Abstract
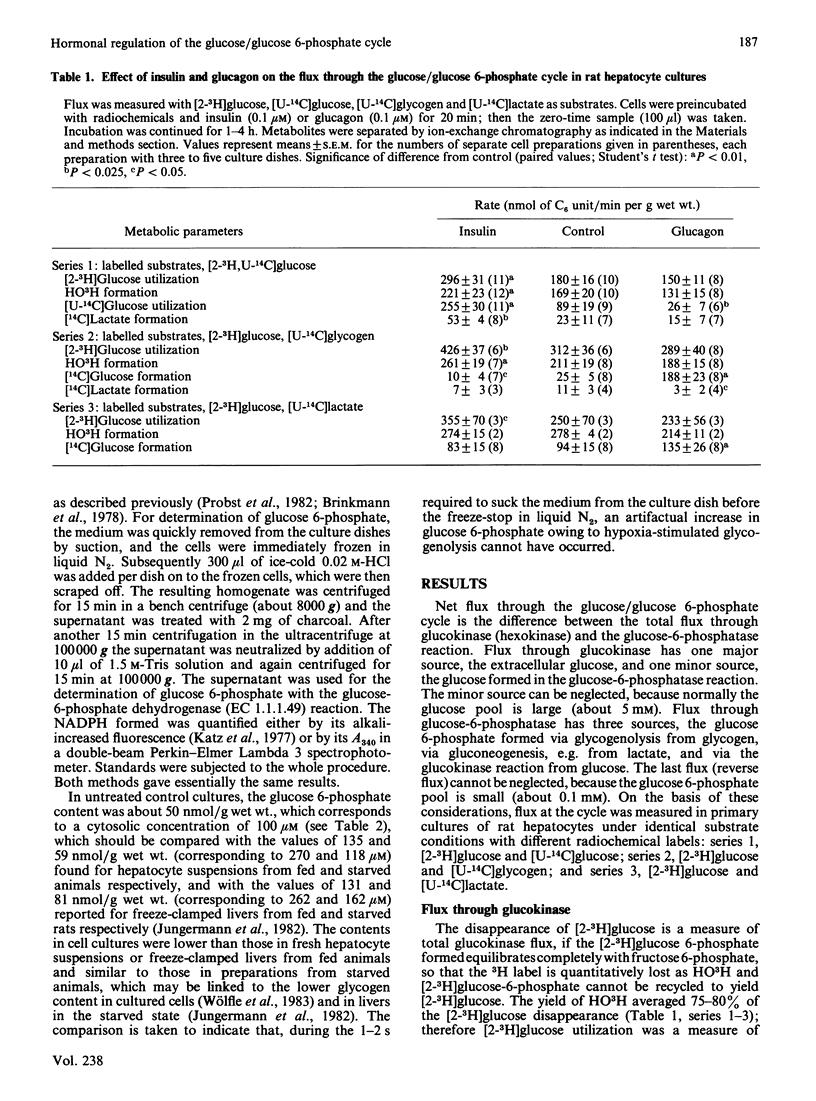
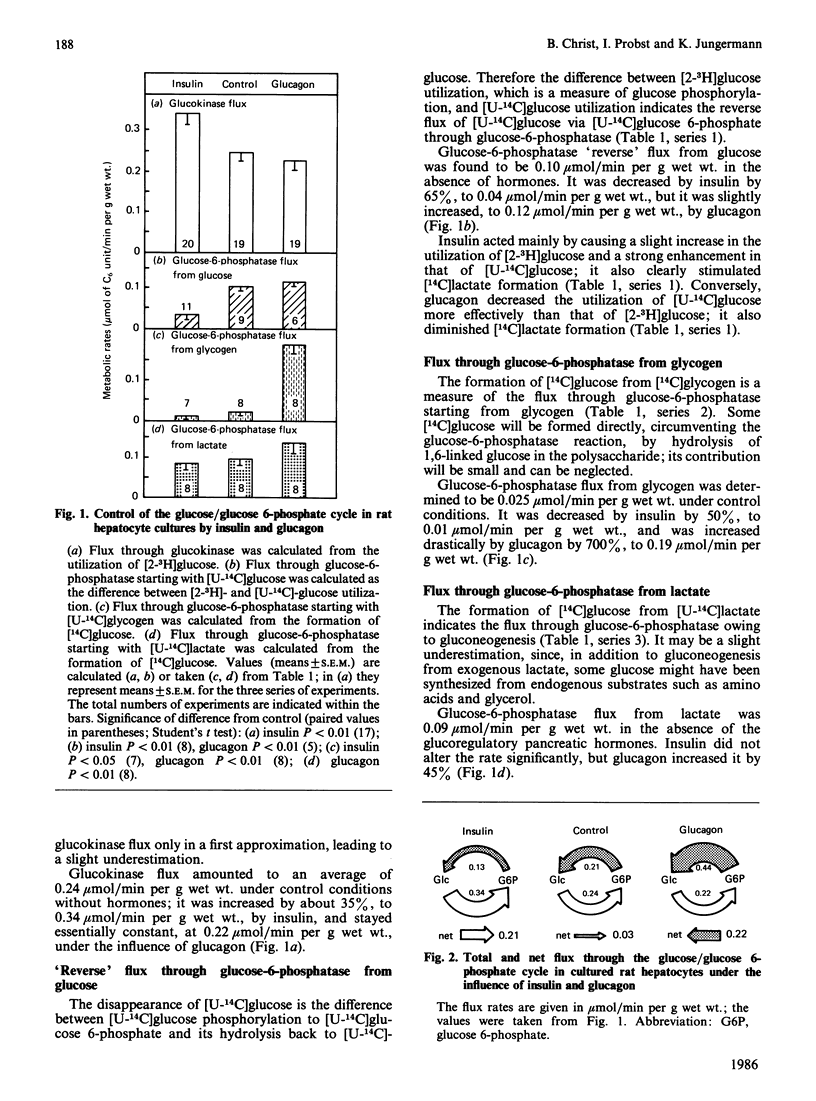
Flux through the glucose/glucose 6-phosphate cycle in cultured hepatocytes was measured with radiochemical techniques. Utilization of [2-3H]glucose was taken as a measure of glucokinase flux. Liberation of [14C]glucose from [U-14C]glycogen and from [U-14C]lactate, as well as the difference between the utilization of [2-3H]glucose and of [U-14C]glucose, were taken as measures of glucose-6-phosphatase flux. At constant 5 mM-glucose and 2 mM-lactate concentrations insulin increased glucokinase flux by 35%; it decreased glucose-6-phosphatase flux from glycogen by 50%, from lactate by 15% and reverse flux from external glucose by 65%, i.e. overall by 40%. Glucagon had essentially no effect on glucokinase flux; it enhanced glucose-6-phosphatase flux from glycogen by 700%, from lactate by 45% and reverse flux from external glucose by 20%, i.e. overall by 110%. At constant glucose concentrations cellular glucose 6-phosphate concentrations were essentially not altered by insulin, but were increased by glucagon by 230%. In conclusion, under basic conditions without added hormones the glucose/glucose 6-phosphate cycle showed only a minor net glucose uptake, of 0.03 mumol/min per g of hepatocytes; this flux was increased by insulin to a net glucose uptake of 0.21 mumol/min per g and reversed by glucagon to a net glucose release of 0.22 mumol/min per g. Since the glucose 6-phosphate concentrations after hormone treatment did not correlate with the glucose-6-phosphatase flux, it is suggested that the hormones influenced the enzyme activity directly.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begley P. J., Craft J. A. Evidence for protein phosphorylation as a regulatory mechanism for hepatic microsomal glucose 6 phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):1029–1034. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90912-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bontemps F., Hue L., Hers H. G. Phosphorylation of glucose in isolated rat hepatocytes. Sigmoidal kinetics explained by the activity of glucokinase alone. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):603–611. doi: 10.1042/bj1740603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann A., Katz N., Sasse D., Jungermann K. Increase of the gluconeogenic and decrease of the glycolytic capacity of rat liver with a change of the metabolic zonation after partial hepatectomy. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Nov;359(11):1561–1571. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Burchell B., Arion W. J., Walls H. E. A critical evaluation of the possible modulation of hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase activity by protein phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1046–1052. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90627-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAHILL G. F., Jr, ASHMORE J., EARLE A. S., ZOTTU S. Glucose penetration into liver. Am J Physiol. 1958 Mar;192(3):491–496. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Rognstad R., Katz J. Isotopic evidence for futile cycles in liver cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):1141–1148. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90811-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D., Lee D., Rognstad R., Katz J. Futile cycles in isolated perfused rat liver and in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):212–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos P., Hers H. G. A molecular order in the synthesis and degradation of glycogen in the liver. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):161–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Refai M., Bergman R. N. Simulation study of control of hepatic glycogen synthesis by glucose and insulin. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1608–1619. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Whitton P. D., Taylor E. A. Glycogen synthesis in the perfused liver of the starved rat. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):529–538. doi: 10.1042/bj1290529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Hue L. Gluconeogenesis and related aspects of glycolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:617–653. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L. The role of futile cycles in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism in the liver. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1981;52:247–331. doi: 10.1002/9780470122976.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K., Heilbronn R., Katz N., Sasse D. The glucose/glucose-6-phosphate cycle in the periportal and perivenous zone of rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):429–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K., Katz N. Functional hepatocellular heterogeneity. Hepatology. 1982 May-Jun;2(3):385–395. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Golden S., Dunn A., Chenoweth M. Estimation of glucose turnover in rats in vivo with tritium labeled glucoses. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Dec;357(10):1387–1394. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.2.1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., McGarry J. D. The glucose paradox. Is glucose a substrate for liver metabolism? J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):1901–1909. doi: 10.1172/JCI111610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Rognstad R. Futile cycles in the metabolism of glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:237–289. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Wals P. A., Rognstad R. Glucose phosphorylation, glucose-6-phosphatase, and recycling in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4530–4536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N., Jungermann K. Autoregulatory shift from fructolysis to lactate gluconeogenisis in rat hepatocyte suspensions. The problem of metabolic zonation of liver parenchyma. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Mar;357(3):359–375. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N., Teutsch H. F., Jungermann K., Sasse D. Heterogeneous reciprocal localization of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and of glucokinase in microdissected periportal and perivenous rat liver tissue. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 15;83(2):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)81021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauck M., Wölfle D., Katz N., Jungermann K. Modulation of the glucagon-dependent induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and tyrosine aminotransferase by arterial and venous oxygen concentrations in hepatocyte cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(3):657–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Evidence for suppression of hepatic glucose-6-phosphatase with carbohydrate feeding. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):192–195. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Hirsch L. J., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Studies on the mechanism by which exogenous glucose is converted into liver glycogen in the rat. A direct or an indirect pathway? J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8046–8052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Moore S. V., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Efficient hepatic glycogen synthesis in refeeding rats requires continued carbon flow through the gluconeogenic pathway. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6958–6963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlie R. C., Lygre D. G. The inhibition by citrate of inorganic pyrophosphate-glucose phosphotransferase and glucose 6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3136–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver I. T., Edwards A. M., Pitot H. C. Hormonal regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in primary cultures of adult-rat liver parenchymal cells. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parniak M., Kalant N. Incorporation of glucose into glycogen in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1985 May;63(5):333–340. doi: 10.1139/o85-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst I., Jungermann K. Short-term regulation of glycolysis by insulin and dexamethasone in cultured rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst I., Schwartz P., Jungermann K. Induction in primary culture of 'gluconeogenic' and 'glycolytic' hepatocytes resembling periportal and perivenous cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(2):271–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06775.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soboll S., Elbers R., Scholz R., Heldt H. W. Subcellular distribution of di- and tricarboxylates and pH gradients in perfused rat liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Jan;361(1):69–76. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth M., Schulze H. U. Hormone-induced effects on the rat liver microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 16;99(1):134–141. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91723-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W. The role of the liver in the homeostasis of blood glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;11:51–97. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152811-9.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden M. C., Watts D. I., Palmer T. N., Myles D. D. Direction of carbon flux in starvation and after refeeding: in vitro and in vivo effects of 3-mercaptopicolinate. Biochem Int. 1983 Sep;7(3):329–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Toyota T., Suzuki H., Goto Y. A putative second messenger of insulin action regulates hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall C. J., Heath D. F. Compartmentation between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in rat liver. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(2):303–312. doi: 10.1042/bj1100303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tippett P. S., Neet K. E. Specific inhibition of glucokinase by long chain acyl coenzymes A below the critical micelle concentration. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12839–12845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Werve G., Jeanrenaud B. Synthase activation is not a prerequisite for glycogen synthesis in the starved liver. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 1):E271–E275. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.2.E271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wölfle D., Schmidt H., Jungermann K. Short-term modulation of glycogen metabolism, glycolysis and gluconeogenesis by physiological oxygen concentrations in hepatocyte cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):405–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


