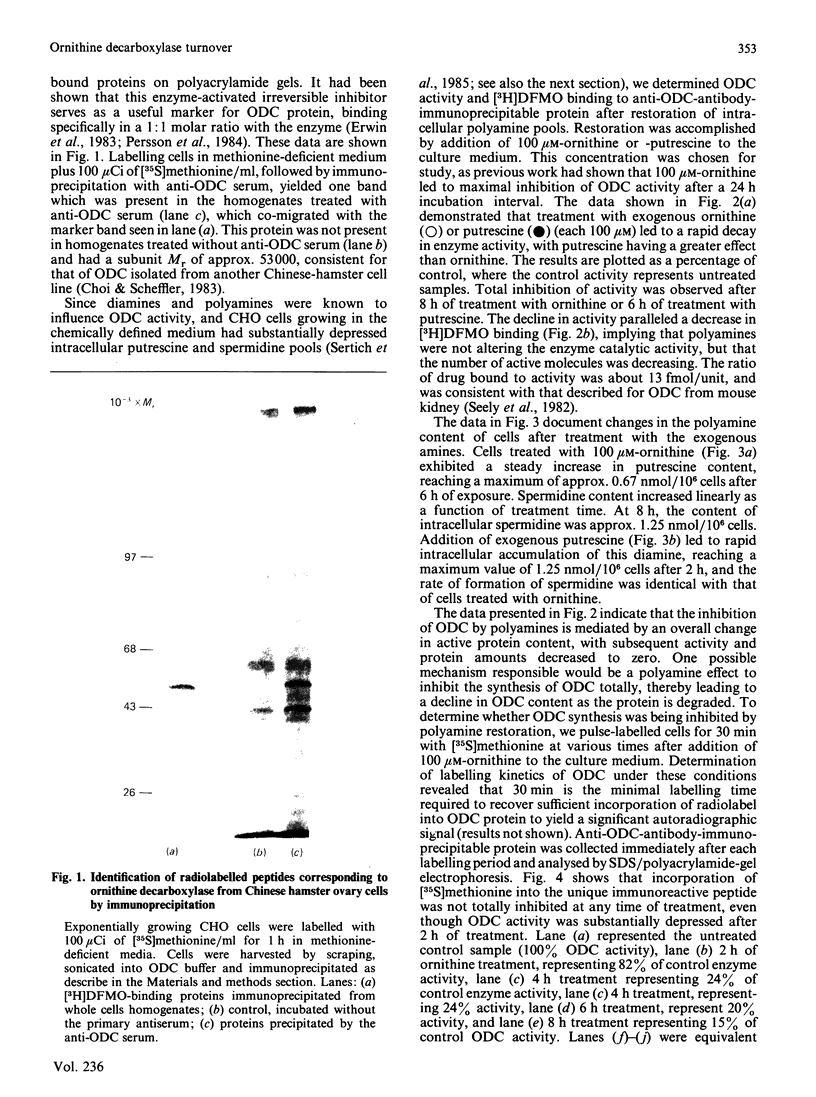
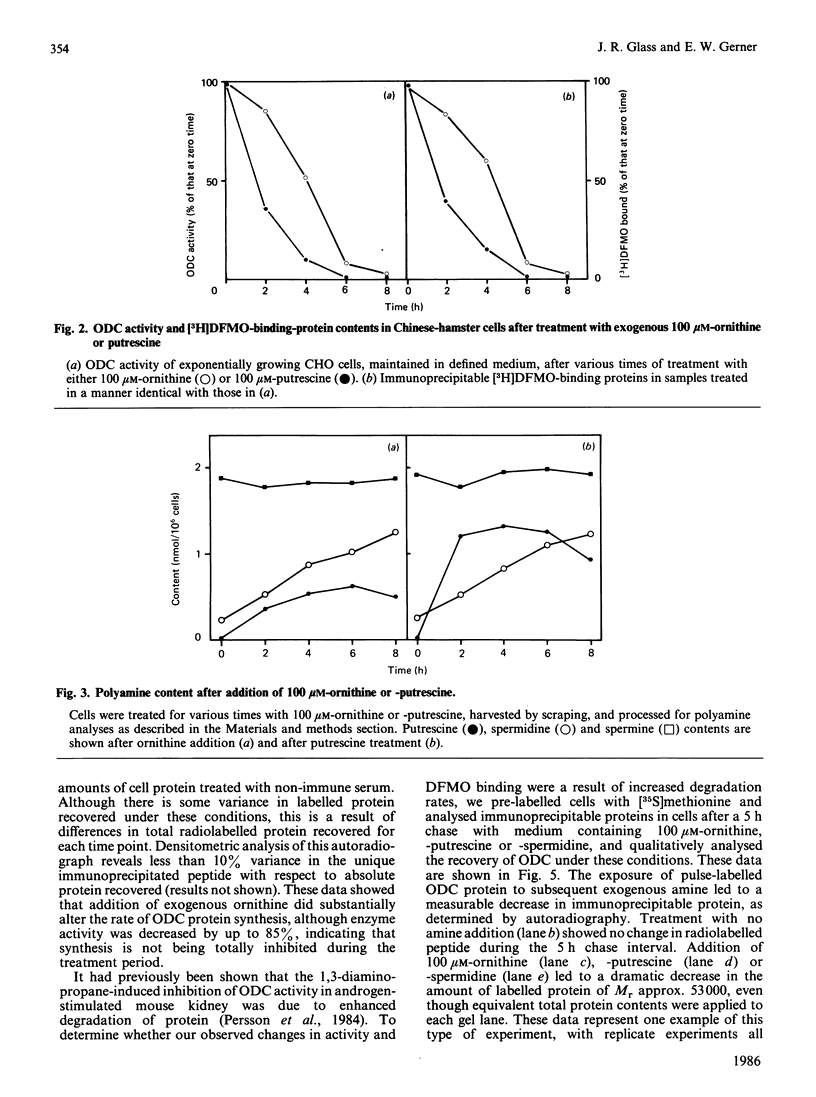
We have used Chinese-hamster ovary (CHO) cells maintained in a chemically defined medium to study the regulation of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) by polyamines. Cells maintained in the defined medium had no detectable putrescine, and approx. 1-3 units of ODC activity/10(6) cells, where 1 unit corresponds to 1 nmol of substrate decarboxylated in 30 min. The defined medium is ornithine-deficient, thus limiting the exogenous substrate for ODC, and subsequently decreasing intracellular polyamine accumulation. Restoration of intracellular putrescine and increased formation of spermidine by addition of exogenous ornithine or putrescine led to a marked decrease in ODC activity, which was paralleled by a decrease in a alpha-DL-difluoromethyl[3,4-3H]ornithine (DFMO)-binding protein of Mr approx. 53,000, which is precipitable with anti-ODC antibody. Calculation of DFMO binding per unit of activity showed no change in the specific activity of the enzyme. We identified [35S]methionine-labelled peptides corresponding to ODC by immunoprecipitation of radiolabeled whole cell proteins. Only one protein was precipitated, of Mr approx. 53 000, which co-migrated with the DFMO-binding protein. Immunoprecipitation of radiolabelled proteins from cells incubated in the presence of exogenous ornithine indicated that the observed activity decrease was not due to an inhibition of ODC protein synthesis. Analysis of immunoprecipitable ODC protein from cells that had been pulse-labelled with [35S]methionine, and then treated for 5 h with 100 microM-ornithine, -putrescine or -spermidine, revealed a distinct disappearance of labelled ODC protein after restoration of intracellular polyamine pools. No detectable turnover of ODC was observed in the absence of exogenous polyamine treatment. These data support the hypothesis that ODC protein, and subsequent activity, is regulated by intracellular polyamine content through mechanisms that influence turnover of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atmar V. J., Kuehn G. D. Phosphorylation of ornithine decarboxylase by a polyamine-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5518–5522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetz A. L., Hubbert W. T., Graham C. K. Developmental changes of free amino acids in bovine fetal fluids with gestational age and the interrelationships between the amino acid concentrations in the fluid compartments. J Reprod Fertil. 1975 Sep;44(3):437–477. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0440437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canellakis E. S., Kyriakidis D. A., Rinehart C. A., Jr, Huang S. C., Panagiotidis C., Fong W. F. Regulation of polyamine biosynthesis by antizyme and some recent developments relating the induction of polyamine biosynthesis to cell growth. Review. Biosci Rep. 1985 Mar;5(3):189–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01119588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canellakis E. S., Viceps-Madore D., Kyriakidis D. A., Heller J. S. The regulation and function of ornithine decarboxylase and of the polyamines. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1979;15:155–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. Y., Canellakis E. S. Enzyme regulation in neuroblastoma cells in a salts/glucose medium: induction of ornithine decarboxylase by asparagine and glutamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3791–3795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi J. H., Scheffler I. E. Chinese hamster ovary cells resistant to alpha-difluoromethylornithine are overproducers of ornithine decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12601–12608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin dependence of selective protein degradation demonstrated in the mammalian cell cycle mutant ts85. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. L., Fuller J. L. Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase in 3T3 cells by putrescine and spermidine: indirect evidence for translational control. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4403–4409. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. L. Specific induction of ornithine decarboxylase in 3T3 mouse fibroblasts by pituitary growth factors: cell density-dependent biphasic response and alteration of half-life. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4668–4674. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwin B. G., Seely J. E., Pegg A. E. Mechanism of stimulation of ornithine decarboxylase activity in transformed mouse fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):3027–3032. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heby O. Role of polyamines in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation. Differentiation. 1981;19(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L., Murden S. Effect of growth conditions on the activity of ornithine decarboxylase in cultured hepatoma cells. I. Effect of amino acid supply. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Jun;83(3):345–351. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänne J., Hölttä E. Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase activity by putrescine and spermidine in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 27;61(2):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90977-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karvonen E., Pösö H. Stabilization of ornithine decarboxylase and N1-spermidine acetyltransferase in rat liver by methylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 7;791(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakidis D. A., Flamigni F., Pawlak J. W., Canellakis E. S. Mode of interaction of ornithine decarboxylase with antizyme and alpha-difluoromethylornithine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 May 1;33(9):1575–1578. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90435-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D., Houben P. W., Bullock L. P. Two forms of ornithine decarboxylase activity in mouse kidney. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Nov;38(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamont P. S., Duchesne M. C., Grove J., Tardif C. Initial characterization of a HTC cell variant partially resistant to the anti-proliferative effect of ornithine decarboxylase inhibitors. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Sep;115(2):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann P. P., Tardif C., Duchesne M. C., Mamont P. S. Effect of alpha-methyl ornithine on ornithine decarboxylase activity of rat hepatoma cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):893–899. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91585-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann P. P., Tardif C., Hornsperger J. M., Böhlen P. Two distinct mechanisms for ornithine decarboxylase regulation by polyamines in rat hepatoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 May;99(2):183–190. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. L., Qasba P., Stofko R. E., Franzen M. A. Ornithine decarboxylase modification and polyamine-stimulated enzyme inactivation in HTC cells. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 1;228(2):297–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2280297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Fujita K., Kameji T., Hayashi S. Accumulation of ornithine decarboxylase-antizyme complex in HMOA cells. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):689–697. doi: 10.1042/bj2250689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E., Conover C., Wrona A. Effects of aliphatic diamines on rat liver ornithine decarboxylase activity. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):651–660. doi: 10.1042/bj1700651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson L., Seely J. E., Pegg A. E. Investigation of structure and rate of synthesis of ornithine decarboxylase protein in mouse kidney. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3777–3783. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard M. L., Seely J. E., Pösö H., Jefferson L. S., Pegg A. E. Binding of radioactive alpha-difluoromethylornithine to rat liver ornithine decarboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun;100(4):1597–1603. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90701-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. H. Posttranslational modification of ornithine decarboxylase by its product putrescine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1167–1172. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90741-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seely J. E., Pegg A. E. Changes in mouse kidney ornithine decarboxylase activity are brought about by changes in the amount of enzyme protein as measured by radioimmunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2496–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seely J. E., Pösö H., Pegg A. E. Measurement of the number of ornithine decarboxylase molecules in rat and mouse tissues under various physiological conditions by binding of radiolabelled alpha-difluoromethylornithine. Biochem J. 1982 Aug 15;206(2):311–318. doi: 10.1042/bj2060311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler N., Knödgen B. High-performance liquid chromatographic procedure for the simultaneous determination of the natural polyamines and their monoacetyl derivatives. J Chromatogr. 1980 Dec 12;221(2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]