Abstract
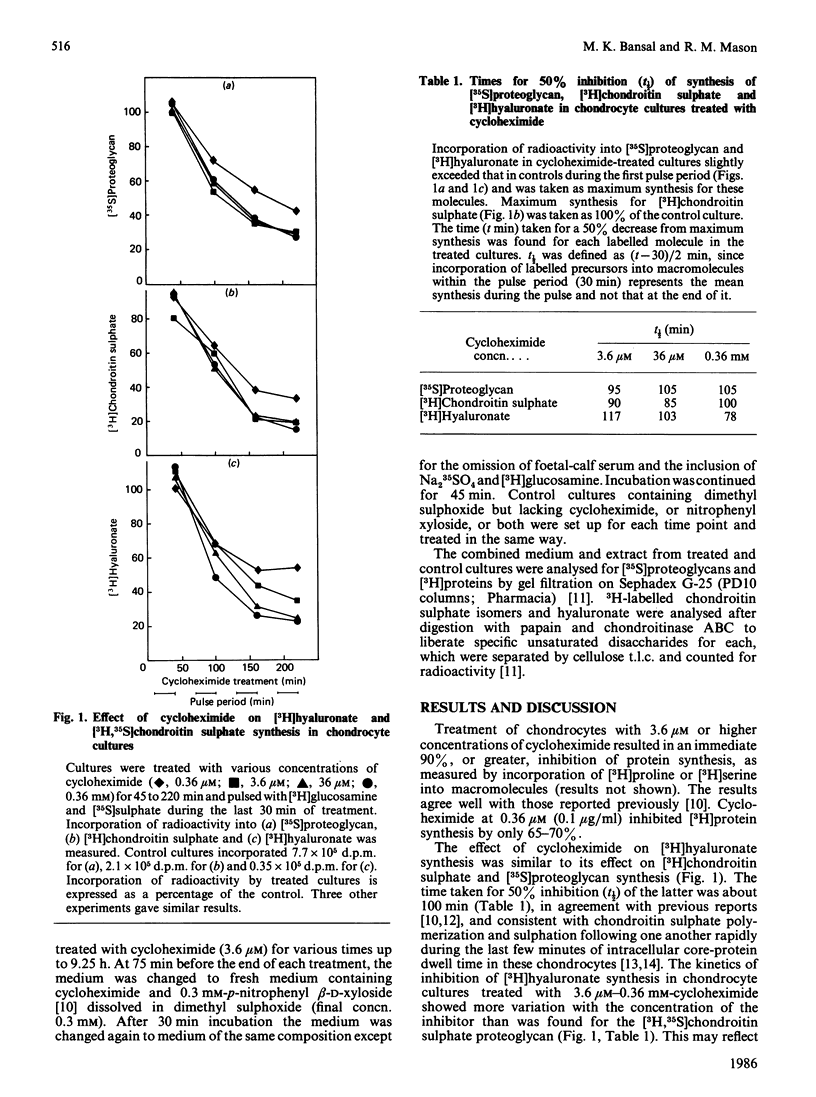
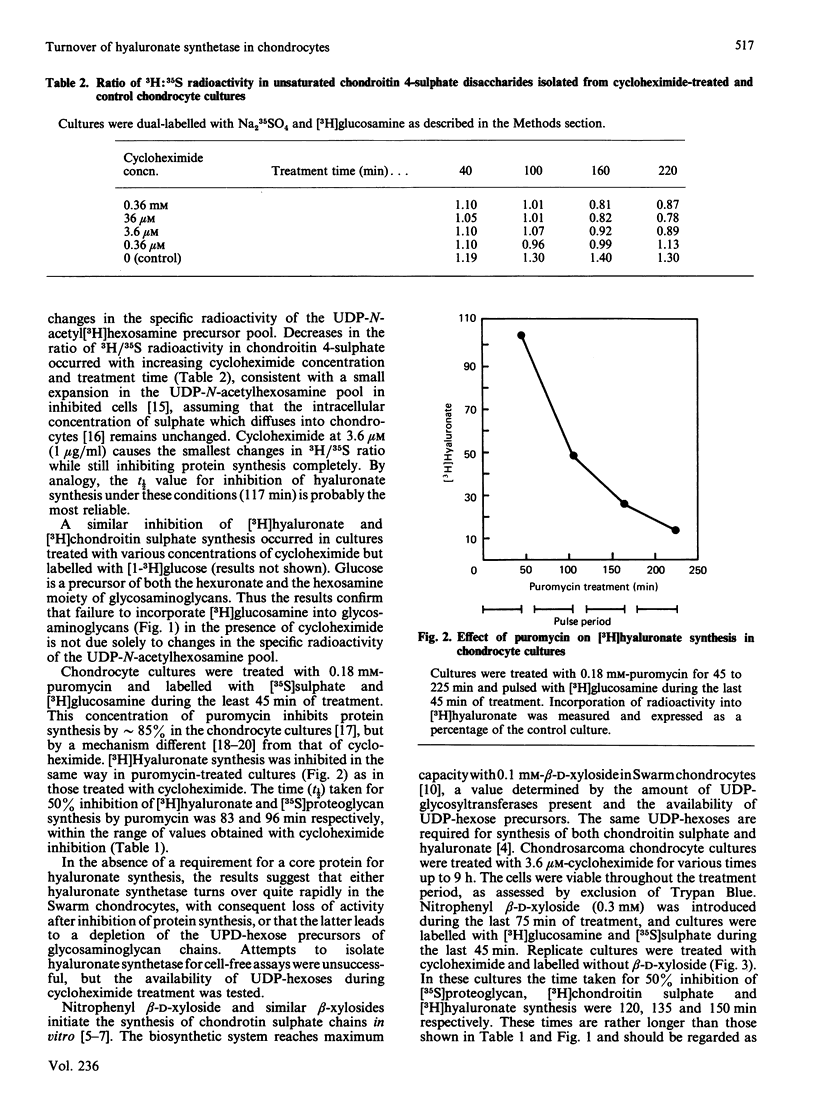
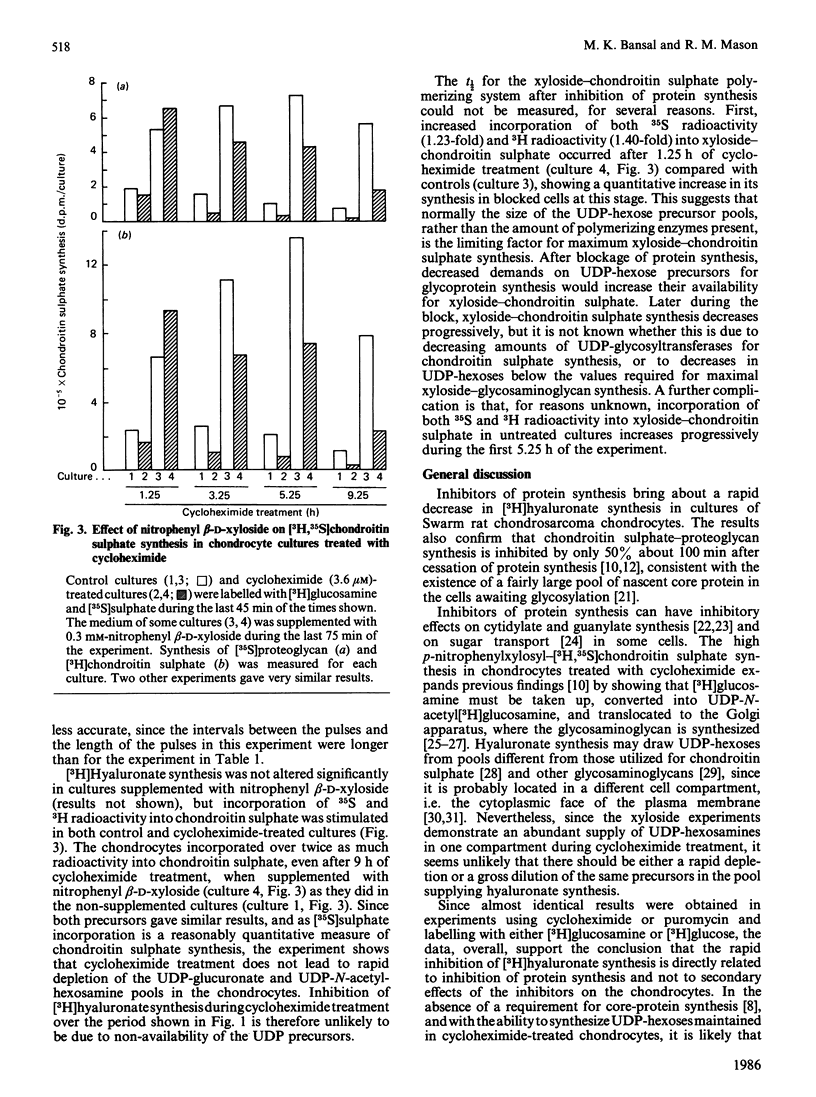
Synthesis of [3H]hyaluronate from [6-3H]glucosamine was investigated in cultures of Swarm rat chondrosarcoma chondrocytes treated with various concentrations (0.1 microM-0.1 mM) of cycloheximide for various times. Concentrations greater than 1 microM inhibited protein synthesis by greater than 90%. Hyaluronate synthesis was decreased, with a t1/2 for 50% inhibition of 80-120 min, depending on the concentration of cycloheximide present. Similar experiments using [1-3H]glucose as a precursor label gave similar results. Experiments using [6-3H]glucosamine as a precursor label and 0.18 mM-puromycin to inhibit protein synthesis inhibited hyaluronate synthesis (t1/2 = 82 min) with similar kinetics to cycloheximide-induced inhibition. Cultures incubated with 3.6 microM-cycloheximide for up to 9 h and supplemented with p-nitrophenyl beta-D-xyloside during the last 75 min of treatment showed increased synthesis of [3H,35S]chondroitin sulphate, demonstrating that UDP-hexose precursors for glycosaminoglycan synthesis are not rapidly depleted on blockage of protein synthesis. Rapid metabolic turnover of hyaluronate synthetase is the most likely cause for decreased hyaluronate synthesis in chondrocytes in which protein synthesis is inhibited.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN D. W., ZAMECNIK P. C. The effect of puromycin on rabbit reticulocyte ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 11;55:865–874. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90899-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Hascall V. C. Effect of puromycin on cartilage proteoglycan structure and capacity to bind hyaluronic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):594–604. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90440-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimata K., Okayama M., Suzuki S., Suzuki I., Hoshino M. Nascent mucopolysaccharides attached to the Golgi membrane of chondrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):606–610. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Caputo C. B., Hascall V. C. The effect of cycloheximide on synthesis of proteoglycans by cultured chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4368–4376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Hardingham T. E., Hascall V. C., Solursh M. Biosynthesis of proteoglycans and their assembly into aggregates in cultures of chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2600–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Lohmander L. S., Hascall V. C. Studies on the biosynthesis of cartilage proteoglycan in a model system of cultured chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(4):261–278. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Thonar E. J., Hascall V. C., Reiner A., Poole A. R. Identification of core protein, an intermediate in proteoglycan biosynthesis in cultured chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7890–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleine T. O. Hyaluronate-proteoglycan complex: evidence for separate biosynthesis mechanisms of the macromolecules. Connect Tissue Res. 1978;5(4):195–199. doi: 10.3109/03008207809152272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo K., Foley J. E. Effect of puromycin on sugar transport in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 11;817(1):187–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberg S. I., Dorfman A. Synthesis and degradation of hyaluronic acid in the cultured fibroblasts of Marfan's disease. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2428–2433. doi: 10.1172/JCI107433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapleson J. L., Buchwald M. Effect of cycloheximide and dexamethasone phosphate on hyaluronic acid synthesis and secretion in cultured human skin fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Nov;109(2):215–222. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas A. Glycosaminoglycan turn-over in articular cartilage. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jul 17;271(912):293–313. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez A., Argüelles F., Cervera J., Gomar F., Jr Sites of sulfatation in the chondrocytes of the articular cartilage of the rabbit. A study by quantitative radioautography of high resolution. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1977 Jan 20;23(1):53–64. doi: 10.1007/BF02889119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. M., Kimura J. H., Hascall V. C. Biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid in cultures of chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2236–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. M. Recent advances in the biochemistry of hyaluronic acid in cartilage. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;54:87–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. M., d'Arville C., Kimura J. H., Hascall V. C. Absence of covalently linked core protein from newly synthesized hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):445–457. doi: 10.1042/bj2070445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon R., Dorfman A. The structure of acid mucopolysaccharides produced by Hurler fibroblasts in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):179–185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikuni-Takagaki Y., Toole B. P. Hyaluronate-protein complex of rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8463–8469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D., Hardingham T. The effects of cycloheximide on the biosynthesis and secretion of proteoglycans by chondrocytes in culture. Biochem J. 1981 May 15;196(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1960521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANS D., LIPMANN F. Amino acid transfer from aminoacyl-ribonucleic acids to protein on ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Apr 15;47:497–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama M., Kimata K., Suzuki S. The influence of p-nitrophenyl beta-d-xyloside on the synthesis of proteochondroitin sulfate by slices of embryonic chick cartilage. J Biochem. 1973 Nov;74(5):1069–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. The use of inhibitors in studies on protein synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:261–282. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L. H., Schwartz N. B. Subcellular localization of hyaluronate synthetase in oligodendroglioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5017–5023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. M., Khym J. X., Jones M. H., Lee W. H., Volkin E. Suppression of cytidylate biosynthesis by protein synthesis antagonists. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3340–3347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P. Hyaluronate is synthesized at plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):597–600. doi: 10.1042/bj2200597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P. Synthesis of hyaluronate in differentiated teratocarcinoma cells. Characterization of the synthase. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 1;211(1):181–189. doi: 10.1042/bj2110181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P. Synthesis of hyaluronate in differentiated teratocarcinoma cells. Mechanism of chain growth. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 1;211(1):191–198. doi: 10.1042/bj2110191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. C., Brett M. J., Tralaggan P. J., Lowther D. A., Okayama M. The effect of D-xylose, beta-D-xylosides and beta-D-galactosides on chondroitin sulphate biosynthesis in embryonic chicken cartilage. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;148(1):25–34. doi: 10.1042/bj1480025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz N. B., Galligani L., Ho P. L., Dorfman A. Stimulation of synthesis of free chondroitin sulfate chains by beta-D-xylosides in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4047–4051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbert J. E., Freilich L. S. Biosynthesis of chondroitin sulphate by a Golgi-apparatus-enriched preparation from cultures of mouse mastocytoma cells. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 15;190(2):307–313. doi: 10.1042/bj1900307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C., Hamerman D. Partial inhibition by cycloheximide of haluronate synthesis in cell culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):988–991. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telser A., Robinson H. C., Dorfman A. The biosynthesis of chondroitin-sulfate protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):912–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thonar E. J., Lohmander L. S., Kimura J. H., Fellini S. A., Yanagishita M., Hascall V. C. Biosynthesis of O-linked oligosaccharides on proteoglycans by chondrocytes from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11564–11570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkin E., Boling M. E., Jones M. H., Lee W. H., Pike L. M. Suppression of the biosynthesis of guanosine triphosphate by protein synthesis inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9105–9109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K., Kiowski W., Buddecke E. Differently labelled glucosamine-precursor pools for the biosynthesis of hyaluronate and heparan sulfate. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 3;40(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


