Abstract
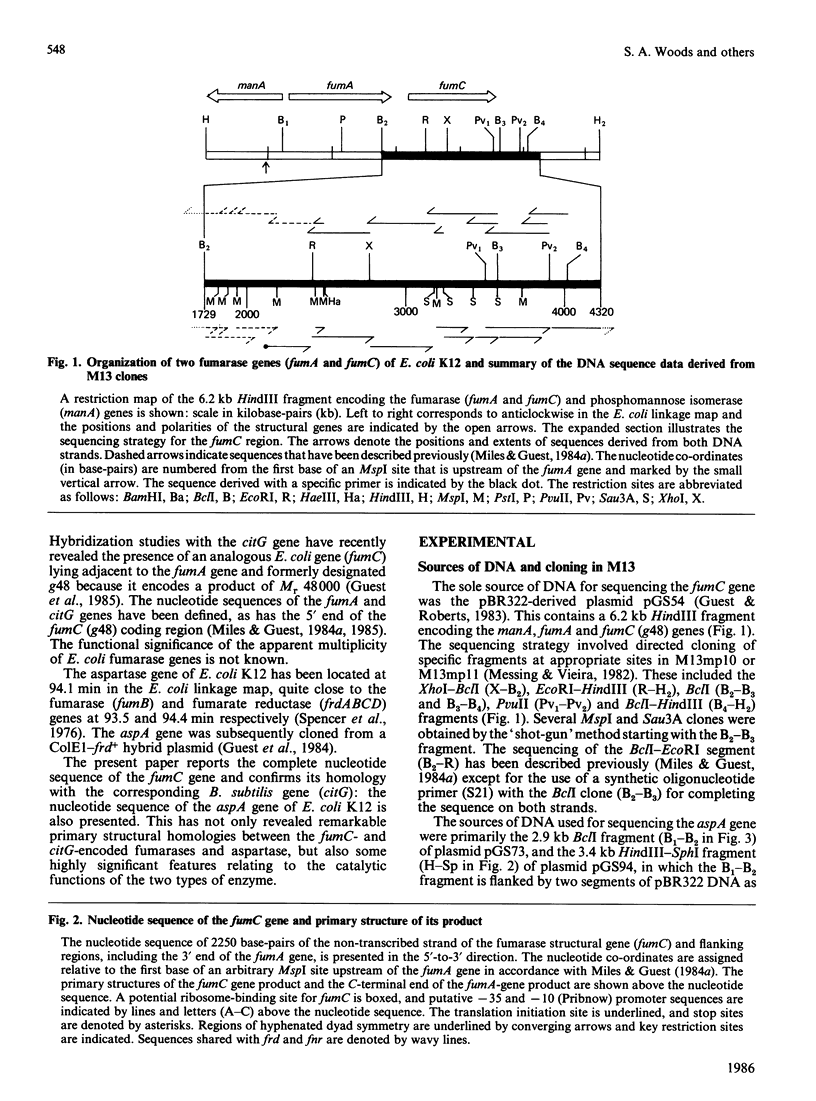
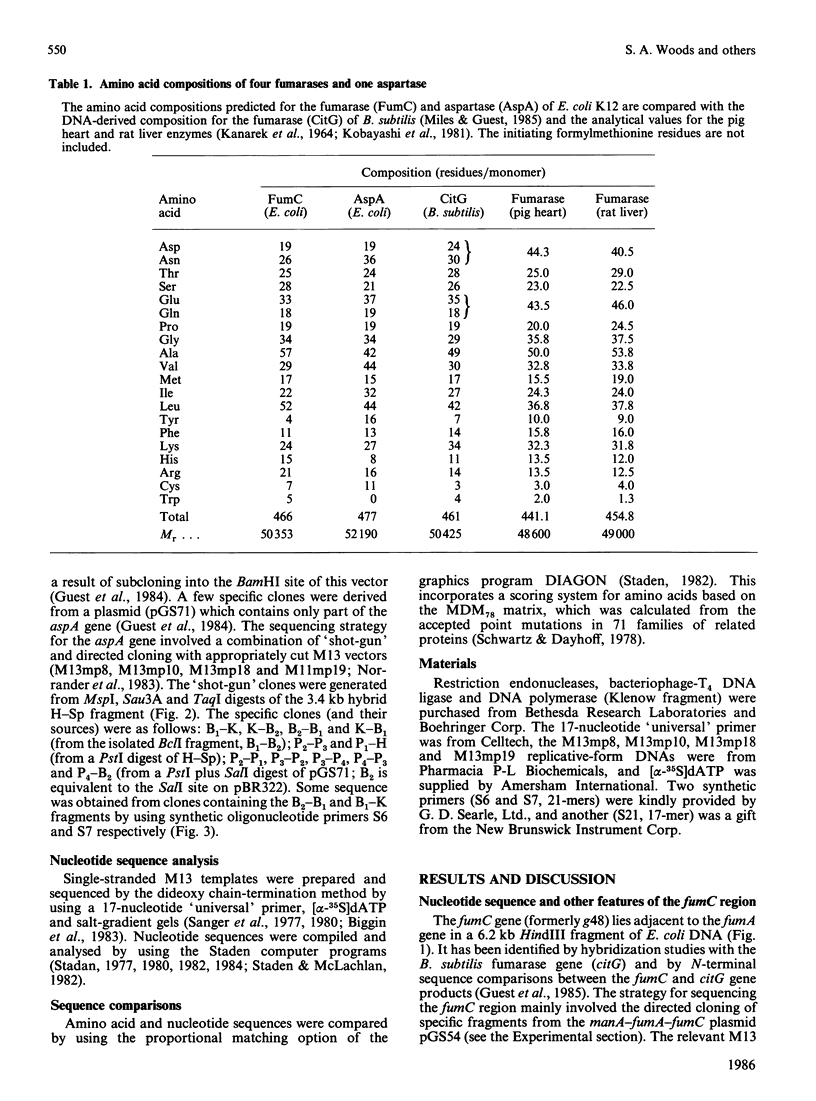
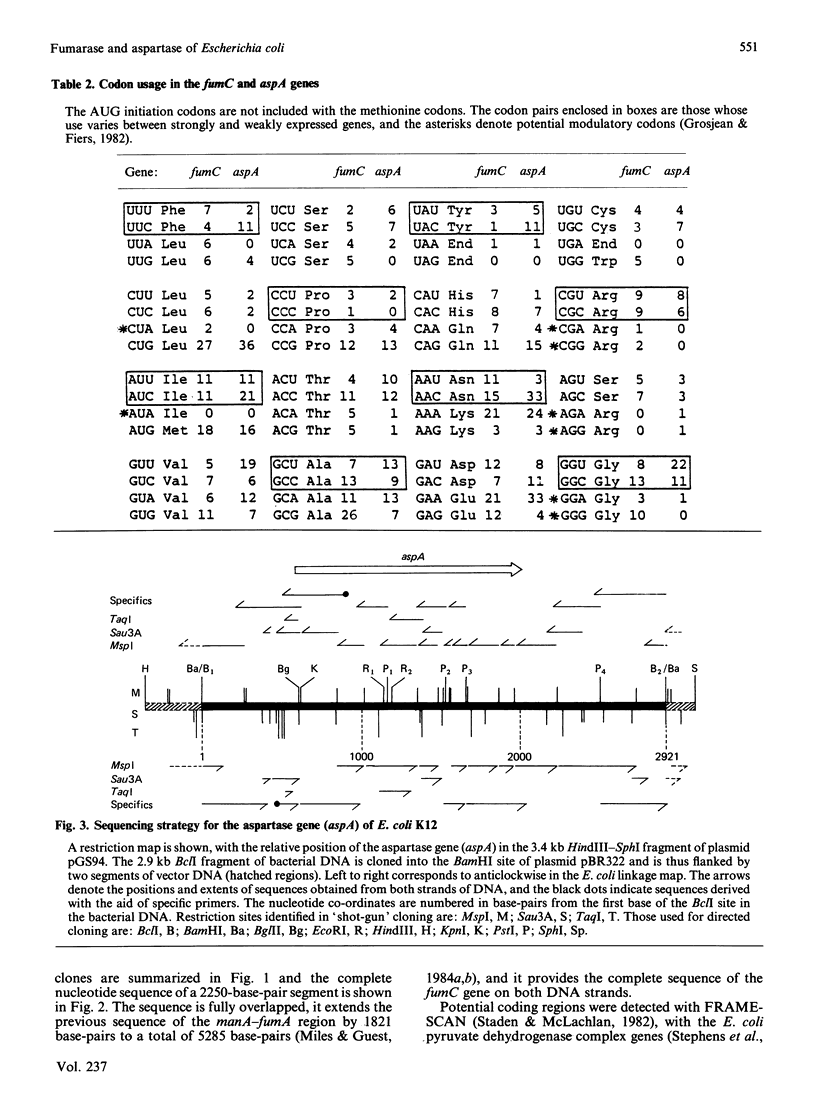
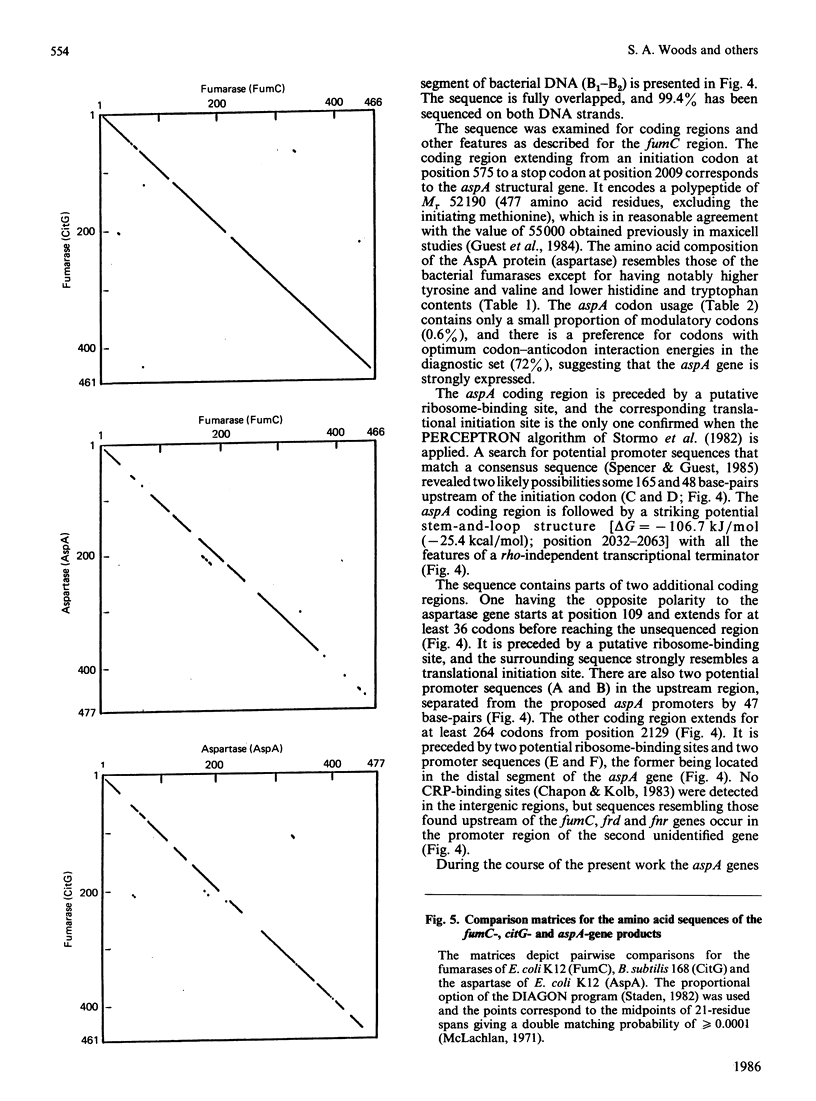
The nucleotide sequences of two segments of DNA (2250 and 2921 base-pairs) containing the functionally related fumarase (fumC) and aspartase (aspA) genes of Escherichia coli K12 were determined. The fumC structural gene comprises 1398 base-pairs (466 codons, excluding the initiation codon), and it encodes a polypeptide of Mr 50353 that resembles the fumarases of Bacillus subtilis 168 (citG-gene product), rat liver and pig heart. The fumC gene starts 140 base-pairs downstream of the structurally-unrelated fumA gene, but there is no evidence that both genes form part of the same operon. The aspA structural gene comprises 1431 base-pairs (477 codons excluding the initiation codon), and it encodes a polypeptide of Mr 52190, similar to that predicted from maxicell studies and for the enzyme from E. coli W. Remarkable homologies were found between the primary structures of the fumarase (fumC and citG) and aspartase (aspA) genes and their products, suggesting close structural and evolutionary relationships.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. S., Cleland W. W. Use of isotope effects to deduce the chemical mechanism of fumarase. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4506–4513. doi: 10.1021/bi00560a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Robinson G. W., Hass G. M., Hill R. L. The reaction of fumarase with iodoacetate and 4-bromocrotonate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 10;244(7):1755–1763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapon C., Kolb A. Action of CAP on the malT promoter in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1135–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1135-1143.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Grundström T., Jaurin B., Robinson J. J., Weiner J. H. Location and nucleotide sequence of frdB, the gene coding for the iron-sulphur protein subunit of the fumarate reductase of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):211–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtright J. B., Henning U. Malate dehydrogenase mutants in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):722–728. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.722-728.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. T., Wimpenny J. W., Mossman M. R. Regulation of metabolism in facultative bacteria. II. Effects of aerobiosis, anaerobiosis and nutrition on the formation of Krebs cycle enzymes in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Miles J. S., Roberts R. E., Woods S. A. The fumarase genes of Escherichia coli: location of the fumB gene and discovery of a new gene (fumC). J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Nov;131(11):2971–2984. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-11-2971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Roberts R. E. Cloning, mapping, and expression of the fumarase gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):588–596. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.588-596.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Roberts R. E., Wilde R. J. Cloning of the aspartase gene (aspA) of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1271–1278. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ida N., Tokushige M. Assignment of catalytically essential cysteine residues in aspartase by selective chemical modification with N-(7-dimethylamino-4-methylcoumarynyl)maleimide. J Biochem. 1985 Sep;98(3):793–797. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ida N., Tokushige M. L-Aspartate-induced activation of aspartase. J Biochem. 1985 Jul;98(1):35–39. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. T., Lowe G., Potter B. V. Evidence against a step-wise mechanism for the fumarase-catalysed dehydration of (2S)-malate. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):433–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANAREK L., MARLER E., BRADSHAW R. A., FELLOWS R. E., HILL R. L. THE SUBUNITS OF FUMARASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4207–4211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Tuboi S. End group analysis of the cytosolic and mitochondrial fumarases from rat liver. J Biochem. 1983 Sep;94(3):707–713. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Yamanishi T., Tuboi S. Physicochemical, catalytic, and immunochemical properties of fumarases crystallized separately from mitochondrial and cytosolic fractions of rat liver. J Biochem. 1981 Jun;89(6):1923–1931. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M., Halpern Y. S. The metabolic pathway of glutamate in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 1;177(2):314–320. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. S., Guest J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of the fumarase gene (citG) of Bacillus subtilis 168. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):131–140. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. S., Guest J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of the fumarase gene fumA, of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3631–3642. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. S., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional start point of the phosphomannose isomerase gene (manA) of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta K., Tokushige M. Studies on aspartase. II. Role of sulfhydryl groups in aspartase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 22;403(1):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A., Feavers I. M., Guest J. R. Characterization of the fumarase gene of Bacillus subtilis 168 cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):3009–3017. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-3009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. J., Bright H. J. 3-Carbanionic substrate analogues bind very tightly to fumarase and aspartase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4772–4780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quastel J. H., Woolf B. The Equilibrium between l-Aspartic Acid, Fumaric Acid and Ammonia in Presence of Resting Bacteria. Biochem J. 1926;20(3):545–555. doi: 10.1042/bj0200545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. W., Bradshaw R. A., Kanarek L., Hill R. L. The thiol groups of fumarase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2709–2718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph F. B., Fromm H. J. The purification and properties of aspartase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the fnr gene and primary structure of the Enr protein of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):6119–6130. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.6119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. W., Neidhardt F. C. Proteins induced by anaerobiosis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):336–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.336-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. E., Guest J. R. Transcription analysis of the sucAB, aceEF and lpd genes of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):145–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00383328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. E., Lebeter V. M., Guest J. R. Location of the Aspartase Gene (aspA) on the linkage map of Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Nov;97(1):73–82. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A computer program to enter DNA gel reading data into a computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):499–503. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Sequence data handling by computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):4037–4051. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Lewis H. M., Darlison M. G., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Use of the 'Perceptron' algorithm to distinguish translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2997–3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Yamaguchi J., Tokushige M. Studies on aspartase. I. Purification and molecular properties of aspartase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 15;321(1):369–381. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi J. S., Fukunaga R., Tokushige M., Katsuki H. Purification, crystallization, and molecular properties of aspartase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Biochem. 1984 Aug;96(2):545–552. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi J. S., Ida N., Tokushige M., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the aspartase gene of Escherichia coli W. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2063–2074. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Kisumi M. Isolation of a versatile Serratia marcescens mutant as a host and molecular cloning of the aspartase gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.1-6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


