Abstract
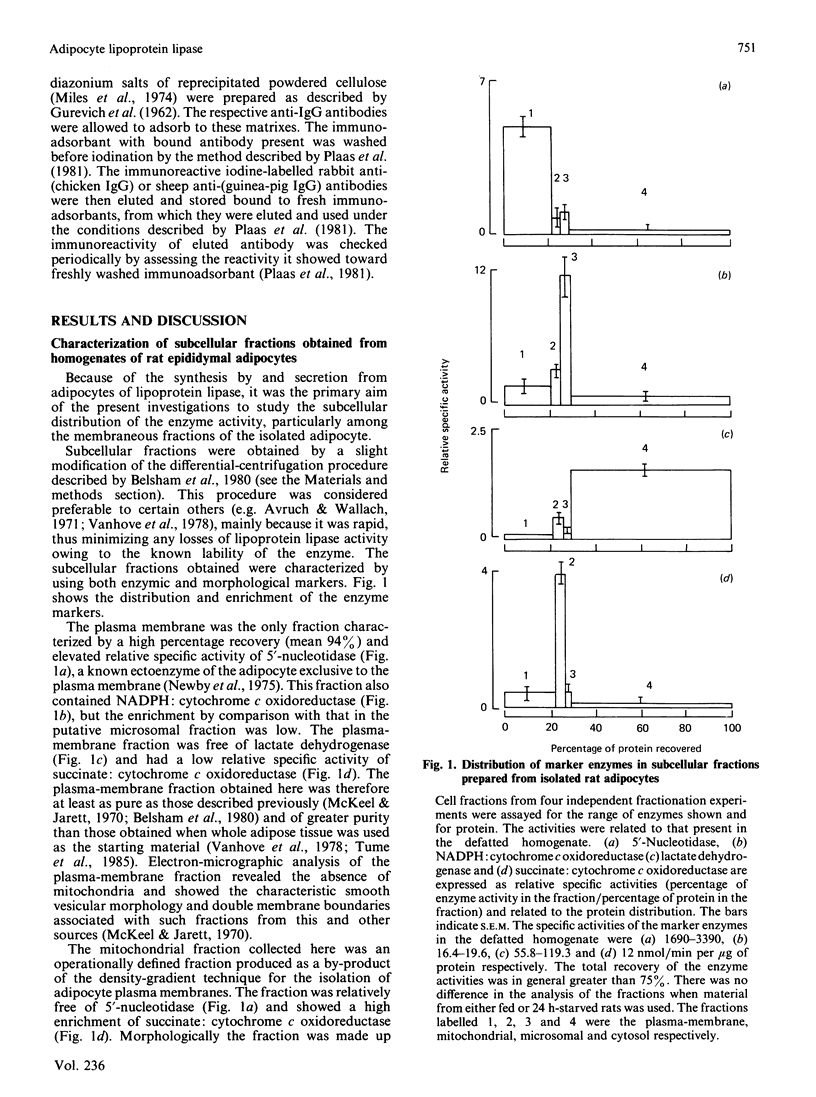
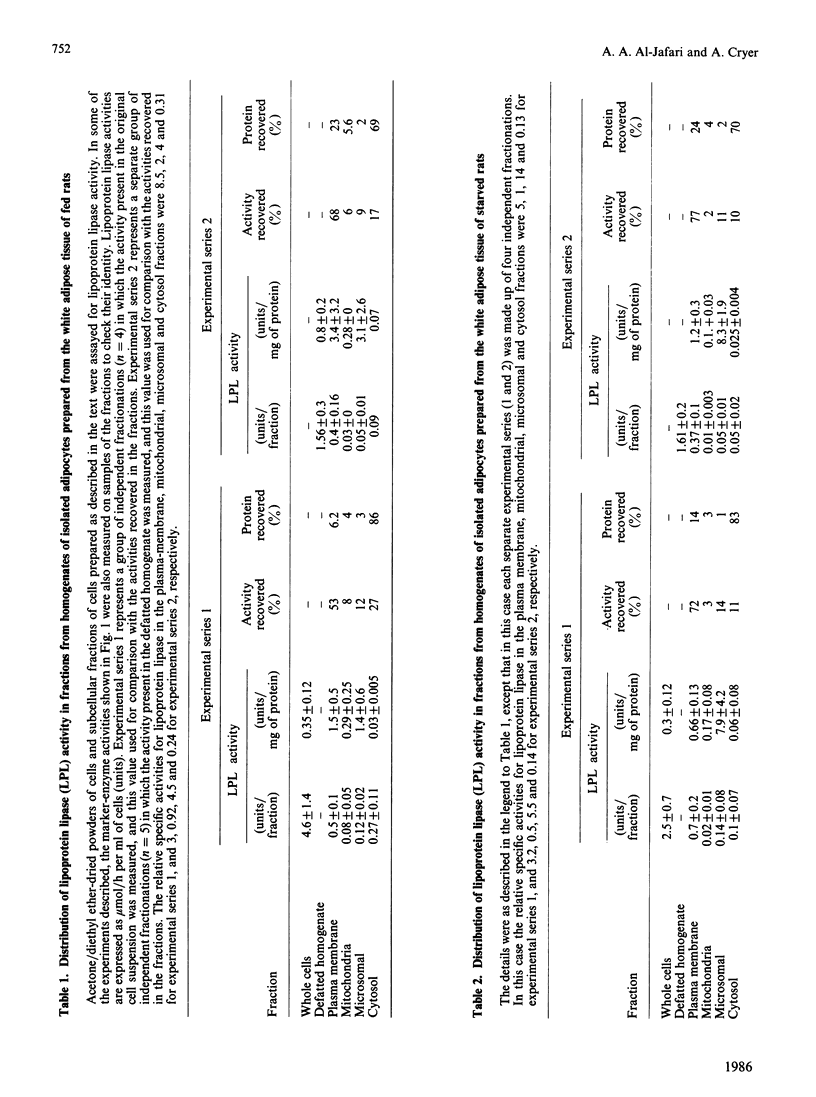
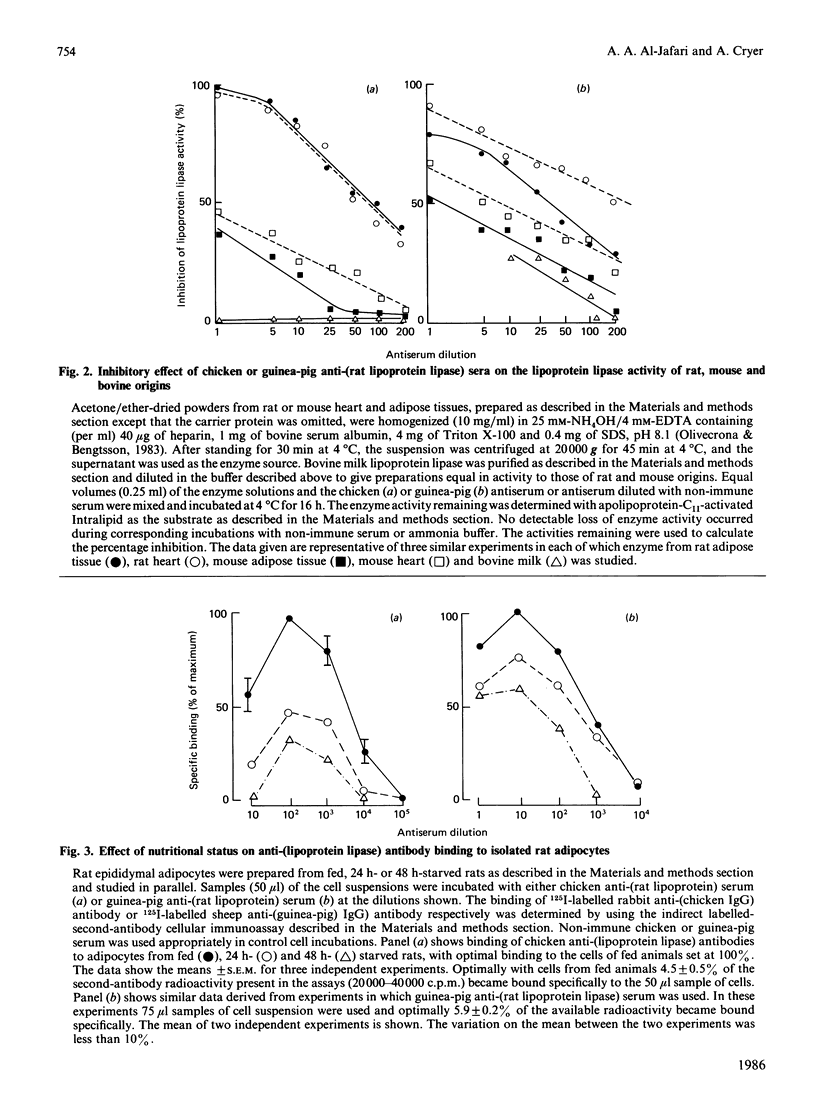
The separation of rat epididymal adipocytes into plasma-membrane, mitochondrial, microsomal and cytosol fractions is described. The fractions, which were characterized by marker-enzyme analysis and electron-micrographic observation, from the cells of fed and 24 h-starved animals were used to prepare acetone/diethyl ether-dried powders for the measurement of lipoprotein lipase activities. The highest specific activities and proportion of recovered lipoprotein lipase activity were found in the plasma-membrane and microsomal fractions. The two fractions from the cells of fed rats showed similar activities and enrichments of the enzyme, these activities being higher than the plasma-membrane and lower than the microsomal activities recovered from the cells of starved animals. Chicken and guinea-pig anti-(rat lipoprotein lipase) sera were prepared, and an indirect labelled-second-antibody cellular immunoassay, using 125I-labelled rabbit anti-(chicken IgG) or 125I-labelled sheep anti-(guinea-pig IgG) antibodies respectively, for the detection of cell-surface enzyme was devised and optimized. The amount of immunodetectable cell-surface lipoprotein lipase was higher for cells isolated from fed animals than for cells from 24 h-starved animals, when either anti-(lipoprotein lipase) serum was used in the assay. The amount of immunodetectable cell-surface lipoprotein lipase fell further when starvation was extended to 48 h. The lipoprotein lipase of plasma-membrane vesicles was shown to be a patent activity and to be immunodetectable in a modification of the cellular immunoassay. Although the functional significance of the adipocyte surface lipoprotein lipase is not known, the possibility of it forming a pool of enzyme en route to the capillary endothelium is advanced.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud J., Boyer J. Hydrolysis and uptake of an aliphatic fatty ester by whole isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 25;486(3):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud J., Nobili O., Boyer J. Differential properties of lipases active as membrane-bound enzymes in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 26;572(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J., Denton R. M., Tanner M. J. Use of a novel rapid preparation of fat-cell plasma membranes employing Percoll to investigate the effects of insulin and adrenaline on membrane protein phosphorylation within intact fat-cells. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):457–467. doi: 10.1042/bj1920457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Scow R. O. Lipolysis and lamellar structures in white adipose tissue of young rats: lipid movement in membranes. J Ultrastruct Res. 1981 Dec;77(3):295–318. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(81)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Scow R. O. Membrane continuities within cells and intercellular contacts in white adipose tissue of young rats. J Ultrastruct Res. 1981 Dec;77(3):277–294. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(81)80025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Otway S., Robinson D. S. Effect of fasting on the clearing factor lipase (lipoprotein lipase) activity of fresh and defatted preparations of rat heart muscle. J Lipid Res. 1970 Mar;11(2):102–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chohan P., Cryer A. Lipoprotein lipase activity of rat cardiac muscle. The intracellular distribution of the enzyme between fractions prepared from cardiac muscle and cells isolated from the hearts of fed and starved animals. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1810083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chohan P., Cryer A. The lipoprotein lipase (clearing-factor lipase) activity of cells isolated from rat cardiac muscle. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):663–666. doi: 10.1042/bj1740663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Davies P., Williams E. R., Robinson D. S. The clearing-factor lipase activity of isolated fat-cells. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):481–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1460481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Gray B. R., Woodhead J. S. Studies on the characterization of bovine adipocyte precursor cells and their differentiation in vitro, using an indirect-labelled-second-antibody cellular immunoassay. J Dev Physiol. 1984 Apr;6(2):159–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Jones H. M. Changes in the lipoprotein lipase (clearing-factor lipase) activity of white adipose tissue during development of the rat. Biochem J. 1978 May 15;172(2):319–325. doi: 10.1042/bj1720319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Riley S. E., Williams E. R., Robinson D. S. Effect of nutritional status on rat adipose tissue, muscle and post-heparin plasma clearing factor lipase activities: their relationship to triglyceride fatty acid uptake by fat-cells and to plasma insulin concentrations. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Mar;50(3):213–221. doi: 10.1042/cs0500213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A. Tissue lipoprotein lipase activity and its action in lipoprotein metabolism. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(5):525–541. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Wusteman F. S., Casey J. J. Glycosaminoglycan: cell interactions; their role in lipoprotein lipase secretion from isolated cardiac muscle cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 1984 Jan;2(1):53–56. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290020114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham V. J., Robinson D. S. Clearing-factor lipase in adipose tissue. Distinction of different states of the enzyme and the possible role of the fat cell in the maintenance of tissue activity. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):203–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1120203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Robinson D. S. Stability of clearing-factor lipase in rat adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):437–439. doi: 10.1042/bj1360437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman G., Chajek-Shaul T., Olivecrona T., Stein O., Stein Y. Fate of milk 125I-labelled lipoprotein lipase in cells in culture. Comparison of lipoprotein lipase- and non-lipoprotein lipase-synthesizing cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 15;711(1):114–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh M., Hamosh P. Lipoprotein lipase: its physiological and clinical significance. Mol Aspects Med. 1983;6(3):199–289. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(83)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V. Uptake of very low density lipoprotein triglyceride by bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. J Lipid Res. 1977 Sep;18(5):561–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder C., Chernick S. S., Fleck T. R., Scow R. O. Lipoprotein lipase and uptake of chylomicron triglyceride by skeletal muscle of rats. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):860–864. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newby A. C., Luzio J. P., Hales C. N. The properties and extracellular location of 5'-nucleotidase of the rat fat-cell plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;146(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj1460625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Bengtsson G. Immunochemical properties of lipoprotein lipase. Development of an immunoassay applicable to several mammalian species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 16;752(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin S. M., Speake B. K., Robinson D. S. Purification and characterization of rat adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):485–495. doi: 10.1042/bj2070485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaas H. A., Woodhead J. S., Cryer A. The use of antiserum with specific reactivity toward fat-cell surface antigen(s) to follow the progression of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation in vitro. Biosci Rep. 1981 Mar;1(3):207–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01114906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakis E. S., Bartley W., Meek G. A. Changes in the activities of respiratory enzymes during the aerobic growth of yeast on different carbon sources. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):298–302. doi: 10.1042/bj0970298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn D., Shirai K., Jackson R. L. Lipoprotein lipase: mechanism of action and role in lipoprotein metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. 1983;22(1):35–78. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(83)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. LOCALIZATION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN FAT CELLS OF RAT ADIPOSE TISSUE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:753–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. P., Robinson D. S. Effects of cold exposure on heart clearing factor lipase and triglyceride utilization in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1974 May;15(3):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Greenbaum A. L. The effect of dietary and hormonal conditions on the activities of glycolytic enzymes in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):405–417. doi: 10.1042/bj1150405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Smith L. C. Role of capillary endothelium in the clearance of chylomicrons. A model for lipid transport from blood by lateral diffusion in cell membranes. Circ Res. 1976 Aug;39(2):149–162. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Smith L. C. Transport of lipid across capillary endothelium. Fed Proc. 1980 Jul;39(9):2610–2617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemankowski R. F., Dreizen P. Canine cardiac myosin with special referrence to pressure overload cardiac hypertrophy. I. Subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8648–8658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tume R. K., Lee S. R., Cryer A. A comparison of the polypeptide composition of plasma membranes prepared from the white adipose tissue and adipocytes of the mouse, rat, rabbit, ox and chicken by a Percoll self-forming gradient procedure. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1985;80(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(85)90433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhove A., Wolf C., Breton M., Glangeaud M. C. Effect of nutrition on subcellular localization of rat fat-cell lipoprotein lipase. Biochem J. 1978 May 15;172(2):239–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1720239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Amri E. Z., Etienne J., Négrel R., Ailhaud G. Maturation and secretion of lipoprotein lipase in cultured adipose cells. I. Intracellular activation of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4424–4431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Jansen H., Négrel R., Ailhaud G. Study of lipoprotein lipase content in Ob17 preadipocytes during adipose conversion. Immunofluorescent localization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12387–12393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vérine A., Salers P., Boyer J. Effects of apoproteins C on lipoprotein lipase activity bound to rat fat cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):E175–E181. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.3.E175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. P., Streeter H. B., Wusteman F. S., Cryer A. Heparan sulphate and the binding of lipoprotein lipase to porcine thoracic aorta endothelium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 15;756(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf C., Vanhove A., Breton M., Etienne J., Bereziat G., Polonovski J. Localisation sub-cellulaire de la lipoprotéine-lipase dans l'adipocyte de rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1975;169(5):1145–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


