Abstract
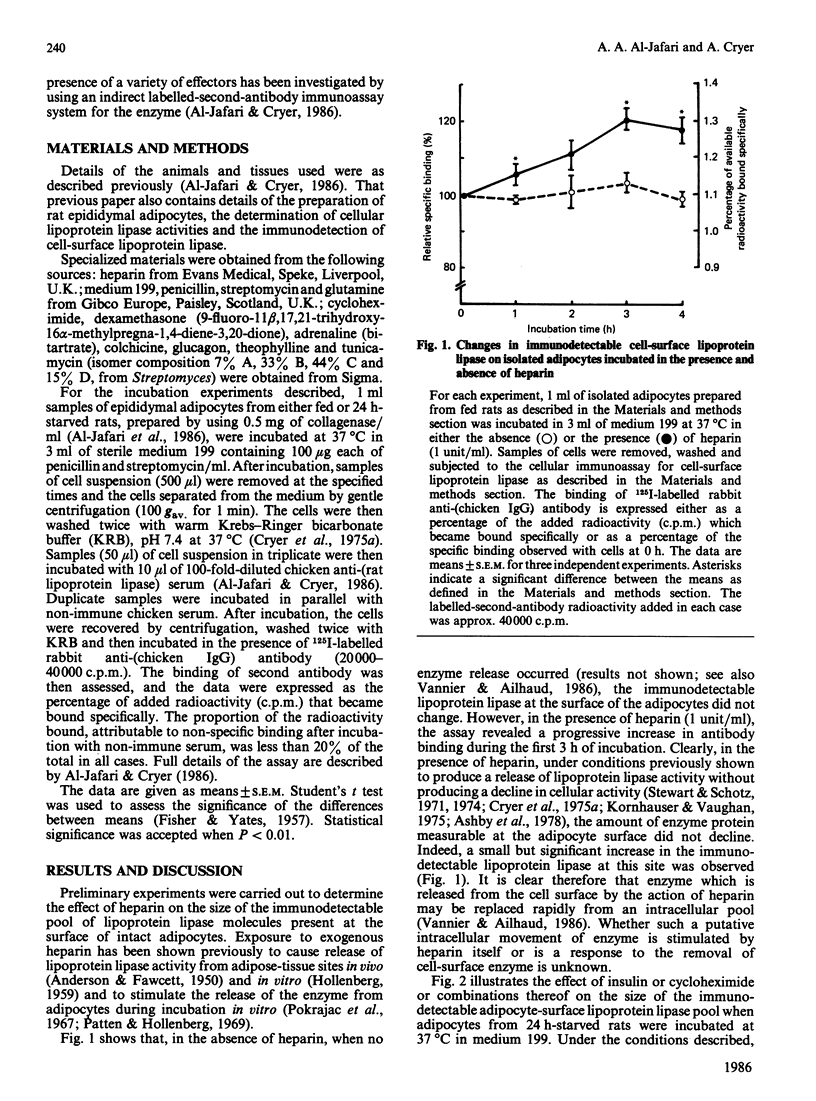
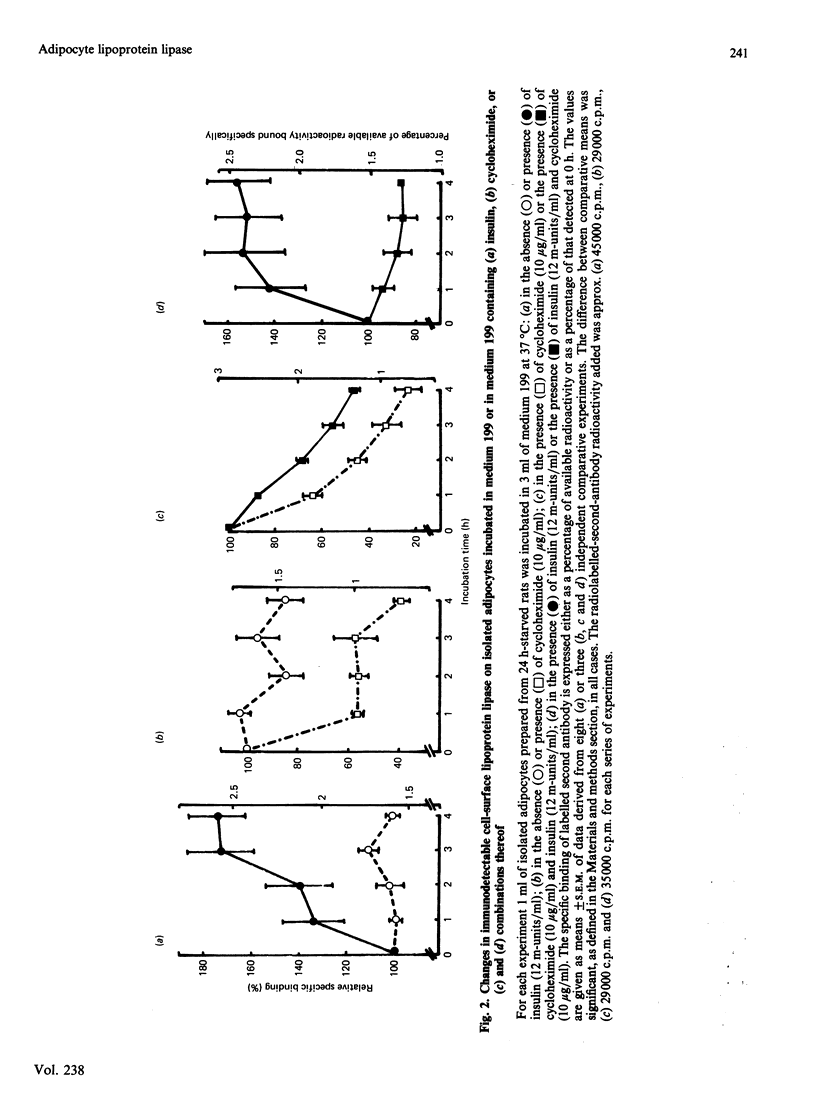
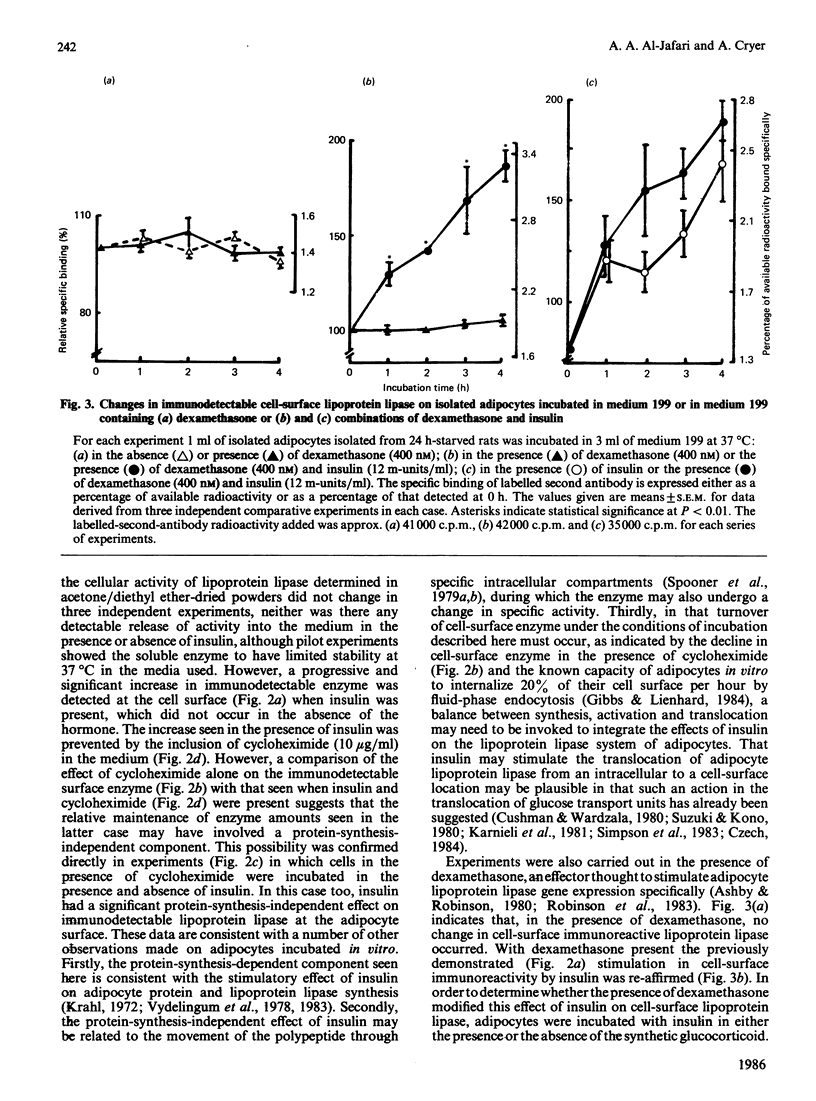
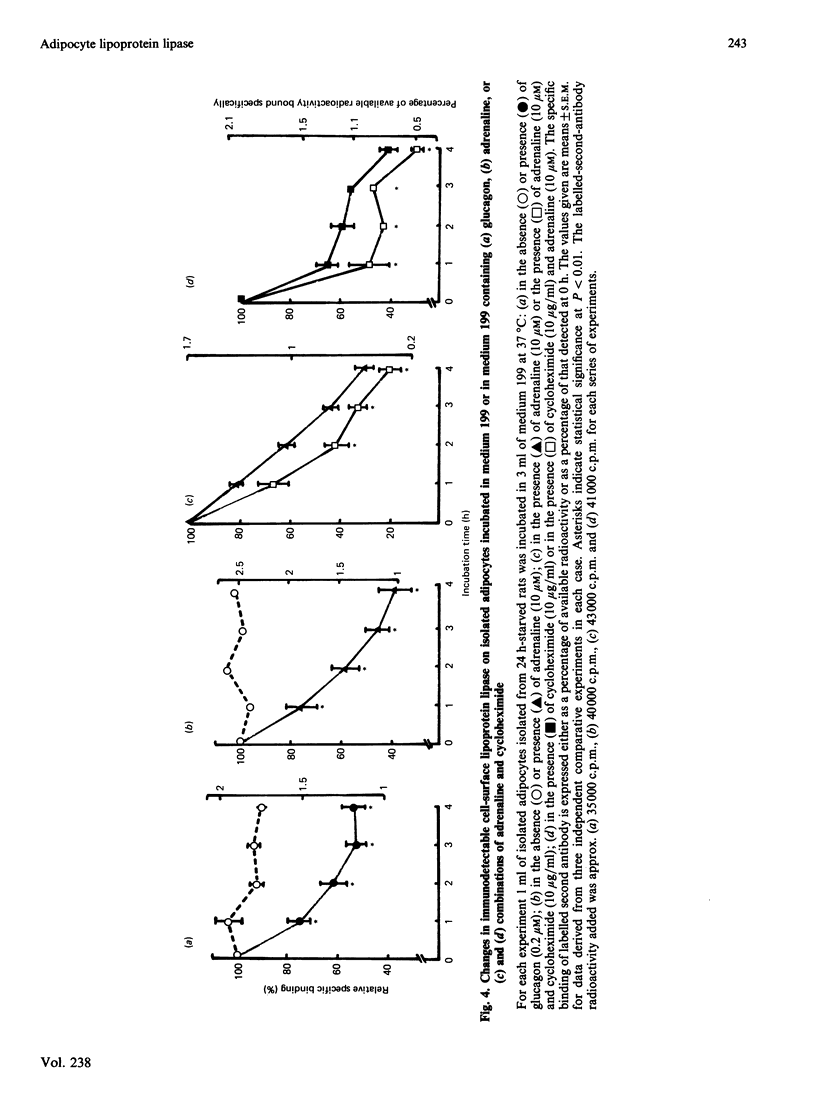
An indirect labelled-second-antibody cellular immunoassay for adipocyte surface lipoprotein lipase was used to assess the changes that occurred during the incubation of cells in the presence and absence of effectors. In the absence of any specific effectors, the amount of immunodetectable lipoprotein lipase present at the surface of adipocytes remained constant throughout the 4 h incubation period at 37 degrees C. Under such conditions total cellular enzyme activity also remained constant, with no activity appearing in the medium. In the presence of heparin, cell-surface immunodetectable lipoprotein lipase increased by up to 20%, whereas in the presence of cycloheximide they decreased by up to 60%. Thus the obvious turnover of enzyme from this cell-surface site was found to be relatively rapid and dependent for its replenishment, at least in part, on protein synthesis. In the presence of insulin alone, a substantial increase in cell-surface lipoprotein lipase protein occurred, only part of which was dependent on protein synthesis. The total cellular activity of lipoprotein lipase was unaffected by the presence of insulin. The insulin-dependent increase in cell-surface enzyme was potentiated somewhat in the presence of dexamethasone, which was not shown to exert any independent effect. Glucagon, adrenaline and theophylline all produced a significant decline in the cell-surface immunodetectable lipoprotein lipase, which in the case examined (adrenaline) was partially additive with regard to the independent effect of cycloheximide. Cell-surface immunodetectable lipoprotein lipase amounts were decreased significantly when cells were incubated in the presence of either colchicine or tunicamycin. The concerted way in which cell-surface lipoprotein lipase altered during the incubations of adipocytes in the presence of effectors suggested that the translocation of enzyme to and from this cellular site was dependent on hormonal action and the integrity of intracellular protein-transport mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON N. G., FAWCETT B. An antichylomicronemic substance produced by heparin injection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Aug;74(4):768–771. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-18042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jafari A. A., Cryer A. The lipoprotein lipase of white adipose tissue. Studies on the intracellular distribution of the adipocyte-associated enzyme. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):749–756. doi: 10.1042/bj2360749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud J., Boyer J. Hydrolysis and uptake of an aliphatic fatty ester by whole isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 25;486(3):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud J., Nobili O., Boyer J. Differential properties of lipases active as membrane-bound enzymes in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 26;572(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby P., Bennett D. P., Spencer I. M., Robinson D. S. Post-translational regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):865–872. doi: 10.1042/bj1760865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby P., Robinson D. S. Effects of insulin, glucocorticoids and adrenaline on the activity of rat adipose-tissue lipoprotein lipids. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):185–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1880185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. J. Heparin-independent release of lipoprotein lipase activity from perfused rat hearts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 29;753(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Rone M. S., Sandros T. Effects of colchicine and cycloheximide on the functional and non-functional lipoprotein lipase fractions of rat heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 19;398(3):394–400. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Stein O., Stein Y. Colchicine-induced inhibition of plasma lipoprotein lipase release in the intact rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 24;380(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Stein O., Stein Y. Interference with the transport of heparin-releasable lipoprotein lipase in the perfused rat heart by colchicine and vinblastine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 22;388(2):260–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Stein O., Stein Y. Lipoprotein lipase of cultured mesenchymal rat heart cells. I. Synthesis, secretion and releasability by heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 30;528(3):456–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Chohan P., Smith J. J. Effectors of lipoprotein lipase secretion from isolated cardiac muscle cells incubated in vitro. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 31;29(9):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Davies P., Williams E. R., Robinson D. S. The clearing-factor lipase activity of isolated fat-cells. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):481–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1460481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., McDonald A., Williams E. R., Robinson D. S. Colchicine inhibition of the heparin-stimulated release of clearing-factor lipase from isolated fat-cells. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):717–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1520717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A. Tissue lipoprotein lipase activity and its action in lipoprotein metabolism. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(5):525–541. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Wusteman F. S., Casey J. J. Glycosaminoglycan: cell interactions; their role in lipoprotein lipase secretion from isolated cardiac muscle cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 1984 Jan;2(1):53–56. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290020114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. New perspectives on the mechanism of insulin action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:347–377. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Cryer A., Robinson D. S. Hormonal control of adipose tissue clearing factor lipase activity. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80860-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. P., Ross R., Bornstein P. Effects of antimicrotubular agents on the secretion of collagen. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):390–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E. Fluid-phase endocytosis by isolated rat adipocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Dec;121(3):569–575. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLENBERG C. H. Effect of nutrition on activity and release of lipase from rat adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1959 Sep;197:667–670. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.3.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh M., Hamosh P. Lipoprotein lipase: its physiological and clinical significance. Mol Aspects Med. 1983;6(3):199–289. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(83)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson P., Holmin T., Nilsson-Ehle P. Microsurgical denervation of rat adipose tissue: lack of effect of lipoprotein lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1254–1257. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen H., Stam H., Kalkman C., Hülsmann W. C. On the dual localization of lipoprotein lipase in rat heart. Studies with a modified perfusion technique. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):411–416. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornhauser D. M., Vaughan M. Release of lipoprotein lipase from fat cells in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 24;380(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Howell S. L., Young D. A., Fink C. J. New hypothesis of insulin secretion. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1177–1179. doi: 10.1038/2191177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Bengtsson G., Marklund S. E., Lindahl U., Hök M. Heparin-lipoprotein lipase interactions. Fed Proc. 1977 Jan;36(1):60–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin S. M., Speake B. K., Robinson D. S. Purification and characterization of rat adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):485–495. doi: 10.1042/bj2070485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten R. L., Hollenberg C. H. The mechanism of heparin stimulation of rat adipocyte lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jul;10(4):374–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokrajac N., Lossow W. J., Chaikoff I. L. The effect of nutritional state on lipoprotein lipase activity in isolated rat adipose tissue cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin D. C., Hinkle P. C. Immunological identification of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5725–5729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer I. M., Hutchinson A., Robinson D. S. The effect of nutritional state on the lipoprotein lipase activity of isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 28;530(3):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner P. M., Chernick S. S., Garrison M. M., Scow R. O. Development of lipoprotein lipase activity and accumulation of triacylglycerol in differentiating 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Effects of prostaglandin F2alpha, 1-methyl-3-isobutylxanthine, prolactin, and insulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1305–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner P. M., Chernick S. S., Garrison M. M., Scow R. O. Insulin regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity and release in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Separation and dependence of hormonal effects on hexose metabolism and synthesis of RNA and protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10021–10029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Sanger L., Stein Y. Colchicine-induced inhibition of lipoprotein and protein secretion into the serum and lack of interference with secretion of biliary phospholipids and cholesterol by rat liver in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):90–103. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. E., Schotz M. C. Release of lipoprotein lipase activity from isolated fat cells. II. Effect of heparin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):904–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. E., Schotz M. C. Studies on release of lipoprotein lipase activity from fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5749–5753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Ailhaud G. A continuous flow method for the study of lipoprotein lipase secretion in adipose cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 12;875(2):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Amri E. Z., Etienne J., Négrel R., Ailhaud G. Maturation and secretion of lipoprotein lipase in cultured adipose cells. I. Intracellular activation of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4424–4431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Etienne J., Ailhaud G. Intracellular localization of lipoprotein lipase in adipose cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 12;875(2):344–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Jansen H., Négrel R., Ailhaud G. Study of lipoprotein lipase content in Ob17 preadipocytes during adipose conversion. Immunofluorescent localization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12387–12393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vydelingum N., Drake R. L., Etienne J., Kissebah A. H. Insulin regulation of fat cell ribosomes, protein synthesis, and lipoprotein lipase. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):E121–E131. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.2.E121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vydelingum N., Kissebah A. H., Wynn V. The role of calcium in insulin action. V. Importance of cyclic guanosine 3':5' monophosphate and calcium ions in insulin stimulation of lipoprotein lipase activity and protein synthesis in adipose tissue. Horm Metab Res. 1978 Jan;10(1):38–46. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vérine A., Salers P., Boyer J. Effects of apoproteins C on lipoprotein lipase activity bound to rat fat cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):E175–E181. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.3.E175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing D. R., Salaman M. R., Robinson D. S. Clearing-factor lipase in adipose tissue. Factors influencing the increase in enzyme activity produced on incubation of tissue from starved rats in vitro. Biochem J. 1966 Jun;99(3):648–656. doi: 10.1042/bj0990648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


