Abstract
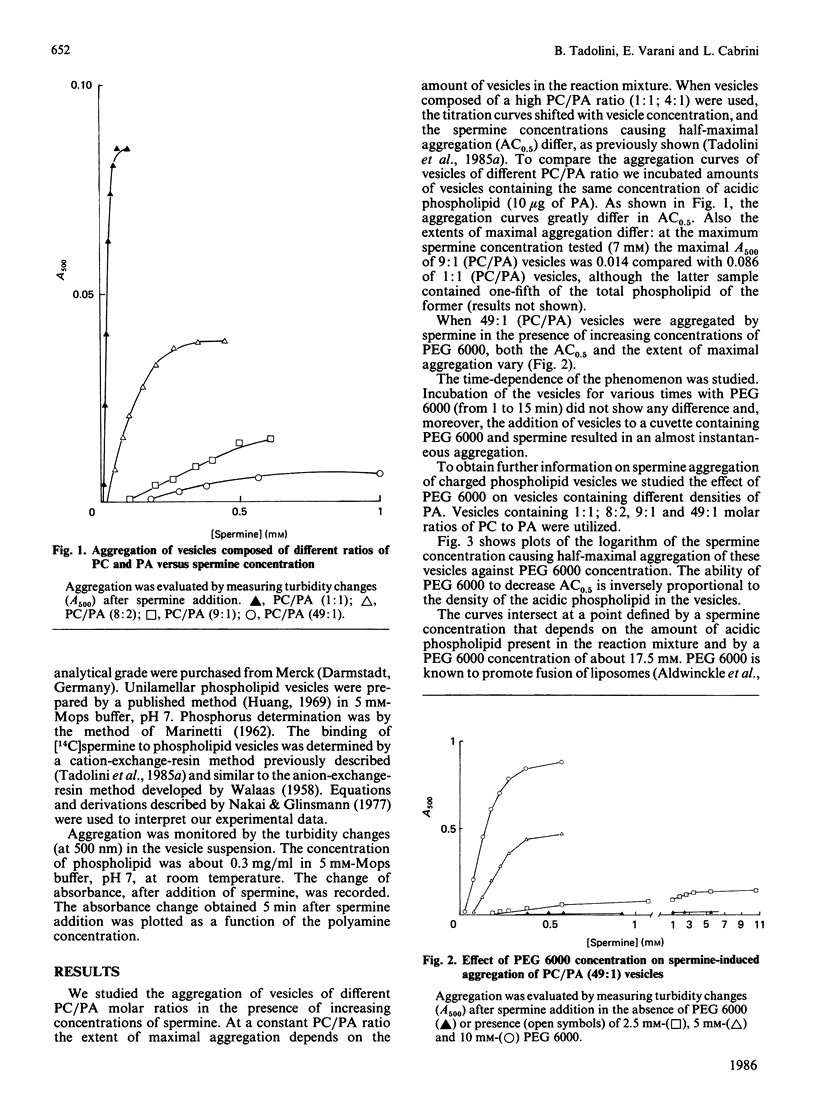
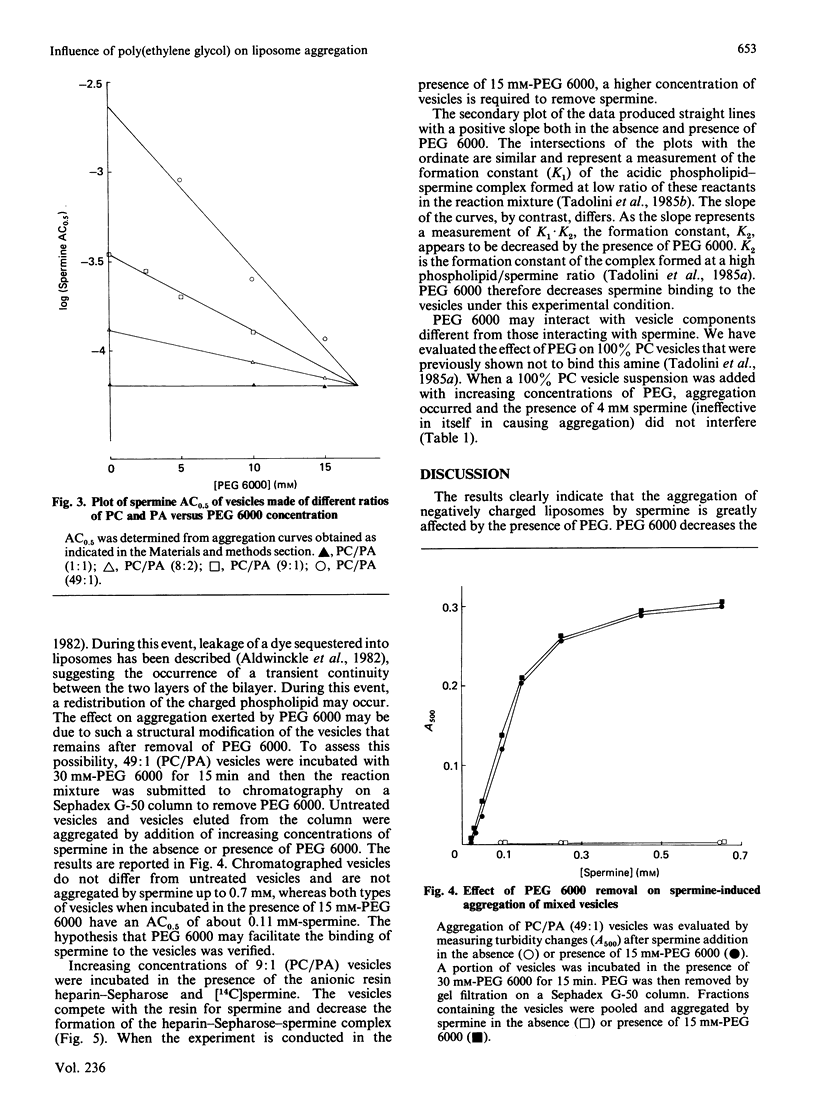
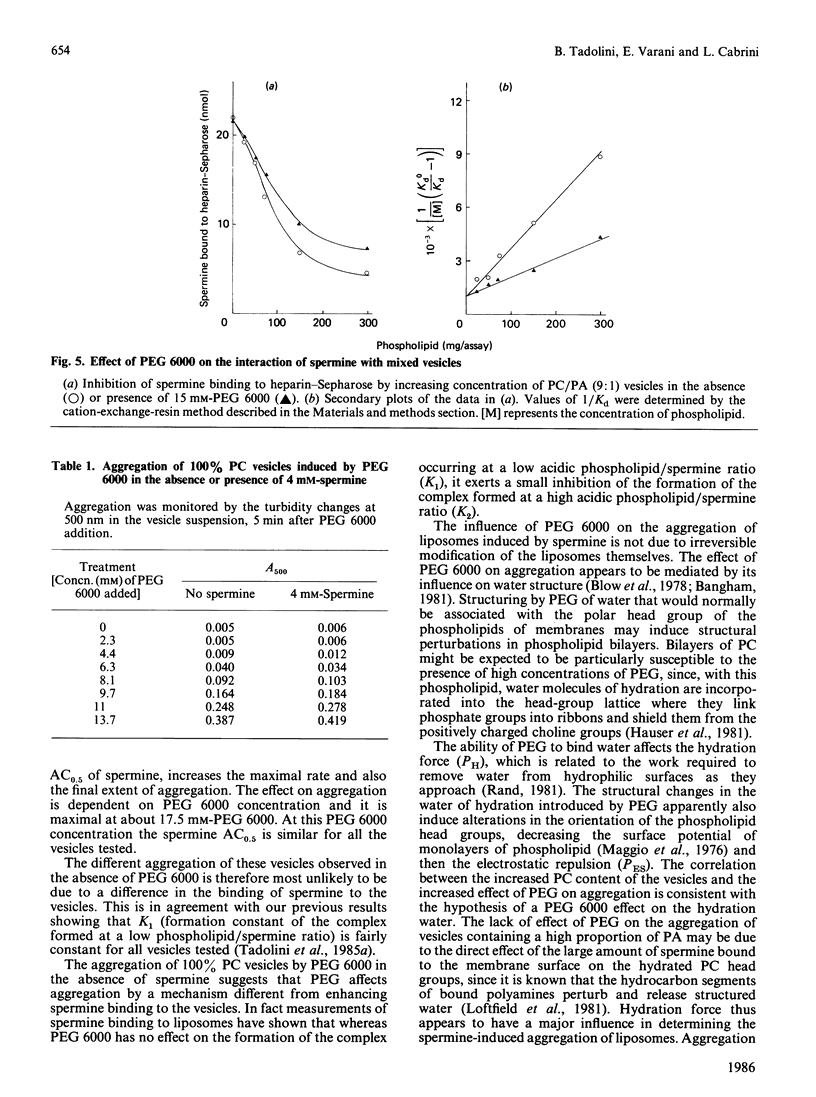
Poly(ethylene glycol) 6000 affected the aggregation of mixed liposomes induced by spermine. It lowered the concentration of spermine causing 50% maximal aggregation, accelerated the rate and increased the extent of aggregation. The effect was inversely proportional to the density of the acidic phospholipid in the vesicles. These effects were not due either to poly(ethylene glycol) 6000-induced permanent structural modification of the liposome or increased binding of spermine to the vesicles. These findings are discussed in relation to a decreased hydration force caused by the ability of poly(ethylene glycol) 6000 to alter the water of hydration of the phospholipid polar groups in the liposome.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldwinckle T. J., Ahkong Q. F., Bangham A. D., Fisher D., Lucy J. A. Effects of poly(ethylene glycol) on liposomes and erythrocytes. Permeability changes and membrane fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 12;689(3):548–560. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90313-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow A. M., Botham G. M., Fisher D., Goodall A. H., Tilcock C. P., Lucy J. A. Water and calcium ions in cell fusion induced by poly(ethylene glycol). FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 15;94(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80963-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Pascher I., Pearson R. H., Sundell S. Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Schuber F., Papahadjopoulos D. Polyamines. Biological modulators of membrane fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Studies on phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Formation and physical characteristics. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):344–352. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Honma R., Tokuno H., Kitada M., Kitagawa H., Hirose S. Effect of polyamines on prostaglandin synthesis in various cell-free systems. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90501-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinck P. H., Perry G. Effect of polyamines on the metabolism of [16-14C]estradiol by rat-liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig H., Goldstone A. D., Lu C. Y. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of Ca2+ fluxes, endocytosis, hexose transport, and amino acid transport in mouse kidney cortex is mediated by polyamine synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7210–7214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig H., Goldstone A., Lu C. Y. Polyamines regulate calcium fluxes in a rapid plasma membrane response. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):530–534. doi: 10.1038/305530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolber M. A., Haynes D. H. Evidence for a role of phosphatidyl ethanolamine as a modulator of membrane-membrane contact. J Membr Biol. 1979 Jun 29;48(1):95–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01869258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio B., Ahkong Q. F., Lucy J. A. Poly(ethylene glycol), surface potential and cell fusion. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 15;158(3):647–650. doi: 10.1042/bj1580647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Mulrine N., Gresalfi T., Vaio G., McLaughlin A. Adsorption of divalent cations to bilayer membranes containing phosphatidylserine. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Apr;77(4):445–473. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol L. W., Ogston A. G., Wills P. R. Effect of inert polymers on protein self-association. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 6;126(1):18–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P. Interacting phospholipid bilayers: measured forces and induced structural changes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:277–314. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuber F., Hong K., Düzgünes N., Papahadjopoulos D. Polyamines as modulators of membrane fusion: aggregation and fusion of liposomes. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6134–6140. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solaini G., Tadolini B. Spermine binding to submitochondrial particles and activation of adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):495–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2180495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadolini B., Cabrini L., Landi L., Varani E., Pasquali P. Polyamine binding to phospholipid vesicles and inhibition of lipid peroxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):550–555. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tellam R. L., Sculley M. J., Nichol L. W., Wills P. R. The influence of poly(ethylene glycol) 6000 on the properties of skeletal-muscle actin. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):651–659. doi: 10.1042/bj2130651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


