Abstract
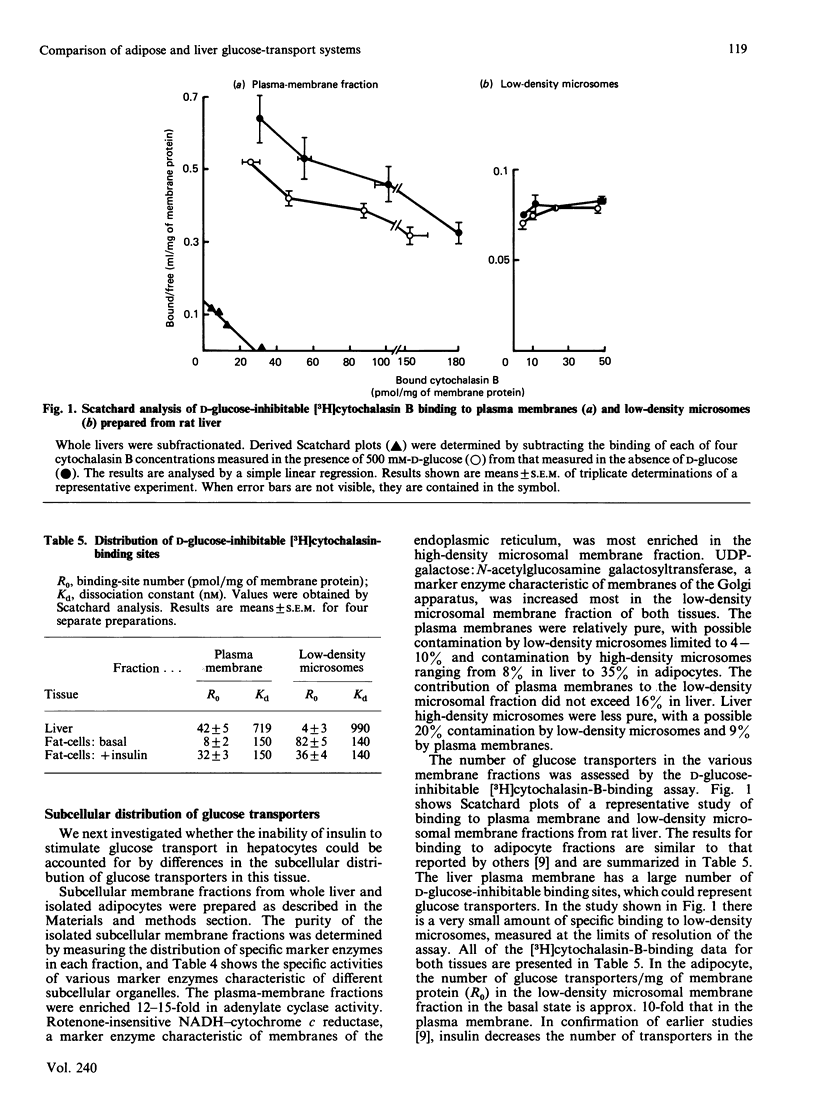
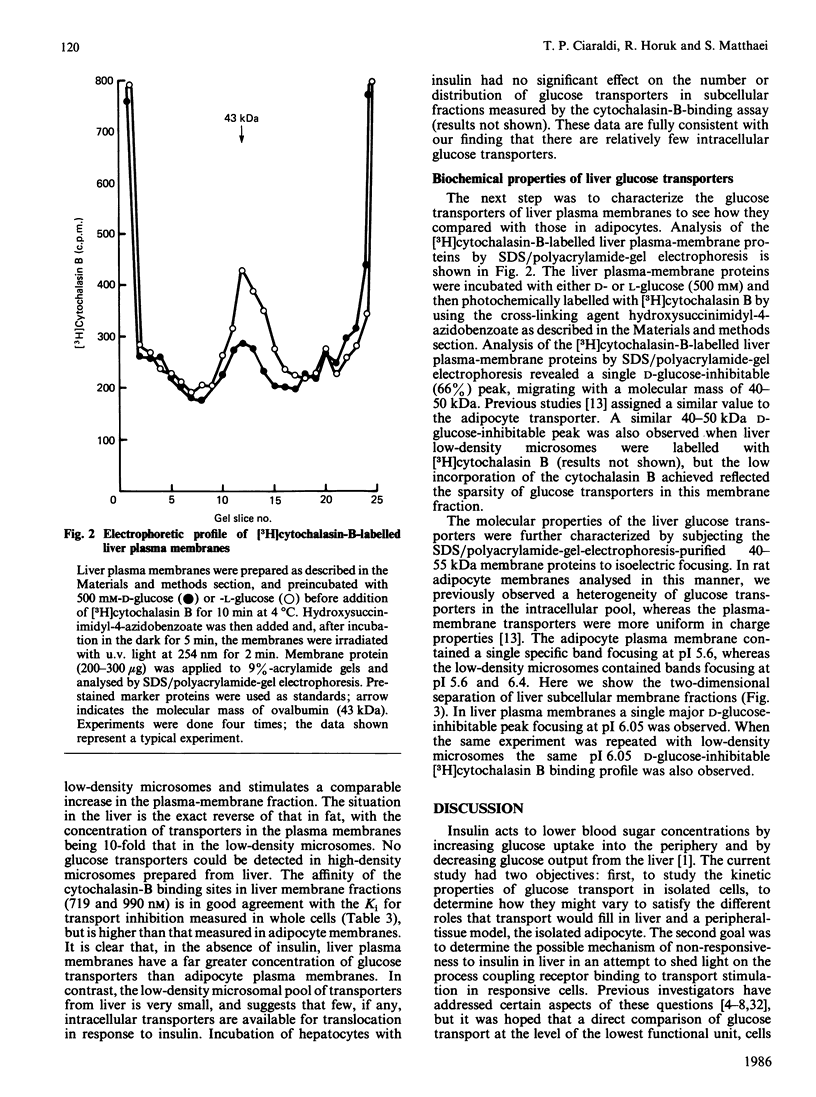
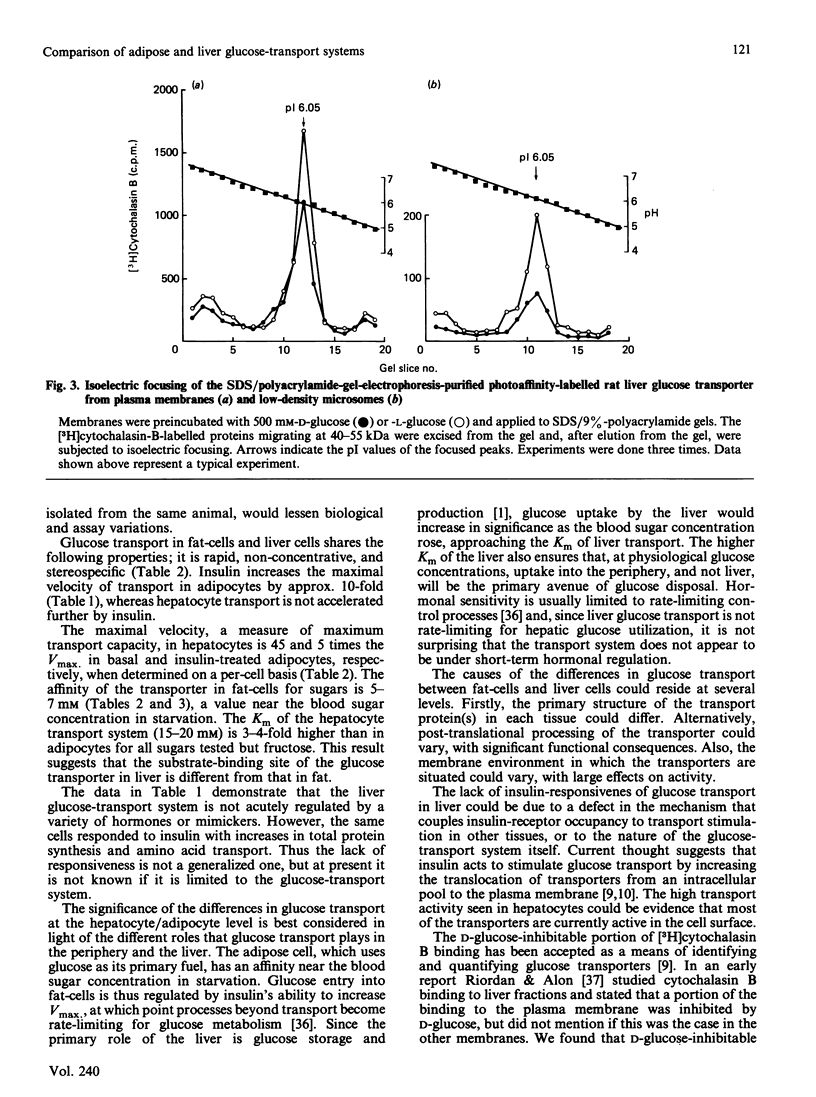
The properties of the glucose-transport systems in rat adipocytes and hepatocytes were compared in cells prepared from the same animals. Hormones and other agents which cause a large stimulation of 3-O-methylglucose transport in adipocytes were without acute effect in hepatocytes. Hepatocytes displayed a lower affinity for 3-O-methylglucose (20 mM) and alternative substrates than adipocytes (6 mM), whereas inhibitor affinities were similar in both cell types. The concentration and distribution of glucose transporters were determined by Scatchard analysis of D-glucose-inhibitable [3H]cytochalasin B binding to subcellular fractions. In liver, most of the transporters were located in the plasma membrane (42 +/- 5 pmol/mg of protein) with a small amount (4 +/- 3 pmol/mg) in the low-density microsomal fraction ('microsomes'), the reverse of the situation in adipocytes. Glucose transporters were covalently labelled with [3H]cytochalasin B by using the photochemical cross-linking agent hydroxysuccinimidyl-4-azidobenzoate and analysed by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. A single D-glucose-inhibitable peak with a molecular mass of 40-50 kDa was seen in both plasma membrane and low-density microsomes. This peak was further characterized by isoelectric focusing and revealed a single peak of specific [3H]cytochalasin B binding at pI 6.05 in both low-density microsomes and plasma membrane, compared with peaks at pI 6.4 and 5.6 in adipocyte membranes. In summary: the glucose-transport system in hepatocytes has a lower affinity and higher capacity than that in adipocytes, and is also not accurately modulated by insulin; the subcellular distribution of glucose transporters in the liver suggests that few intracellular transporters would be available for translocation; the liver transporter has a molecular mass similar to that of the adipocyte transporter; the liver glucose transporter exists as a single charged form (pI 6.05), compared with the multiple forms in adipocytes. This difference in charge could reflect a functionally important difference in molecular structure between the two cell types.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J. D., Pilch P. F. Unique cytochalasin B binding characteristics of the hepatic glucose carrier. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2222–2227. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur H., Heldt H. W. Transport of hexoses across the liver-cell membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):397–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeley J. A., Stevenson S. M., Beeley J. G. Polyacrylamide gel isoelectric focusing of proteins: determination of isoelectric points using an antimony electrode. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 28;285(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90313-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N. Integrated control of hepatic glucose metabolism. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):265–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Olefsky J. M. Comparison of the effects of insulin and H2O2 on adipocyte glucose transport. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Mar;110(3):323–328. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik J. D., Elliott K. R. Kinetics of 3-O-methyl-D-glucose transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):503–508. doi: 10.1042/bj1820503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik J. D., Elliott K. R. Transport of D-fructose and D-galactose into isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):373–375. doi: 10.1042/bj1920373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Insulin action and the regulation of hexose transport. Diabetes. 1980 May;29(5):399–409. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.5.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Biogenesis of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. II. Synthesis of constitutive microsomal enzymes in developing rat hepatocyte. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):97–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott K. R., Bate A. J., Craik J. D. Specificity of the rat hepatocyte monosaccharide transporter. Int J Biochem. 1984;16(12):1251–1253. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(84)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Smith J. D., Cobelli C., Toffolo G., Pilo A., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of insulin on the distribution and disposition of glucose in man. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):357–364. doi: 10.1172/JCI111969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. Isolation and characterization of Golgi apparatus and membranes from rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:180–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Kervina M. Subcellular fractionation of rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:6–41. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R. Fructose metabolism in adipose tissue. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1972;542:37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1972.tb05317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J., Gallian E. Methods for the determination of adipose cell size in man and animals. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Beckner S., Lin M., Wright D. E., Chrambach A. Purification of the photoaffinity-labeled glucagon receptor by gel electrophoretic methods. Prep Biochem. 1984;14(2):99–121. doi: 10.1080/10826068408070618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Matthaei S., Olefsky J. M., Baly D. L., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Biochemical and functional heterogeneity of rat adipocyte glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1823–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Rodbell M., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Identification and characterization of the rat adipocyte glucose transporter by photoaffinity crosslinking. FEBS Lett. 1983 Dec 12;164(2):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesko L., Donlon M., Marinetti G. V., Hare J. D. A rapid method for the isolation of rat liver plasma membranes using an aqueous two-phase polymer system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 22;311(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A. Reflections on the mechanism of action of hormones. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 25;117 (Suppl):K121–K134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of the ability of insulin to activate the glucose-transport system in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):137–145. doi: 10.1042/bj1720137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Tillotson L. G., Yamada K., Gitomer W., Carter-Su C., Mora R., Isselbacher K. J., Czech M. P. Identification of the stereospecific hexose transporter from starved and fed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2286–2290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Alon N. Binding of [3H]ctyochalasin B and [3H]colchicine to isolated liver plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 4;464(3):547–561. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerheber R. D., Esgate J. A., Kuhn C. E. Alcohols inhibit adipocyte basal and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and increase the membrane lipid fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 24;691(1):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt U. M., Eddy B., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C., Semenza G. Isolation of (a subunit of) the Na+/D-glucose cotransporter(s) of rabbit intestinal brush border membranes using monoclonal antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of rat liver cells. 3. Enzymatic requirements for tissue dispersion. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Dec;82(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan M. F., Olson S. A., Weber M. J., Lienhard G. E., Gorga J. C. Photolabeling of glucose-sensitive cytochalasin B binding proteins in erythrocyte, fibroblast and adipocyte membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 16;107(1):38–43. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91666-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin D. C., Hinkle P. C. Characterization of the glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(4):447–453. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Jeanrenaud B. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat diaphragm. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport units to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7090–7093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Smith M. M., Robinson F. W., Kono T. Insulin action on glucose transport in cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13117–13122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell R. R., Gliemann J. Kinetic parameters of transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5276–5283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. F., Exton J. H., Park C. R., Regen D. M. Stereospecific transport of glucose in the perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1968 Nov;215(5):1200–1209. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.5.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


