Abstract
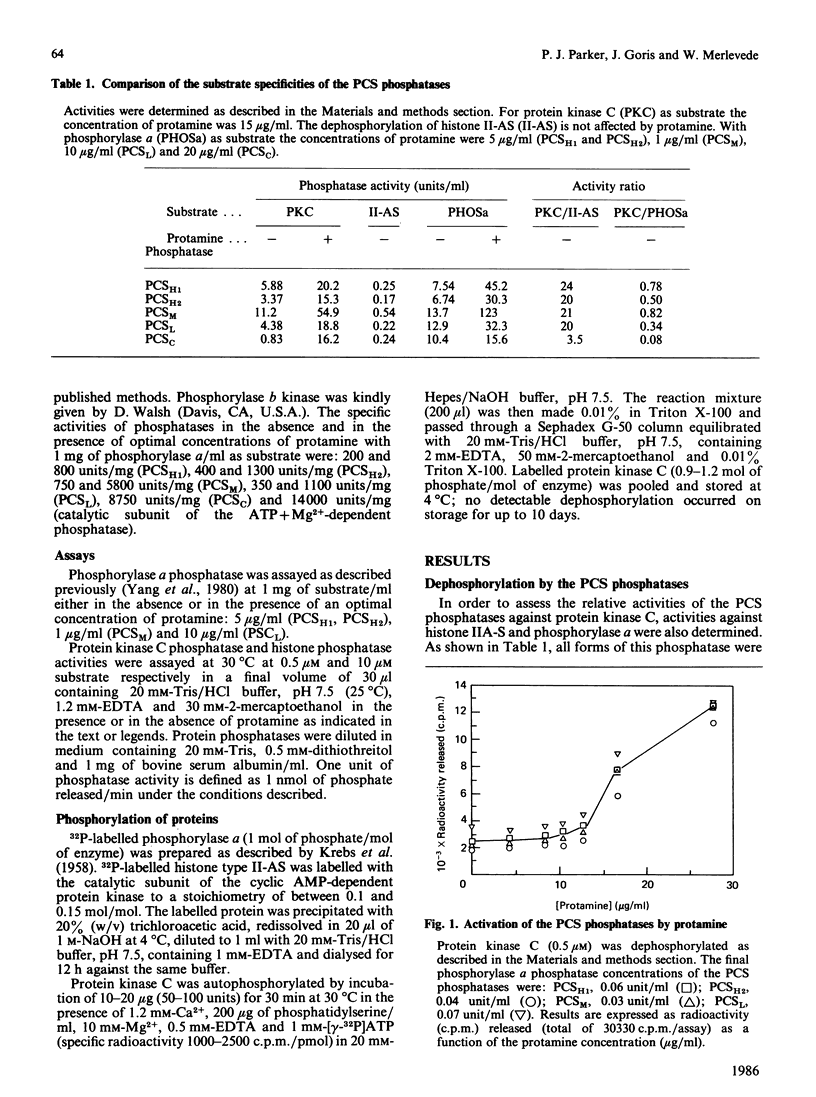
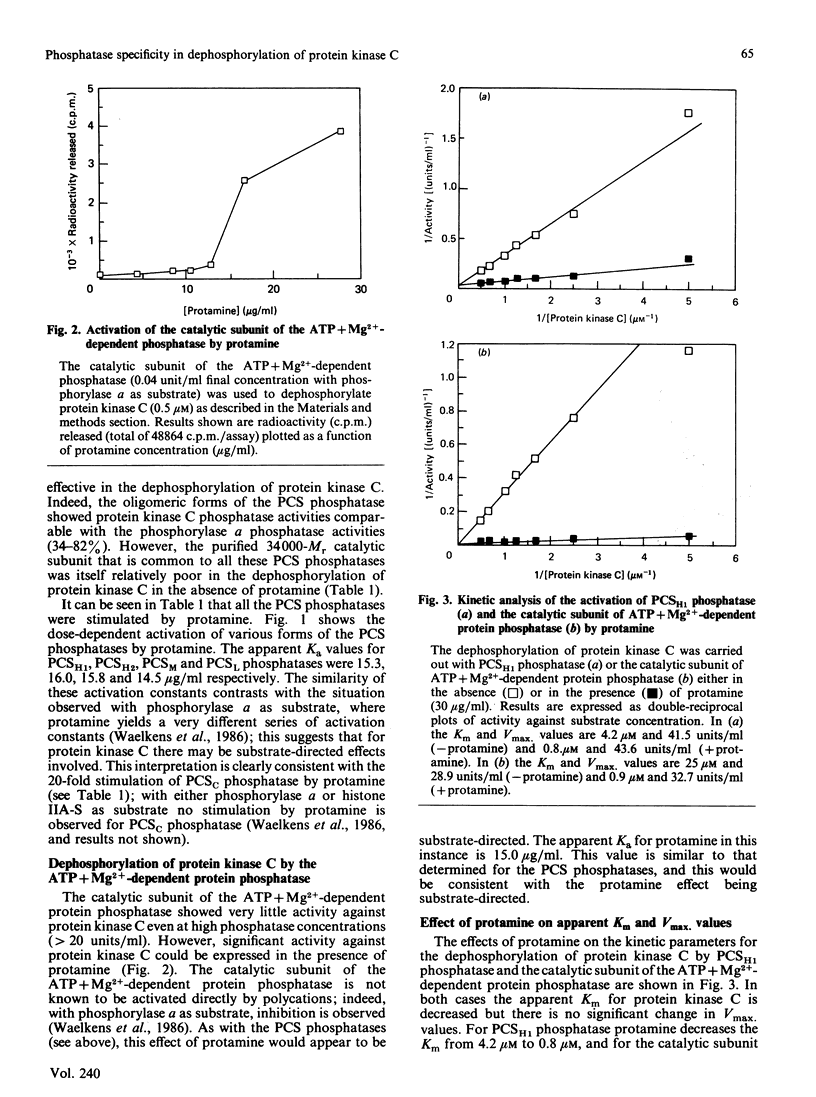
Protein kinase C can autophosphorylate in vitro and has also been shown to be phosphorylated in vivo. In order to investigate the factors that may determine the phosphorylation state of protein kinase C in vivo, we determined the ability of the ATP + Mg2+-dependent phosphatase and the polycation-stimulated (PCS) phosphatases to dephosphorylate protein kinase C in vitro. These studies show that all the oligomeric forms of the PCS phosphatases (PCSH1, PCSH2, PCSM and PCSL phosphatases) are effective in the dephosphorylation of protein kinase C, showing 34-82% of the activity displayed with phosphorylase a as substrate. In contrast both the catalytic subunit of the PCS phosphatase and that of the ATP+Mg2+-dependent phosphatase showed only weak activity with protein kinase C as substrate. All these phosphatases, however, were activated by protamine (Ka 14-16 micrograms/ml) through what appears to be a substrate-directed effect. The relative role of these phosphatases in the control of protein kinase C is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M. J., Gebhardt A., Parker P. J., Foulkes J. G. Phosphatidylinositol turnover and transformation of cells by Abelson murine leukaemia virus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3173–3178. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Camps T., Merlevede W. Regulation of protein phosphatase activity by the deinhibitor protein. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:467–484. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W. Dephosphorylation of the deinhibitor protein by the PCSH protein phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W. Identification of the phosphatase deinhibitor protein phosphatases in rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):109–114. doi: 10.1042/bj2390109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., KENT A. B., FISCHER E. H. The muscle phosphorylase b kinase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Yang S. D. Regulation of ATP-Mg-dependent protein phosphatase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:177–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D. Purification to homogeneity of protein kinase C from bovine brain--identity with the phorbol ester receptor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):953–959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett-Gies C. A., Walsh D. A. Subunit phosphorylation and activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Divalent metal ion, ATP, and protein concentration dependence. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2046–2056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resink T. J., Hemmings B. A., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. Characterisation of a reconstituted Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):455–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strålfors P., Hiraga A., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Purification and characterisation of the glycogen-bound form of protein phosphatase-1 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P. M., Murray A. W. Modulation of Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in platelets treated with a tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):158–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung H. Y., Alemany S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 2. Purification, subunit structure and properties of protein phosphatases-2A0, 2A1, and 2A2 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):253–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung H. Y., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Comparison of native and reconstituted Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatases from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens E., Goris J., Merlevede W. Activation of the PCSM-protein phosphatase by a Ca2+-dependent protease. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 18;192(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Glass D. B., Chou C. H., Raynor R. L., Katoh N., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Kibler R. F., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. II. Substrate specificity and inhibition by various agents. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8489–8495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Merlevede W. ATP x Mg-dependent protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. I. Purification of the enzyme and its regulation by the interaction with an activating protein factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11759–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


