Abstract
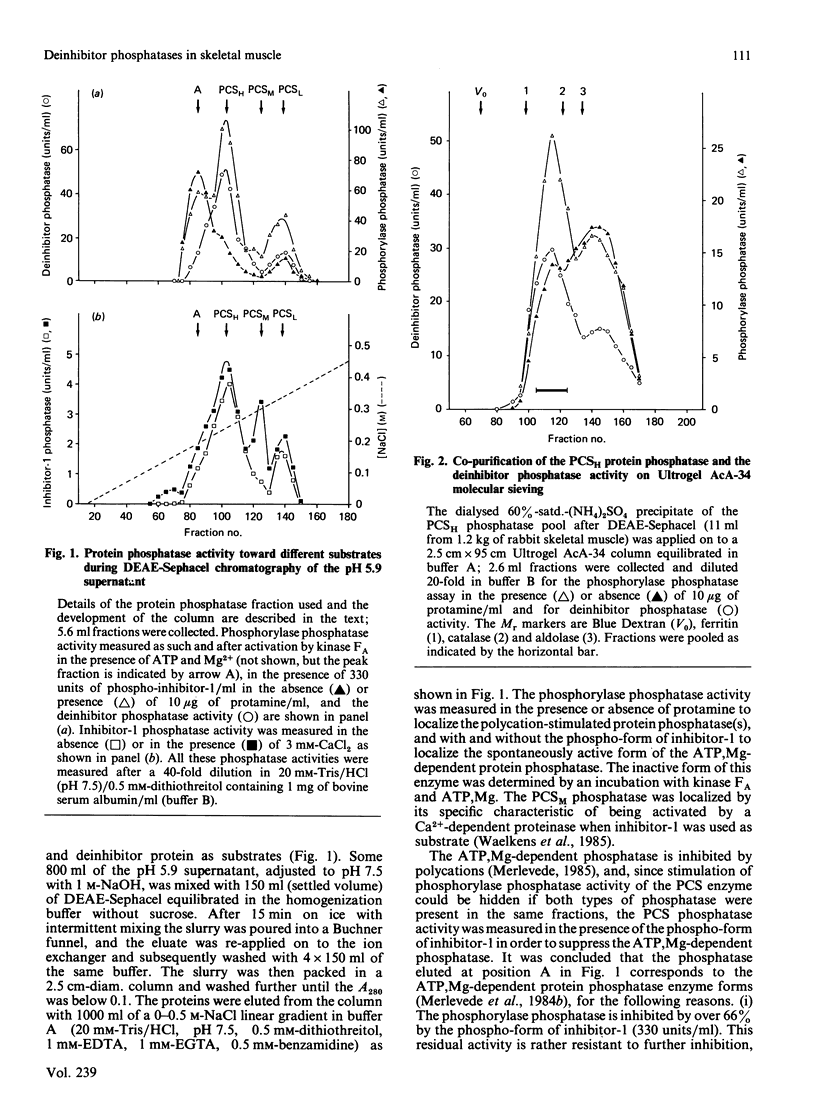
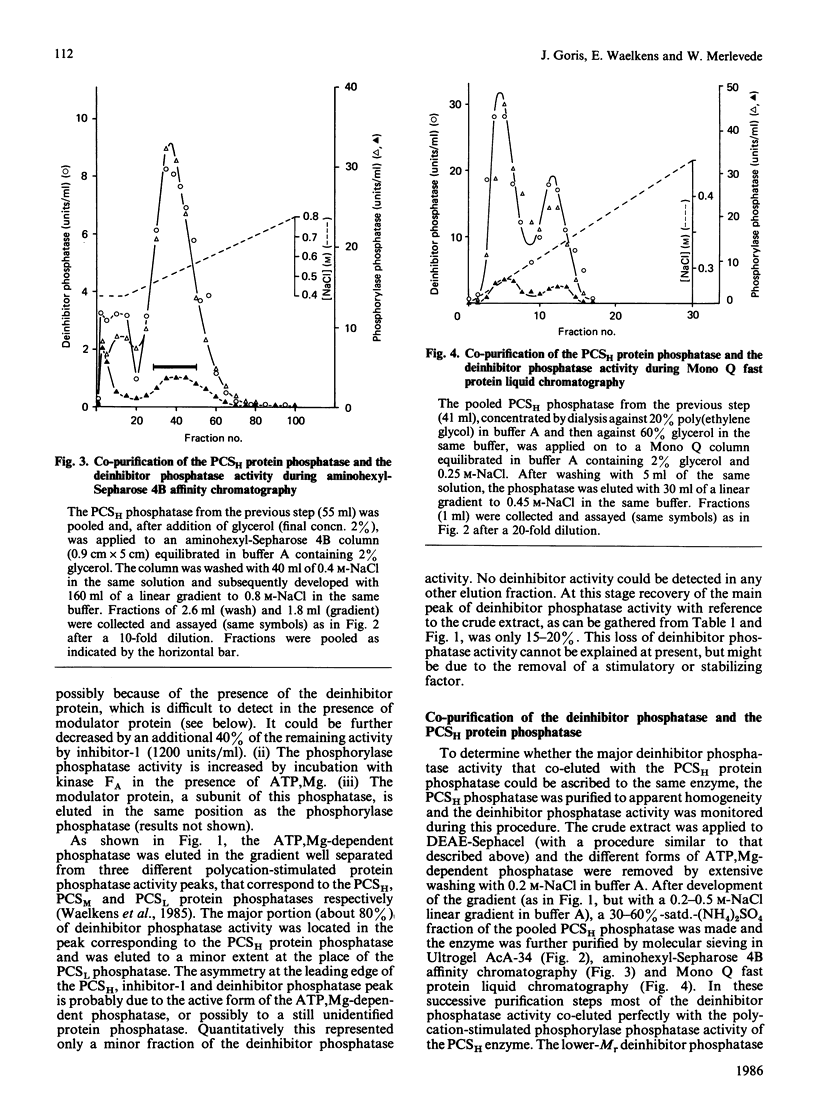
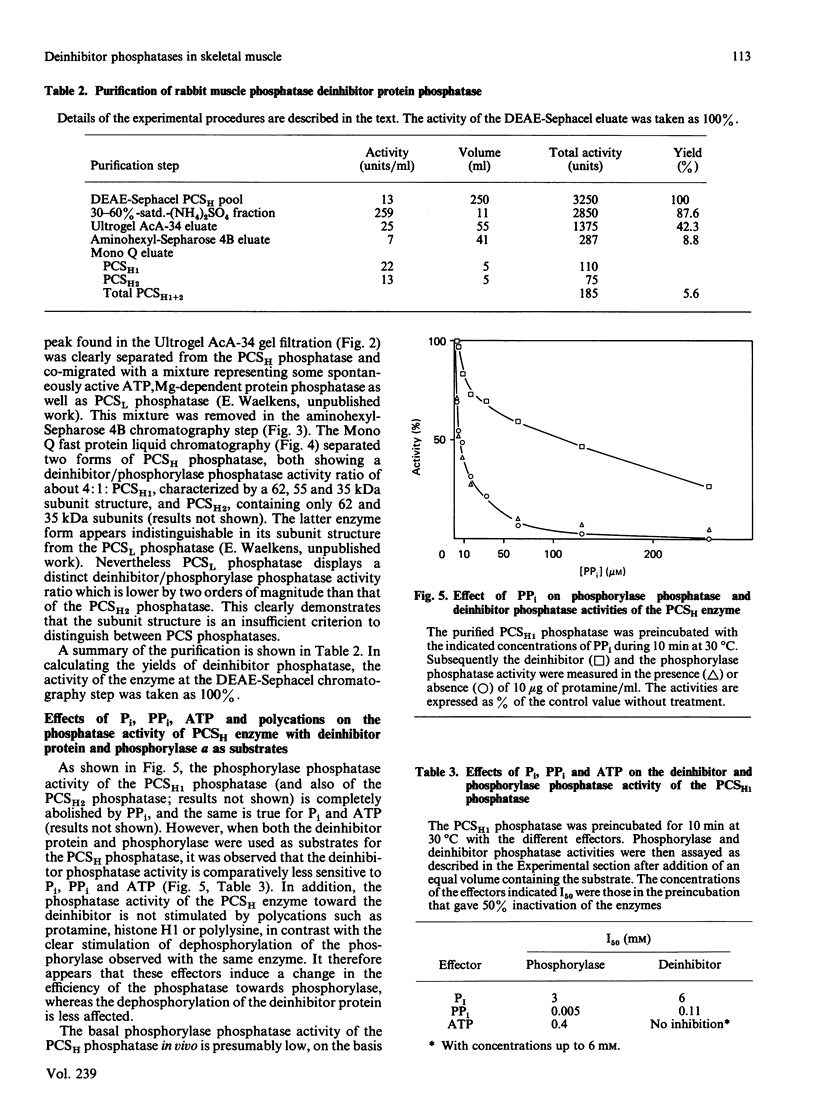
In rabbit skeletal muscle the polycation-stimulated (PCS) protein phosphatases [Merlevede (1985) Adv. Protein Phosphatases 1, 1-18] are the only phosphatases displaying significant activity toward the deinhibitor protein. Among them, the PCSH protein phosphatase represents more than 80% of the measurable deinhibitor phosphatase activity associated with the PCS phosphatases. The deinhibitor phosphatase activity co-purifies with the PCSH phosphatase to apparent homogeneity. In the last purification step two forms of PCSH phosphatase were separated (PCSH1, containing 62, 55 and 34 kDa subunits, and PCSH2, containing 62 and 35 kDa subunits), both showing the same deinhibitor/phosphorylase phosphatase activity ratio. The activity of the PCSH phosphatase toward the deinhibitor is not stimulated by polycations such as protamine, histone H1 or polylysine, unlike the stimulation observed with phosphorylase as the substrate. The phosphorylase phosphatase activity of PCSH phosphatase is inhibited by ATP, PPi and Pi, whereas the deinhibitor phosphatase activity of the enzyme is much less sensitive to these agents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Bilham T., Cohen P. Complete primary structure of protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(2):235–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;14:117–196. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152814-0.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defreyn G., Goris J., Merlevede W. A deinhibitor protein neutralizing the effect of the protein inhibitors on dog liver phosphorylase phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. The isolation and crystallization of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Camps T., Defreyn G., Merlevede W. The dephosphorylation of protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 is controlled by the deinhibitor protein. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 16;134(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80599-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Parker P. J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W. The deinhibitor protein: regulation by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):405–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Camps T., Merlevede W. Regulation of protein phosphatase activity by the deinhibitor protein. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:467–484. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W. Dephosphorylation of the deinhibitor protein by the PCSH protein phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Resink T. J., Cohen P. Reconstitution of a Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatase and its activation through a phosphorylation mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80760-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurgensen S., Shacter E., Huang C. Y., Chock P. B., Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W. On the mechanism of activation of the ATP X Mg(II)-dependent phosphoprotein phosphatase by kinase FA. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5864–5870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., KENT A. B., FISCHER E. H. The muscle phosphorylase b kinase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlevede W., Goris J., Vandenheede J. R., Waelkens E., Yang S. D. Control of the ATP,Mg-dependent protein phosphatase by heat-stable regulatory proteins. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Oct;177(1):3–11. doi: 10.3181/00379727-177-41904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Yang S. D. Regulation of ATP-Mg-dependent protein phosphatase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:177–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett-Gies C. A., Walsh D. A. Subunit phosphorylation and activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Divalent metal ion, ATP, and protein concentration dependence. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2046–2056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Hemmings B. A., Cohen P., Goris J., Merlevede W. The MgATP-dependent protein phosphatase and protein phosphatase 1 have identical substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Yang S. D., Camps T., Merlevede W. Conversion of active protein phosphatase to the ATP-Mg-dependent enzyme form by inhibitor-2. FEBS Lett. 1981 May 5;127(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Yang S. D., Goris J., Merlevede W. ATP x Mg-dependent protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. II. Purification of the activating factor and its characterization as a bifunctional protein also displaying synthase kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11768–11774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Yang S. D., Merlevede W. Rabbit skeletal muscle protein phosphatase(s). Identity of phosphorylase and synthase phosphatase and interconversion to the ATP-Mg-dependent enzyme form. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5894–5900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Yang S. D., Merlevede W. Role of the modulator protein in the interconversion of rabbit skeletal muscle protein phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 30;115(3):871–877. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens E., Goris J., Di Salvo J., Merlevede W. Inhibitor-1 phosphatase activity in vascular smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):397–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens E., Goris J., Merlevede W. Activation of the PCSM-protein phosphatase by a Ca2+-dependent protease. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 18;192(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Merlevede W. ATP x Mg-dependent protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. I. Purification of the enzyme and its regulation by the interaction with an activating protein factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11759–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W. A simplified procedure for the purification of the protein phosphatase modulator (inhibitor-2) from rabbit skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):293–295. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W. Identification of inhibitor-2 as the ATP-mg-dependent protein phosphatase modulator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10231–10234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


