Abstract
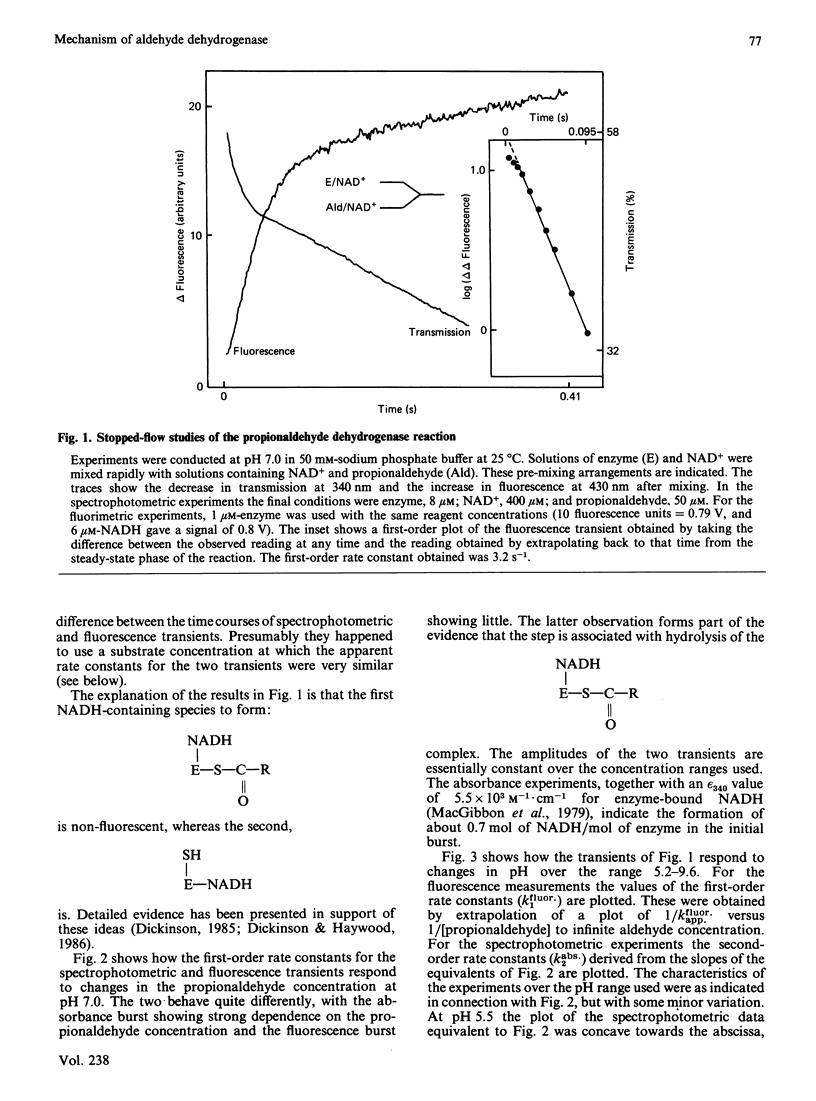
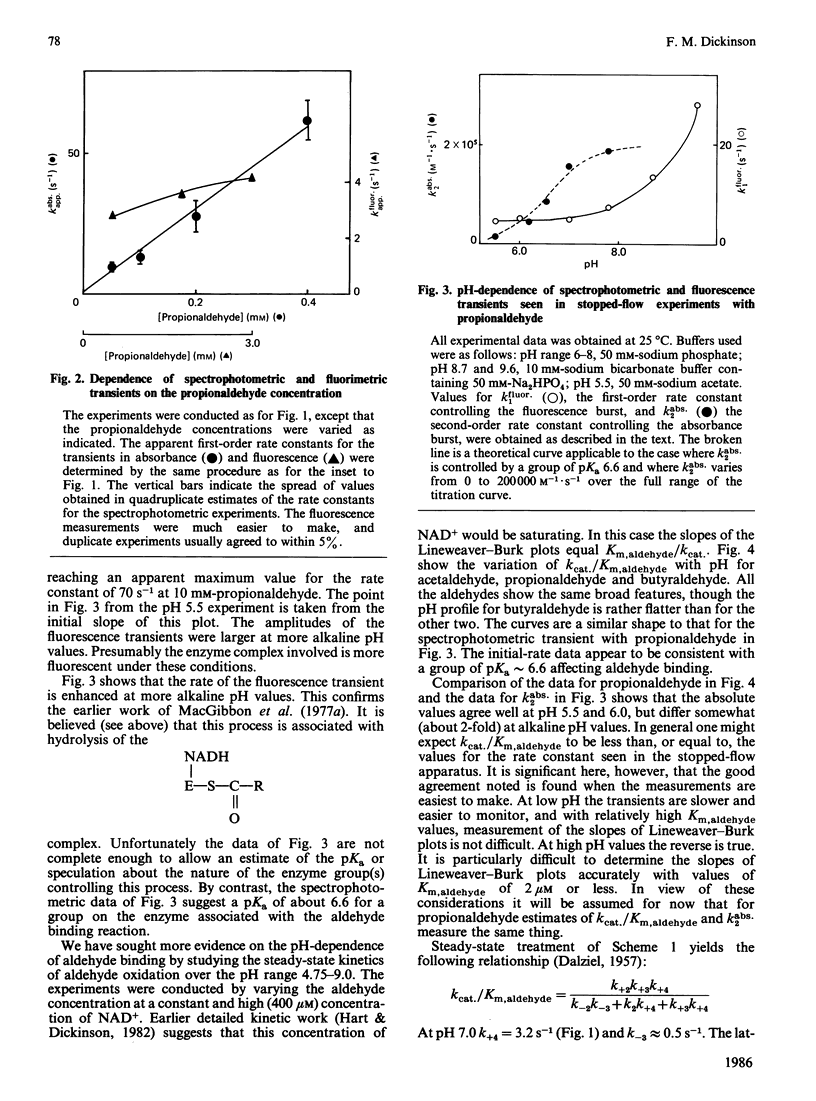
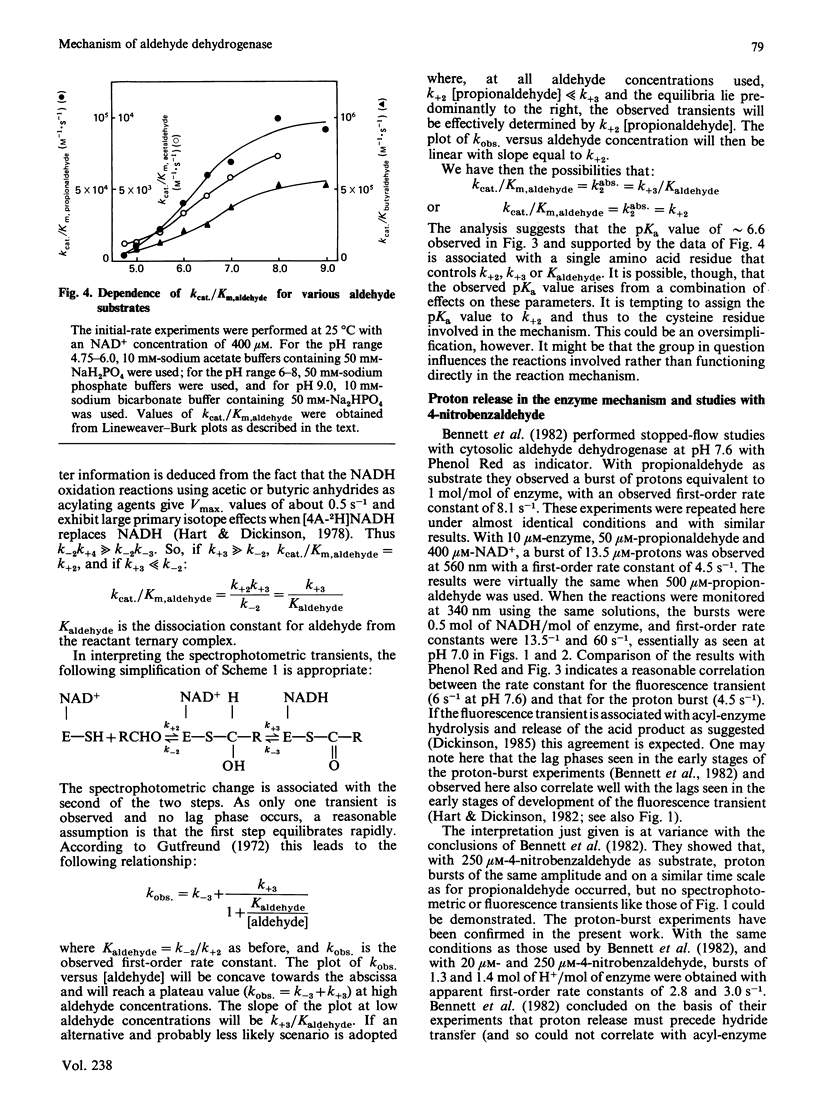
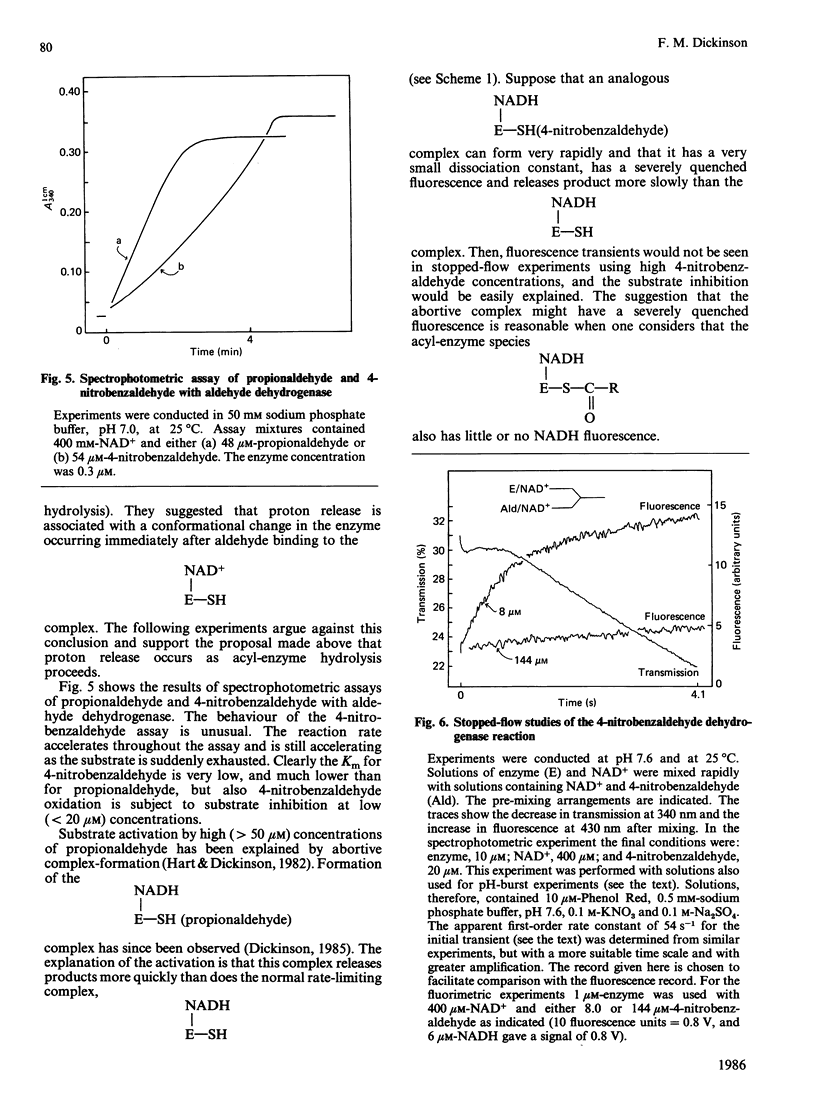
Initial-rate measurements and stopped-flow spectrophotometric experiments over a wide range of pH implicate an enzyme group of pKa approximately 6.6 affecting the aldehyde binding reactions. It is possible, though not proved, that the group involved is the cysteine residue involved in catalysis. Stopped-flow fluorescence studies show that a group of pKa greater than 8.5 facilitates hydrolysis of the NADH-containing acyl-enzyme species. The identity of this group is quite unknown. Studies with 4-nitrobenzaldehyde show that this substrate gives marked substrate inhibition at quite low (less than 20 microM) concentrations. The mechanism of catalysis seems to be the same as for propionaldehyde oxidation. It is argued that proton release occurs with both substrates on hydrolysis of the NADH-containing acyl-enzyme and not before hydride transfer, as has been previously suggested [Bennett, Buckley & Blackwell (1982) Biochemistry 21, 4407-4413].
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A. F., Buckley P. D., Blackwell L. F. Proton release during the pre-steady-state oxidation of aldehydes by aldehyde dehydrogenase. Evidence for a rate-limiting conformational change. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4407–4413. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. Kinetic studies of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:244–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0840244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Hart G. J., Kitson T. M. The use of pH-gradient ion-exchange chromatography to separate sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from mitochondrial enzyme contamination, and observations on the interaction between the pure cytoplasmic enzyme and disulfiram. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):573–579. doi: 10.1042/bj1990573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Haywood G. W. The effects of Mg2+ on certain steps in the mechanisms of the dehydrogenase and esterase reactions catalysed by sheep liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Support for the view that dehydrogenase and esterase activities occur at the same site on the enzyme. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):877–883. doi: 10.1042/bj2330877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M. Studies on the mechanism of sheep liver cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):159–165. doi: 10.1042/bj2250159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Kinetic properties of highly purified preparations of sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 1;203(3):617–627. doi: 10.1042/bj2030617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Partial reversal of the acetaldehyde and butyraldehyde oxidation reactions catalysed by aldehyde dehydrogenases from sheep liver. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):753–756. doi: 10.1042/bj1750753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Some properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1630261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. The coenzyme-binding characteristics of highly purified preparations of sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):363–371. doi: 10.1042/bj2110363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. High concentrations of aldehydes slow the reaction of cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase with thiol-group modifiers. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):765–767. doi: 10.1042/bj2280765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Kinetics of sheep-liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Pre-steady-state kinetic studies on cytoplasmic sheep liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):469–477. doi: 10.1042/bj1670469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Motion R. L., Crow K. E., Buckley P. D., Blackwell L. F. Purification and properties of sheep-liver aldehyde dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):585–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


